Abstract
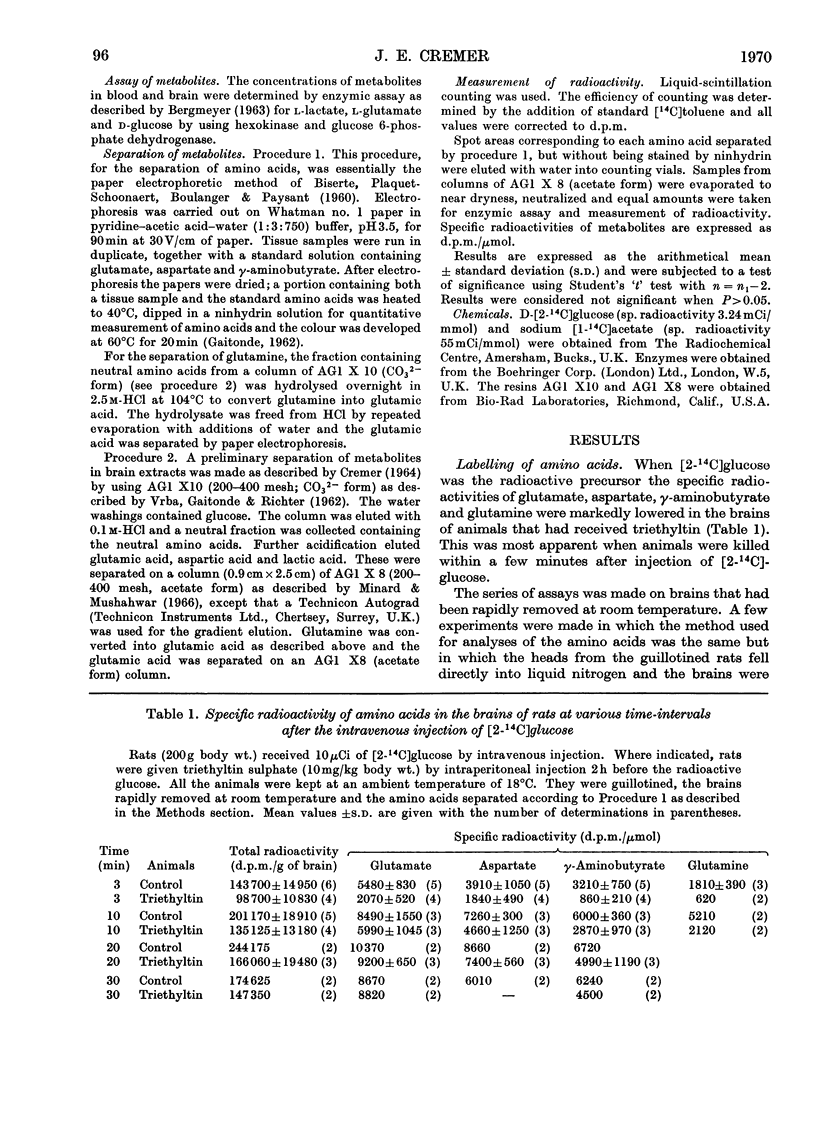
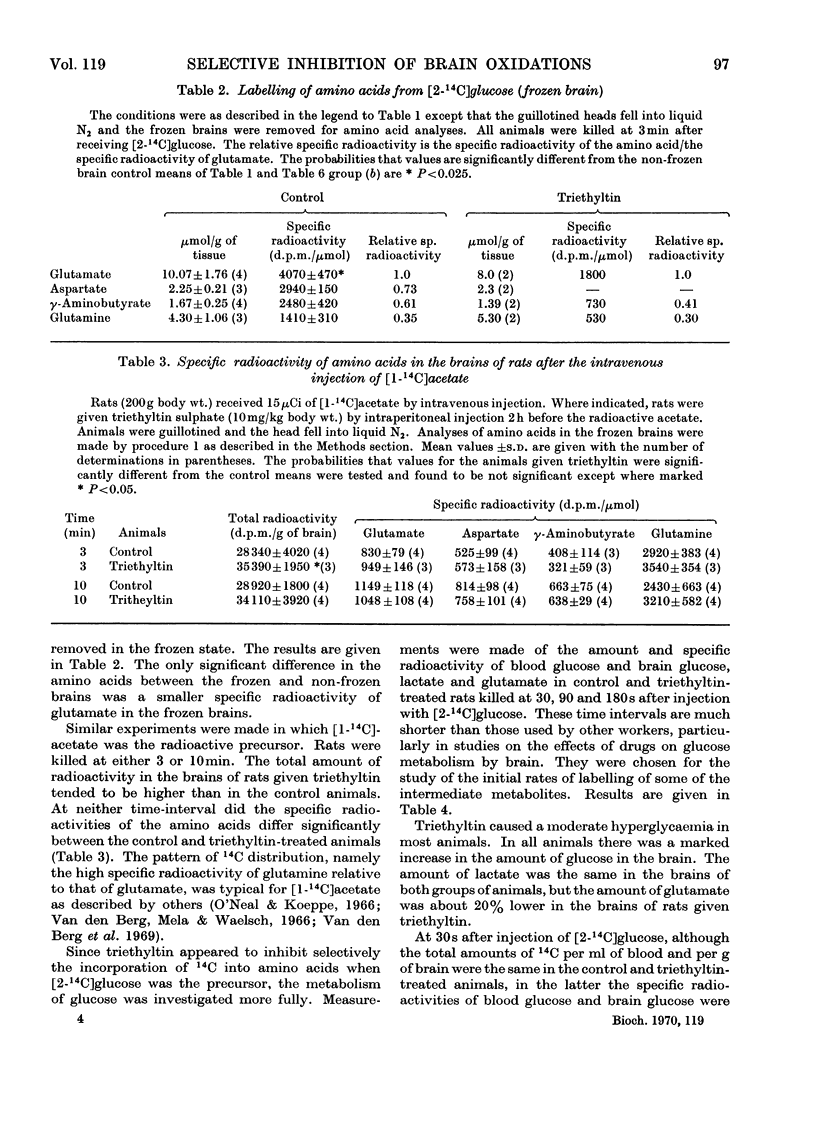
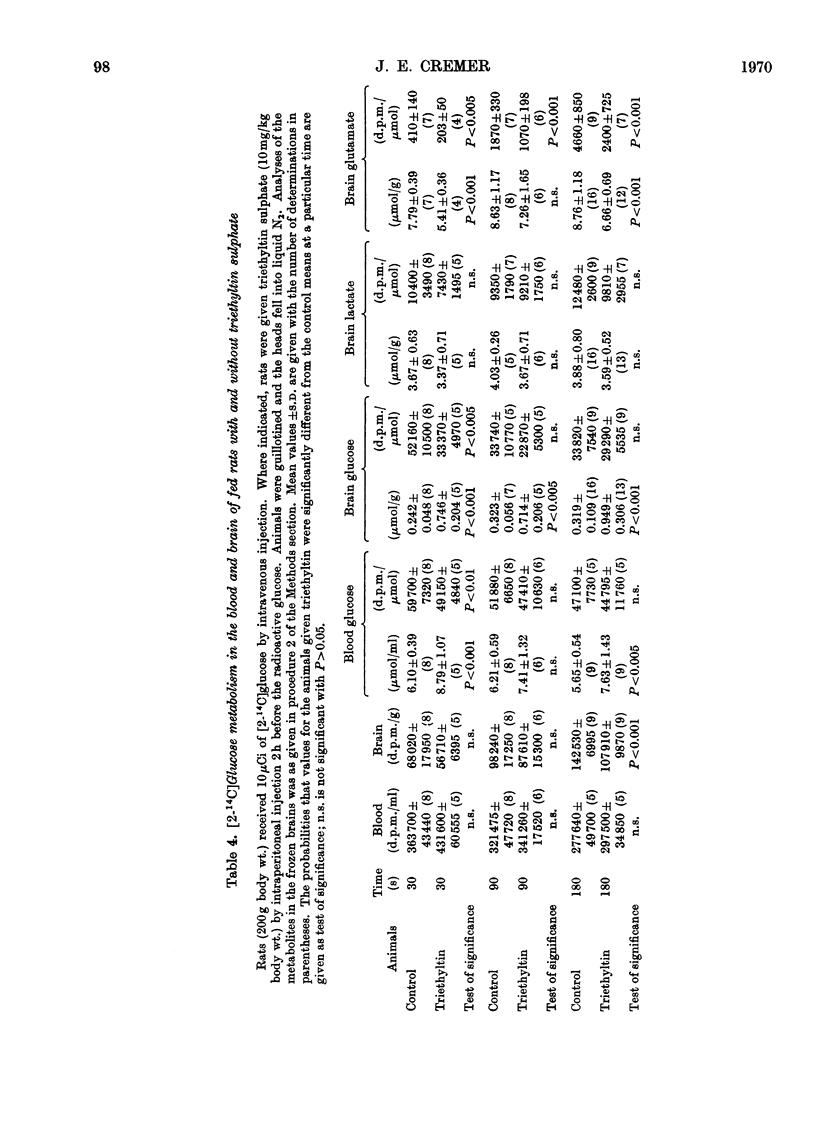
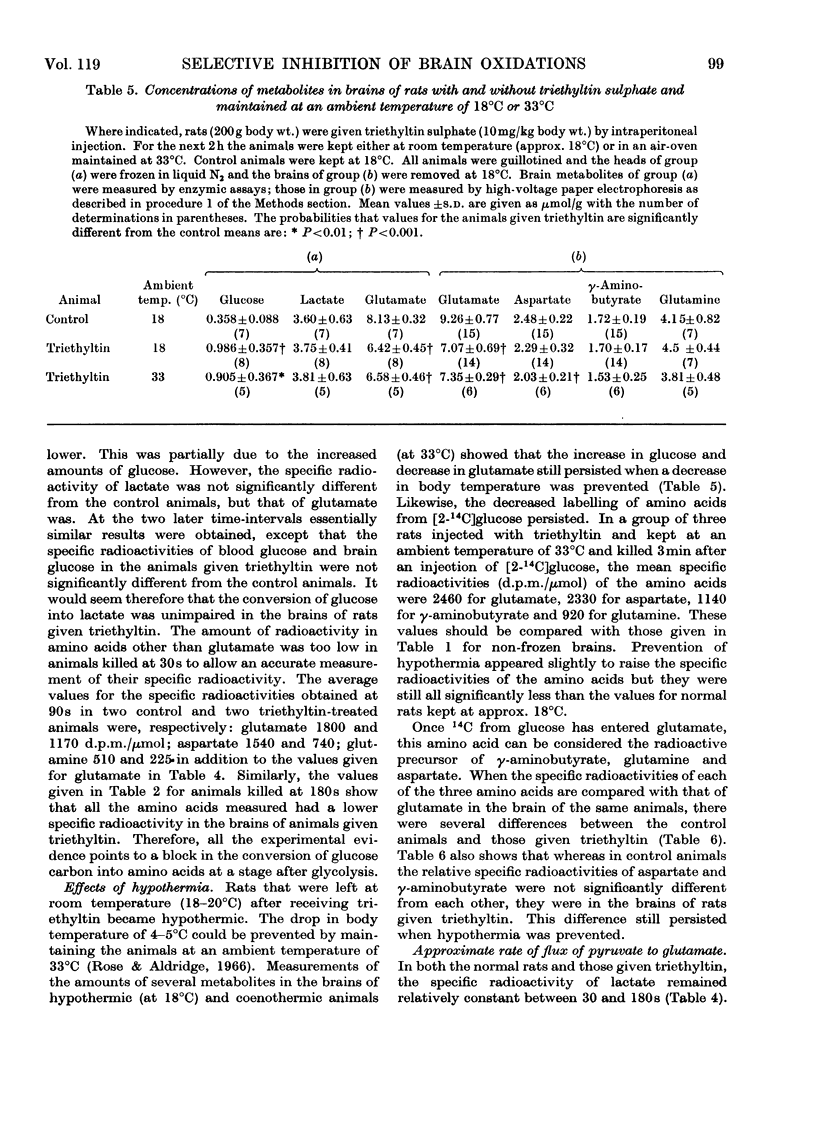
Results are reported of a comparative study in vivo of the metabolism of [2-14C]-glucose and [1-14C]acetate in brains of rats intoxicated with triethyltin sulphate. The incorporation of 14C from glucose into glutamate, glutamine, γ-aminobutyrate and aspartate was greatly decreased. The incorporation of 14C from acetate into these amino acids was unaffected. The experimental data indicated that the main action of triethyltin was to decrease the rate at which pyruvate formed from glucose is oxidized. Glycolysis was not inhibited. Changes in glucose metabolism in the brain are shown not to be directly due to hypothermia. Some of the advantages of measuring the labelling of intermediates at very short time intervals after the injection of the labelled glucose are demonstrated.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALDRIDGE W. N. The biochemistry of organotin compounds: trialkyltins and oxidative phosphorylation. Biochem J. 1958 Jul;69(3):367–376. doi: 10.1042/bj0690367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldridge W. N., Rose M. S. The mechanism of oxidative phosphorylation A hypothesis derived from studies of trimethyltin and triethyltin compounds. FEBS Lett. 1969 Jul;4(2):61–68. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80197-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldridge W. N., Street B. W. Mitochondria from brown adipose tissue. Biochem J. 1968 Mar;107(2):315–317. doi: 10.1042/bj1070315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALAZS R., HASLAM J. EXCHANGE TRANSAMINATION AND THE METABOLISM OF GLUTAMATE IN BRAIN. Biochem J. 1965 Jan;94:131–141. doi: 10.1042/bj0940131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachelard H. S., Lindsay J. R. Effects of neurotropic drugs on glucose metabolism in rat brain in vivo. Biochem Pharmacol. 1966 Aug;15(8):1053–1058. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(66)90270-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berl S., Frigyesi T. L. Effect of reserpine on the turnover of glutamate, glutamine, aspartate and GABA labeled with [1-14C]acetate in caudate nucleus, thalamus and sensorimotor cortex(cat). Brain Res. 1969 Aug;14(3):683–695. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90208-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREMER J. E. AMINO ACID METABOLISM IN RAT BRAIN STUDIED WITH 14C-LABELLED GLUCOSE. J Neurochem. 1964 Mar;11:165–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1964.tb06127.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREMER J. E. The action of triethyl tin, triethyl lead, ethyl mercury and other inhibitors on the metabolism of brain and kidney slices in vitro using substrates labelled with 14C. J Neurochem. 1962 May-Jun;9:289–298. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1962.tb09451.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury A. K., Spector R. G. The influence of psychotropic drugs and ambient temperature on glycogen and reducing substances in mouse brain and liver. Biochem Pharmacol. 1969 May;18(5):1248–1251. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(69)90132-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremer J. E. Studies on brain-cortex slices. Differences in the oxidation of 14-C-labelled glucose and pyruvate revealed by the action of triethyltin and other toxic agents. Biochem J. 1967 Jul;104(1):212–222. doi: 10.1042/bj1040212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flock E. V., Tyce G. M., Owen C. A., Jr Glucose metabolism in brains of diabetic rats. Endocrinology. 1969 Sep;85(3):428–437. doi: 10.1210/endo-85-3-428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAITONDE M. K. RATE OF UTILIZATION OF GLUCOSE AND 'COMPARTMENTATION' OF ALPHA-OXOGLUTARATE AND GLUTAMATE IN RAT BRAIN. Biochem J. 1965 Jun;95:803–810. doi: 10.1042/bj0950803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAITONDE M. K. The composition of brain lipoprotein fractions obtained by different procedures. J Neurochem. 