Abstract
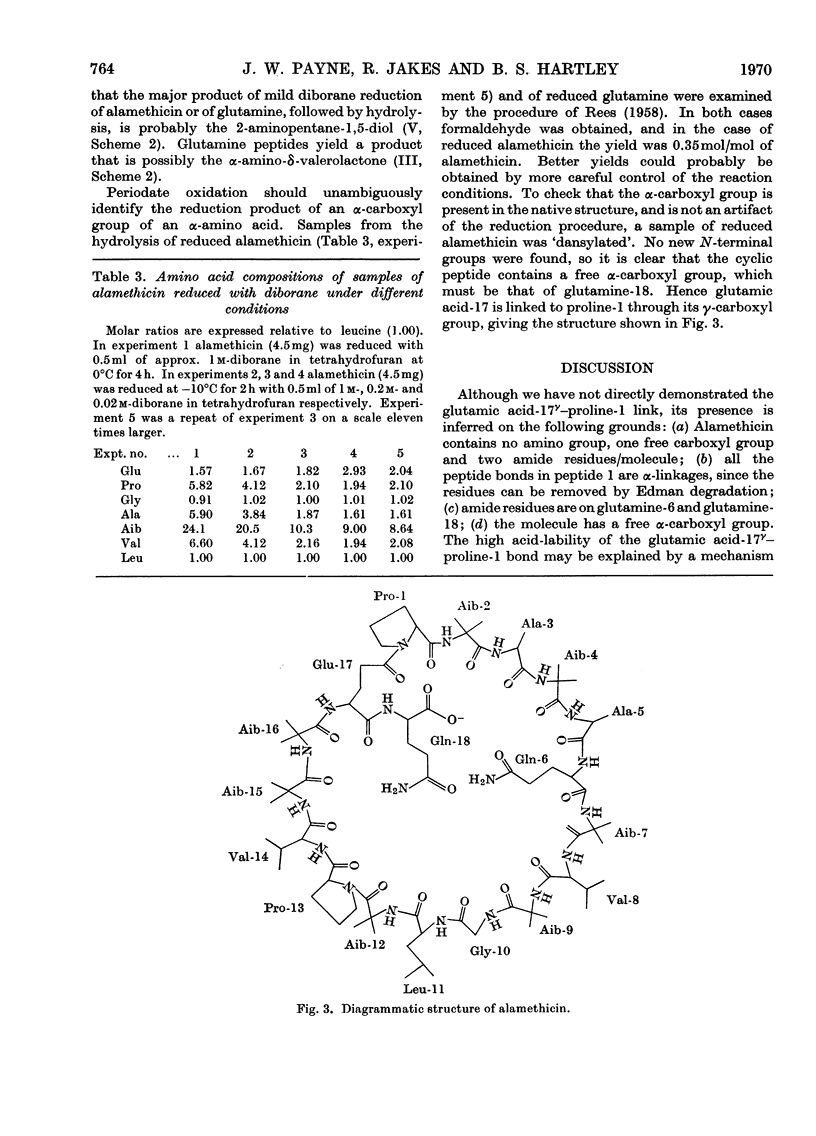
Alamethicin, an antibiotic that can transport cations and induce action potentials in synthetic membranes, is shown to be a cyclic peptide with 18 residues including 7-α-aminoisobutyric acid residues, two glutamine residues and one free carboxyl group. The composition indicates microheterogeneity. Alamethicin itself and many peptides derived from it are immune to enzymic digestion, but specific partial acid cleavages have allowed determination of the complete sequence. Diborane reduction has shown that the α-carboxyl group of glutamine-18 is free, but the ring is formed by a peptide bond between the imino group of proline-1 and the γ-carboxyl group of glutamic acid-17. The structure is contrasted with that of other cation-transporting antibiotics. Model building allows a structure that could stack to form a tunnel with a lipophilic exterior and hydrophilic interior and flexible internal arms formed by the pendant C-terminal glutamine residue.
