Abstract
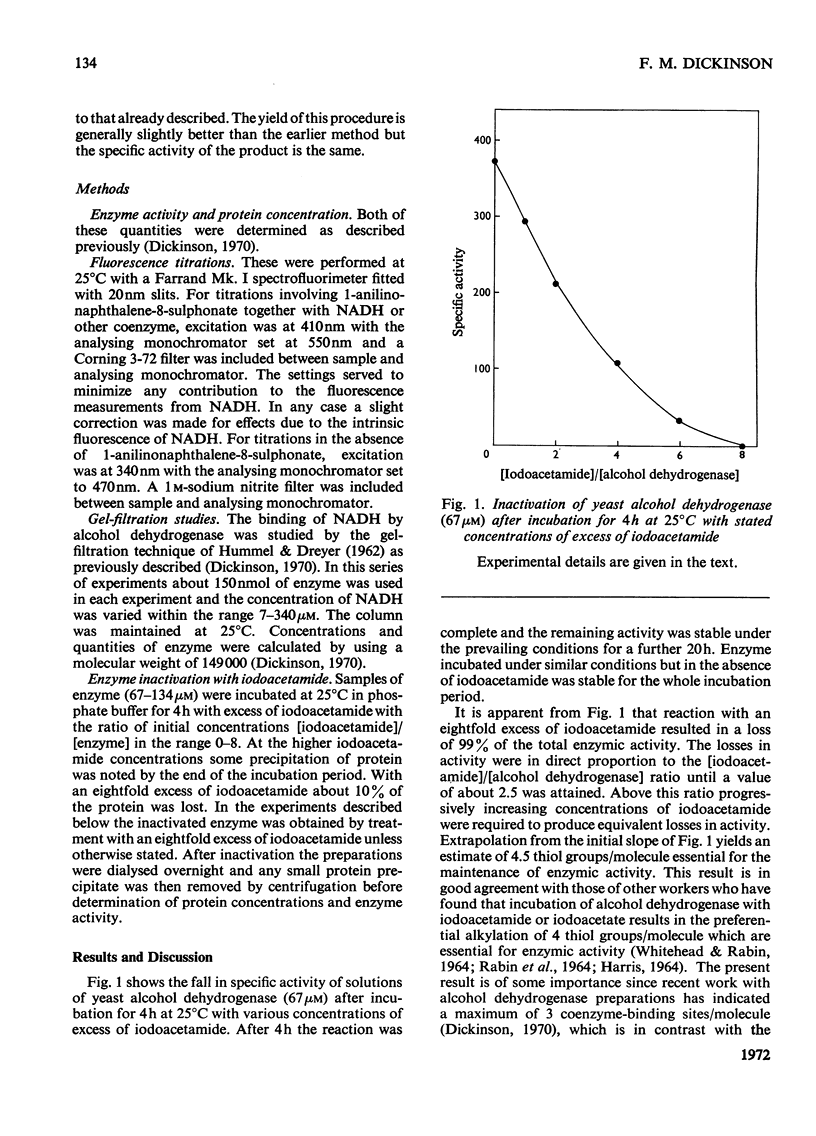
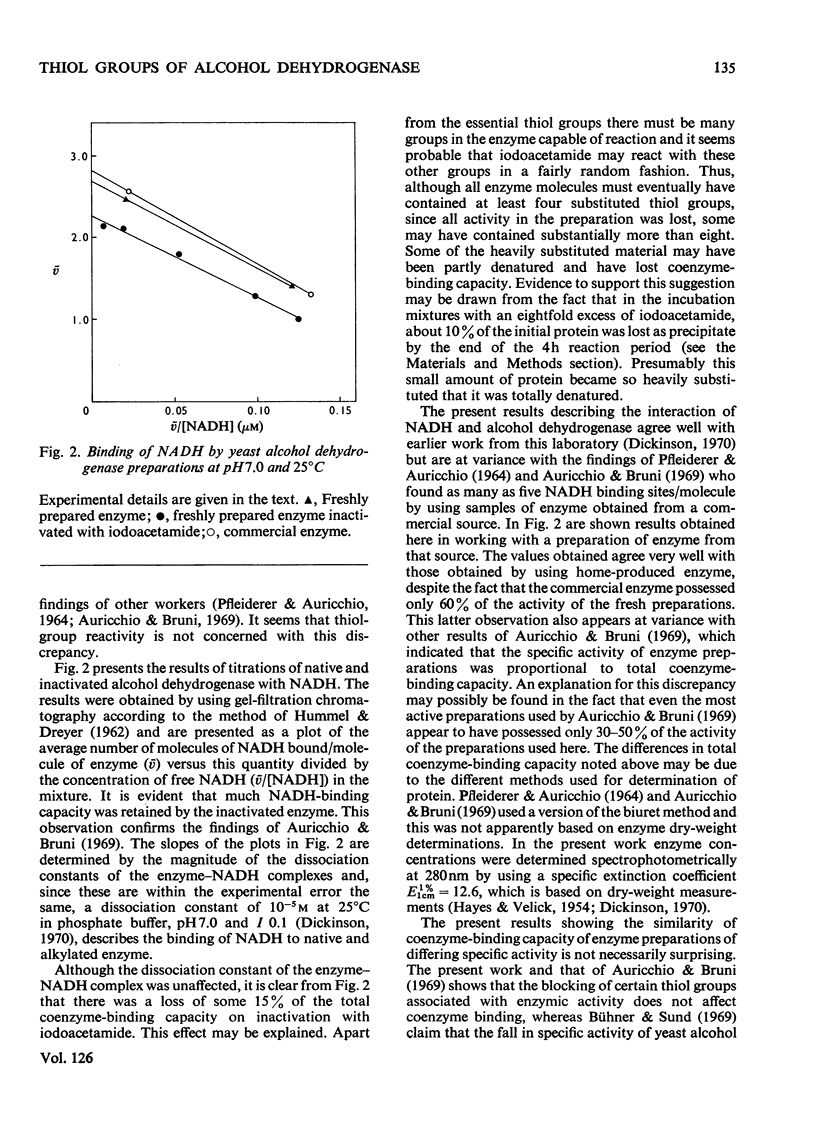
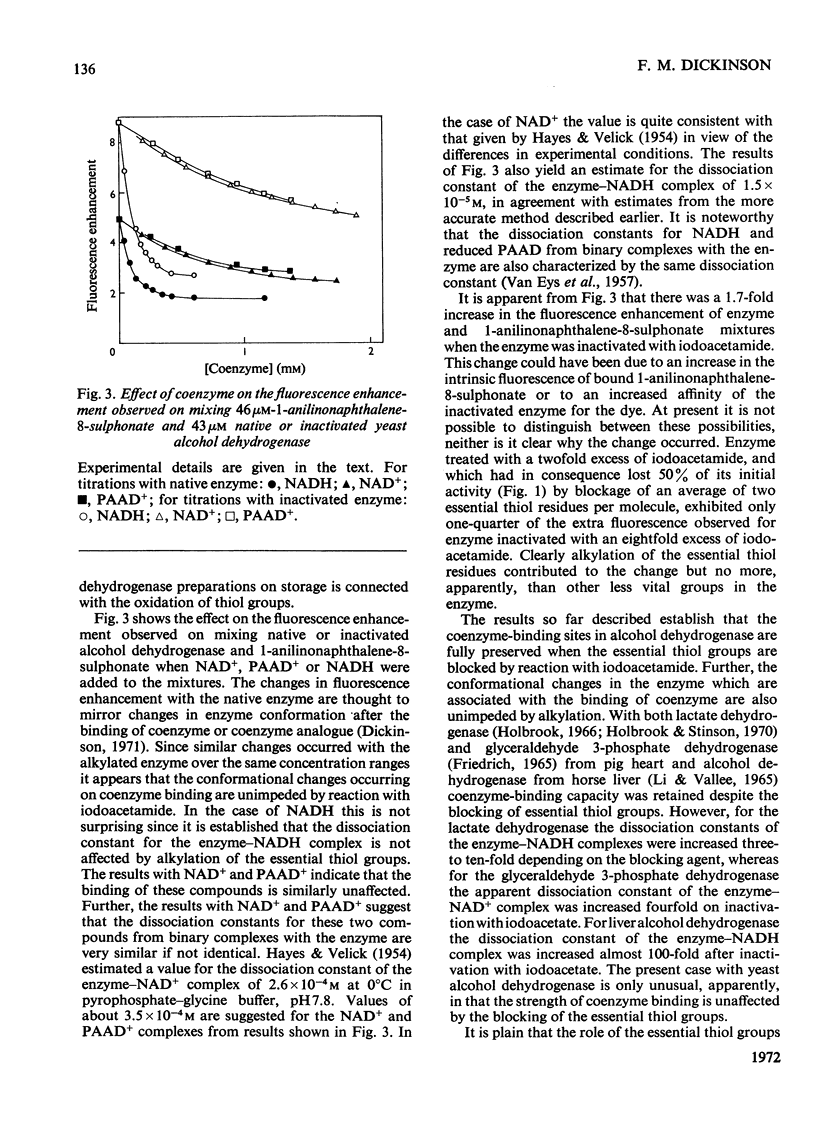
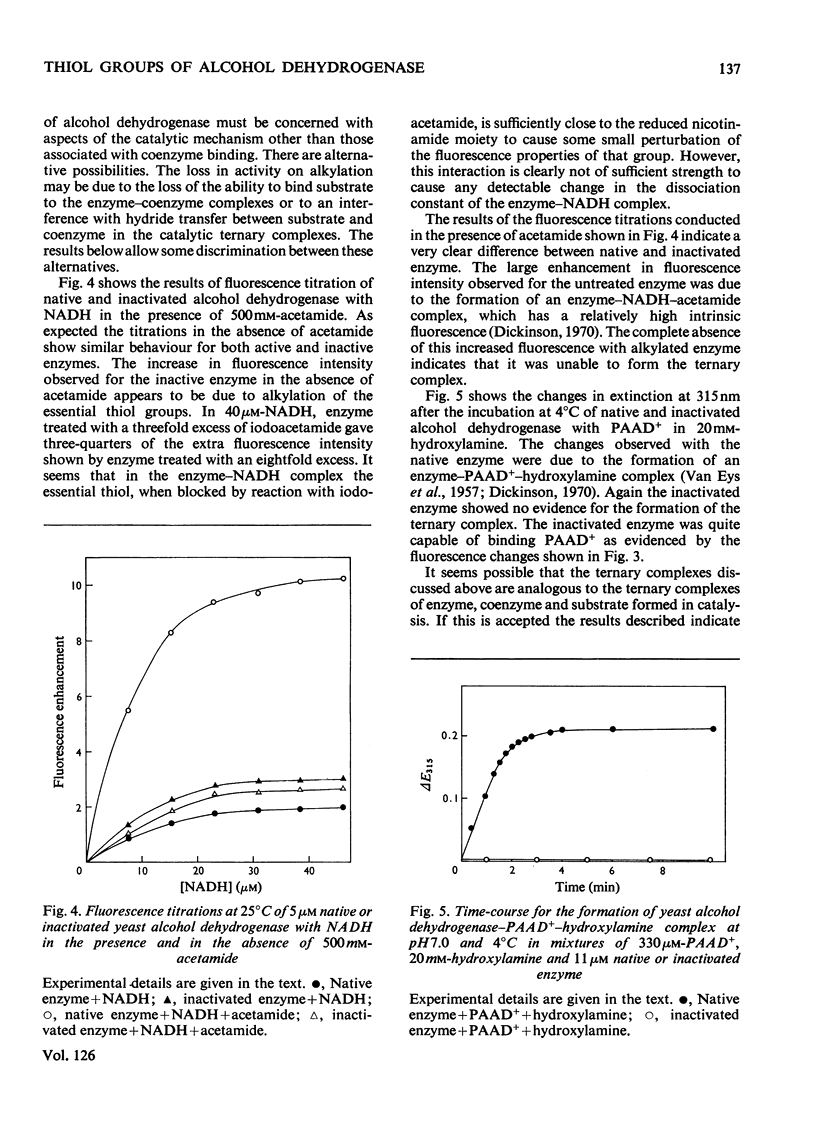
1. Yeast alcohol dehydrogenase inactivated by reaction with iodoacetamide retains 85% of the original NADH-binding capacity as measured under conditions of saturating coenzyme concentration. 2. The dissociation constant of the enzyme–NADH complex is unaffected by inactivation of the enzyme with iodoacetamide, and the affinity of the enzyme for NAD+ and pyridine-3-aldehyde–adenine dinucleotide (PAAD+) appears to be similarly unaffected. 3. Enzyme inactivated with iodoacetamide has lost the ability to form normal ternary complexes of the type enzyme–NADH–acetamide and enzyme–PAAD+–hydroxylamine that are characteristic of the native enzyme.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auricchio F., Bruni C. B. The role of essential-SH groups of yeast alcohol dehydrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;185(2):461–463. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90439-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bühner M., Sund H. Yeast alcohol dehydrogenase: SH groups, disulfide groups, quaternary structure, and reactivation by reductive cleavage of disulfide groups. