Abstract
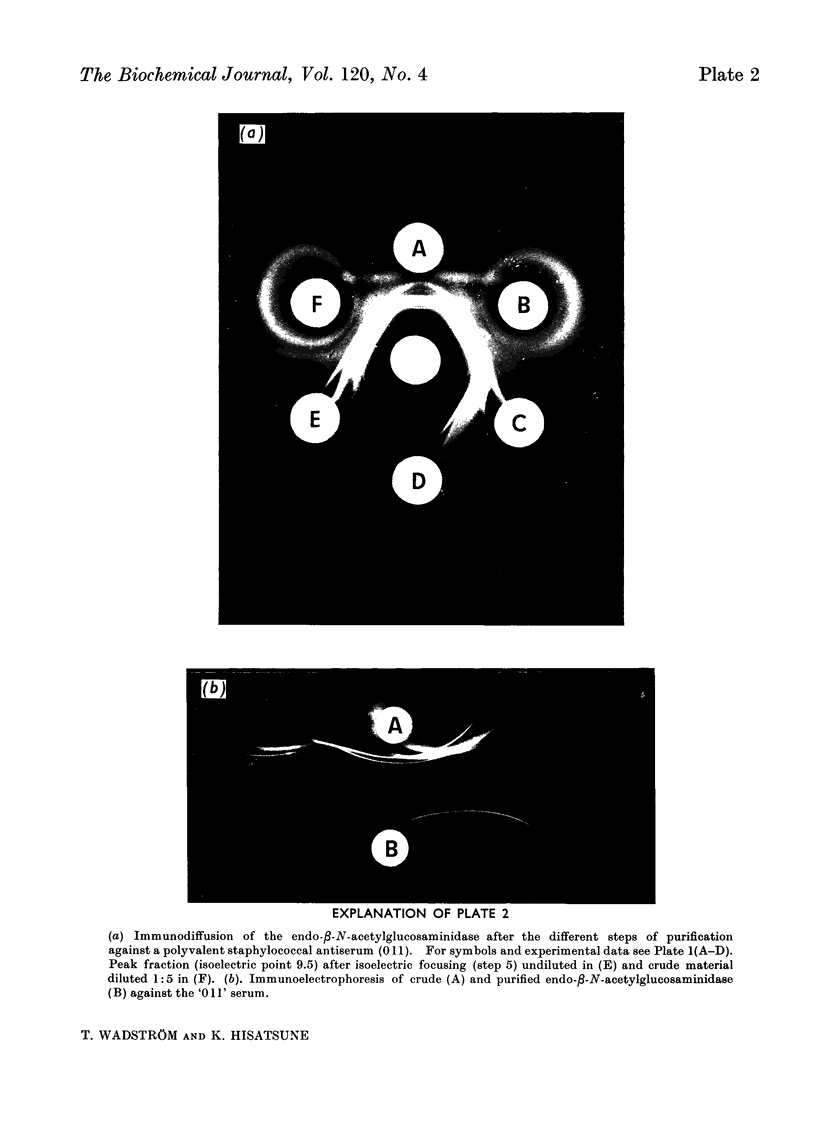
On cultivation of Staphylococcus aureus in a complex liquid medium, bacteriolytic activity is found extracellularly. The maximal amount was found at the end of the exponential growth phase in batch culture, but in continuous culture run under similar conditions the yield was doubled. Isoelectric focusing of dialysed crude culture supernatants showed that the bacteriolytic activity of all four strains studied (M18, 524, Wood 46 and Duncan) was heterogeneous. The most alkaline peak of activity (isoelectric point 9.5±0.1) was assayed against Micrococcus lysodeikticus turbidimetrically. This bacteriolytic activity was purified more than 70-fold after continuous dialysis by adsorption on CM-Sephadex, precipitation with ethanol, heat purification, isoelectric focusing and Sephadex G-100 chromatography. The purified enzyme (isoelectric point 9.6±0.1) was found to give a single band on polyacrylamide-gel and cellulose acetate electrophoresis and was devoid of all 14 staphylococcal enzymes and toxins assayed for. The molecular weight is 70000±5000 as estimated by Sephadex G-100 and G-200 chromatography. The marked instability of the partially and highly purified enzyme was investigated. The mode of action and some properties of this enzyme are given in the following papers (Wadström & Hisatsune, 1970; Wadström, 1970). These results indicate that this extracellular enzyme which is produced by several strains of S. aureus is not a `lysozyme' (endo-β-N-acetylmuramidase) as previously suggested, but an endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidase.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. The gel-filtration behaviour of proteins related to their molecular weights over a wide range. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):595–606. doi: 10.1042/bj0960595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARKULIS S. S., SMITH C., BOLTRALIK J. J., HEYMANN H. STRUCTURE OF STREPTOCOCCAL CELL WALLS. IV. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF STREPTOCOCCAL PHAGE MURALYSIN. J Biol Chem. 1964 Dec;239:4027–4033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWDER H. P., ZYGMUNT W. A., YOUNG J. R., TAVORMINA P. A. LYSOSTAPHIN: ENZYMATIC MODE OF ACTION. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Apr 23;19:383–389. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90473-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doughty C. C., Mann J. A. Purification and properties of a bacteriophage-induced cell wall peptidase from Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):1089–1095. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.1089-1095.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flatmark T., Vesterberg O. On the heterogeneity of beef heart cytochrome c. IV. Isoelectric fractionation by electrolysis in a natural pH-gradient. Acta Chem Scand. 1966;20(6):1497–1503. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.20-1497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLADSTONE G. P., VAN HEYNINGEN W. E. Staphylococcal leucocidins. Br J Exp Pathol. 1957 Apr;38(2):123–137. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghuysen J. M. Use of bacteriolytic enzymes in determination of wall structure and their role in cell metabolism. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Dec;32(4 Pt 2):425–464. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossgebauer K., Schmidt B., Langmaack H. Lysozyme production as an aid for identification of potentially pathogenic strains of staphylococci. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Nov;16(11):1745–1747. doi: 10.1128/am.16.11.1745-1747.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawiger J. Frequency of staphylococcal lysozyme production tested by plate method. J Clin Pathol. 1968 May;21(3):390–393. doi: 10.1136/jcp.21.3.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawiger J. Purification and properties of lysozyme produced by Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):376–384. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.376-384.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjertén S., Jerstedt S., Tiselius A. Some aspects of the use of "continuous" and "discontinuous" buffer systems in polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1965 May;11(2):219–223. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff E., Silverman C. S. Lysis of Staphylococcus aureus cell walls by a soluble staphylococcal enzyme. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jan;95(1):99–106. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.1.99-106.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay J. M. Production of lysozyme by staphylococci and its correlation with three other extracellular substances. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):1804–1810. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.1804-1810.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIIL F. Development of a parallel-flow artificial kidney in plastics. Acta Chir Scand Suppl. 1960;Suppl 253:142–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL P., MOYLE J. Autolytic release and osmotic properties of protoplasts from Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Feb;16(1):184–194. doi: 10.1099/00221287-16-1-184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORNSTEIN L. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. I. BACKGROUND AND THEORY. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:321–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARRY R. M., Jr, CHANDAN R. C., SHAHANI K. M. A RAPID AND SENSITIVE ASSAY OF MURAMIDASE. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Jun;119:384–386. doi: 10.3181/00379727-119-30188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALSTON D. J., BAER B., LIEBERMAN M., KRUEGER A. P. Virolysin, a virus-induced lysin: its appearance and function in phage-infected staphylococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Mar;24:313–325. doi: 10.1099/00221287-24-3-313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISFELD R. A., LEWIS U. J., WILLIAMS D. E. Disk electrophoresis of basic proteins and peptides on polyacrylamide gels. Nature. 1962 Jul 21;195:281–283. doi: 10.1038/195281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHMOND M. H. Lytic enzymes of Staphylococcus aureus 524. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Feb;31(2):564–565. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90041-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROGERS H. J. The rate of formation of hyaluronidase, coagulase and total extracellular protein by strains of Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Apr;10(2):209–220. doi: 10.1099/00221287-10-2-209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strominger J. L., Ghuysen J. M. Mechanisms of enzymatic bacteriaolysis. Cell walls of bacteri are solubilized by action of either specific carbohydrases or specific peptidases. Science. 1967 Apr 14;156(3772):213–221. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3772.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama H., Kashiba S., Amano T., Kotani S., Imanishi T. Purification and properties of a staphylolytic factor produced by a strain of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Biken J. 1967 Sep;10(3):109–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipper D. J. Mechanism of autolysis of isolated cell walls of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):837–847. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.837-847.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesterberg O., Svensson H. Isoelectric fractionation, analysis, and characterization of ampholytes in natural pH gradients. IV. Further studies on the resolving power in connection with separation of myoglobins. Acta Chem Scand. 1966;20(3):820–834. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.20-0820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesterberg O., Wadström T., Vesterberg K., Svensson H., Malmgren B. Studies on extracellular PROTEINS FROM Staphylococcus aureus. I. Separation and characterization of enzymes and toxins by isoelectric focusing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Apr 11;133(3):435–445. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(67)90547-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadström T., Hisatsune K. Bacteriolytic enzymes from Staphylococcus aureus. Specificity of ction of endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase. Biochem J. 1970 Dec;120(4):735–744. doi: 10.1042/bj1200735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]