Abstract
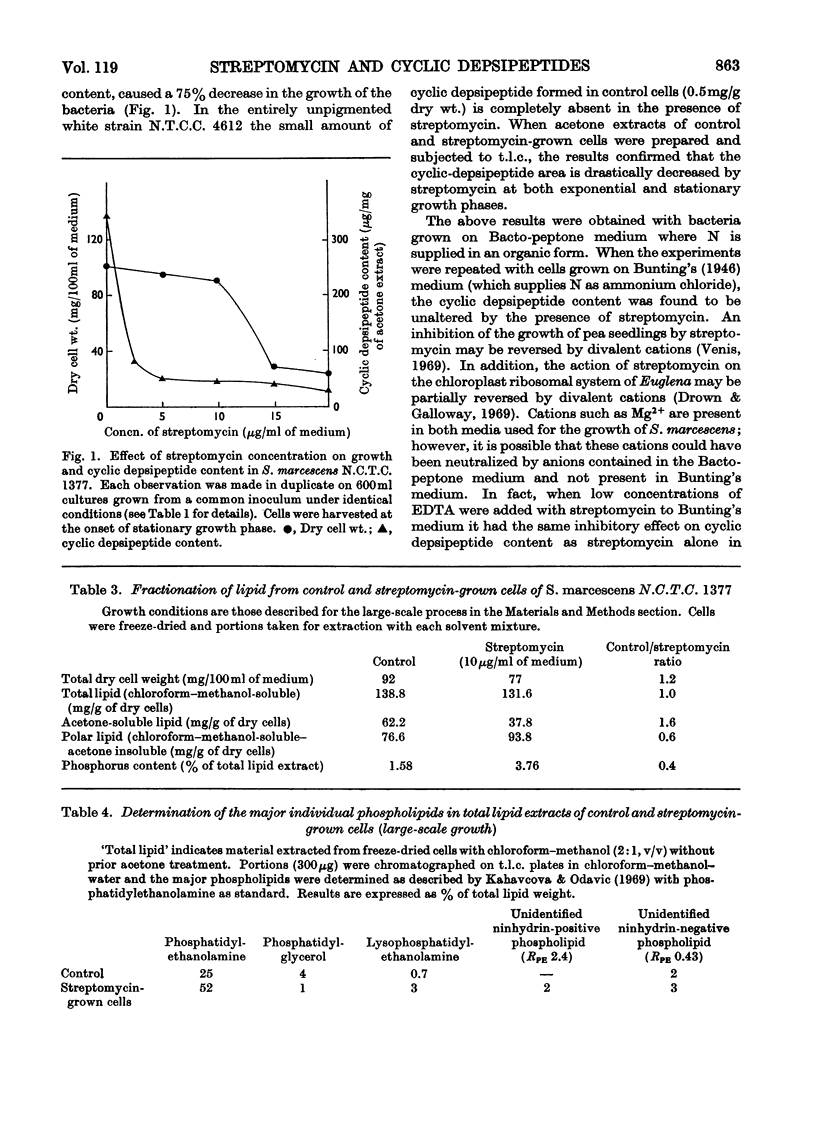
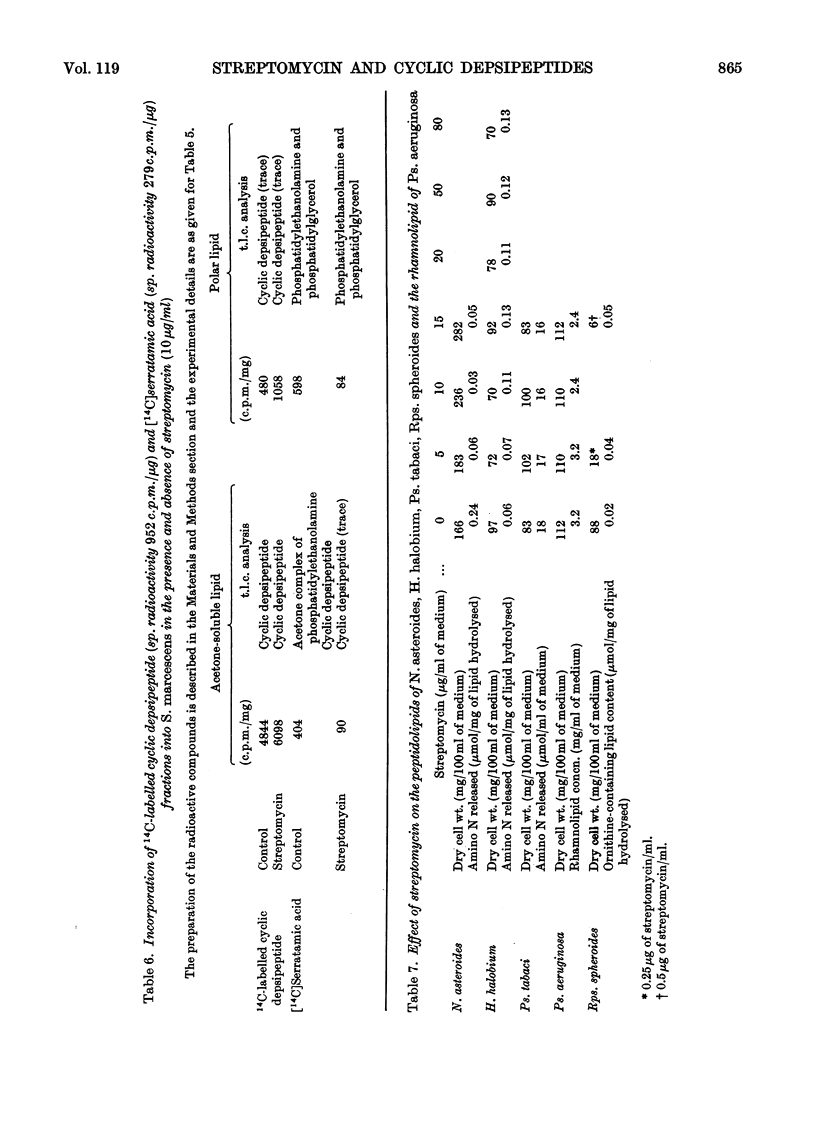
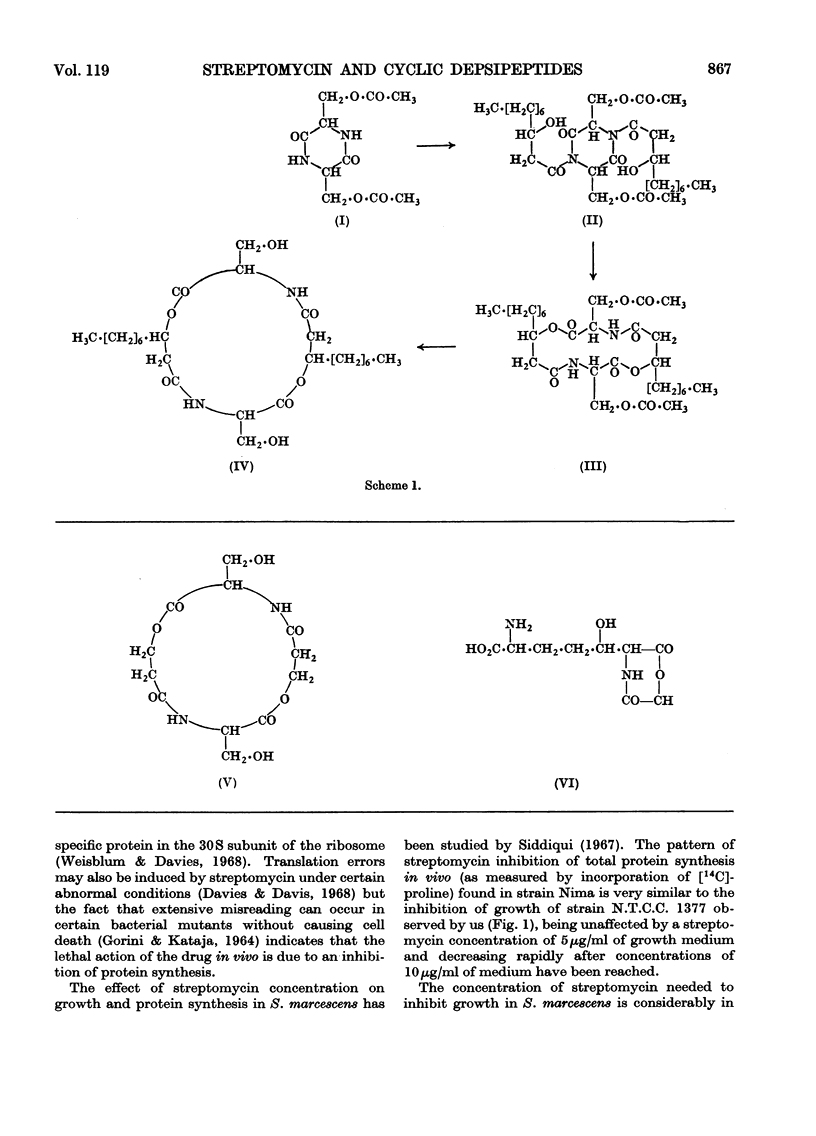
The addition of low concentrations of streptomycin (5–10μg/ml of medium) to Serratia marcescens caused significant alterations in the lipid composition of this organism, but neither growth nor pigmentation was affected. The acetone-soluble cyclic depsipeptides, which comprise on average 15% of the total lipid, were decreased almost to zero and the total lipid phosphorus was more than doubled in the presence of streptomycin. Most of the phospholipid increase was due to an increase in phosphatidylethanolamine. Cyclic depsipeptides were not leached from the cell in the presence of streptomycin, indicating a definite inhibition of the biosynthetic pathway. The effect of streptomycin on the reported peptidolipids of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides, Halobacterium halobium, Nocardia asteroides and Pseudomonas tabaci was investigated. In the case of the only strictly comparable cellular cyclic depsipeptide (that of N. asteroides) the biosynthesis was strongly inhibited by streptomycin, but cell weight was maintained or even slightly increased. A possible mode and site of action of low concentrations of streptomycin on bacterial lipids is discussed.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barber M., Wolstenholme W. A., Guinand M., Michel G., Das B. C., Lederer E. Determination of amino acid sequences in oligopeptides by mass spectrometry. II. The structure of peptidolipin NA. Tetrahedron Lett. 1965 May;(18):1331–1336. doi: 10.1016/s0040-4039(00)77207-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bermingham M. A., Deol B. S., Still J. L. The occurrence of bound serine in acetone extracts of Serratia marcescens exclusively in compounds of a cyclic depsipeptide structure related to serratamolide. Biochem J. 1970 Feb;116(4):759–761. doi: 10.1042/bj1160759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARTWRIGHT N. J. Serratamic acid, a derivative of L-serine produced by organisms of the Serratia group. Biochem J. 1955 Jun;60(2):238–242. doi: 10.1042/bj0600238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Davis B. D. Misreading of ribonucleic acid code words induced by aminoglycoside antibiotics. The effect of drug concentration. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 25;243(12):3312–3316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobler M., Dunitz J. D., Krajewski J. Structure of the K+ complex with enniatin B, a macrocyclic antibiotic with K+ transport properties. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jun 28;42(3):603–606. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90249-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drown D., Galloway R. A. A study of the mechanism of action of streptomycin in Euglena gracilis. Arch Mikrobiol. 1969;68(4):377–386. doi: 10.1007/BF00408861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORINI L., KATAJA E. STREPTOMYCIN-INDUCED OVERSUPPRESSION IN E. COLI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jun;51:995–1001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.6.995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUINAND M., MICHEL G., LEDERER E. Sur les lipides de Nocardia astéroïdes; isolement de lipopeptides. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1958 Feb 3;246(5):848–851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gevers W., Kleinkauf H., Lipmann F. Peptidyl transfers in gramicidin S bisoynthesis from enzyme-bound thioester intermediates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1335–1342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorchein A. Distribution and metabolism of ornithine in Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1968 Jul 2;170(1020):265–278. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1968.0038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAUSER G., KARNOVSKY M. L. Studies on the production of glycolipide by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1954 Dec;68(6):645–654. doi: 10.1128/jb.68.6.645-654.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahovcová J., Odavić R. A simple method for the quantitative analysis of phospholipids separated by thin layer chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1969 Mar 11;40(1):90–96. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)96622-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennarz W. J., Nesbitt J. A., 3rd, Reiss J. The participation of sRNA in the enzymatic synthesis of O-L-lysyl phosphatidylgylcerol in Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Apr;55(4):934–941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.4.934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzzatto L., Apirion D., Schlessinger D. Mechanism of action of streptomycin in E. coli: interruption of the ribosome cycle at the initiation of protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jul;60(3):873–880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.3.873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzzatto L., Apirion D., Schlessinger D. Polyribosome depletion and blockage of the ribosome cycle by streptomycin in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jun 14;42(2):315–335. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90046-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall C. L., Brown A. D. The membrane lipids of Halobacterium halobium. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(3):441–448. doi: 10.1042/bj1100441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modolell J., Davis B. D. Mechanism of inhibition of ribosomes by streptomycin. Nature. 1969 Oct 25;224(5217):345–348. doi: 10.1038/224345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEHGAL S. N., GIBBONS N. E. Effect of some metal ions on the growth of Halobacterium cutirubrum. Can J Microbiol. 1960 Apr;6:165–169. doi: 10.1139/m60-018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger D. Ribosomes: development of some current ideas. Bacteriol Rev. 1969 Dec;33(4):445–453. doi: 10.1128/br.33.4.445-453.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VACZI L., FARKAS L. Association between lipid metabolism and antibiotic sensitivity. I. The lipid composition of antibiotic sensitive and resistant Staphy lococcus aureus strains. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1961;8:205–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOLLEY D. W., SCHAFFNER G., BRAUN A. C. Studies on the structure of the phytopathogenic toxin of Pseudomonas tabaci. J Biol Chem. 1955 Aug;215(2):485–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisblum B., Davies J. Antibiotic inhibitors of the bacterial ribosome. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Dec;32(4 Pt 2):493–528. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuthier R. E. Purification of lipids from nonlipid contaminants on Sephadex bead columns. J Lipid Res. 1966 Jul;7(4):558–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMAGUCHI J., FUKUSHI K., MOTOMIYA M., MUNAKATA K., SHINOHARA C. Biochemical studies on mycobacteria. I. Lipopolysaccharides of Mycobacterium treated with dihydrostreptomycin. Jpn J Tuberc. 1961 Jun;9:1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


