Abstract
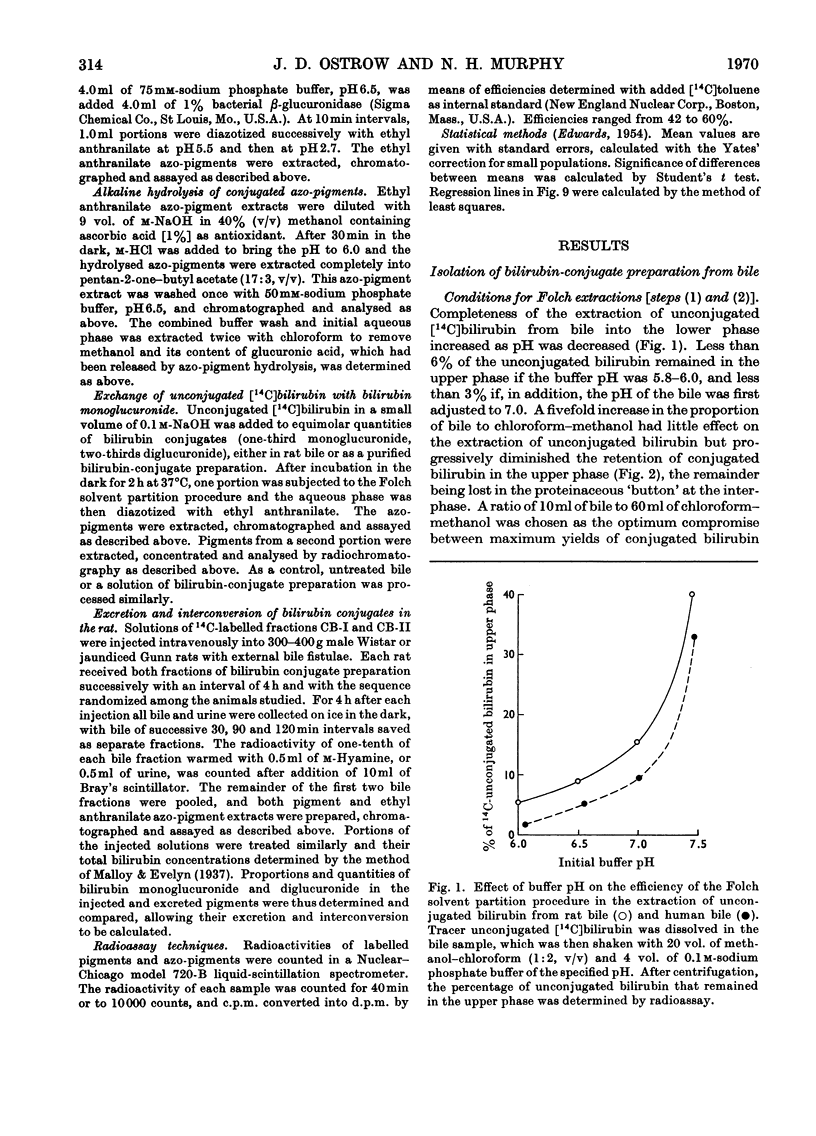
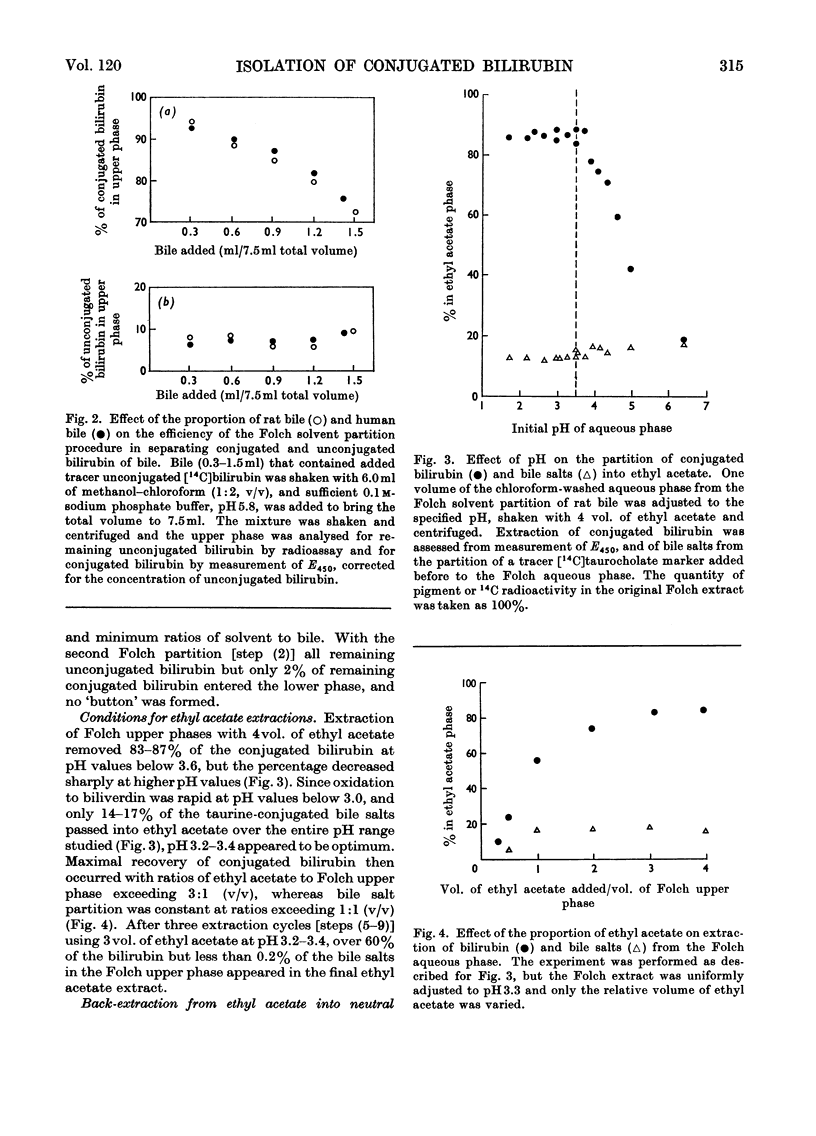
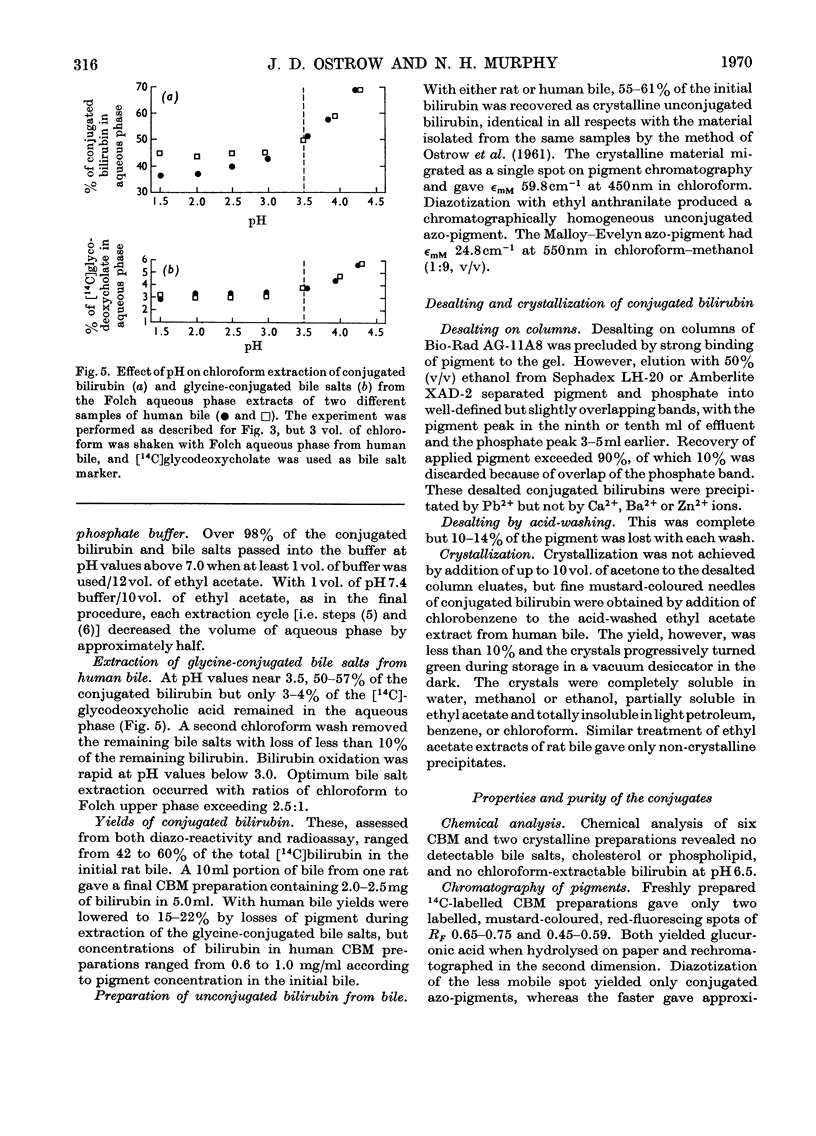
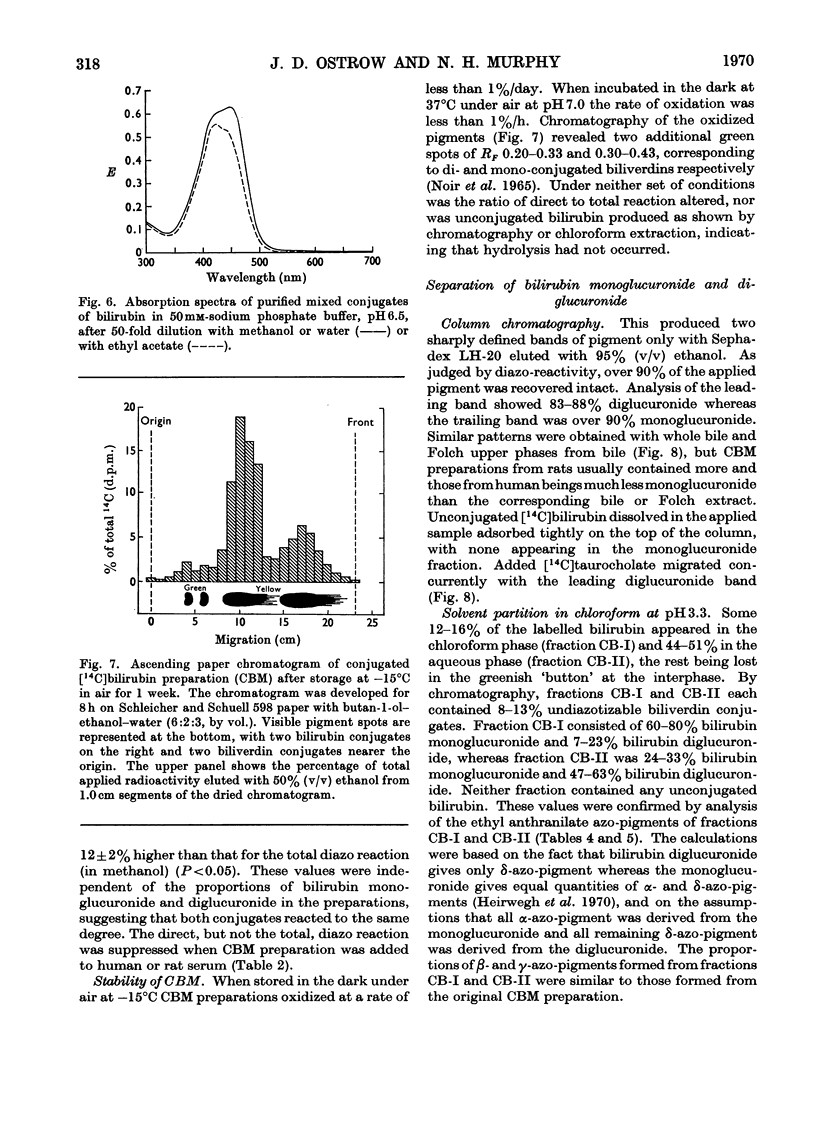
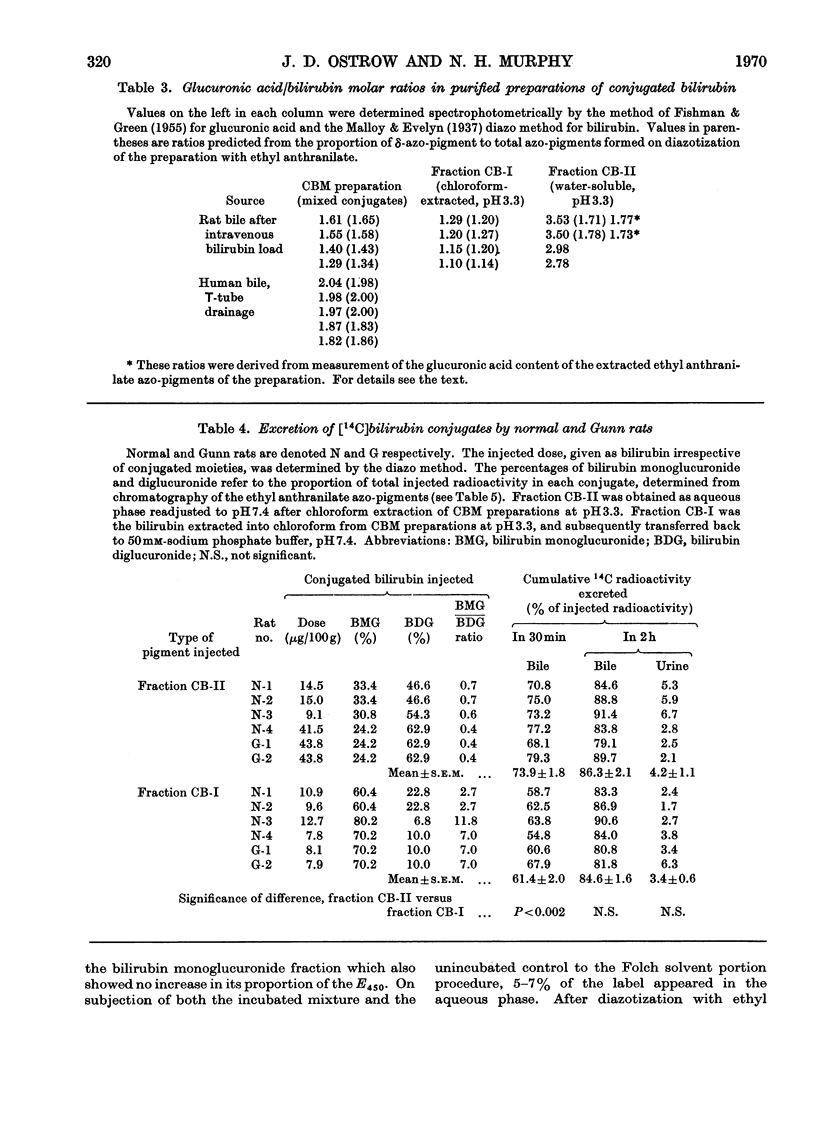
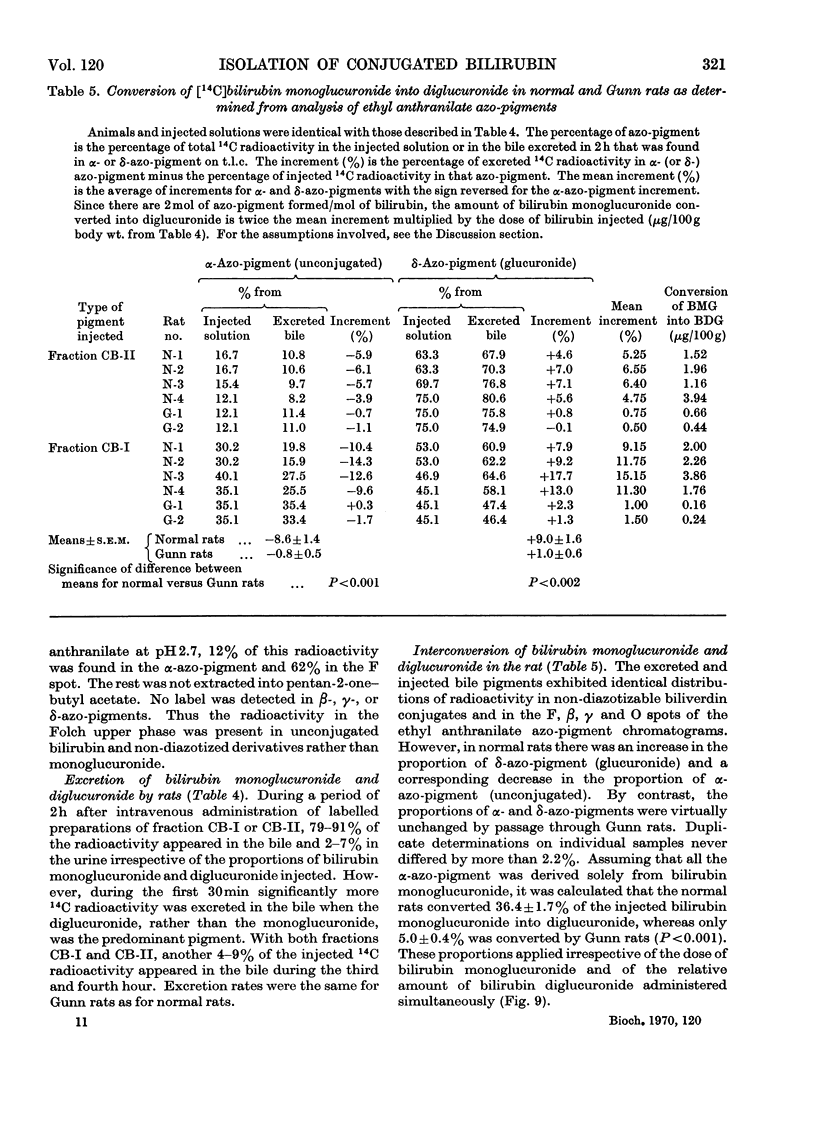
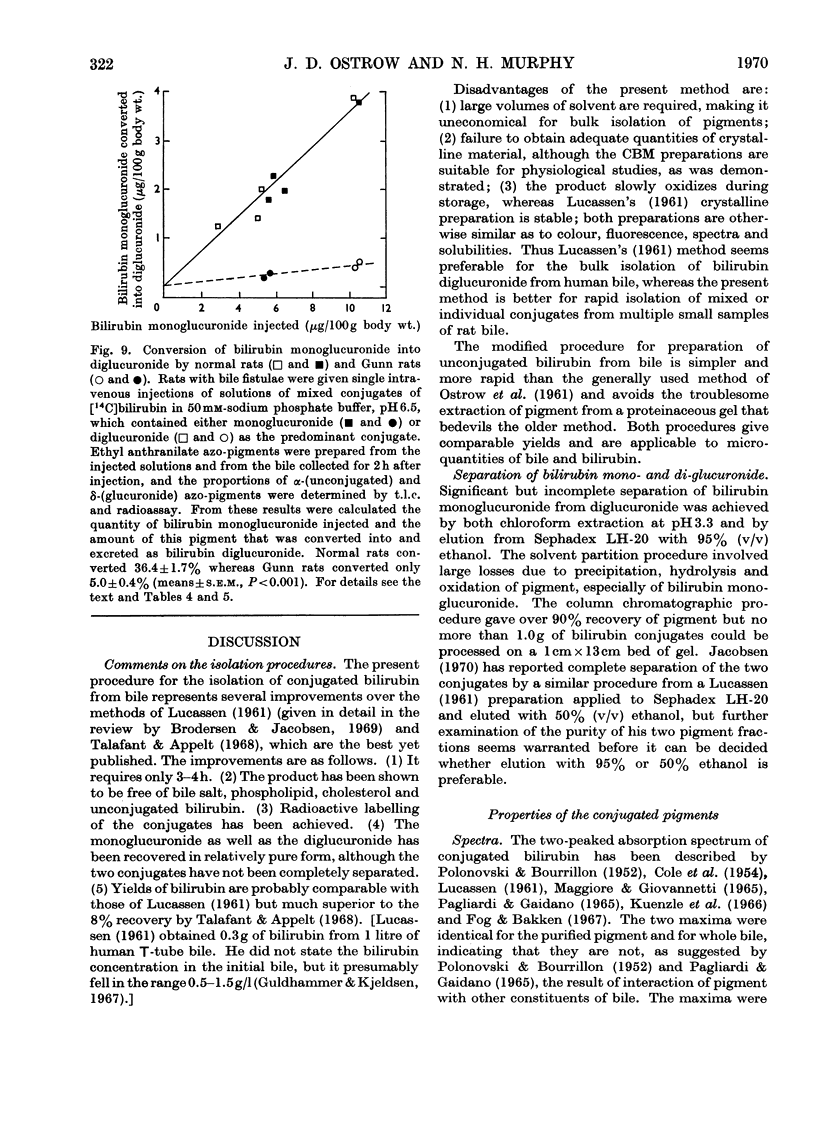
1. A simple, rapid solvent partition method is described for isolation of conjugated bilirubin, free of unconjugated bilirubin, bile salts, phospholipids and cholesterol, from rat bile. Yields are 40–58%. The product is a phosphate-buffered solution containing approx. 0.4mg of bilirubin/ml, principally as mono- and di-glucuronide conjugates. The method may be modified for isolation of conjugates from human bile with 15–22% yield, and for preparation of unconjugated bilirubin from rat or human bile with yields of 55–62%. 2. The conjugated pigment has red–brown fluorescence and an absorption maximum at 450nm with ∈mM 59.8cm−1. Diazotization by the Malloy–Evelyn method gives a direct Van den Bergh reaction (in water) 12% greater than the total reaction (in methanol), with ∈total 28.4×103lmol−1cm−1 at 550nm. After desalting by elution from Sephadex LH-20 in 50% (v/v) ethanol, the product gave water-soluble mustard-yellow crystalline needles. Such desalted conjugates were precipitated by Pb2+ but not by Ba2+, Ca2+ or Zn2+. 3. At pH7.0 and 37°C the conjugated bilirubin was oxidized at a rate of 1%/h without hydrolysis, whereas 84% was hydrolysed by β-glucuronidase or aqueous alkali. 