Abstract
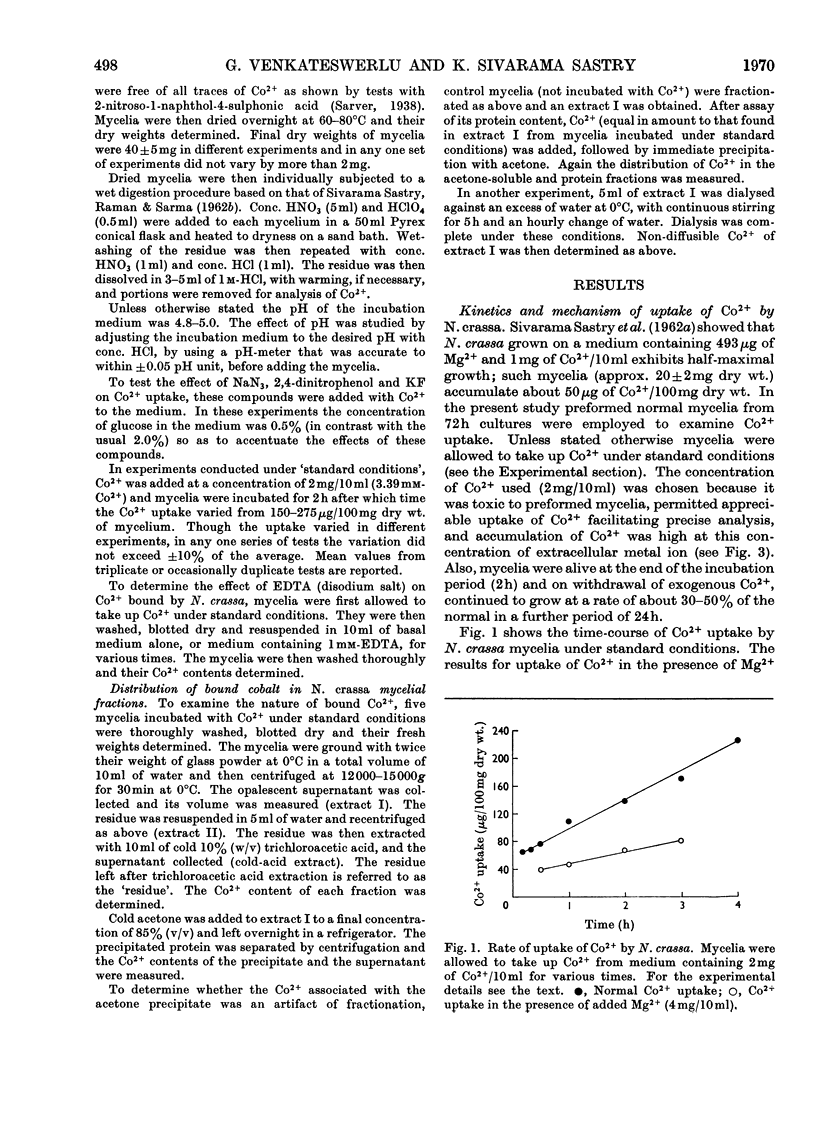
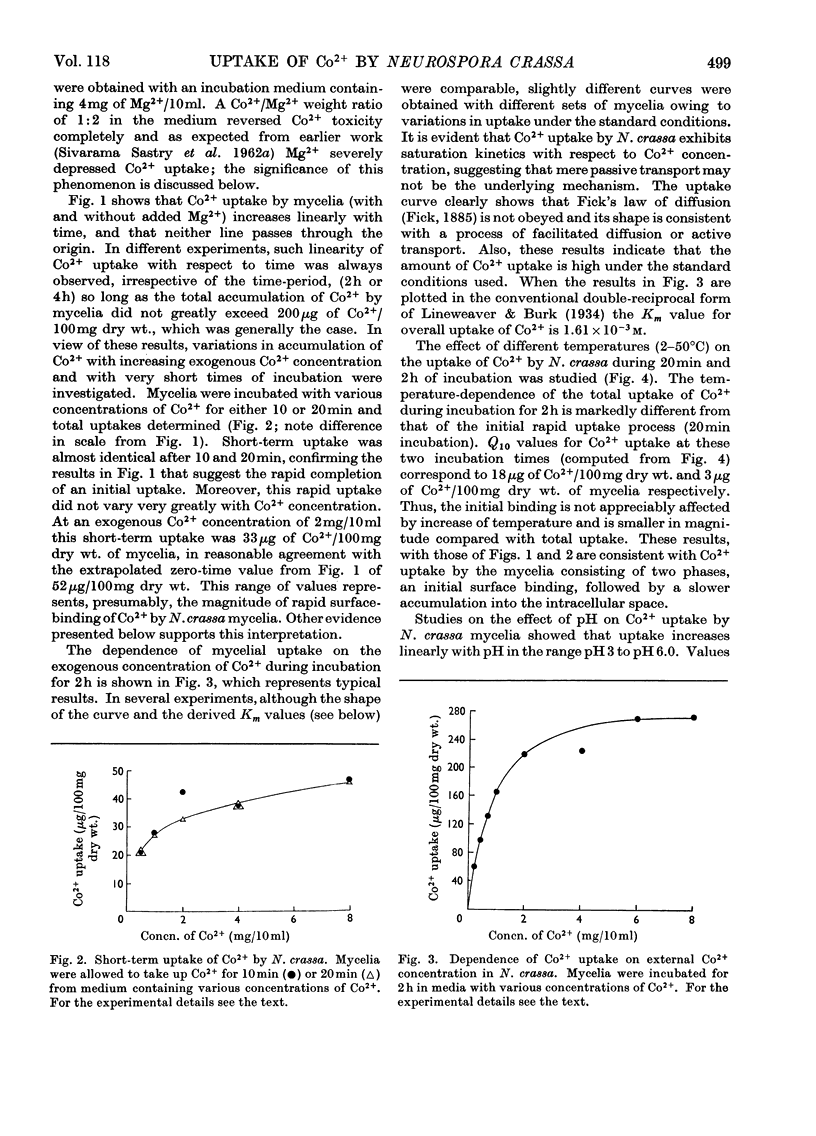
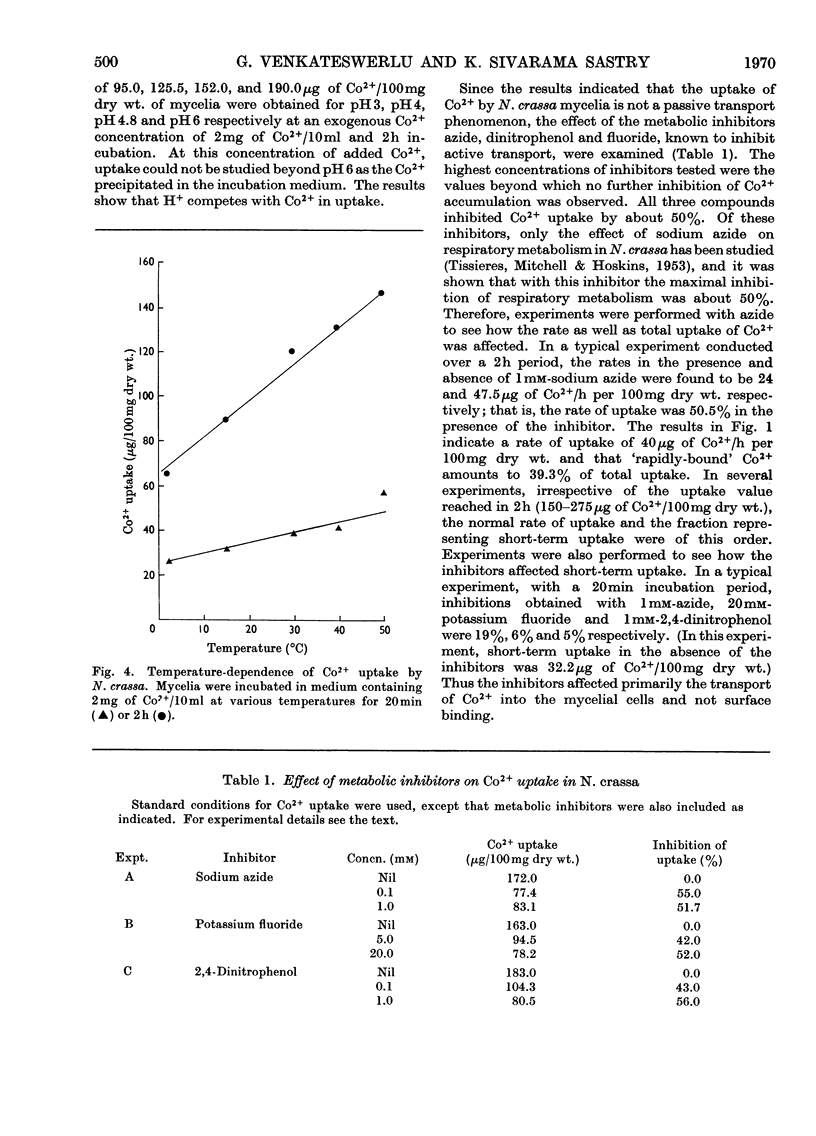
Uptake of Co2+ by 3-day-old mycelia of Neurospora crassa involves cell-surface binding as well as transport into the intracellular space. The surface binding is rapid and accounts for 30–40% of the total Co2+ uptake. Transport of Co2+ occurs at a rate of 40μg/h per 100mg dry wt. Surface binding and overall uptake show different temperature dependence. Metabolic inhibitors such as azide, dinitrophenol and fluoride depress transport of Co2+. The overall uptake of Co2+ exhibits a high Km value and hence the concentration mechanism is one of low `affinity' for the metal. The uptake of Co2+ varies linearly with pH in the range pH3 to pH6. Mg2+ inhibits both surface binding and transport of Co2+. It is suggested that the system that transports Mg2+ is also involved in Co2+ uptake by N. crassa.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABELSON P. H., ALDOUS E. Ion antagonisms in microorganisms; interference of normal magnesium metabolism by nickel, cobalt, cadmium, zinc, and manganese. J Bacteriol. 1950 Oct;60(4):401–413. