Abstract
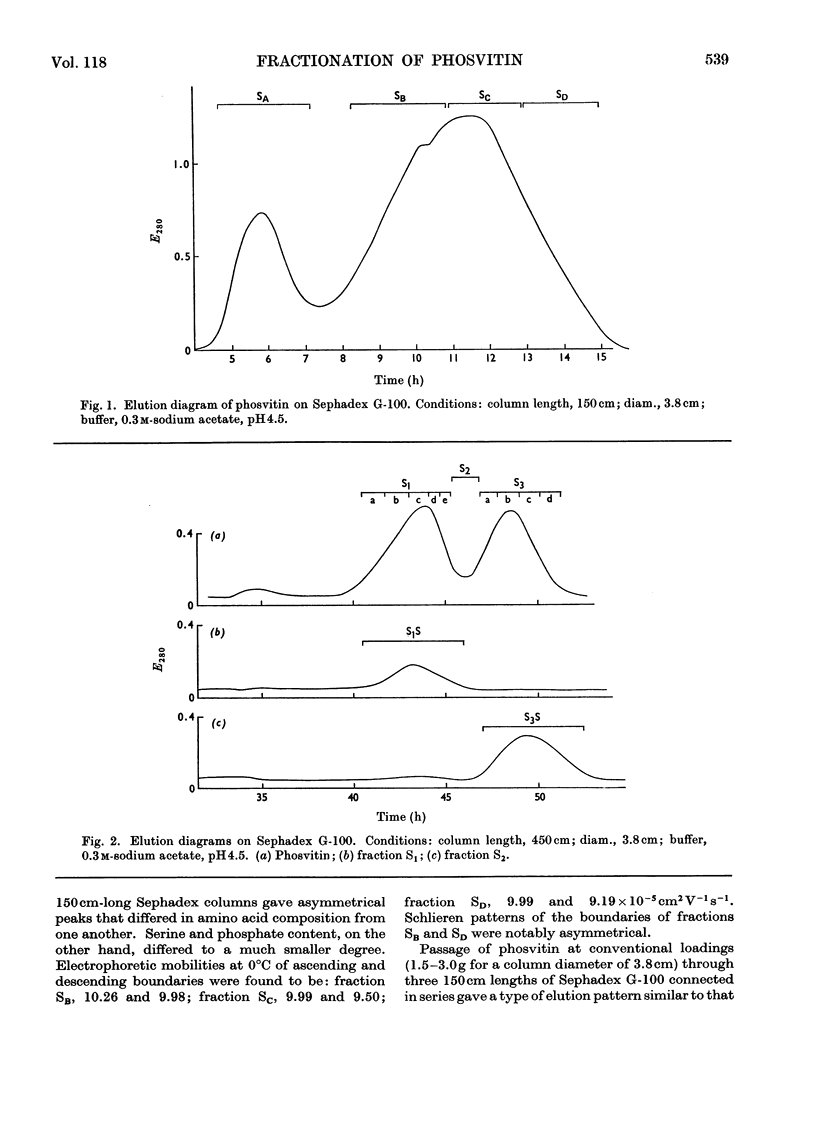
1. Phosvitin extracted from domestic hen's-egg yolk was resolved on Sephadex G-100 into two phosphoprotein components. 2. The major component has a molecular weight of about 3.4×104 and alanine as an N-terminal residue. Glucosamine is present, but tyrosine is virtually absent. 3. The minor component has a molecular weight of about 2.8×104 and lysine as an N-terminal residue. Missing residues are glucosamine, methionine and leucine. Lysine, histidine, threonine, glycine, phenylalanine and tyrosine contents differ significantly from those of the major component. 4. Sephadex G-100 also removes small amounts of an impurity with a much higher molecular weight.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allerton S. E., Perlmann G. E. Chemical characterization of the phosphoprotein phosvitin. J Biol Chem. 1965 Oct;240(10):3892–3898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONNELLY C., TABORSKY G. Chromatographic fractionation of phosvitin. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1364–1368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman P., Begg G. A protein sequenator. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Mar;1(1):80–91. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-25813-2_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY W. R., HARTLEY B. S. THE STRUCTURE OF A CHYMOTRYPTIC PEPTIDE FROM PSEUDOMONAS CYTOCHROME C-551. Biochem J. 1963 Nov;89:379–380. doi: 10.1042/bj0890379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho C., Magnuson J. A., Wilson J. B., Magnuson N. S., Kurland R. J. Phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance studies of phosphoproteins and phosphorylated molecules. II. Chemical nature of phosphorus atoms in alpha S-casein B and phosvitin. Biochemistry. 1969 May;8(5):2074–2082. doi: 10.1021/bi00833a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOUBERT F. J., COOK W. H. Preparation and characterization of phosvitin from hen egg yolk. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1958 Apr;36(4):399–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOUBERT F. J., COOK W. H. Separation and characterization of lipovitellin from hen egg yolk. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1958 Apr;36(4):389–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara K., Tanford C. Viscosity and density of aqueous solutions of urea and guanidine hydrochloride. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jul 10;241(13):3228–3232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOK C. C., MARTIN W. G., COMMON R. H. A comparison of phosvitins prepared from hen's serum and from hen's egg yolk. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1961 Jan;39:109–117. doi: 10.1139/o61-012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORRISON W. R. A FAST, SIMPLE AND RELIABLE METHOD FOR THE MICRODETERMINATION OF PHOSPHORUS IN BIOLOGICAL MATERIALS. Anal Biochem. 1964 Feb;7:218–224. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90231-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mok C. C., Grant C. T., Taborsky G. Countercurrent distribution of phosvitin. Biochemistry. 1966 Aug;5(8):2517–2523. doi: 10.1021/bi00872a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANGER F., THOMPSON E. O. Halogenation of tyrosine during acid hydrolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 May 14;71:468–471. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91108-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TABORSKY G., ALLENDE C. C. A rearrangement in the structure of phosvitin. Biochemistry. 1962 May 25;1:406–411. doi: 10.1021/bi00909a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TABORSKY G. Interaction between phosvitin and iron and its effect on a rearrangement of phosvitin structure. Biochemistry. 1963 Mar-Apr;2:266–271. doi: 10.1021/bi00902a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taborsky G., Mok C. C. Phosvitin. Homogeneity and molecular weight. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 10;242(7):1495–1501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YPHANTIS D. A. EQUILIBRIUM ULTRACENTRIFUGATION OF DILUTE SOLUTIONS. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:297–317. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


