Abstract
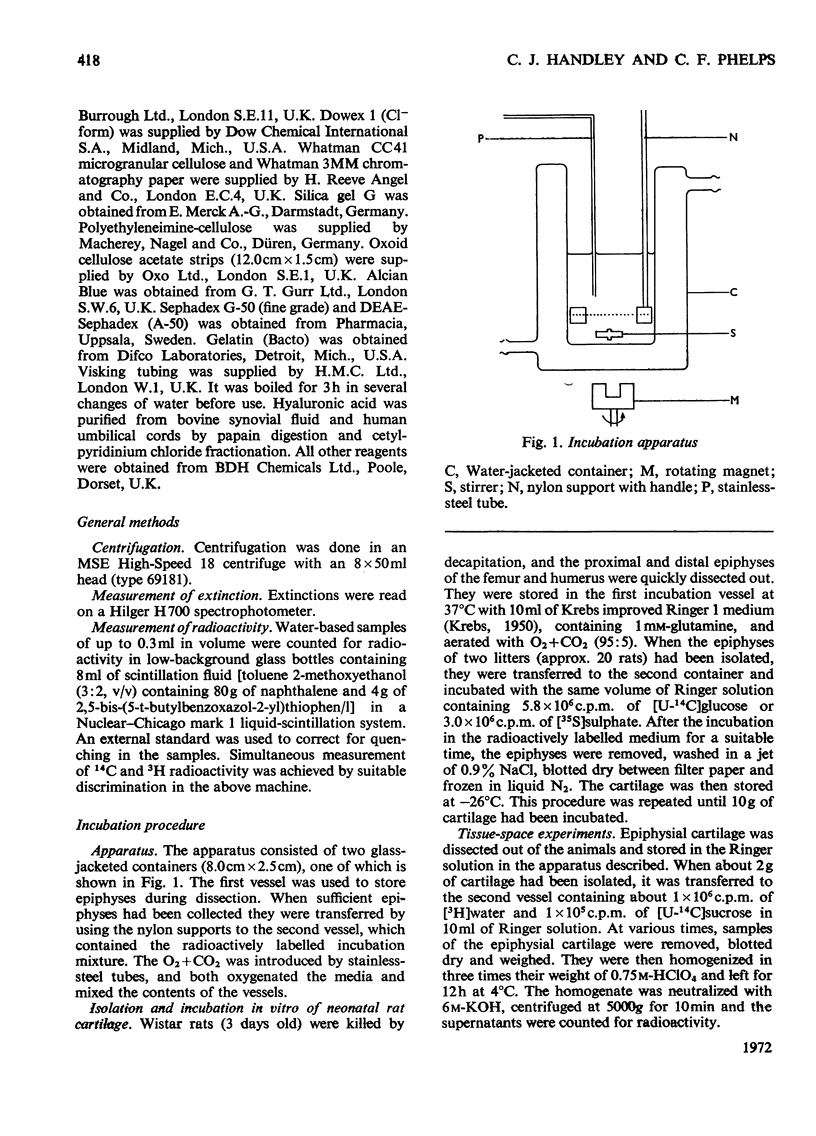
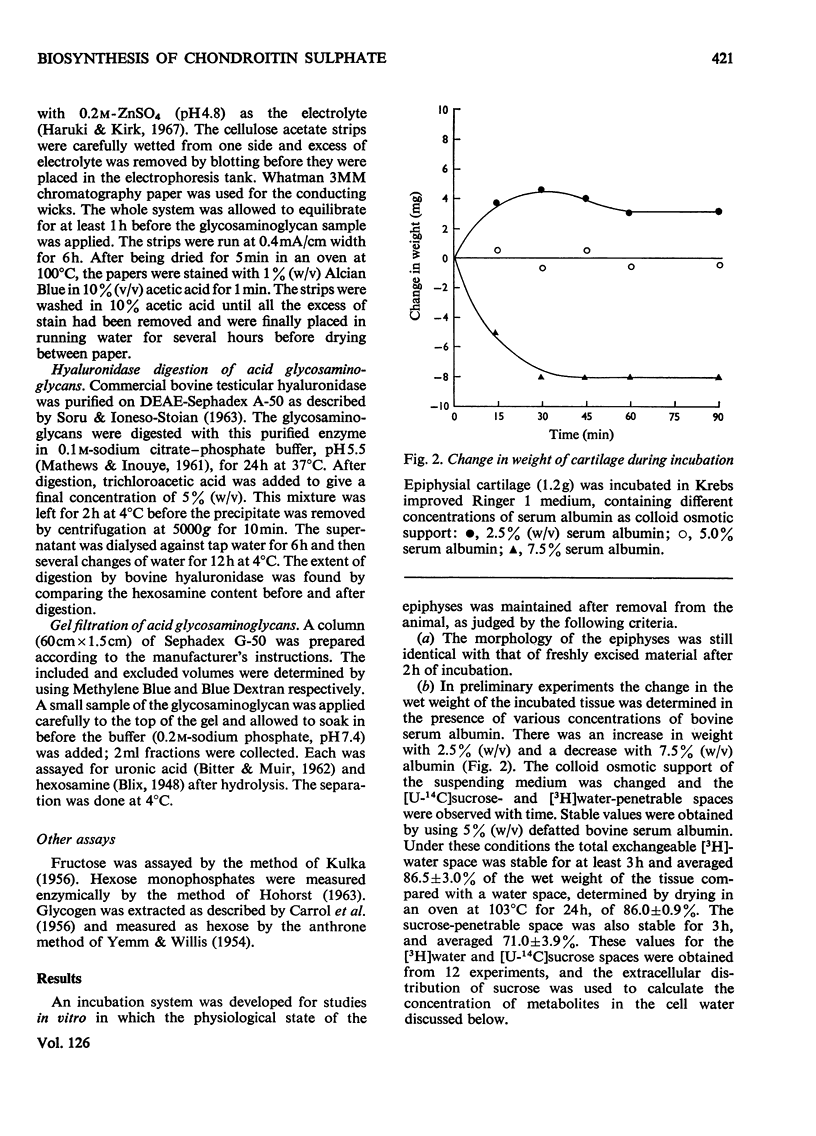
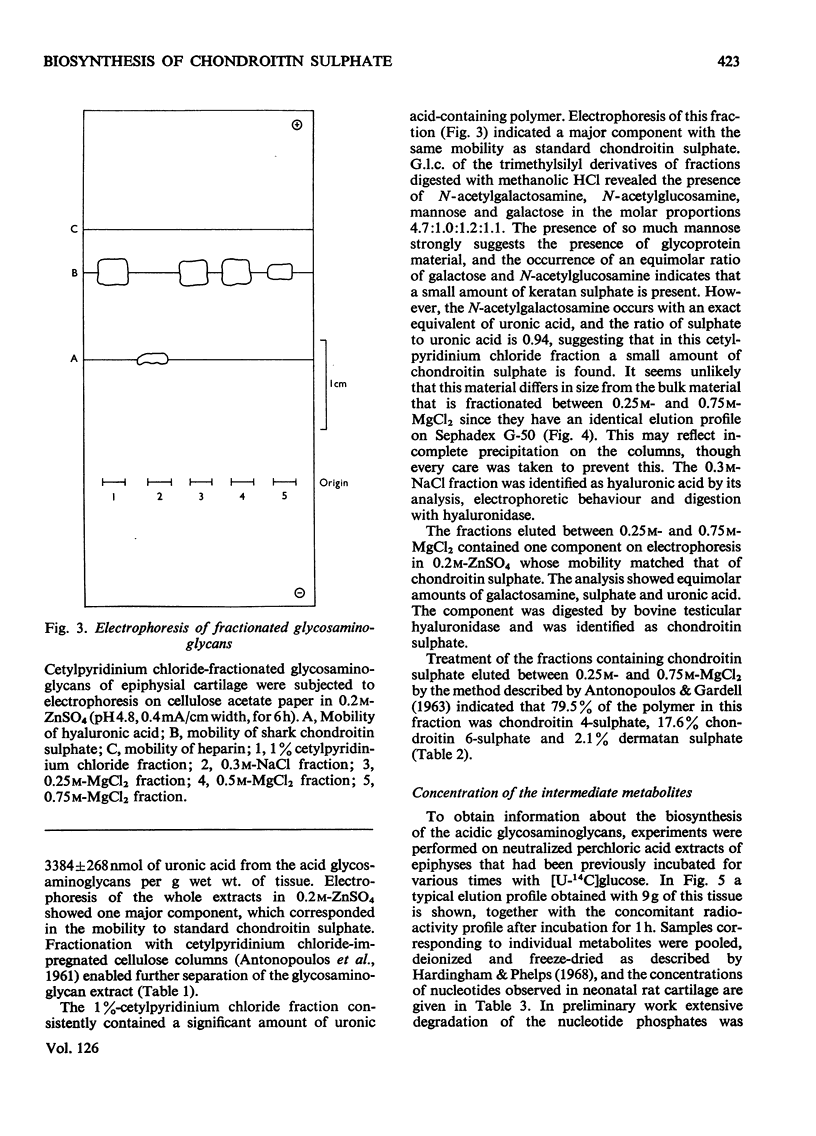
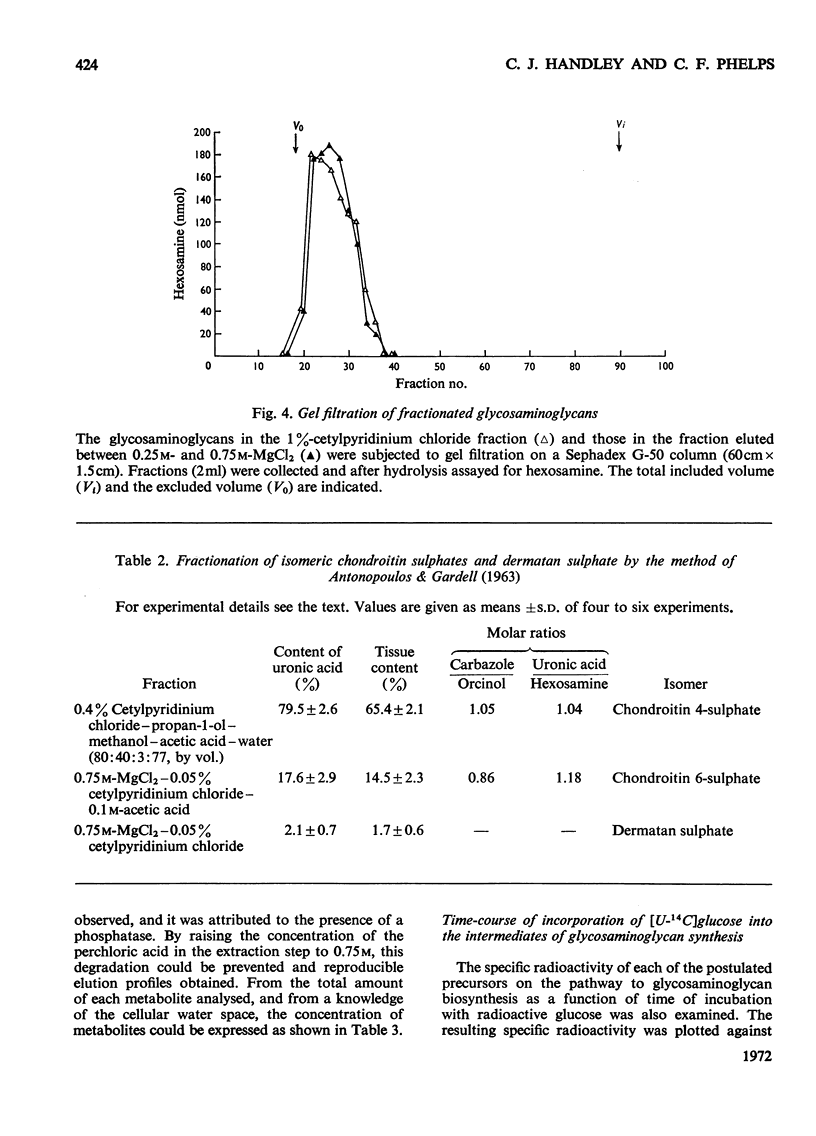
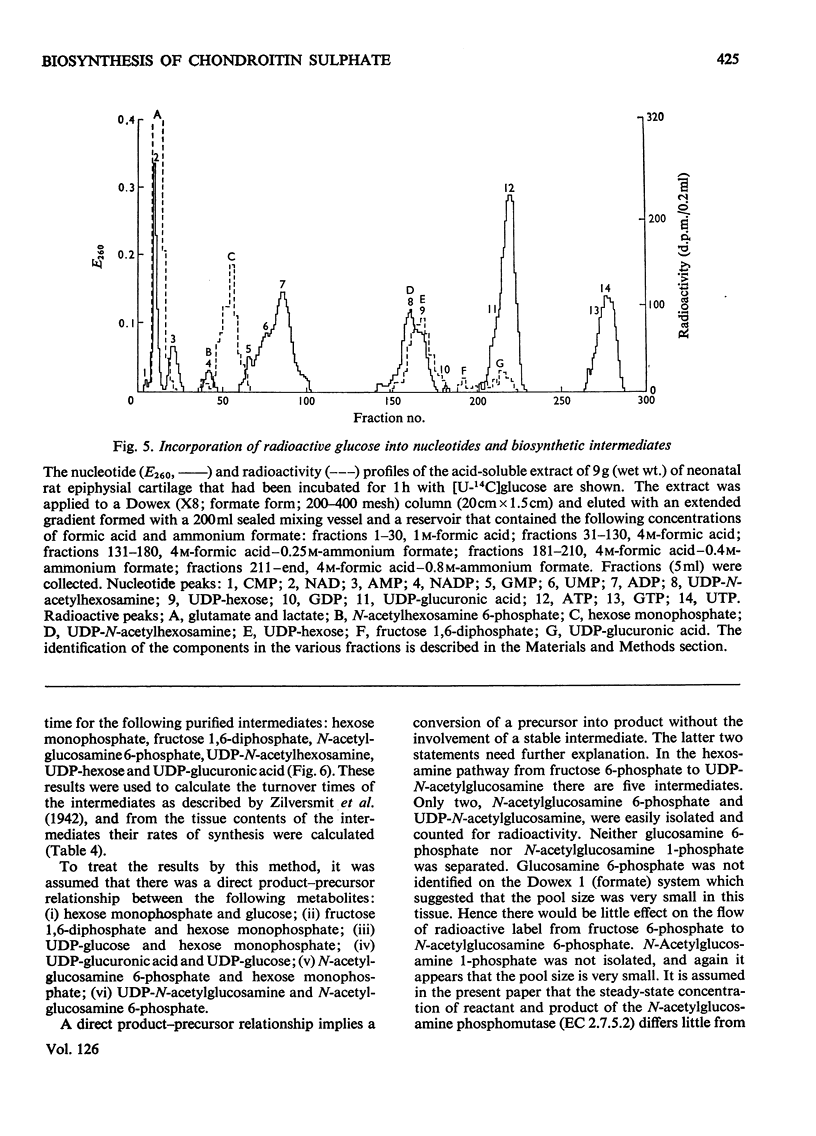
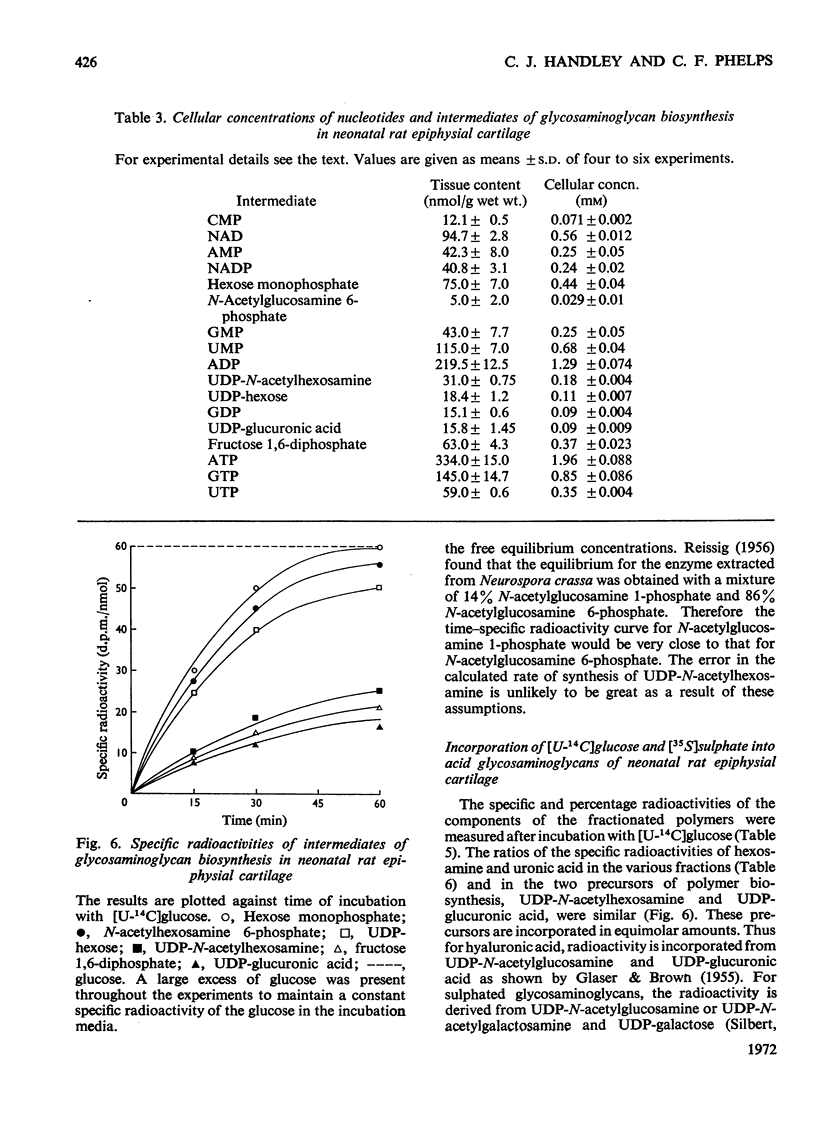
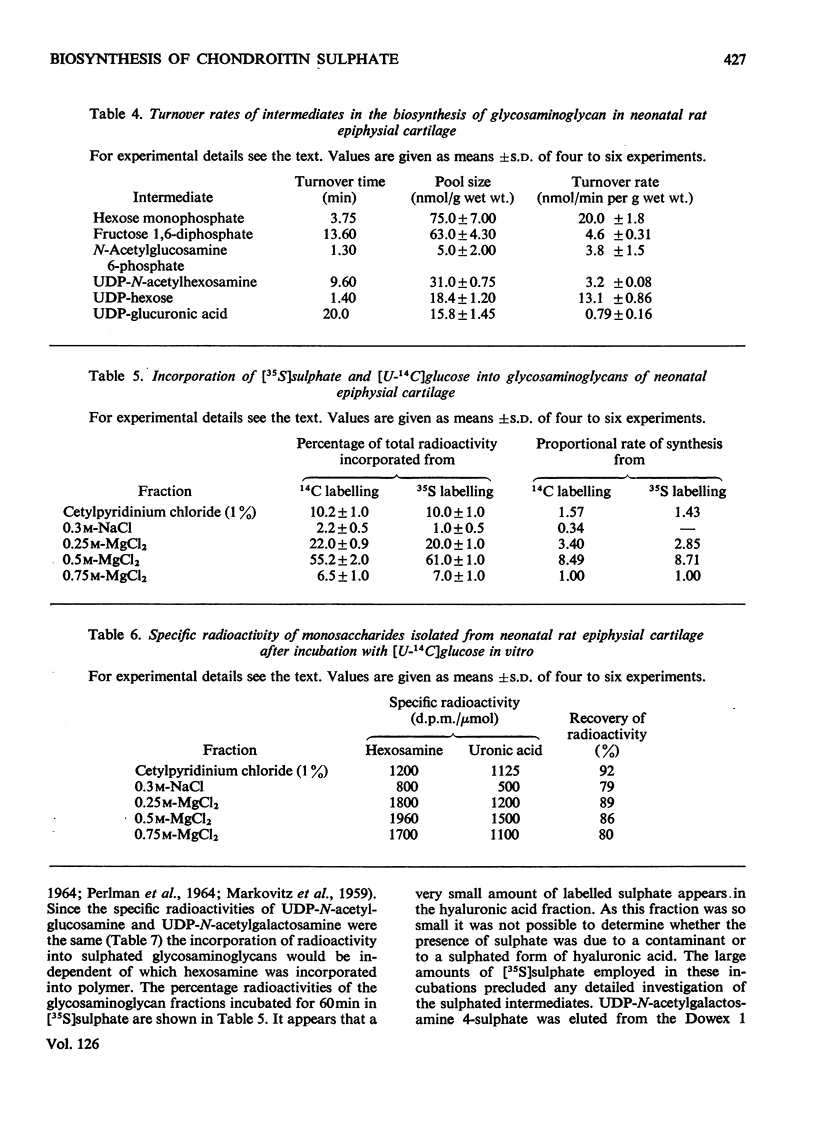
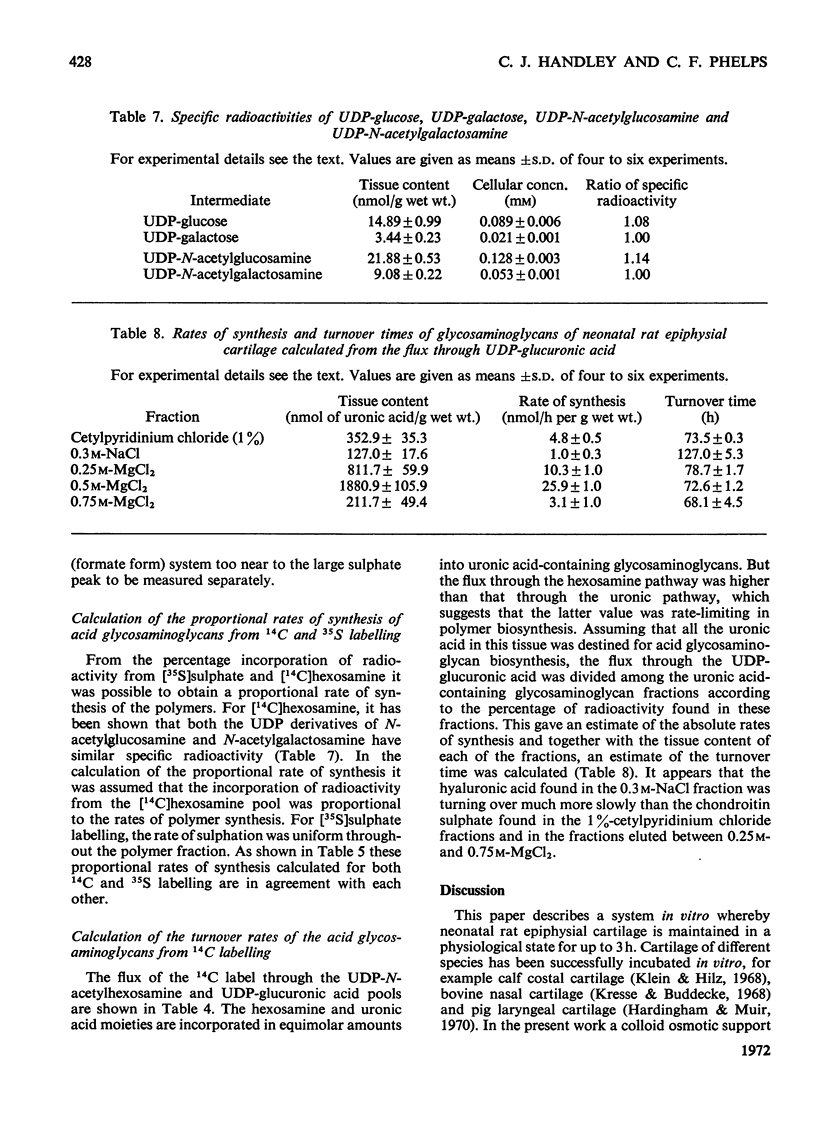
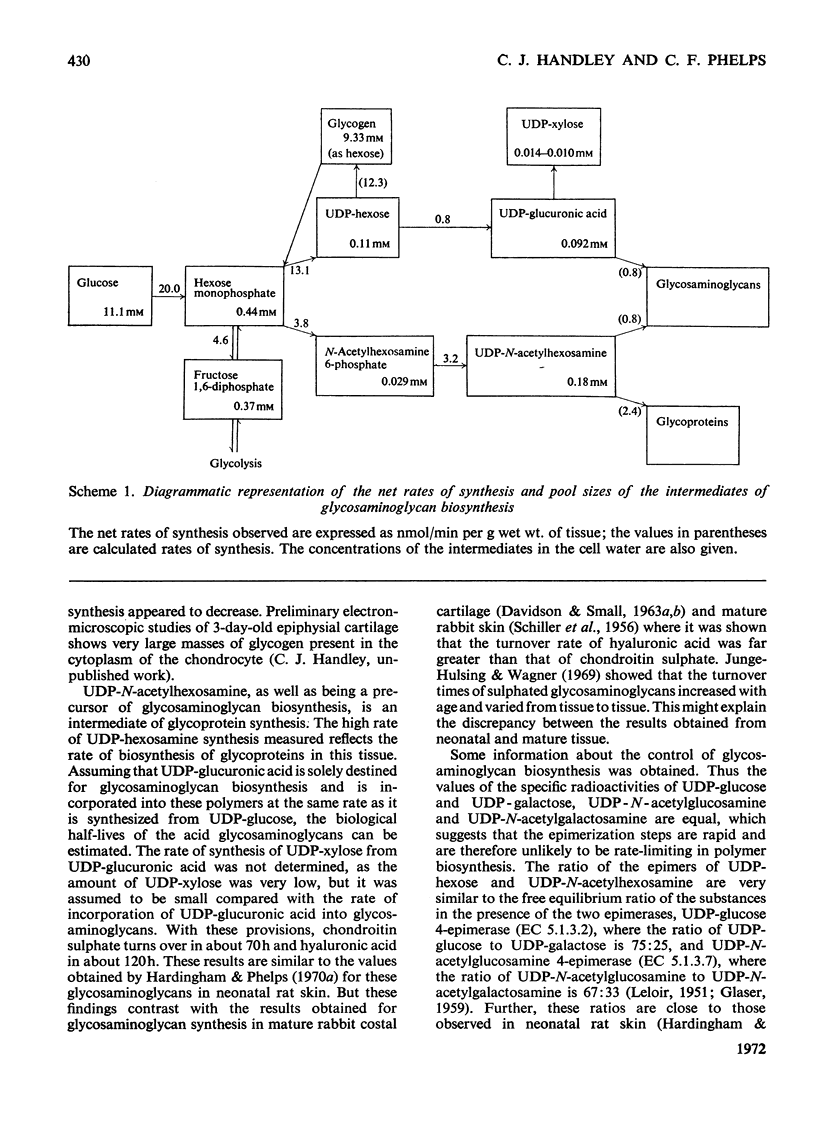
1. A system is described, which was used to incubate neonatal rat epiphysial cartilage in vitro with [U-14C]glucose and [35S]sulphate. 2. The acid glycosaminoglycans of neonatal rat epiphyses were extracted and fractionated on cetylpyridinium chloride–cellulose columns. The major components were chondroitin 4-sulphate (65%), chondroitin 6-sulphate (15%), hyaluronic acid (4%) and keratan sulphate (2%). 3. The acid-soluble nucleotides and intermediates of glycosaminoglycan synthesis were separated on a Dowex 1 (formate) system. The tissue contents and cellular concentrations of these metabolites were determined. 4. The rates of synthesis of UDP-glucuronic acid and UDP-N-acetyl-hexosamine from [U-14C]glucose were found to be 0.79±0.16 and 3.2±0.08nmol/min per g wet wt. respectively. 5. The incorporation of [U-14C]glucose into the uronic acid and hexosamine moieties of the polymers was also measured and the turnover rates of the glycosaminoglycans were calculated. It was found that chondroitin sulphate was turning over in about 70h and hyaluronic acid in about 120h. 6. The relative rates of synthesis of the sulphated glycosaminoglycans were calculated from [35S]sulphate incorporation and were found to be in good agreement with those obtained from [U-14C]glucose labelling.