Abstract
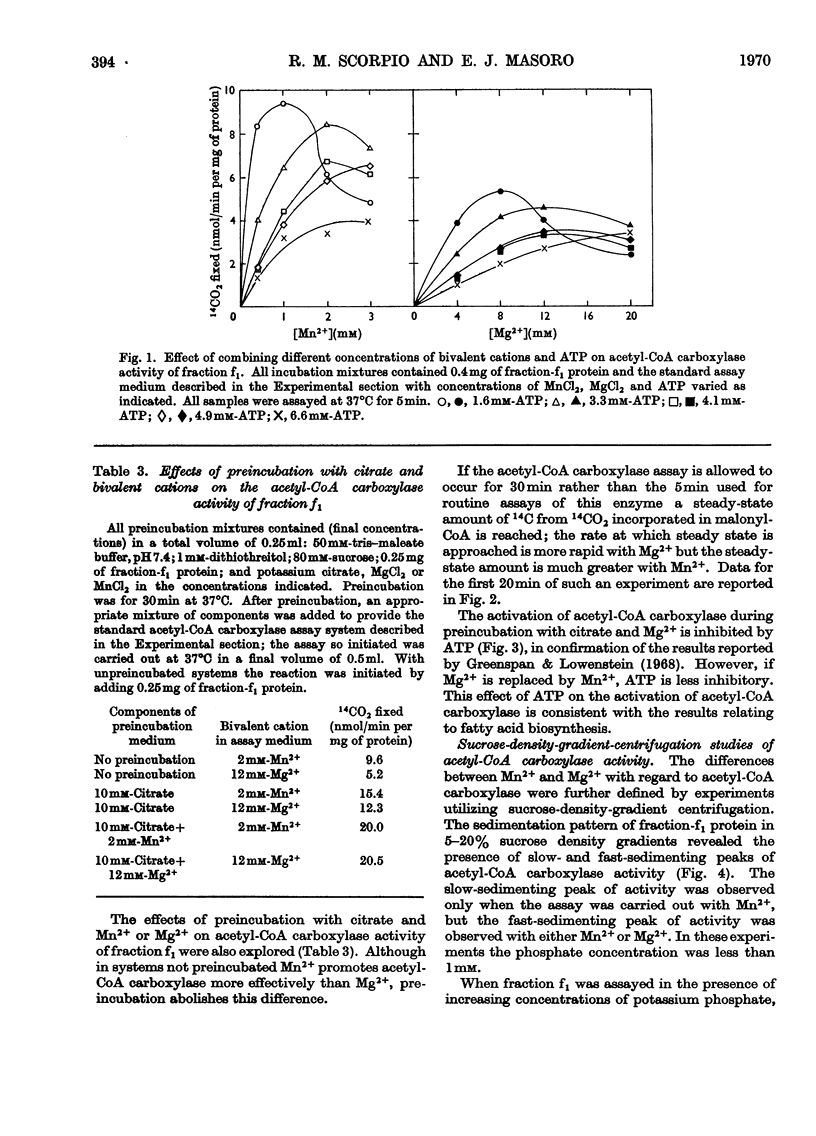
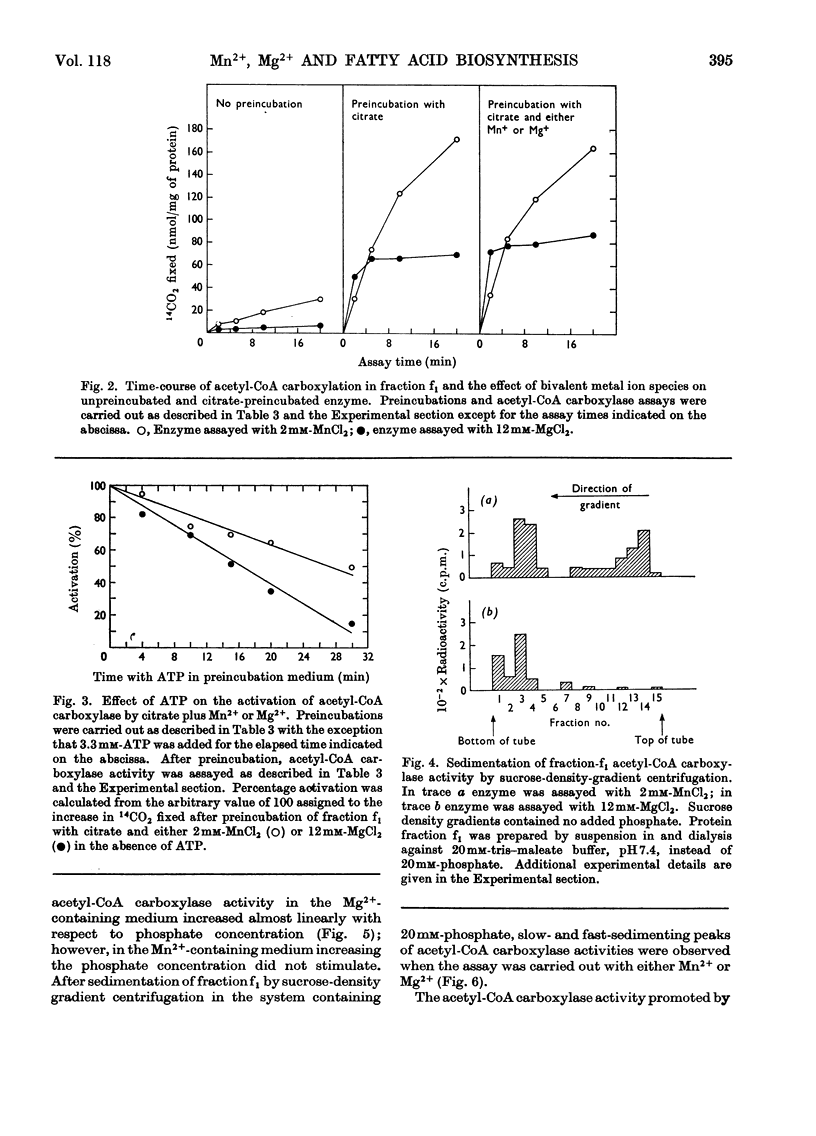
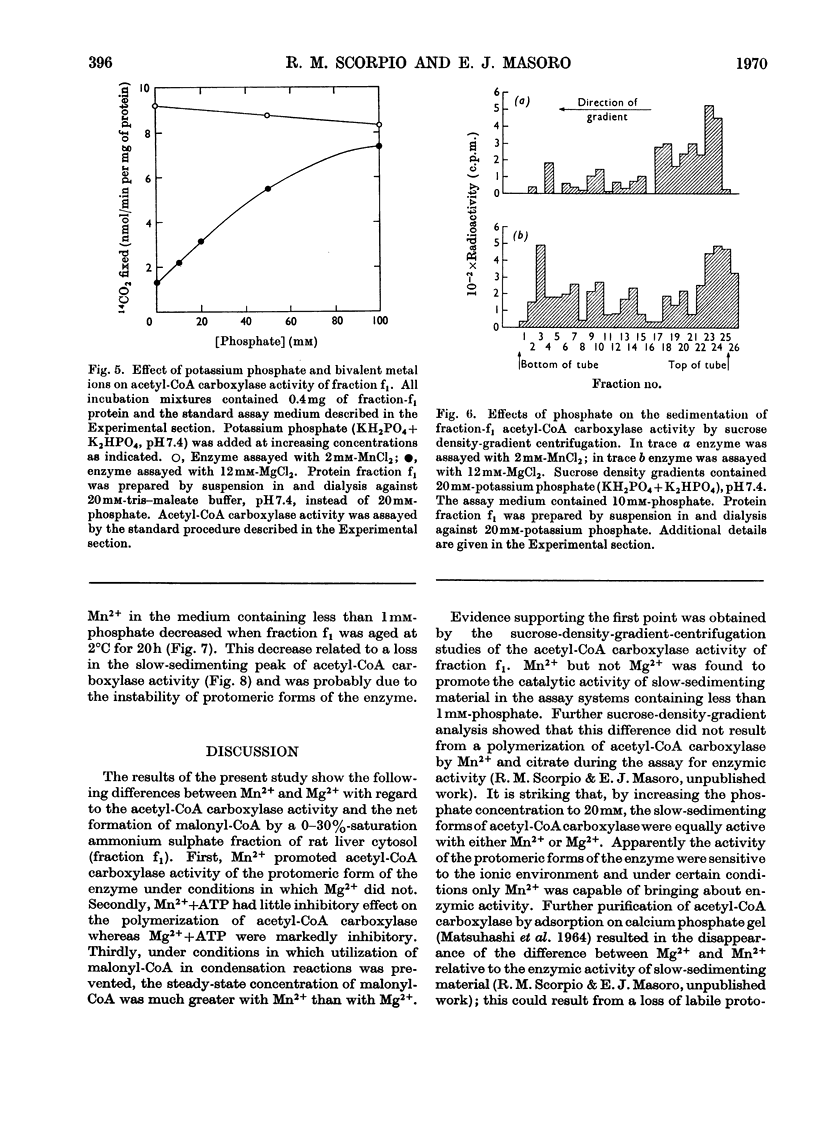
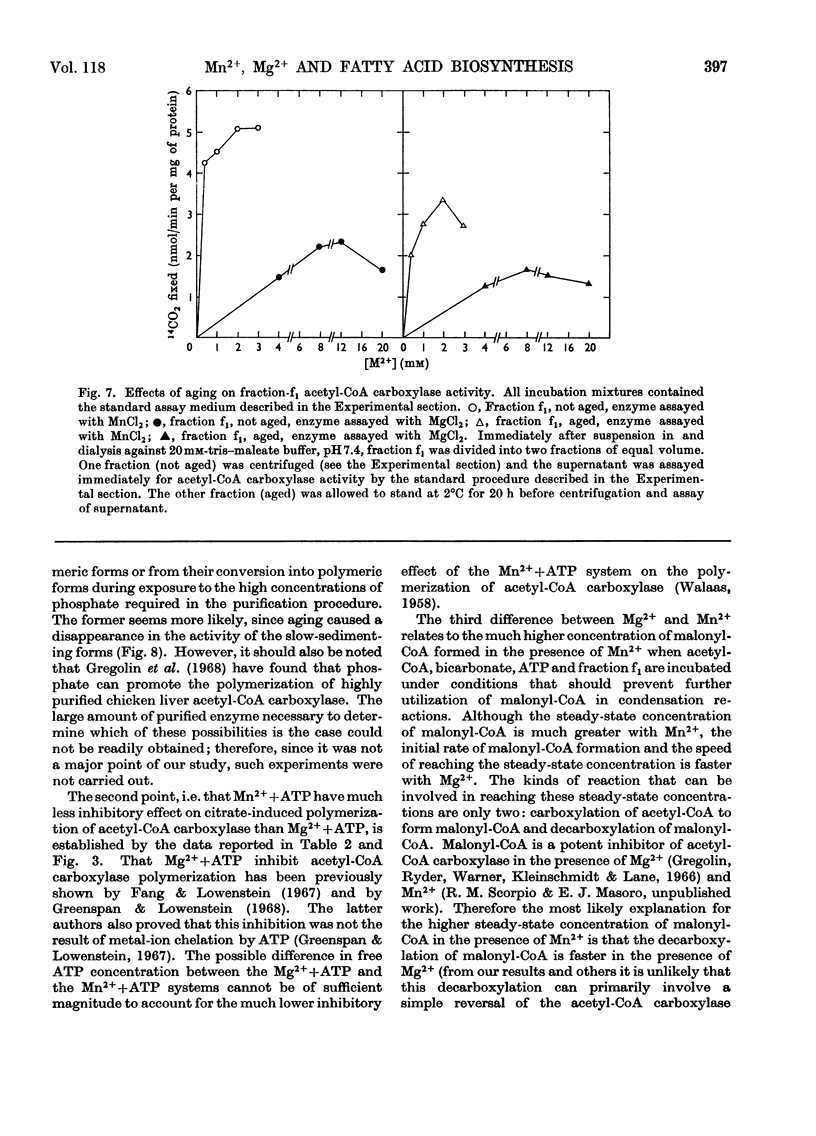
Fatty acid-biosynthetic activity in rat liver cytosol fractions is much greater when the bivalent cation in the assay system is Mn2+ than when it is Mg2+. This difference between bivalent cations can be abolished if the cytosol fractions are preincubated with isocitrate and the bivalent cation for 30min before assay of fatty acid-biosynthetic activity. In a search for the biochemical basis of this phenomenon, the following differences between Mg2+ and Mn2+ were established: (1) Mn2+ promotes acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity of the protomeric form of the enzyme under conditions in which Mg2+ does not; (2) Mn2++ATP have little inhibitory effect on the polymerization of acetyl-CoA carboxylase whereas Mg2++ATP are markedly inhibitory; (3) under conditions in which utilization of malonyl-CoA in condensation reactions is prevented, the steady-state concentration of malonyl-CoA formed by a cytosol fraction is much greater with Mn2+ than with Mg2+. The role that each of these specific differences between Mn2+ and Mg2+ might play in causing liver cytosol preparations to have greater fatty acid-biosynthetic activity in the presence of Mn2+ is discussed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BORTZ W. M., LYNEN F. THE INHIBITION OF ACETYL COA CARBOXYLASE BY LONG CHAIN ACYL COA DERIVATIVES. Biochem Z. 1963 Aug 14;337:505–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang M., Lowenstein