4. Mono- and di-glucuronides were separated by elution from Sephadex LH-20 in 95% (v/v) ethanol or by extraction with chloroform at pH3.2–3.4. The monoconjugated bilirubin did not become labelled during incubation with unconjugated [14C]bilirubin, and chromatographed as a single spot without dissociating into unconjugated bilirubin and diglucuronide as would be expected of a complex. 5. After intravenous injection of mono- or di-conjugated [14C]bilirubin into normal or Gunn rats, 79–91% was excreted in bile and 2–7% in urine over 2h. In these experiments injected diglucuronide was not hydrolysed whereas 30–41% of injected monoglucuronide was converted into diglucuronide by the normal but not by the Gunn rats. The evidence favours the existence of a true bilirubin mono-glucuronide that is not a complex.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acocella G., Tenconi L. T., Armas-Merino R., Raia S., Billing B. H. Does deconjugation of bilirubin glucuronide occur in obstructive jaundice? Lancet. 1968 Jan 13;1(7533):68–69. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90069-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali M. A., Billing B. H. Effect of acid-base changes on renal clearance of bile pigments. Clin Sci. 1966 Jun;30(3):543–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
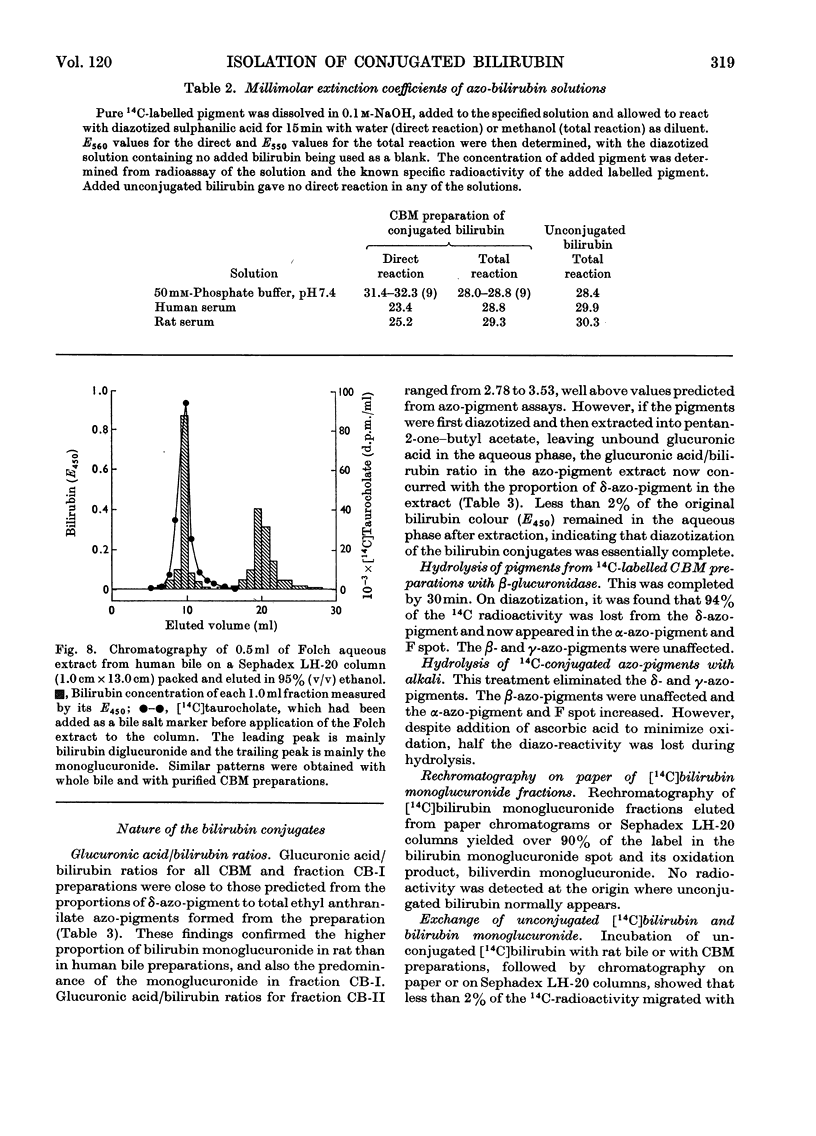
