Abstract
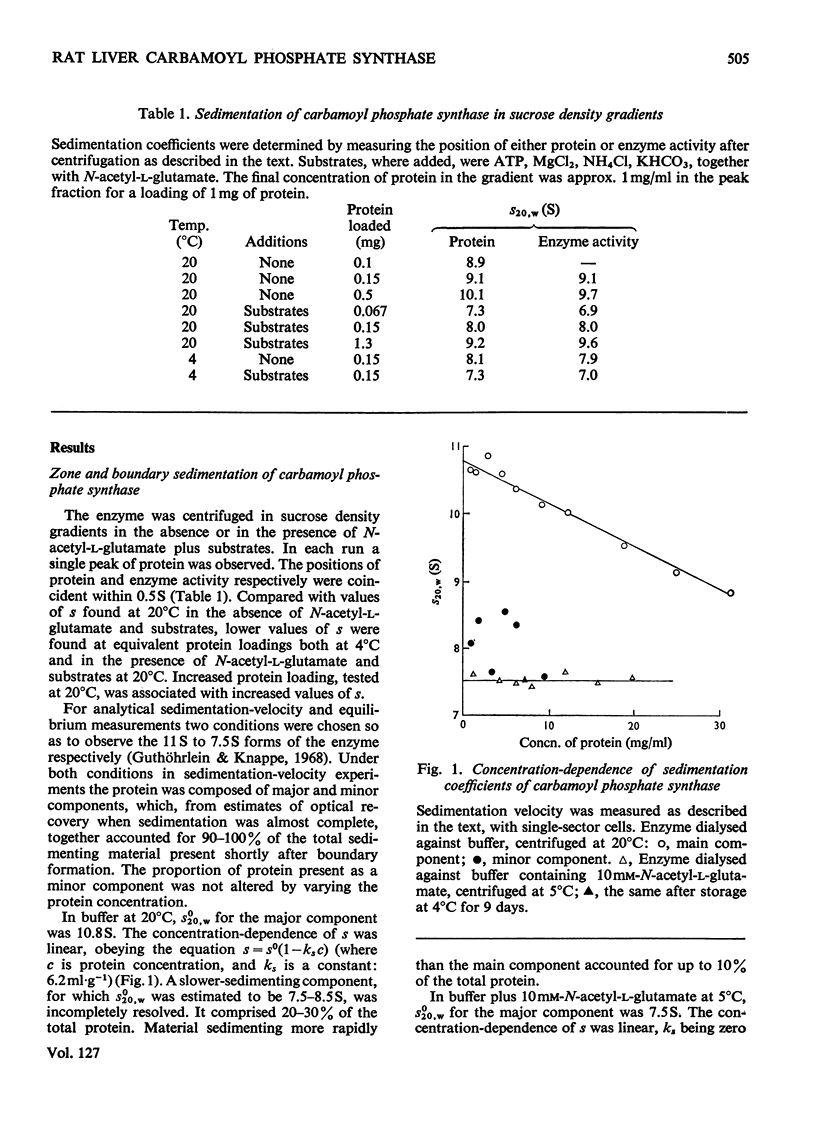
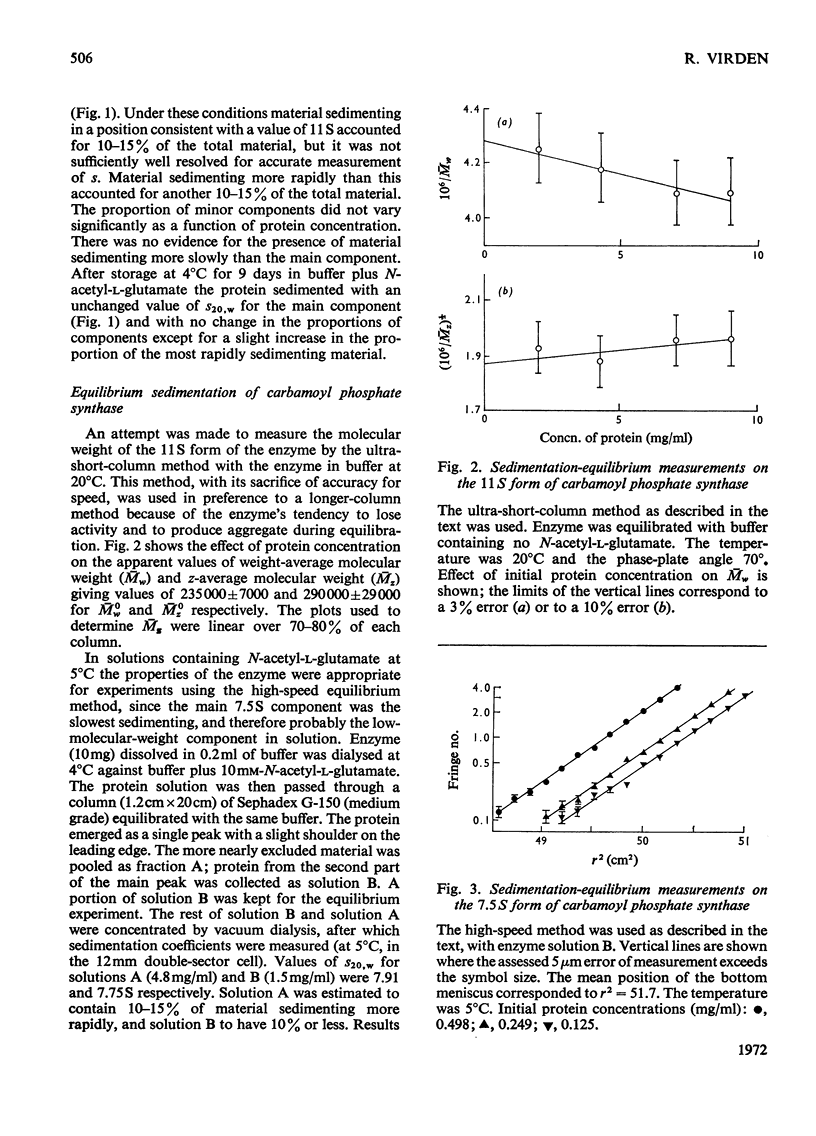
1. N-Acetylglutamate-dependent carbamoyl phosphate synthase from rat liver was centrifuged in sucrose density gradients. The concentration-dependence of s was consistent with a chemical equilibrium existing between the 11S and 7.5S forms of the enzyme. 2. Under conditions favouring the 11S form, the properties of the enzyme in ultra-short-column equilibrium experiments suggest a molecular weight of 316000±42000 for the 11S form. 3. Under conditions favouring the 7.5S form, high-speed equilibrium-sedimentation measurements gave a value of 160000±10000 as the molecular weight of the 7.5S form of the enzyme.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cohen P. P. Biochemical differentiation during amphibian metamorphosis. Science. 1970 May 1;168(3931):533–543. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3931.533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creeth J. M., Knight C. G. On the estimation of the shape of macromolecules from sedimentation and viscosity measurements. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jul 22;102(2):549–558. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(65)90145-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAHIEN L. A., COHEN P. P. A KINETIC STUDY OF CARBAMYL PHOSPHATE SYNTHETASE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jun;239:1925–1934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthöhrlein G., Knappe J. Structure and function of carbamoylphosphate synthase. I. Transitions between two catalytically inactive forms and the active form. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Dec;7(1):119–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb19582.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSHALL M., METZENBERG R. L., COHEN P. P. Purification of carbamyl phosphate synthetase from frog liver. J Biol Chem. 1958 Jul;233(1):102–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi S., Ito K., Tatibana M. Two types of carbamyl phosphate synthetase in rat liver: chromatographic resolution and immunological distinction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Dec 9;33(5):774–781. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90227-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards E. G., Teller D. C., Schachman H. K. Ultracentrifuge studies with Rayleigh interference optics. II. Low-speed sedimentation equilibrium of homogeneous systems. Biochemistry. 1968 Mar;7(3):1054–1076. doi: 10.1021/bi00843a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YPHANSTIS D. A. Rapid determination of molecular weights of peptides and preteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Aug 31;88:586–601. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb20055.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YPHANTIS D. A. EQUILIBRIUM ULTRACENTRIFUGATION OF DILUTE SOLUTIONS. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:297–317. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