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Nov;11(1):73–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00741.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson F. M. The binding of dihydronicotinamide--adenine dinucleotide and pyridine-3-aldehyde--adenine dinucleotide by yeast alcohol dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1970 Dec;120(4):821–830. doi: 10.1042/bj1200821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson F. M. The interaction of 1-anilino-8-naphthalene sulphonate with yeast alcohol dehydrogenase. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jun 2;15(1):17–20. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80068-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDRICH P. AN ULTRAVIOLET ABSORPTION BAND DUE TO THE INTERACTION OF NAD AND GLYCERALDEHYDE-3-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 May 18;99:371–375. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(65)80136-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS I. STRUCTURE AND CATALYTIC ACTIVITY OF ALCOHOL DEHYDROGENASES. Nature. 1964 Jul 4;203:30–34. doi: 10.1038/203030a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYES J. E., Jr, VELICK S. F. Yeast alcohol dehydrogenase: molecular weight, coenzyme binding, and reaction equilibria. J Biol Chem. 1954 Mar;207(1):225–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMMEL J. P., DREYER W. J. Measurement of protein-binding phenomena by gel filtration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Oct 8;63:530–532. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90124-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook J. J., Stinson R. A. Reactivity of the essential thiol group of lactate dehydrogenase and substrate binding. Biochem J. 1970 Nov;120(2):289–297. doi: 10.1042/bj1200289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook J. J. The importance of SH-groups for enzymic activity. V. The coenzyme-binding capacity of pig heart lactate dehydrogenase, isozyme I, after inhibition by various maleinimides. Biochem Z. 1966 Mar 28;344(2):141–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li T. K., Vallee B. L. Reactivity and function of sulfhydryl groups in horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1965 Jun;4(6):1195–1202. doi: 10.1021/bi00882a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfleiderer G., Auricchio F. The DPNH-binding capacity of various dehydrogenases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964 May 22;16(1):53–59. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90210-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RABIN B. R., WHITEHEAD E. P. Mechanism of action of yeast alcohol dehydrogenase. Nature. 1962 Nov 17;196:658–660. doi: 10.1038/196658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabin B. R., Cruz J. R., Watts D. C., Whitehead E. P. The reaction of yeast alcohol dehydrogenase with iodoacetamide as determined with a silver-silver iodide electrode. Biochem J. 1964 Mar;90(3):539–542. doi: 10.1042/bj0900539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W., Yielding K. L. 8-Anilino naphthalene sulfonate binding as a probe for conformational changes induced in glutamate dehydrogenase by regulatory reagents. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Aug;126(2):399–406. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90424-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN EYS J., CIOTTI M. M., KAPLAN N. O. Yeast alcohol dehydrogenase. II. Properties of the catalytically active site. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Mar;23(3):581–587. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90380-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead E. P., Rabin B. R. The thiol groups of yeast alcohol dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1964 Mar;90(3):532–539. doi: 10.1042/bj0900532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