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.4.401-413.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson-Kottö I., Hevesy G. C. Zinc uptake by Neurospora. Biochem J. 1949;44(4):407–409. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALLENTINE R., STEPHENS D. G. The biosynthesis of stable cobalt proteins by plants. J Cell Physiol. 1951 Jun;37(3):369–387. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030370303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benko P. V., Wood T. C., Segel I. H. Multiplicity and regulation of amino acid transport in Penicillium chrysogenum. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Feb;129(2):498–508. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90207-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHIRIGOS M. A., GREENGARD P., UDENFRIEND S. Uptake of tyrosine by rat brain in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jul;235:2075–2079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILBERT J. C. MECHANISM OF SUGAR TRANSPORT IN BRAIN SLICES. Nature. 1965 Jan 2;205:87–88. doi: 10.1038/205087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padmanaban G., Sarma P. S. Cobalt toxicity and iron metabolism in Neurospora crassa. Biochem J. 1966 Jan;98(1):330–334. doi: 10.1042/bj0980330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SASTRY K. S., ADIGA P. R., VENKATASUBRAMANYAM V., SARMA P. S. Interrelationships in trace-element metabolism in metal toxicities in Neurospora crassa. Biochem J. 1962 Dec;85:486–491. doi: 10.1042/bj0850486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLAYMAN C. W., TATUM E. L. POTASSIUM TRANSPORT IN NEUROSPORA. I. INTRACELLULAR SODIUM AND POTASSIUM CONCENTRATIONS, AND CATION REQUIREMENTS FOR GROWTH. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Nov 29;88:578–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TISSIERES A., MITCHELL H. K., HASKINS F. A. Studies on the respiratory system of the poky strain of Neurospora. J Biol Chem. 1953 Nov;205(1):423–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZALOKAR M. Studies on biosynthesis of carotenoids in Neurospora crassa. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1954 May;50(1):71–80. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(54)90010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


