Epidemiological analyses indicate that disease attributable to smoking is a leading contributor to the large gap in premature mortality between the 15 countries that formerly made up the European Union and the new member states from central and eastern Europe.1 However, the prevalence of smoking in most countries has not been measured in a sufficiently consistent way, or over a long enough period, to be used to predict trends in diseases caused by smoking.
Participants, methods, and results
Lung cancer mortality can provide a useful measure of a population's exposure to smoking,2,3 especially the population segment aged 35-54, when around 80-90% of cases are caused by smoking. We used trends, for each sex, in age standardised mortality due to lung cancer for ages 35-54 to map the lagged effects of the smoking epidemic in the 15 original EU member states and new members from central and eastern Europe, and to infer the earlier trends in tobacco exposure. We calculated death rates, using five year age groups, from deaths attributed to lung cancer in national data and population estimates submitted to the World Health Organization (http://www3.who.int/whosis/mort/text/download.cfm?path=whosis,mort,mort_download&language=English).
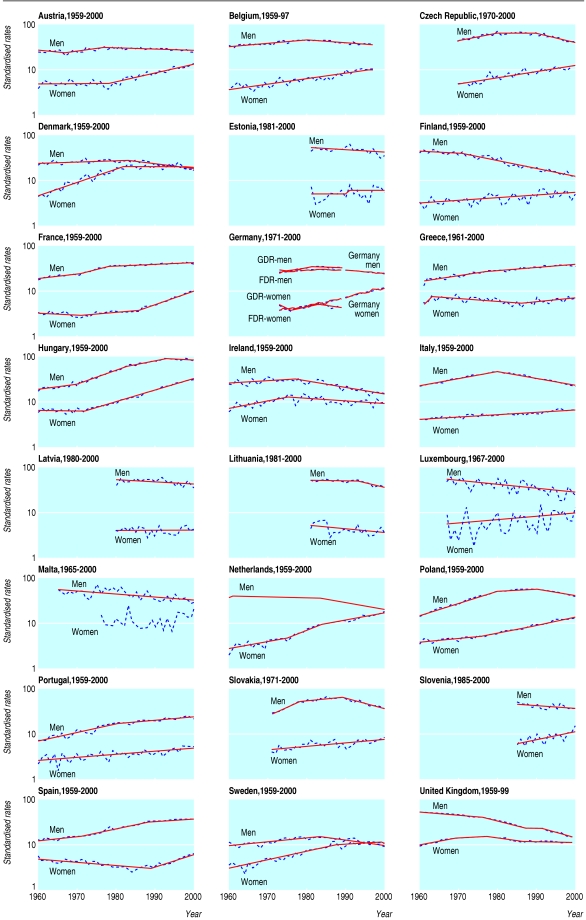
Most EU countries, including all new member states from central and eastern Europe, are now experiencing falling death rates from lung cancer in men. Four countries are, however, exempt from this favourable trend: Portugal, Greece, Spain, and France show no evidence of a decline across the 35-54 age range (figure).
Figure 1.
Lung cancer mortality in the European Union at age 35-54. Dotted (blue) lines denote standardised mortality for lung cancer; solid (red) lines denote time trends calculated by software Joinpoint (http://srab.cancer.gov/joinpoint). Cyprus was not included in the analysis because of lack of data.
Mortality from lung cancer in women is still rising in most EU countries, except for the United Kingdom and, to some extent, Ireland and Denmark. The greatest increases in the past decade were observed in France, Spain, and Hungary; the estimated annual percentage changes are 7.2%, 6.8%, and 6%, respectively. In Latvia, Lithuania, Spain, and Portugal, death rates due to lung cancer remain very low. Rates for women in Hungary exceed those for women in all other member states (mirroring those for Hungarian men) and also exceed the rates for men in more than half the states in the EU. In three countries, lung cancer rates among women are the same as or higher than thosefound among men (Sweden, Denmark, and the Netherlands; figure).
What is already known on this topic
Lung cancer mortality among men is higher in central and eastern Europe than in the 15 original (western) states of the European Union
For each sex, lung cancer rates are distinctly higher in Hungary than elsewhere
What this study adds
Lung cancer mortality is now falling in middle aged men in all new EU states in central and eastern Europe but is still rising among women in most EU countries
Comment
Falling death rates due to lung cancer in the male populations of central and eastern Europe since at least the mid-1990s imply that trends in tobacco exposure in young men have been favourable since at least the early 1980s. The reasons for this need to be explored further and may include changes in prevalence, consumption, or modifications made to cigarettes since this time.4
Lung cancer epidemics among women show no consistent pattern that follows those in men, either in timing or in relative magnitude. This implies that the model advanced by Lopez et al in 19925 is too simple in this respect. The very high mortality figures for Hungary merit further investigation.
When attention is focused not on the absolute rates, in men, of diseases caused by smoking but rather on the direction and magnitude of change in younger adults, new EU member states from central and eastern Europe are no longer at the bottom of the class. The favourable trends for men would also hold promise for future trends in women if these could be predicted from trends in men. However, these data show that this is unlikely to be the case, emphasising the continuing need for strong antismoking programmes for both sexes.
Contributors: JD conducted the analysis and cowrote the paper. MM conducted the analysis, cowrote, and edited the paper. AMcN and JP took part in editing the paper. WZ planned, conducted the analysis, wrote, and edited the paper. WZ is the guarantor.
Funding: This work was supported by the Closing the Gap Project, funded by the European Union Directorate for Health and Consumer Protection, Action 2003121.
Competing interests: None declared.
References
- 1.Peto R, Lopez AD, Boreham J, Thun M, Heath JrC. Mortality from smoking in developed countries 1950-2000. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1994.
- 2.Peto R, Darby S, Deo H, Silcocks P, Whitley E, Doll R. Smoking, smoking cessation, and lung cancer in the UK since 1950: combination of national statistics with two case-control studies. BMJ 2000;321: 323-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Brennan P, Bray I. Recent trends and future directions for lung cancer mortality in Europe. Br J Cancer 2002;87: 43-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Zatonski W. Tobacco smoking in central European countries: Poland. In: Boyle P, Gray N, Henningfield J, Seffrin J, Zatonski W, eds. Tobacco and public health: science and policy. Oxford: Oxford: University Press, 2004: 235-52.
- 5.Lopez AD, Collishaw NE, Piha T. A descriptive model of the cigarette epidemic in developed countries. Tob Control 1994;3: 243-7. [Google Scholar]