Abstract
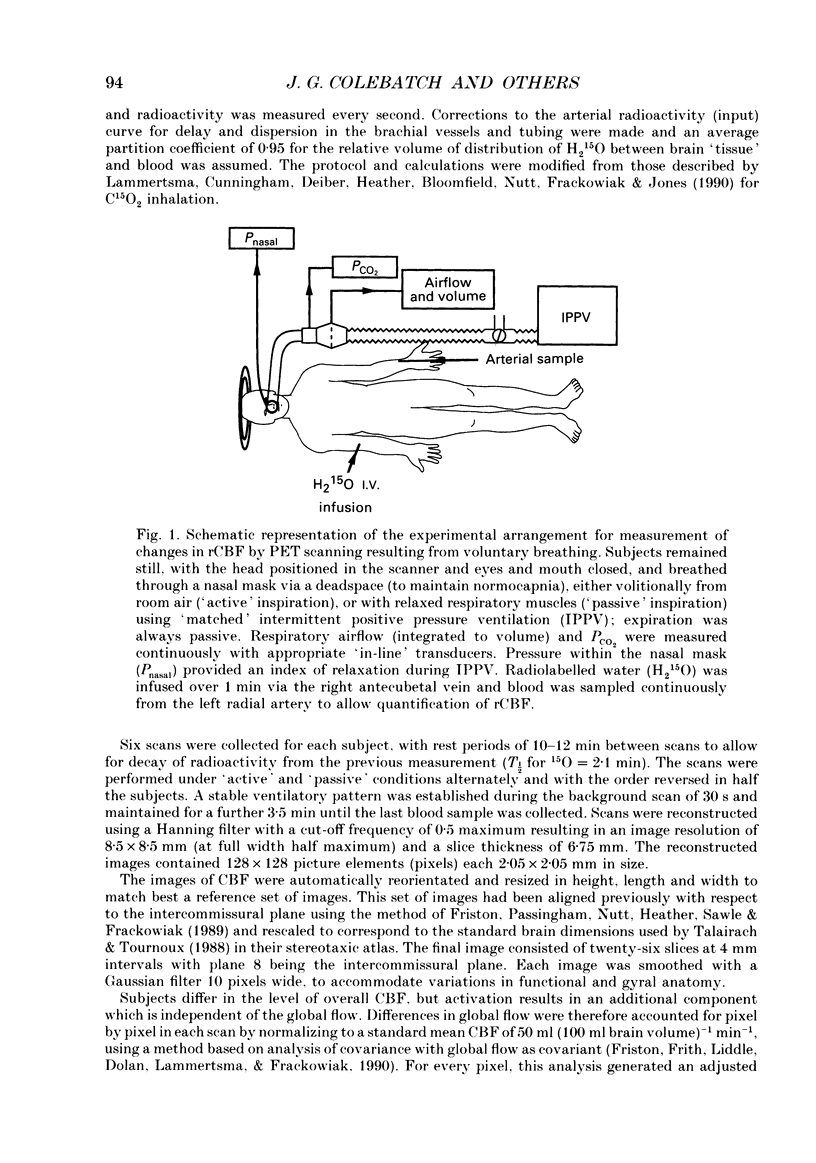
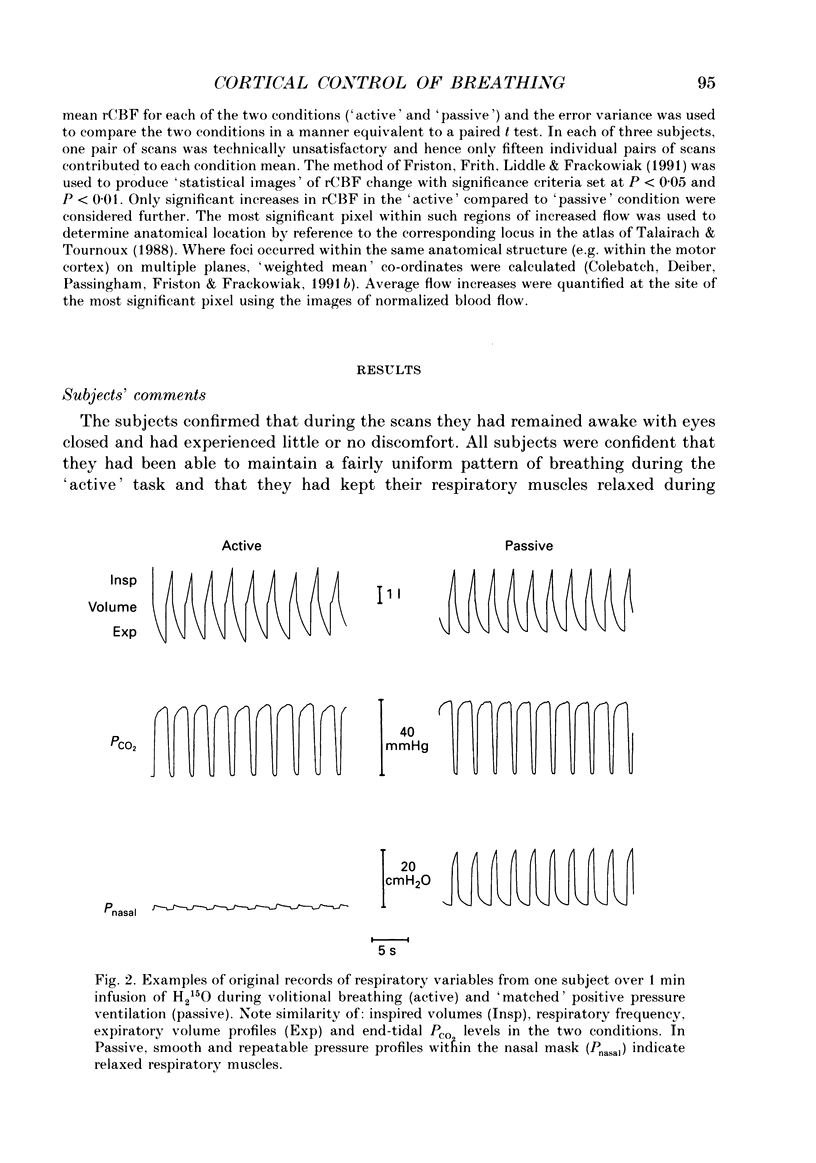
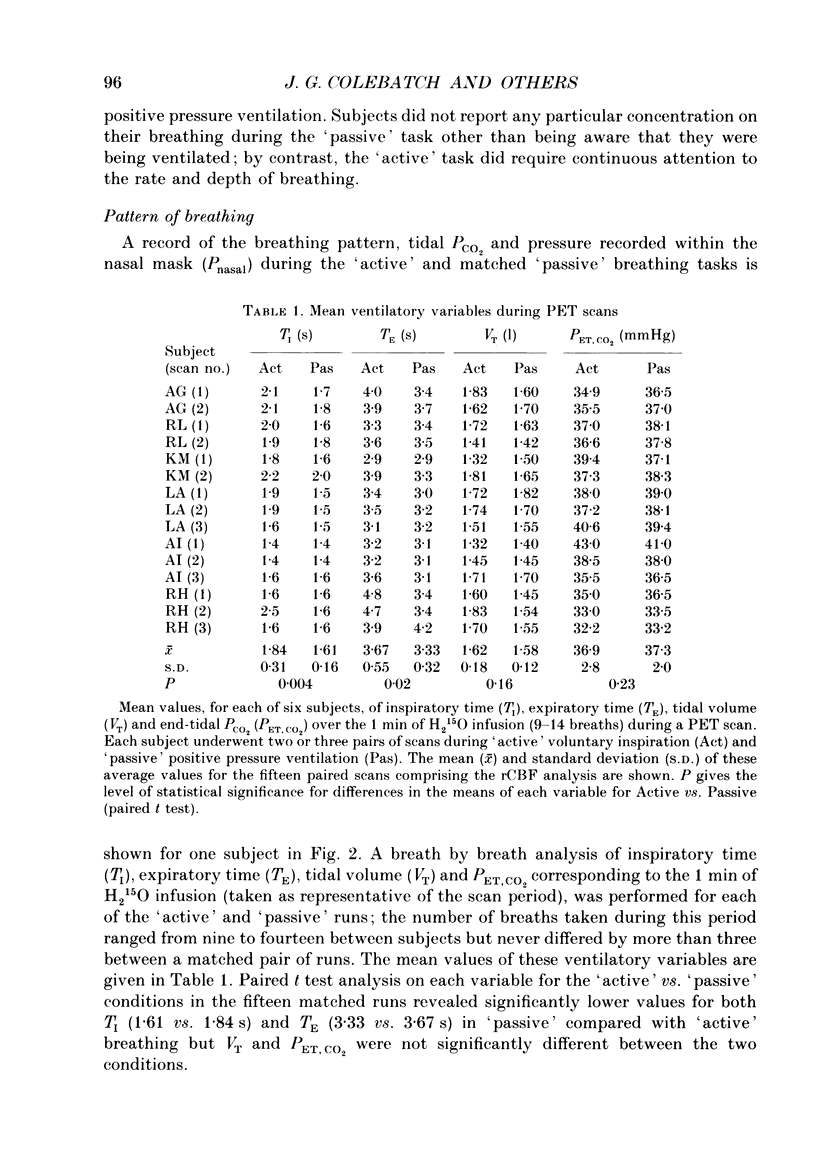
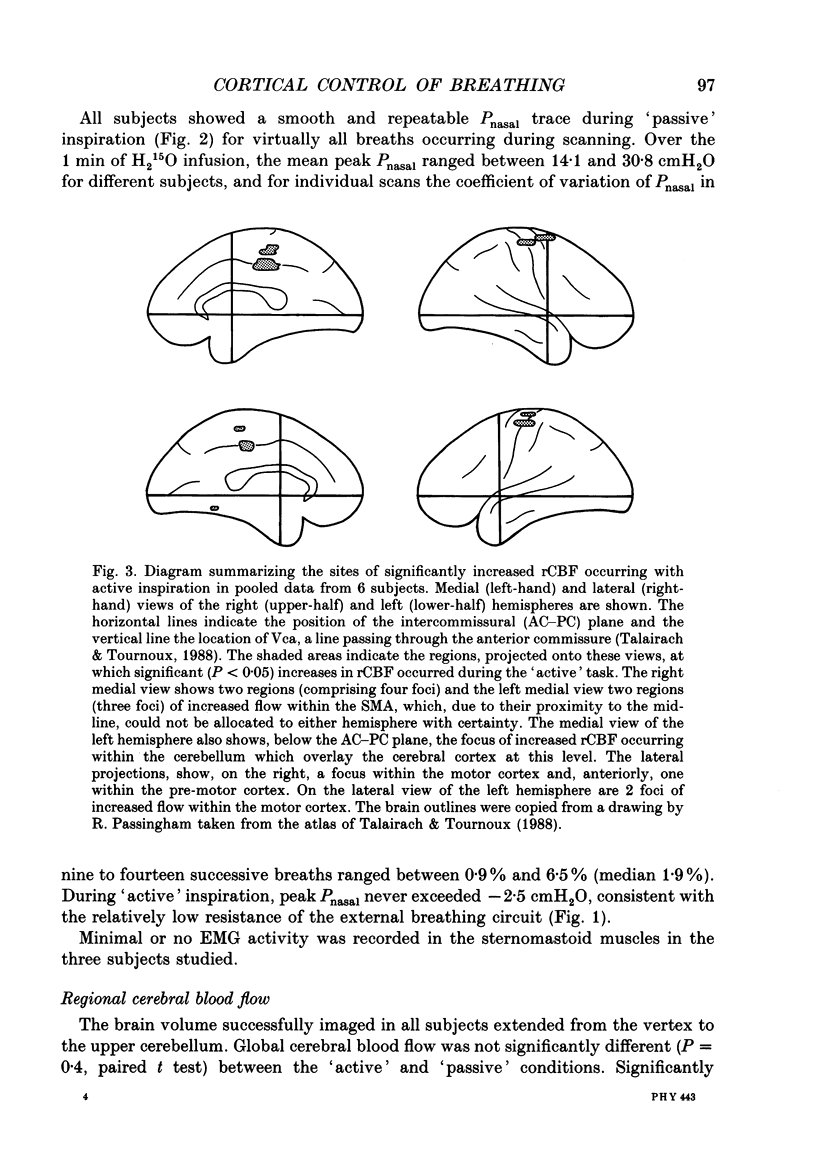
1. Positron emission tomographic imaging of brain blood flow was used to identify areas of motor activation associated with volitional inspiration in six normal male subjects. 2. Scans were performed using intravenous infusion of H2(15)O during voluntary targeted breathing and positive pressure passive ventilation at the same level. 3. Regional increases in brain blood flow, due to active inspiration, were derived using a pixel by pixel comparison of images obtained during the voluntary and passive ventilation phases. 4. Pooling data from all subjects revealed statistically significant increases in blood flow bilaterally in the primary motor cortex (left, 5.4%; right, 4.3%), in the right pre-motor cortex (7.6%), in the supplementary motor area (SMA; 3.1%) and in the cerebellum (4.9%). 5. The site of increased neural activation in the motor cortex, associated with volitional inspiration, is consistent with an area which when stimulated, either directly during neurosurgery or transcranially with a magnetic stimulus, results in activation of the diaphragm. 6. The presence of additional sites of neural activation in the pre-motor cortex and SMA appears analogous to the results of studies on voluntary limb movement. The site of the increase in the SMA was posterior to that previously reported for arm movements. These areas are believed to have a role 'upstream' of the motor cortex in the planning and organization of movement. 7. This technique provides a means of studying the volitional motor control of respiratory related tasks in man.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aminoff M. J., Sears T. A. Spinal integration of segmental, cortical and breathing inputs to thoracic respiratory motoneurones. J Physiol. 1971 Jun;215(2):557–575. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassal M., Bianchi A. L. Inspiratory onset or termination induced by electrical stimulation of the brain. Respir Physiol. 