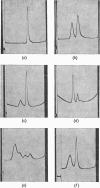
Abstract
1. Human α2-macroglobulin was prepared from a fraction obtained during the large-scale separation of normal human plasma proteins for clinical use. 2. Sedimentation-equilibrium measurements indicated a molecular weight of 725000. A value of 18.1S was obtained for s020,w. 3. The dissociation that occurs in the pH range 4.5–2.5 and in the region of neutrality in urea-containing solutions is consistent with a dimeric structure of the molecule. 4. The effects of the thiol reagents mercaptoethanol, mercaptoethylamine and N-acetylcysteine were investigated over a range of experimental conditions. Distinct components having sedimentation coefficients of 15, 12 and 8.5S were identified. 5. Conditions were found under which limited reduction with thiol liberated a subunit with a molecular weight approximately one-quarter of that of the intact molecule. This subunit retains the serological specificity of the whole molecule.
Full text
PDF




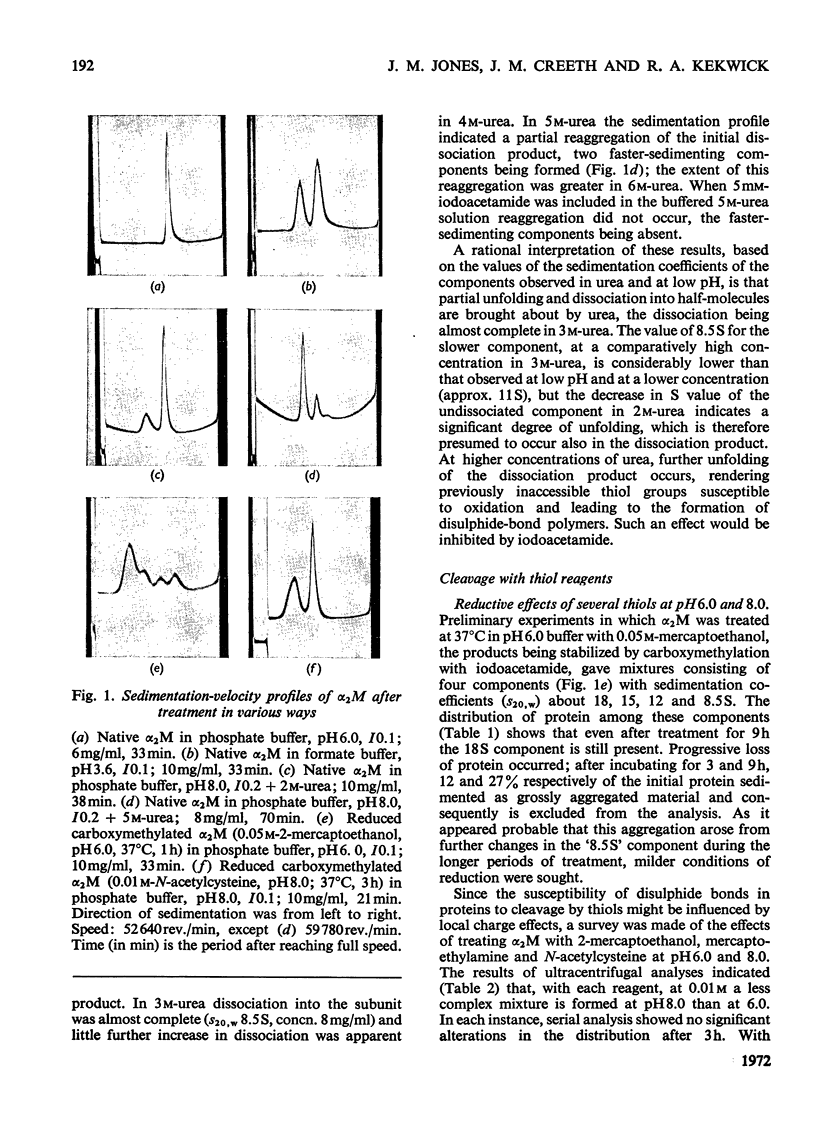
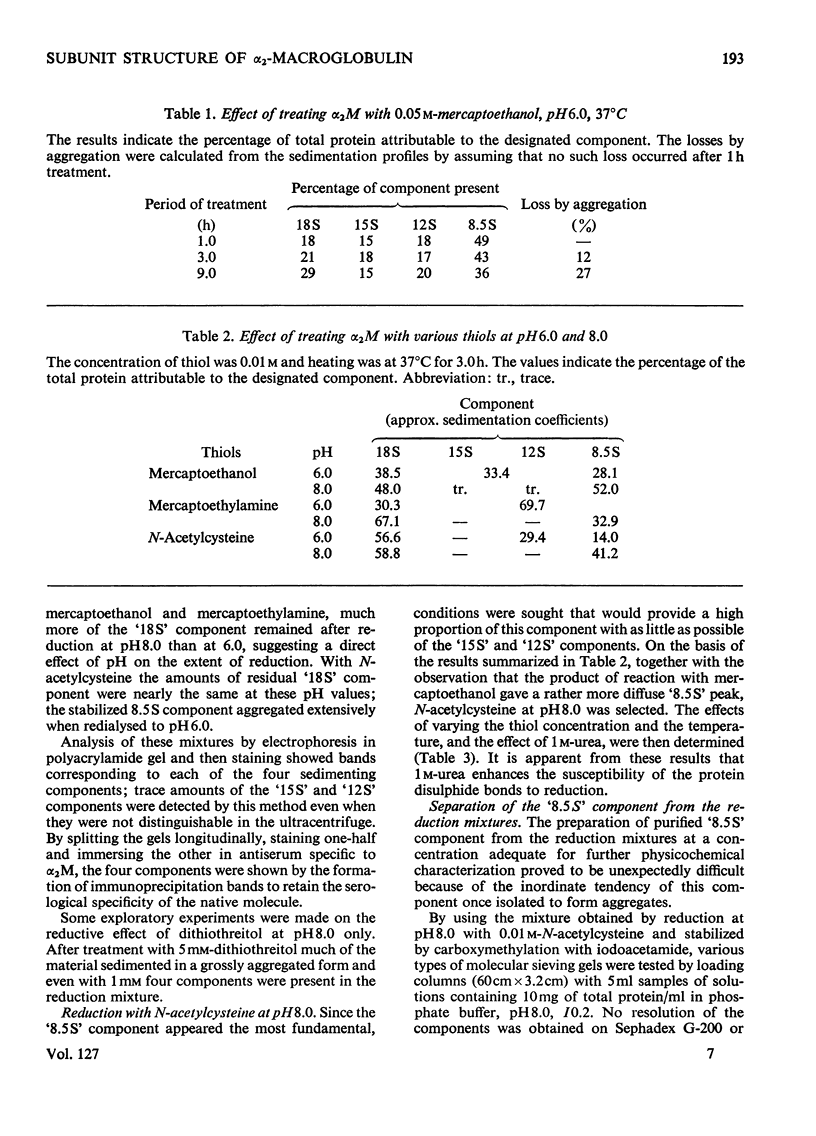
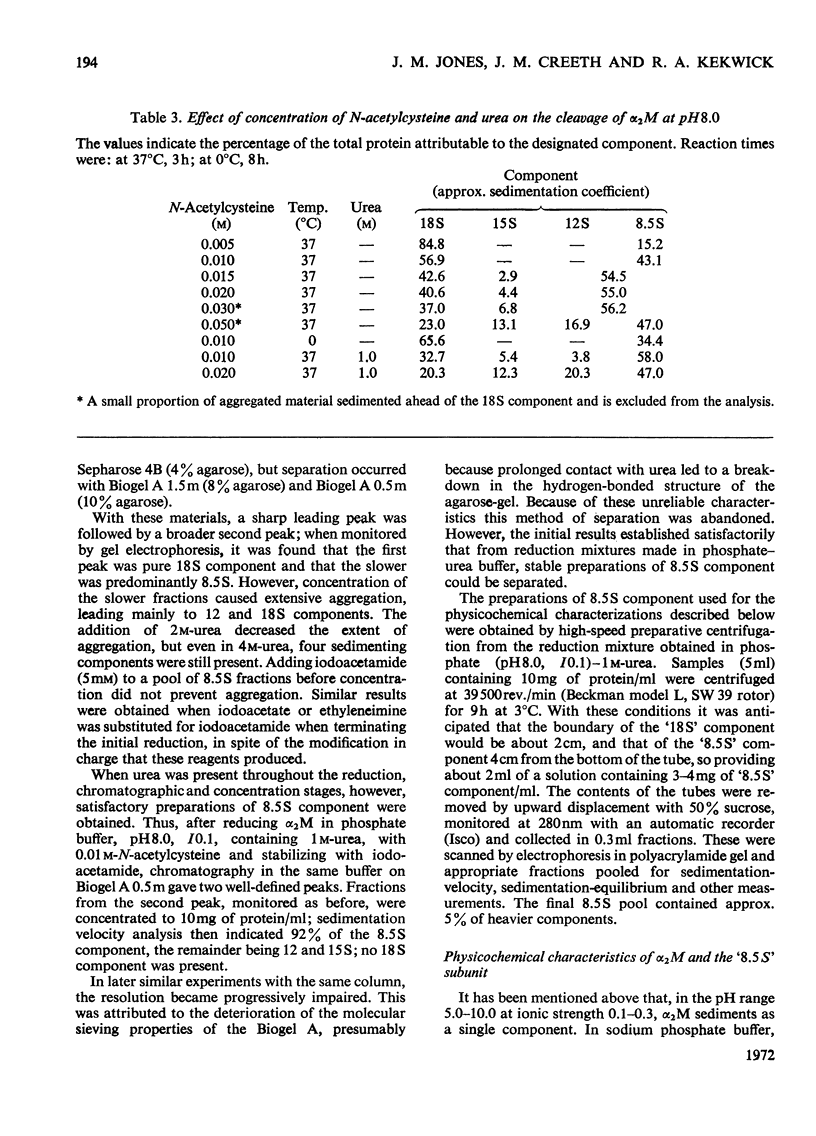



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armand Y. J., Guinand S. Composition et structure de L'alpha-2-macroglobuline isolée du serum de porc. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Feb 21;133(2):289–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creeth J. M., Denborough M. A. The use of equilibrium-density-gradient methods for the preparation and characterization of blood-group-specific glycoproteins. Biochem J. 1970 May;117(5):879–891. doi: 10.1042/bj1170879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creeth J. M., Pain R. H. The determination of molecular weights of biological macromolecules by ultracentrifuge methods. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1967;17:217–287. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(67)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. T., Spiro R. G. The alpha 2-macroglobulin of human plasma. I. Isolation and composition. J Biol Chem. 1967 Dec 10;242(23):5549–5555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganrot P. O. Inhibition of plasmin activity by alpha-2-macroglobulin. Clin Chim Acta. 1967 May;16(2):328–329. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(67)90201-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentou C. Relations entre les structures tertiaire et quaternaire des macroglobulines humaines normales. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1965 Jun 14;260(24):6468–6471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISLIKER H. Zur Chemie der Makroglobuline. Helv Med Acta. 1958 Apr;25(1):41–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James K., Taylor F. B., Jr, Fudenberg H. H. Trypsin stabilizers in human serum. The role of alpha-2-macroglobulin. Clin Chim Acta. 1966 Mar;13(3):359–368. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(66)90216-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEKWICK R. A., MACKAY M. E., NANCE M. H., RECORD B. R. The purification of human fibrinogen. Biochem J. 1955 Aug;60(4):671–683. doi: 10.1042/bj0600671b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffitt W., Yang J. T. THE OPTICAL ROTATORY DISPERSION OF SIMPLE POLYPEPTIDES. I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1956 Sep;42(9):596–603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.42.9.596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa S., Sugihara H., Han B. H., Suzuki T. Studies on alpha 2-macroglobulin in bovine plasma. I. Purification, physical properties, and chemical compositions. J Biochem. 