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANTONOPOULOS C. A., BORELIUS E., GARDELL S., HAMNSTROM B., SCOTT J. E. The precipitation of polyanions by long-chain aliphatic ammonium compounds. IV. Elution in salt solutions of mucopolysaccharide-quaternary ammonium complexes adsorbed on a support. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Dec 9;54:213–226. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BITTER T., MUIR H. M. A modified uronic acid carbazole reaction. Anal Biochem. 1962 Oct;4:330–334. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARROLL N. V., LONGLEY R. W., ROE J. H. The determination of glycogen in liver and muscle by use of anthrone reagent. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jun;220(2):583–593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clamp J. R., Dawson G., Hough L. The simultaneous estimation of 6-deoxy-L-galactose (L-fucose), D-mannose, D-galactose, 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-D-glucose (N-acetyl-D-glucosamine) and N-acetylneuraminic acid (sialic acid) in glycopeptides and glycoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Nov 28;148(2):342–349. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIDSON E. A., SMALL W. Metabolism in vivo of connective-tissue mucopolysaccharides. I. Chondroitin sulfate C and keratosulfate of nucleus pulposus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Mar 5;69:445–452. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91292-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIDSON E. A., SMALL W. Metabolism in vivo of connective-tissue mucopolysaccharides. II. Chondroitin sulfate B and hyaluronic acid of skin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Mar 5;69:453–458. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91293-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGSON K. S. Determination of inorganic sulphate in studies on the enzymic and non-enzymic hydrolysis of carbohydrate and other sulphate esters. Biochem J. 1961 Feb;78:312–319. doi: 10.1042/bj0780312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLASER L. The biosynthesis of N-acetylgalactosamine. J Biol Chem. 1959 Nov;234:2801–2805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser L., Brown D. H. THE ENZYMATIC SYNTHESIS IN VITRO OF HYALURONIC ACID CHAINS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1955 May 15;41(5):253–260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.41.5.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURLBERT R. B., SCHMITZ H., BRUMM A. F., POTTER V. R. Nucleotide metabolism. II. Chromatographic separation of acid-soluble nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1954 Jul;209(1):23–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Muir H. The effect of temperature on the biosynthesis of chondroitin 4-sulphate in cartilage slices in vitro. FEBS Lett. 1970 