1982 Oct;50(1):23–40. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(82)90004-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLE J., MASSION J. Effet de la stimulation du cortex moteur sur l'activité électrique des nerfs phréniques et médians. Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1958 Nov;66(4):496–514. doi: 10.3109/13813455809084226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colebatch J. G., Deiber M. P., Passingham R. E., Friston K. J., Frackowiak R. S. Regional cerebral blood flow during voluntary arm and hand movements in human subjects. J Neurophysiol. 1991 Jun;65(6):1392–1401. doi: 10.1152/jn.1991.65.6.1392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colebatch J. G., Findley L. J., Frackowiak R. S., Marsden C. D., Brooks D. J. Preliminary report: activation of the cerebellum in essential tremor. Lancet. 1990 Oct 27;336(8722):1028–1030. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92489-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta A. K., Shea S. A., Horner R. L., Guz A. The influence of induced hypocapnia and sleep on the endogenous respiratory rhythm in humans. J Physiol. 1991;440:17–33. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deecke L. Bereitschaftspotential as an indicator of movement preparation in supplementary motor area and motor cortex. Ciba Found Symp. 1987;132:231–250. doi: 10.1002/9780470513545.ch14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldridge F. L., Millhorn D. E., Waldrop T. G. Exercise hyperpnea and locomotion: parallel activation from the hypothalamus. Science. 1981 Feb 20;211(4484):844–846. doi: 10.1126/science.7466362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINK B. R., KATZ R., REINHOLD H., SCHOOLMAN A. Suprapontine mechanisms in regulation of respiration. Am J Physiol. 1962 Feb;202:217–220. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.202.2.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox P. T., Fox J. M., Raichle M. E., Burde R. M. The role of cerebral cortex in the generation of voluntary saccades: a positron emission tomographic study. J Neurophysiol. 