- BILLING B. H., COLE P. G., LATHE G. H. The excretion of bilirubin as a diglucuronide giving the direct van den Bergh reaction. Biochem J. 1957 Apr;65(4):774–784. doi: 10.1042/bj0650774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BILLING B. H., LATHE G. H. Bilirubin metabolism in jaundice. Am J Med. 1958 Jan;24(1):111–121. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(58)90366-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRODERSEN R., VIND I. Chloroform extraction of serum bilirubin in relation to its binding to proteins. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1963;15:107–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodersen R. Bilirubin diglucuronide in normal human blood serum. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1966;18(4):361–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLE P. G., LATHE G. H., BILLING B. H. Separation of the bile pigments of serum, bile and urine. Biochem J. 1954 Jul;57(3):514–518. doi: 10.1042/bj0570514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan E. W., Jr, Schmid R. Excretion of unconjugated bilirubin in the bile of Gunn rats. Gastroenterology. 1969 Aug;57(2):134–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz-Rubio M., Diaz-Rubio M., Jr, Agullo J. L. Aclaramiento renal de las fracciones glucurónicas de la bilirrubina. Rev Esp Enferm Apar Dig. 1966 Dec;25(10):1099–1104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diáz-Rubio M., Diáz-Rubio M., Jr, Martín-Santos J. Investigaciones sobre las fracciones glucuronizadas de la bilirrubina. II. Su conducta tras la sobrecarga con bilirrubina linre en la rata intoxicada aqudamente con CCl4. Rev Clin Esp. 1967 Feb 