Abstract
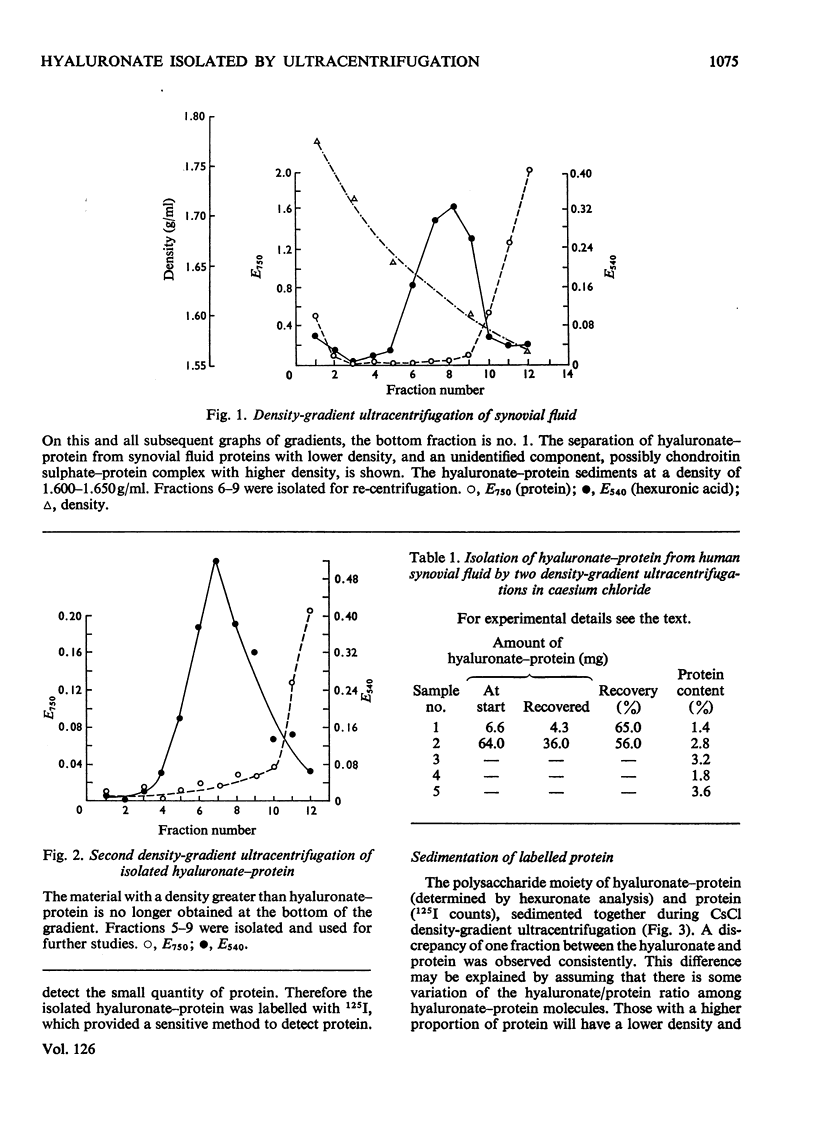
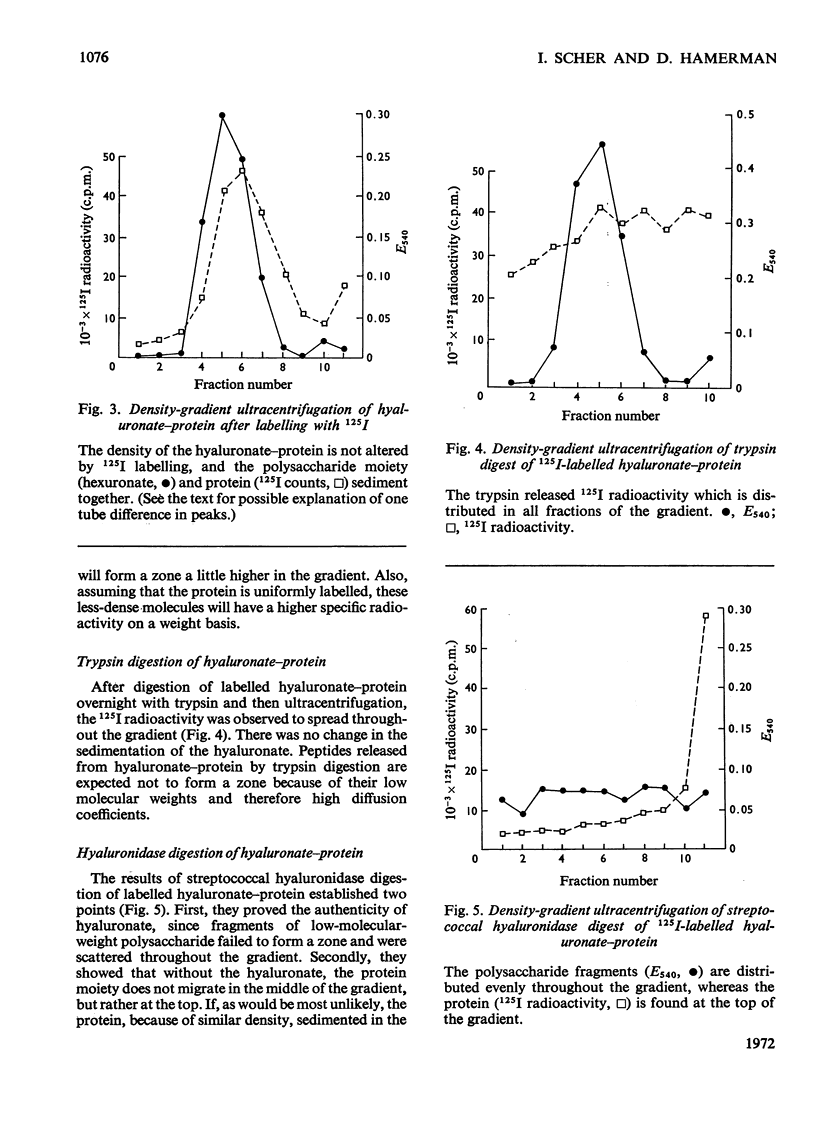
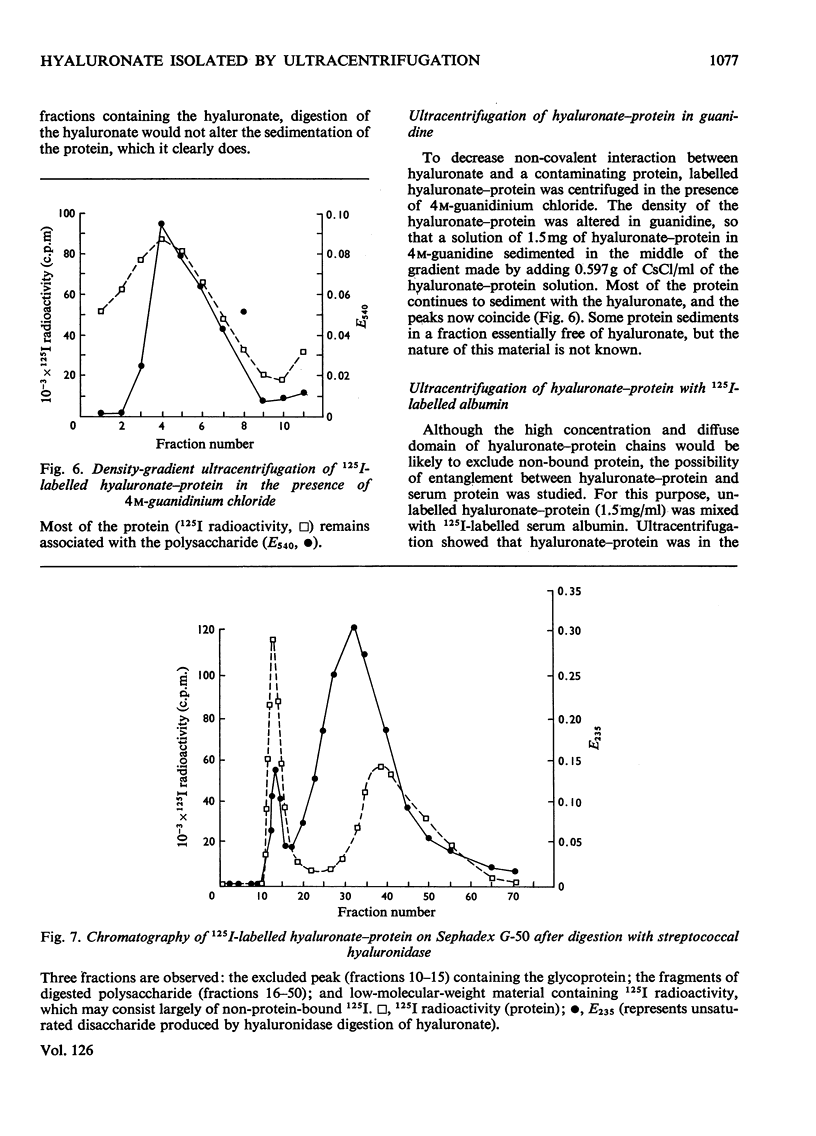
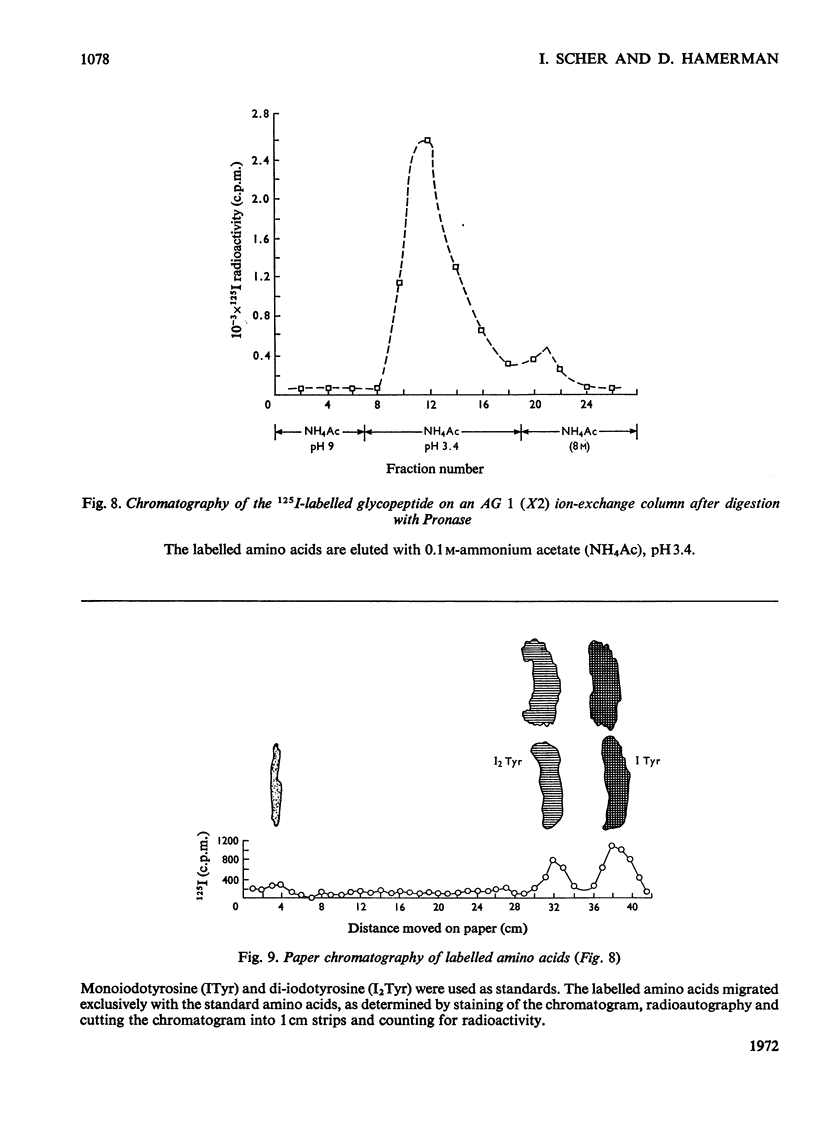
1. A compound of hyaluronate and protein, called hyaluronate–protein was isolated from pooled human synovial fluids by caesium chloride density-gradient ultracentrifugation. 2. The isolated hyaluronate–protein was labelled with [125I]iodide and the following studies were done. (a) Ultracentrifugation in caesium chloride showed that the protein moiety (125I counts) and hyaluronate (hexuronate) sedimented together in the middle of the gradient. (b) The labelled hyaluronate–protein was treated with trypsin, and ultracentrifugation showed that peptide fragments (125I counts) were dispersed throughout the gradient, indicating proteolytic digestion. Hyaluronate sedimented in the middle of the gradient. (c) The labelled hyaluronate–protein was digested with streptococcal hyaluronidase, and ultracentrifugation showed that hyaluronate fragments were dispersed throughout the gradient, indicating digestion of the polysaccharide. The protein moiety, without attached hyaluronate, now sedimented at the top of the gradient. (d) Ultracentrifugation of labelled hyaluronate–protein in 4m-guanidinium chloride showed that protein and hyaluronate sedimented together. 3. These studies confirm that hyaluronate is combined with a small quantity of protein in normal human synovial fluid. A mild method for the rapid isolation of hyaluronate–protein in good yield is described.