1961 Dec;8:234–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1961.tb13548.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godin Y., Mark J., Mandel P. The effects of 4-hydroxybutyric acid on the biosynthesis of amino acids in the central nervous system. J Neurochem. 1968 Oct;15(10):1085–1091. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1968.tb06826.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda O., Quastel J. H. Transport and metabolism of acetate in rat brain cortex in vitro. Biochem J. 1966 Jul;100(1):83–94. doi: 10.1042/bj1000083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegab E. S., Miller J. A., Jr Ether anesthesia, hypothermia, and carbohydrate metabolism in adult guinea pigs. J Appl Physiol. 1968 Aug;25(2):130–133. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1968.25.2.130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAHIRI S., QUASTEL J. H. FLUOROACETATE AND THE METABOLISM OF AMMONIA IN BRAIN. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:157–163. doi: 10.1042/bj0890157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynn W. S., Straub K. D. ADP kinase and ATPase in chloroplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jun;63(2):540–547. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.2.540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mark J., Godin Y., Mandel P. Glucose and lactic acid content of the rat brain. J Neurochem. 1968 Feb;15(2):141–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1968.tb06185.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidle A., van den Berg C. J., Grynbaum A. The heterogeneity of rat brain mitochondria isolated on continuous sucrose gradients. J Neurochem. 1969 Feb;16(2):225–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb05940.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neal R. M., Koeppe R. E. Precursors in vivo of glutamate, aspartate and their derivatives of rat brain. J Neurochem. 1966 Sep;13(9):835–847. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb05879.