Sep 6;9(3):145–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80339-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Phelps C. F. Studies on the incorporation of (U-14C)glucose and (35S)sulphate into the acid glycosaminoglycans of neonatal rat skin. Biochem J. 1970 Oct;119(5):885–893. doi: 10.1042/bj1190885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Phelps C. F. The glycosaminoglycans of neonatal rat skin. Biochem J. 1970 May;117(5):813–818. doi: 10.1042/bj1170813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Phelps C. F. The tissue content and turnover rates of intermediates in the biosynthesis of glycosaminoglycans in young rat skin. Biochem J. 1968 Jun;108(1):9–16. doi: 10.1042/bj1080009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haruki F., Kirk J. E. A method for separation of chondroitin sulfate B from isomers A and C by paper electrophoresis with zinc sulphate or zinc acetate solution as electrolyte medium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Mar 22;136(2):391–393. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90086-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIELLEY W. W., BRONK J. R. Oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondrial fragments obtained by sonic vibration. J Biol Chem. 1958 Jan;230(1):521–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNFELD S., KORNFELD R., NEUFELD E. F., O'BRIEN P. J. THE FEEDBACK CONTROL OF SUGAR NUCLEOTIDE BIOSYNTHESIS IN LIVER. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Aug;52:371–379. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREBS H. A. Body size and tissue respiration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1950 Jan;4(1-3):249–269. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(50)90032-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KULKA R. G. Colorimetric estimation of ketopentoses and ketohexoses. Biochem J. 1956 Aug;63(4):542–548. doi: 10.1042/bj0630542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleine T. O., Hilz H. Untersuchungen zur Biosynthese der Chondroitinsulfat-Proteine. I. Charakterisierung der Protein-Polysaccharide aus Kalberrippenknorpel und ihre In-vitro-Markierung mit zweiwertig 35S-Sulfat. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1968 Aug;349(8):1027–1036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klethi J., Mandel P. Recherches sur la biochimie du cristallin. II. Les nucléodtides libres du cristallin. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1968;50(4):709–723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kresse H., Buddecke E. Makromolekulare Polysaccharid-Proteine. 3. Stoffwechselheterogenität von Chondroitin-4-sulfat-Proteinen und Kollagenstoffwechsel in Rindernasenknorpel. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1968 Nov;349(11):1497–1506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogh A. The rate of diffusion of gases through animal tissues, with some remarks on the coefficient of invasion. J Physiol. 1919 May 20;52(6):391–408. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1919.sp001838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LELOIR L. F. The enzymatic transformation of uridine diphosphate glucose into a galactose derivative. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1951 Sep;33(2):186–190. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(51)90096-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDEL P., HARTH S. Free nucleotides of the brain in various mammals. J Neurochem. 1961 Nov;8:116–125. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1961.tb13533.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKOVITZ A., CIFONELLI J. A., DORFMAN A. The biosynthesis of hyaluronic acid by group A Streptococcus. VI. Biosynthesis from uridine nucleotides in cell-free extracts. J Biol Chem. 1959 Sep;234:2343–2350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATHEWS M. B., INOUYE M. The determination of chondroitin sulfate C-type polysaccharides in mixtures with other acid mucopolysaccharides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Nov 11;53:509–513. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90209-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYER K., HOFFMAN P., LINKER A. Mucopolysaccharides of costal cartilage. Science. 1958 Oct 17;128(3329):896–896. doi: 10.1126/science.128.3329.896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEUFELD E. F., HALL C. W. INHIBITION OF UDP-D-GLUCOSE DEHYDROGENASE BY UDP-D-XYLOSE: A POSSIBLE REGULATORY MECHANISM. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 May 3;19:456–461. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90146-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERLMAN R. L., TELSER A., DORFMAN A. THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF CHONDROITIN SULFATE BY A CELL-FREE PREPARATION. J Biol Chem. 1964 Nov;239:3623–3629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISSIG J. L. Phosphoacetylglucosamine mutase of Neurospora. J Biol Chem. 1956 Apr;219(2):753–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randerath E., Randerath K. Ion-exchange thin-layer chromatography. XII. Quantitative elution and microdetermination of nucleoside monophosphates, ATP, and other nucleotide coenzymes. Anal Biochem. 1965 Jul;12(1):83–93. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90145-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rokosová-Cmuchalová B., Bentley J. P. Relation of collagen synthesis to chondroitin sulfate synthesis in cartilage. Biochem Pharmacol. 1968 Mar;(Suppl):315–328. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(68)90317-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHILLER S., MATHEWS M. B., CIFONELLI J. A., DORFMAN A. The metabolism of mucopolysaccharides in animals. III. Further studies on skin utilizing C14-glucose, C14-acetate, and S35-sodium sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):139–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCOTT J. E. Aliphatic ammonium salts in the assay of acidic polysaccharides from tissues. Methods Biochem Anal. 1960;8:145–197. doi: 10.1002/9780470110249.