Abstract
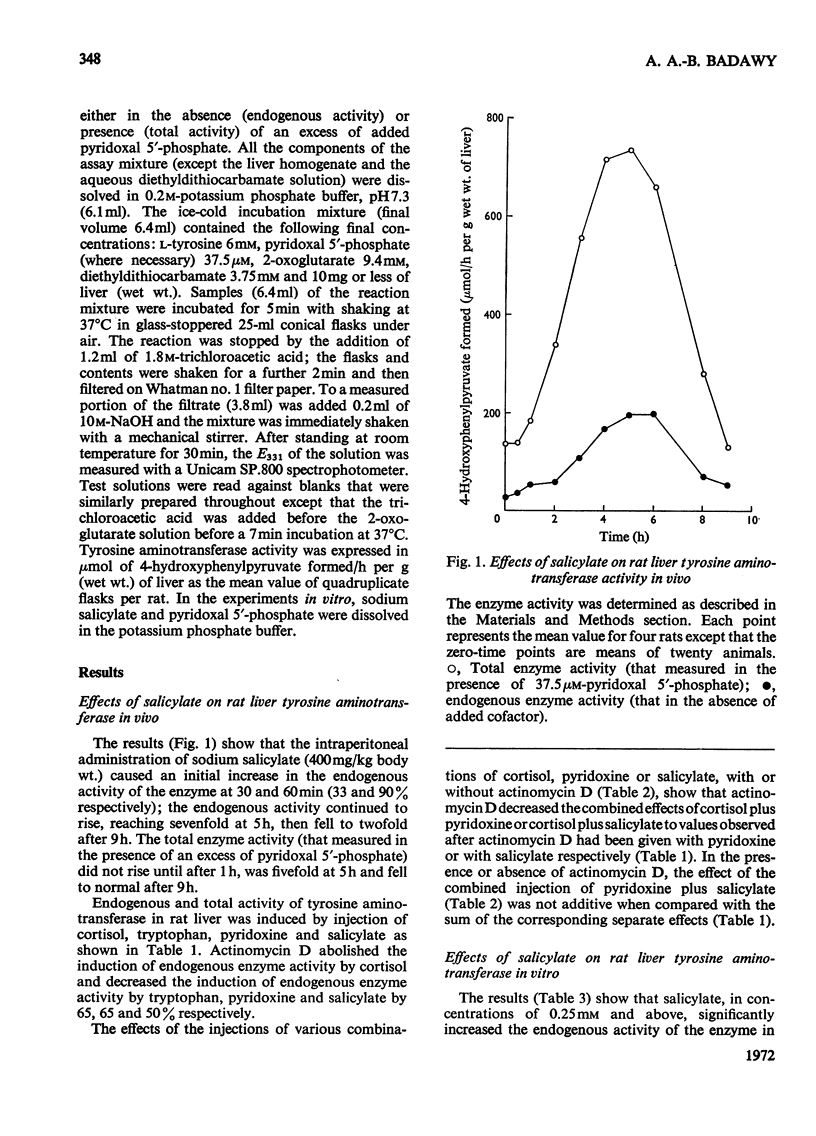
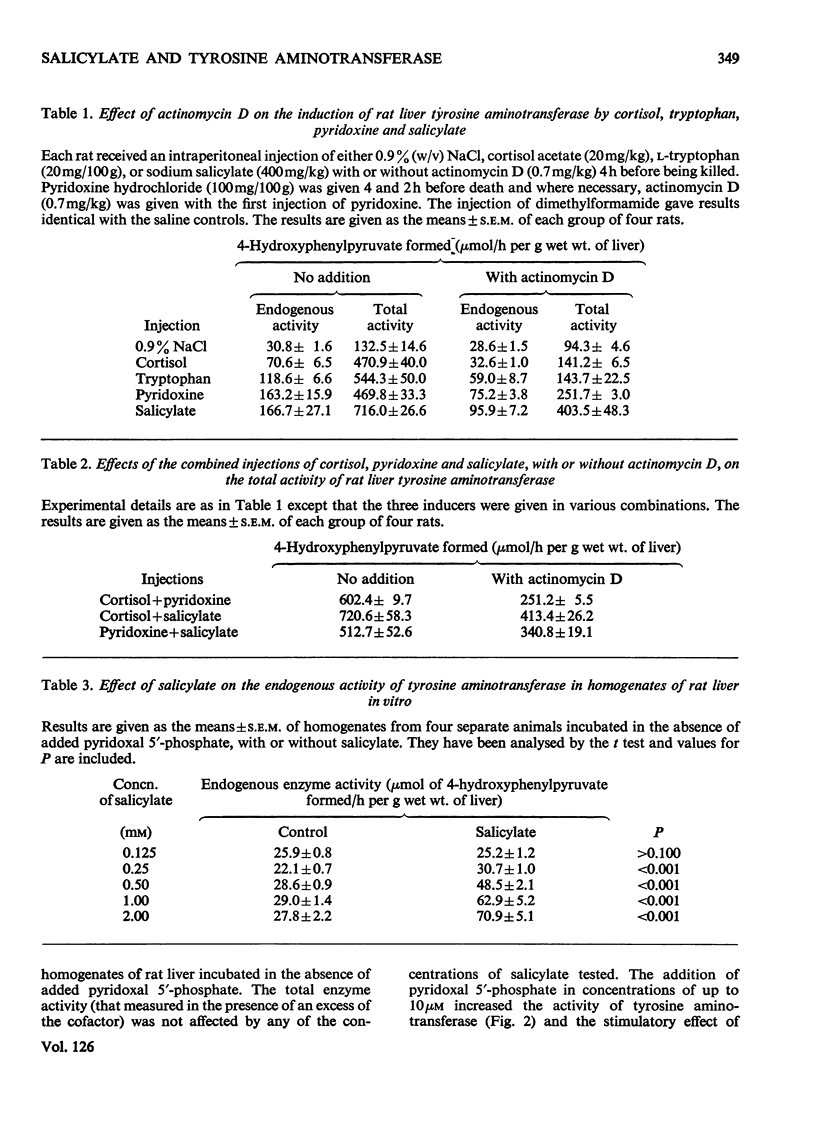
1. Salicylate, in concentrations of 0.25mm and above, enhances the basal activity of tyrosine–2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase in homogenates of rat liver incubated in the absence of added pyridoxal 5′-phosphate (endogenous activity). The effect is decreased by increasing the concentration of the cofactor. 2. The intraperitoneal administration of sodium salicylate enhances the activity of rat liver tyrosine aminotransferase; the major effect during the first hour being on the enzyme in the absence of added pyridoxal phosphate. Actinomycin D prevents the induction of the enzyme by cortisol and tryptophan. Induction by pyridoxine or salicylate is 50% inhibited by actinomycin D. The effects of the injections of various combinations of cortisol, pyridoxine and salicylate were also studied in the absence or presence of actinomycin D. 3. It is suggested that salicylate induces rat liver tyrosine aminotransferase by displacing its protein-bound cofactor and that a cofactor-type induction of the hepatic enzyme occurs in pyridoxine-treated rats.