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOWNESS J. M. Application of the carbazole reaction to the estimation of glucuronic acid and flucose in some acidic polysaccharides and in urine. Biochem J. 1957 Oct;67(2):295–300. doi: 10.1042/bj0670295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker S. A., Hawkins C. F., Hewins M. Mucopolysaccharides in synovial fluid detection of chondroitin sulphate. Ann Rheum Dis. 1966 May;25(3):209–213. doi: 10.1136/ard.25.3.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau S., Janis R., Hamerman D., Sandson J. Cellular origin of hyaluronateprotein in human synovial membrane. Science. 1965 Oct 15;150(3694):353–355. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3694.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De la Haba G., Holtzer H. Chondroitin sulfate: inhibition of synthesis by puromycin. Science. 1965 Sep 10;149(3689):1263–1265. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3689.1263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS J., LEBLOND C. P. The presence of free iodinated compounds in the thyroid and their passage into the circulation. Endocrinology. 1951 Jun;48(6):714–725. doi: 10.1210/endo-48-6-714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamerman D., Rojkind M., Sandson J. Protein bound to hyaluronate: chemical and immunological studies. Fed Proc. 1966 May-Jun;25(3):1040–1045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Sajdera S. W. Proteinpolysaccharide complex from bovine nasal cartilage. The function of glycoprotein in the formation of aggregates. J Biol Chem. 1969 May 10;244(9):2384–2396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- How M. J., Long V. J., Stanworth D. R. The association of hyaluronic acid with protein in human synovial fluid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Nov 11;194(1):81–90. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(69)90183-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer K. Discussion: protein-polysaccharide interaction. Fed Proc. 1966 May-Jun;25(3):1046–1046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OGSTON A. G., PHELPS C. F. The partition of solutes between buffer solutions and solutions containing hyaluronic acid. Biochem J. 1961 Apr;78:827–833. doi: 10.1042/bj0780827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIGMAN W., RIZVI S., HOLLEY H. Preparation and stability of hyaluronic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Oct 28;53:254–262. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90438-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANDSON J., HAMERMAN D. Isolation of hyaluronateprotein from human synovial fluid. J Clin Invest. 1962 Oct;41:1817–1830. doi: 10.1172/JCI104639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sajdera S. W., Hascall V. C. Proteinpolysaccharide complex from bovine nasal cartilage. A comparison of low and high shear extraction procedures. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jan 10;244(1):77–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silpananta P., Dunstone J. R., Ogston A. G. Fractionation of a hyaluronic acid preparation in a density gradient. The isolation and identification of a chondroitin sulphate. Biochem J. 1967 Aug;104(2):404–409. doi: 10.1042/bj1040404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silpananta P., Dunstone J. R., Ogston A. G. Fractionation of ahyaluronic acid preparation in a density gradient. Some properties of the hyaluronic acid. Biochem J. 1968 Aug;109(1):43–50. doi: 10.1042/bj1090043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C., Hamerman D. Partial inhibition by cycloheximide of haluronate synthesis in cell culture. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Apr;127(4):988–991. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoolmiller A. C., Dorfman A. The biosynthesis of hyaluronic acid by Streptococcus. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jan 25;244(2):236–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swann D. A. Studies on hyaluronic acid. II. The protein component(s) of rooster comb hyaluronic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 May 6;160(1):96–105. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90068-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telser A., Robinson H. C., Dorfman A. The biosynthesis of chondroitin-sulfate protein complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):912–919. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