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILBERT J. E. INCORPORATION OF 14C AND 3H FROM LABELED NUCLEOTIDE SUGARS INTO A POLYSACCHARIDE IN THE PRESENCE OF A CELL-FREE PREPARATION FROM CARTILAGE. J Biol Chem. 1964 May;239:1310–1315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLAPIKOFF S., FESSENDEN J. M., MOLDAVE K. ENZYMATIC INCORPORATION OF AMINO ACID FROM AMINOACYL SOLUBLE RIBONUCLEIC ACID INTO RIBOSOMAL RIBONUCLEIC ACID AND RIBOSOMAL PROTEIN. J Biol Chem. 1963 Nov;238:3670–3676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SORU E., IONESCU-STOIAN F. The purification of hyaluronate lyase on DEAE-sephadex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Mar 5;69:538–543. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91305-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims E. A., Landau B. R. Insulin responsive and nonresponsive pools of glucose 6-phosphate in diaphragmatic muscle. Fed Proc. 1966 May-Jun;25(3):835–839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winterburn P. J., Phelps C. F. Studies on the control of hexosamine biosynthesis by glucosamine synthetase. Biochem J. 1971 Feb;121(4):711–720. doi: 10.1042/bj1210711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YEMM E. W., WILLIS A. J. The estimation of carbohydrates in plant extracts by anthrone. Biochem J. 1954 Jul;57(3):508–514. doi: 10.1042/bj0570508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