1985 Aug;54(2):348–369. doi: 10.1152/jn.1985.54.2.348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox P. T., Raichle M. E. Stimulus rate dependence of regional cerebral blood flow in human striate cortex, demonstrated by positron emission tomography. J Neurophysiol. 1984 May;51(5):1109–1120. doi: 10.1152/jn.1984.51.5.1109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox P. T., Raichle M. E. Stimulus rate determines regional brain blood flow in striate cortex. Ann Neurol. 1985 Mar;17(3):303–305. doi: 10.1002/ana.410170315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox P. T., Raichle M. E., Thach W. T. Functional mapping of the human cerebellum with positron emission tomography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7462–7466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friston K. J., Frith C. D., Liddle P. F., Dolan R. J., Lammertsma A. A., Frackowiak R. S. The relationship between global and local changes in PET scans. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1990 Jul;10(4):458–466. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1990.88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friston K. J., Frith C. D., Liddle P. F., Frackowiak R. S. Comparing functional (PET) images: the assessment of significant change. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1991 Jul;11(4):690–699. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1991.122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friston K. J., Passingham R. E., Nutt J. G., Heather J. D., Sawle G. V., Frackowiak R. S. Localisation in PET images: direct fitting of the intercommissural (AC-PC) line. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1989 Oct;9(5):690–695. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1989.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandevia S. C., Macefield G. Projection of low-threshold afferents from human intercostal muscles to the cerebral cortex. Respir Physiol. 1989 Aug;77(2):203–214. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(89)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandevia S. C., Rothwell J. C. Activation of the human diaphragm from the motor cortex. J Physiol. 1987 Mar;384:109–118. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Brinkman C., Porter R. A quantitative study of the distribution of neurons projecting to the precentral motor cortex in the monkey (M. fascicularis). J Comp Neurol. 1987 May 15;259(3):424–444. doi: 10.1002/cne.902590309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell J. B. Behavioural breathlessness. Thorax. 1990 Apr;45(4):287–292. doi: 10.1136/thx.45.4.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hummelsheim H., Bianchetti M., Wiesendanger M., Wiesendanger R. Sensory inputs to the agranular motor fields: a comparison between precentral, supplementary-motor and premotor areas in the monkey. Exp Brain Res. 1988;69(2):289–298. doi: 10.1007/BF00247574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kety S. S., Schmidt C. F. THE EFFECTS OF ALTERED ARTERIAL TENSIONS OF CARBON DIOXIDE AND OXYGEN ON CEREBRAL BLOOD FLOW AND CEREBRAL OXYGEN CONSUMPTION OF NORMAL YOUNG MEN. J Clin Invest. 1948 Jul;27(4):484–492. doi: 10.1172/JCI101995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammertsma A. A., Cunningham V. J., Deiber M. P., Heather J. D., Bloomfield P. M., Nutt J., Frackowiak R. S., Jones T. Combination of dynamic and integral methods for generating reproducible functional CBF images. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1990 Sep;10(5):675–686. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1990.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon R. N., Porter R. Afferent input to movement-related precentral neurones in conscious monkeys. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1976 Oct 29;194(1116):313–339. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1976.0082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipski J., Bektas A., Porter R. Short latency inputs to phrenic motoneurones from the sensorimotor cortex in the cat. Exp Brain Res. 1986;61(2):280–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00239518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macefield G., Gandevia S. C. The cortical drive to human respiratory muscles in the awake state assessed by premotor cerebral potentials. J Physiol. 