15;104(3):221–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Díaz-Rubio M. Concepto y diagnóstico de las gastritis crónicas (aportación personal) Rev Clin Esp. 1966 Apr 30;101(2):81–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHMAN W. H., GREEN S. Microanalysis of glucuronide glucuronic acid as applied to beta-glucuronidase and glucuronic acid studies. J Biol Chem. 1955 Aug;215(2):527–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOG J., JELLUM E. Structure of bilirubin. Nature. 1963 Apr 6;198:88–89. doi: 10.1038/198088b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fog J., Bakken A. F. Conjugated and unconjugated bilirubin determined in icteric sera by direct spectrophotometry. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1967;20(1):88–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDSTEIN G. W., LESTER R. REDUCTION OF BILIVERDIN-C-14 TO BILIRUBIN-C-14 IN VIVO. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Dec;117:681–683. doi: 10.3181/00379727-117-29666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREGORY C. H. Studies of conjugated bilirubin. III. Pigment I, a complex of conjugated and free bilirubin. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Jun;61:917–925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guldhammer E. H., Kjeldsen K. Bile flow, pH, electrolytes, and bilirubin in hepatic bile following choledochotomy. Acta Chir Scand. 1967;133(6):483–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASLEWOOD G. A. Recent developments in our knowledge of bile salts. Physiol Rev. 1955 Jan;35(1):178–196. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1955.35.1.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFFMAN H. N., 2nd, WHITCOMB F. F., Jr, BUTT H. R., BOLLMAN J. L. Bile pigments of jaundice. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jan;39:132–142. doi: 10.1172/JCI104011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISSELBACHER K. J., McCARTHY E. A. Studies on bilirubin sulfate and other nonglucuronide conjugates of bilirubin. J Clin Invest. 1959 Apr;38(4):645–651. doi: 10.1172/JCI103842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kottke B. A., Wollenweber J., Owen C. A., Jr Quantitative thin-layer chromatography of free and conjugated cholic acid in human bile and duodenal contents. J Chromatogr. 1966 Mar;21(3):439–447. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)91338-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuenzle C. C., Sommerhalder M., Rüttner J. R., Maier C. Separation and quantitative estimation of four bilirubin fractions from serum and of three bilirubin fractions from bile. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 Feb;67(2):282–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester R., Klein P. D. Bile pigment excretion: a comparison of the biliary excretion of bilirubin and bilirubin derivatives. J Clin Invest. 1966 Dec;45(12):1839–1846. doi: 10.1172/JCI105487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester R., Klein P. D. Biosynthesis of tritiated bilirubin and studies of its excretion in the rat. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 Jun;67(6):1000–1012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester R., Troxler R. F. Recent advances in bile pigment metabolism. Gastroenterology. 1969 Jan;56(1):143–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAKI T., SATO T., SATO T. A study on the activity of beta-glucuronidase in bile in connection with precipitation of calcium bilirubinate. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1962 Jul 25;77:179–186. doi: 10.1620/tjem.77.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAJJAR V. A., CHILDS B. The crystallization and properties of serum bilirubin. J Biol Chem. 1953 Sep;204(1):359–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOIR B. A., GARAY E. R., ROYER M. SEPARATION AND PROPERTIES OF CONJUGATED BILIVERDIN. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 May 4;100:403–410. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neiderhiser D. H., Roth H. P. Cholesterol solubilization by solutions of bile salts and bile salts plus lecithin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 May;128(1):221–225. doi: 10.3181/00379727-128-32983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSTROW J. D., HAMMAKER L., SCHMID R. The preparation of crystalline bilirubin-C14. J Clin Invest. 1961 Aug;40:1442–1452. doi: 10.1172/JCI104375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okolicsanyi L., Magnenat P., Frei J. Deconjugation of bilirubin glucuronide by the liver. Lancet. 