J. M. Citrate and the conversion of carbohydrate into fat. The regulation of fatty acid synthesis by rat liver extracts. Biochem J. 1967 Nov;105(2):803–811. doi: 10.1042/bj1050803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GANGULY J. Studies on the mechanism of fatty acid synthesis. VII. Biosynthesis of fatty acids from malonyl CoA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 May 6;40:110–118. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91320-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenspan M. D., Lowenstein J. M. Effects of magnesium ions, adenosine triphosphate, palmitoylcarnitine, and palmitoyl coenzyme A on acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 10;243(23):6273–6280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregolin C., Ryder E., Lane M. D. Liver acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase. I. Isolation and cat- alytic properties. J Biol Chem. 1968 Aug 25;243(16):4227–4235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregolin C., Ryder E., Warner R. C., Kleinschmidt A. K., Chang H. C., Lane M. D. Liver acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase. II. Further molecular characterization. J Biol Chem. 1968 Aug 25;243(16):4236–4245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregolin C., Ryder E., Warner R. C., Kleinschmidt A. K., Lane M. D. Liver acetyl coa carboxylase: the dissociation-reassociation process and its relation to catalytic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Dec;56(6):1751–1758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.6.1751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALENZ D. R., LANE M. D. Properties and purification of mitochondrial propionyl carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:878–884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORCHAK H. M., MASORO E. J. Changes in the level of the fatty acid synthesizing enzymes during starvation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Apr 9;58:354–356. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)91022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORCHAK H. M., MASORO E. J. FREE FATTY ACIDS AS LIPOGENIC INHIBITORS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Dec 2;84:750–753. doi: 10.1016/0926-6542(64)90034-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN D. B., VAGELOS P. R. The mechanism of tricarboxylic acid cycle regulation of fatty acid synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jun;237:1787–1792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASORO E. J., KORCHAK H. M., PORTER E. A study of the lipogenic inhibitory mechanisms induced by fasting. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Apr 23;58:407–416. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATSUHASHI M., MATSUHASHI S., LYNEN F. ZUR BIOSYNTHESE DER FETTSAEUREN. V. DIE ACETYL-COA CARBOXYLASE AUS RATTENLEBER UND IHRE AKTIVIERUNG DURCH CITRONENSAEURE. Biochem Z. 1964 Aug 11;340:263–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malila A., DeMartinis F. D., Masoro E. J. Involvement of phospholipids in Rb+ transport by kidney cortex tubules. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 10;243(23):6115–6122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NUMA S., MATSUHASHI M., LYNEN F. [On disorders of fatty acid synthesis in hunger and alloxan diabetes. I. Fatty acid synthesis in the liver of normal and fasting rats]. Biochem Z. 1961;334:203–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numa S., Ringelmann E., Lynen F. Zur Hemmung der Acetyl-CoA-Carboxylase durch Fettsäure-Coenzym A-Verbindungen. Biochem Z. 1965 Dec 1;343(3):243–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scorpio R. M., Masoro E. J. Requirements for Mn++ and Mg++ in rat liver acetyl-CoA carboxylase and fatty acid biosynthesis activities. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Jun 28;31(6):950–959. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90545-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAGELOS P. R., ALBERTS A. W., MARTIN D. B. Studies on the mechnism of activation of acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase by citrate. J Biol Chem. 1963 Feb;238:533–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAITE M., WAKIL S. J. Studies on the mechanism of fatty acid synthesis. XII. Acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1962 Sep;237:2750–2757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAKIL S. J., PORTER J. W., GIBSON D. M. Studies on the mechanism of fatty acid synthesis. I. Preparation and purification of an enzymes system for reconstruction of fatty acid synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Jun;24(3):453–461. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90233-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