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Badawy A. A., Smith M. J. The effects of salicylate on the activity of rat liver tryptophan pyrrolase in vitro and in vivo. Biochem J. 1971 Jun;123(2):171–174. doi: 10.1042/bj1230171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEMPSEY W. B., CHRISTENSEN H. N. The specific binding of pyridoxal 5'-phosphate to bovine plasma albumin. J Biol Chem. 1962 Apr;237:1113–1120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOULD B. J., SMITH M. J. SALICYLATE AND AMINOTRANSFERASES. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1965 Feb;17:83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1965.tb07618.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENGARD O., GORDON M. THE COFACTOR-MEDIATED REGULATION OF APOENZYME LEVELS IN ANIMAL TISSUES. I. THE PYRIDOXINE-INDUCED RISE OF RAT LIVER TYROSINE TRANSAMINASE LEVEL IN VIVO. J Biol Chem. 1963 Nov;238:3708–3710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holten D., Wicks W. D., Kenney F. T. Studies on the role of vitamin B6 derivatives in regulating tyrosine alpha-ketoglutarate transaminase activity in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1967 Mar 10;242(5):1053–1059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIN E. C., CIVEN M., KNOX W. E. Effect of vitamin B6 deficiency on the basal and adapted levels of rat liver tyrosine and tryptophan transaminases. J Biol Chem. 1958 Nov;233(5):1183–1185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