1968 Jun 1;1(7553):1173–1174. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)91867-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLONOVSKI M., BOURRILLON R. Métabolisme de la bilirubine. II. Etat physico-chimique de la bilirubine dans la bile. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1952;34(10):973–984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SATO T., SAITOH T. A QUANTITATIVE FRACTIONATION METHOD FOR BILIRUBIN IN HUMAN BILE. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1965 Jan 25;84:329–338. doi: 10.1620/tjem.84.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHACHTER D. Estimation of bilirubin mono- and diglucuronide in the plasma and urine of patients with nonhemolytic jaundice. J Lab Clin Med. 1959 Apr;53(4):557–562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOENFIELD L. J., BOLLMAN J. L. Further studies on the nature and source of the conjugated bile pigments. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Apr;112:929–932. doi: 10.3181/00379727-112-28213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOENFIELD L. J., BOLLMAN J. L., HOFFMAN H. N., 2nd Sulfate and glucuronide conjugates of bilirubin in experimental liver injury. J Clin Invest. 1962 Jan;41:133–140. doi: 10.1172/JCI104455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOENFIELD L. J., GRINDLAY J. H., FOULK W. T., BOLLMAN J. L. Identification of extrahepatic bilirubin monoglucuronide and its conversion to pigment 2 by isolated liver. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Feb;106:438–441. doi: 10.3181/00379727-106-26362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki N., Toyoda M. On infrared absorption spectra of bilirubin and calcium bilirubinate. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1966 Apr 25;88(4):353–360. doi: 10.1620/tjem.88.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALAFANT E. Properties and composition of the bile pigment giving a direct diazo reaction. Nature. 1956 Aug 11;178(4528):312–312. doi: 10.1038/178312a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talafant E., Appelt J. Preparation of bilirubin-diglucuronide concentrates from dog bladder bile. Clin Chem. 1968 Mar;14(3):208–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tygstrup N., Brodersen R. The diagnostic use of specific determination of unconjugated bilirubin. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1968;21(1):62–64. doi: 10.3109/00365516809076977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Roy F. P., Heirwegh K. P. Determination of bilirubin glucuronide and assay of glucuronyltransferase with bilirubin as acceptor. Biochem J. 1968 Apr;107(4):507–518. doi: 10.1042/bj1070507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBER A. P., SCHALM L., WITMANS J. Bilirubin monoglucuronide (pigment I): a complex. Acta Med Scand. 1963 Jan;173:19–24. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1963.tb16500.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