1991 Aug;439:545–558. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macpherson J. M., Marangoz C., Miles T. S., Wiesendanger M. Microstimulation of the supplementary motor area (SMA) in the awake monkey. Exp Brain Res. 1982;45(3):410–416. doi: 10.1007/BF01208601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maskill D., Murphy K., Mier A., Owen M., Guz A. Motor cortical representation of the diaphragm in man. J Physiol. 1991 Nov;443:105–121. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy K., Mier A., Adams L., Guz A. Putative cerebral cortical involvement in the ventilatory response to inhaled CO2 in conscious man. J Physiol. 1990 Jan;420:1–18. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp017898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardo J. V., Fox P. T., Raichle M. E. Localization of a human system for sustained attention by positron emission tomography. Nature. 1991 Jan 3;349(6304):61–64. doi: 10.1038/349061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roland P. E., Larsen B., Lassen N. A., Skinhøj E. Supplementary motor area and other cortical areas in organization of voluntary movements in man. J Neurophysiol. 1980 Jan;43(1):118–136. doi: 10.1152/jn.1980.43.1.118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roland P. E., Meyer E., Shibasaki T., Yamamoto Y. L., Thompson C. J. Regional cerebral blood flow changes in cortex and basal ganglia during voluntary movements in normal human volunteers. J Neurophysiol. 1982 Aug;48(2):467–480. doi: 10.1152/jn.1982.48.2.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shea S. A., Walter J., Pelley C., Murphy K., Guz A. The effect of visual and auditory stimuli upon resting ventilation in man. Respir Physiol. 1987 Jun;68(3):345–357. doi: 10.1016/s0034-5687(87)80019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