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. S., Aldridge W. N. The interaction of triethyltin with components of animal tissues. Biochem J. 1968 Feb;106(4):821–828. doi: 10.1042/bj1060821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. S., Aldridge W. N. Triethyltin and the incorporation of [32P] phosphate into rat brain phospholipids. J Neurochem. 1966 Feb;13(2):103–108. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb03337.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALGANICOFF L., DEROBERTIS E. SUBCELLULAR DISTRIBUTION OF THE ENZYMES OF THE GLUTAMIC ACID, GLUTAMINE AND GAMMA-AMINOBUTYRIC ACID CYCLES IN RAT BRAIN. J Neurochem. 1965 Apr;12:287–309. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1965.tb06766.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salganicoff L., Koeppe R. E. Subcellular distribution ot pyruvate carboxylase, diphosphopyridine nucleotide and triphosphopyridine nucleotide isocitrate dehydrogenases, and malate enzyme in rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 25;243(12):3416–3420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VRBA R., GAITONDE M. K., RICHTER D. The conversion of glucose carbon into protein in the brain and other organs of the rat. J Neurochem. 1962 Sep-Oct;9:465–475. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1962.tb04199.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Berg C. J., Krzalić L., Mela P., Waelsch H. Compartmentation of glutamate metabolism in brain. Evidence for the existence of two different tricarboxylic acid cycles in brain. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(2):281–290. doi: 10.1042/bj1130281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Berg C. J., Mela P., Waelsch H. On the contribution of the tricarboxylic acid cycle to the synthesis of glutamate, glutamine and aspartate in brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 May 25;23(4):479–484. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90753-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