1970 Jun;67(6):809–819. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POULIK M. D. The use of urea-starch-gel electrophoresis in studies of reductive cleavage of an alpha 2-macroglobulin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Nov 4;44:390–393. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91590-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley D., Turner K. J. Passive sensitization of Salmonella adelaide to the bactericidal action of antibody and complement. Nature. 1968 Feb 17;217(5129):657–658. doi: 10.1038/217657a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHONENBERGER M., SCHMIDTBERGER R., SCHULTZE H. E. Uber das alpha 2-Makroglobulin. Z Naturforsch B. 1958 Dec;13B(12):761–772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULTZE H. E., HAUPT H., HEIDE K., MOESCHLIN G., SCHMIDTBERGER R., SCHWICK G. [Studies on gamma macroglobulin in human serum]. Z Naturforsch B. 1962 May;17B:313–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbuch M., Blatrix C., Josso F. Alpha-2-macroglobulin as progressive antithrombin. Nature. 1967 Nov 4;216(5114):500–501. doi: 10.1038/216500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOZER B. T., PIRT S. J. SUSPENSION CULTURE OF MAMMALIAN CELLS AND MACROMOLECULAR GROWTH-PROMOTING FRACTIONS OF CALF SERUM. Nature. 1964 Jan 25;201:375–378. doi: 10.1038/201375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilding P., Adham N. F., Mehl J. W., Haverback B. J. Alpha-2-macroglobulin concentrations in human serum. Nature. 1967 Jun 17;214(5094):1226–1227. doi: 10.1038/2141226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YPHANTIS D. A. EQUILIBRIUM ULTRACENTRIFUGATION OF DILUTE SOLUTIONS. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:297–317. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]