Full text
PDF



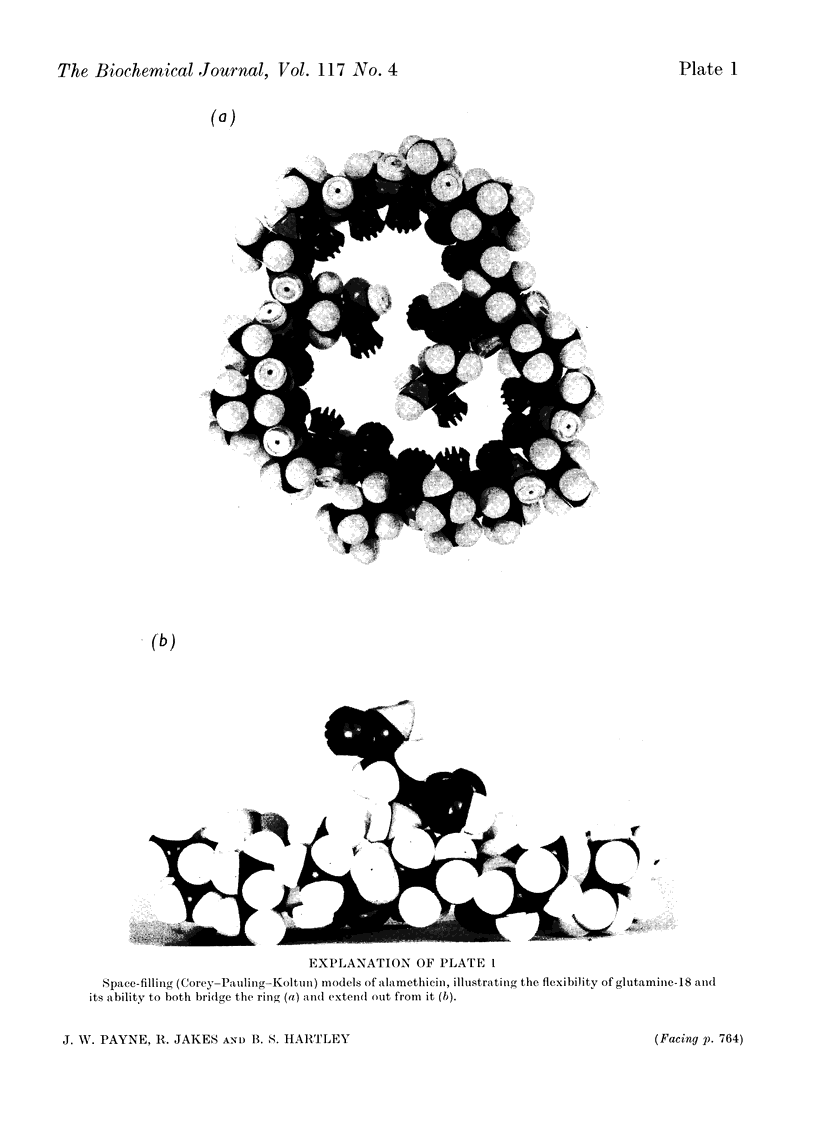


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agtarap A., Chamberlin J. W., Pinkerton M., Steinrauf L. The structure of monensic acid, a new biologically active compound. J Am Chem Soc. 1967 Oct 25;89(22):5737–5739. doi: 10.1021/ja00998a062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atassi M. Z., Rosenthal A. F. Specific reduction of carboxyl groups in peptides and proteins by diborane. Biochem J. 1969 Feb;111(4):593–601. doi: 10.1042/bj1110593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blow D. M. The study of alpha-chymotrypsin by x-ray diffraction. The Third CIBA Medal Lecture. Biochem J. 1969 Apr;112(3):261–268. doi: 10.1042/bj1120261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodanszky M., Perlman D. Peptide antibiotics. Science. 1969 Jan 24;163(3865):352–358. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3865.352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHIBNALL A. C., MANGAN J. L., REES M. W. Studies on the amide and C-terminal residues in proteins. 3. The esterification of proteins. Biochem J. 1958 Jan;68(1):114–118. doi: 10.1042/bj0680114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHIBNALL A. C., REES M. W. Studies on the amide and C-terminal residues in proteins. 1. The characterization of the C-terminal residue. Biochem J. 1958 Jan;68(1):105–111. doi: 10.1042/bj0680105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobler M., Dunitz J. D., Krajewski J. Structure of the K+ complex with enniatin B, a macrocyclic antibiotic with K+ transport properties. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jun 28;42(3):603–606. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90249-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenman G. Ion permeation of cell membranes and its models. Fed Proc. 1968 Nov-Dec;27(6):1249–1251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEILMANN J., BARROLLIER J., WATZKE E. Beitrag zur Aminosäurebestimmung auf Papierchromatogrammen. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1957;309(4-6):219–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN D. C., OUGHTON B. M. Possible molecular models for gramicidin S and their relationship to present ideas of protein structure. Biochem J. 1957 Apr;65(4):752–756. doi: 10.1042/bj0650752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes D. H., Kowalsky A., Pressman B. C. Application of nuclear magnetic resonance to the conformational changes in valinomycin during complexation. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jan 25;244(2):502–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov V. T., Laine I. A., Abdulaev N. D., Senyavina L. B., Popov E. M. The physicochemical basis of the functioning of biological membranes: the conformation of valinomycin and its K+ complex in solution. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Mar 31;34(6):803–811. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90251-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilbourn B. T., Dunitz J. D., Pioda L. A., Simon W. Structure of the K+ complex with nonactin, a macrotetrolide antibiotic possessing highly specific K+ transport properties. J Mol Biol. 1967 Dec 28;30(3):559–563. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90370-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara H., Singer A., Sasaki R. M. Effect of proline residue on the hydrolysis of substrates by thermolysin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Mar 10;34(5):719–724. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90798-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer C. E., Reusser F. A polypeptide antibacterial agent isolated from Trichoderma viride. Experientia. 1967 Feb 15;23(2):85–86. doi: 10.1007/BF02135929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P., Rudin D. O. Action potentials induced in biomolecular lipid membranes. Nature. 1968 Feb 24;217(5130):713–719. doi: 10.1038/217713a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offord R. E. Electrophoretic mobilities of peptides on paper and their use in the determination of amide groups. Nature. 1966 Aug 6;211(5049):591–593. doi: 10.1038/211591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi M., Urry D. W. Temperature dependence of amide proton chemical shifts: the secondary structures of gramicidin S and valinomycin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Jul 23;36(2):194–202. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90314-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkerton M., Steinrauf L. K., Dawkins P. The molecular structure and some transport properties of valinomycin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 May 22;35(4):512–518. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90376-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podleski T., Changeux J. P. Effects associated with permeability changes caused by gramicidin A in electroplax membrane. Nature. 1969 Feb 8;221(5180):541–545. doi: 10.1038/221541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressman B. C., Harris E. J., Jagger W. S., Johnson J. H. Antibiotic-mediated transport of alkali ions across lipid barriers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Nov;58(5):1949–1956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.5.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressman B. C. Ionophorous antibiotics as models for biological transport. Fed Proc. 1968 Nov-Dec;27(6):1283–1288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reusser F. Biosynthesis of antibiotic U-22,324, a cyclic polypeptide. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jan 25;242(2):243–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH I. Colour reactions on paper chromatograms by a dipping technique. Nature. 1953 Jan 3;171(4340):43–44. doi: 10.1038/171043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I., Berger A. The hydrolysis of diastereoisomers of alanine peptides by carboxypeptidase A and leucine aminopeptidase. Biochemistry. 1966 Oct;5(10):3371–3375. doi: 10.1021/bi00874a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shean G. M., Sollner K. Carrier mechanisms in the movement of ions across porous and liquid ion exchanger membranes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jul 14;137(2):759–776. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb50198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotton D. M., Hartley B. S. Amino-acid sequence of porcine pancreatic elastase and its homologies with other serine proteinases. Nature. 1970 Feb 28;225(5235):802–806. doi: 10.1038/225802a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern A., Gibbons W. A., Craig L. C. A conformational analysis of gramicidin S-A by nuclear magnetic resonance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):734–741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosteson D. C. Effect of macrocyclic compounds on the ionic permeability of artificial and natural membranes. Fed Proc. 1968 Nov-Dec;27(6):1269–1277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach D. F., Zahler P. H. Protein conformations in cellular membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Nov;56(5):1552–1559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.5.1552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wipf H. K., Pache W., Jordan P., Zähner H., Keller-Schierlein W., Simon W. Mechanism of alkali cation transport in bulk membranes using macrotetrolide antibiotics. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Aug 7;36(3):387–393. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90576-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]