Abstract
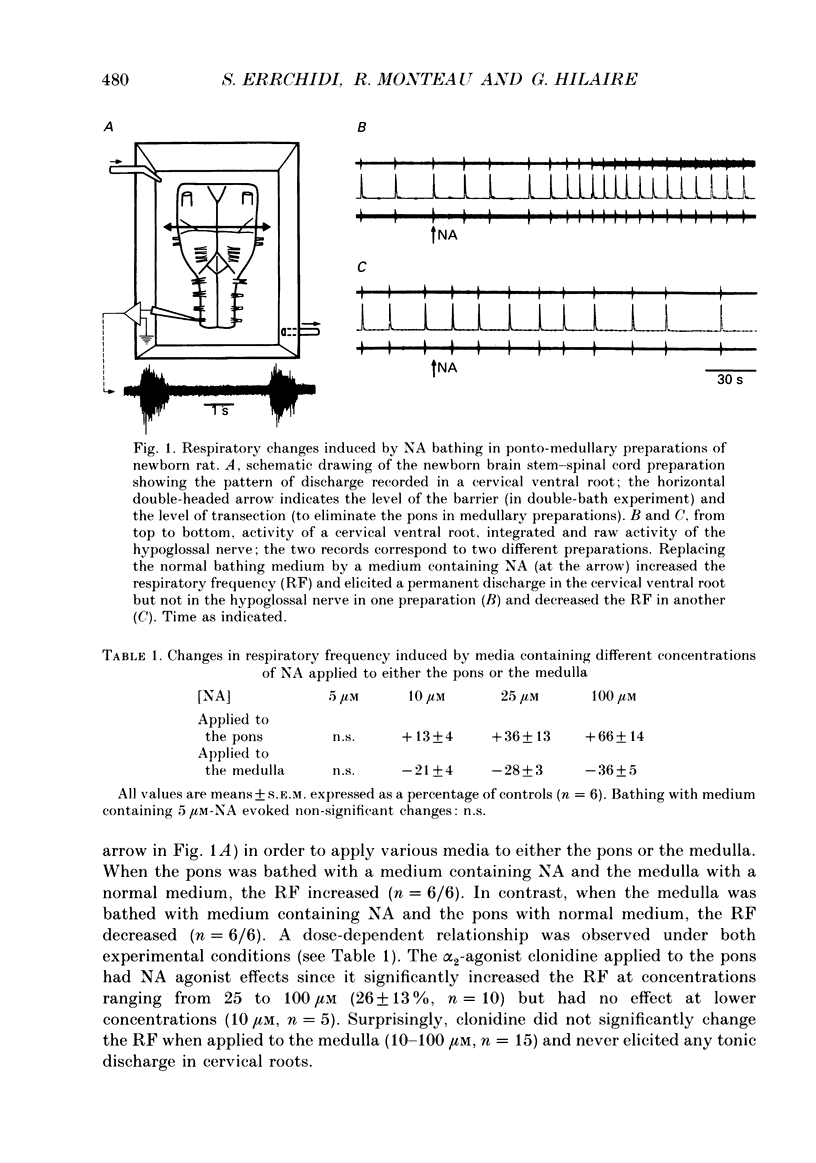
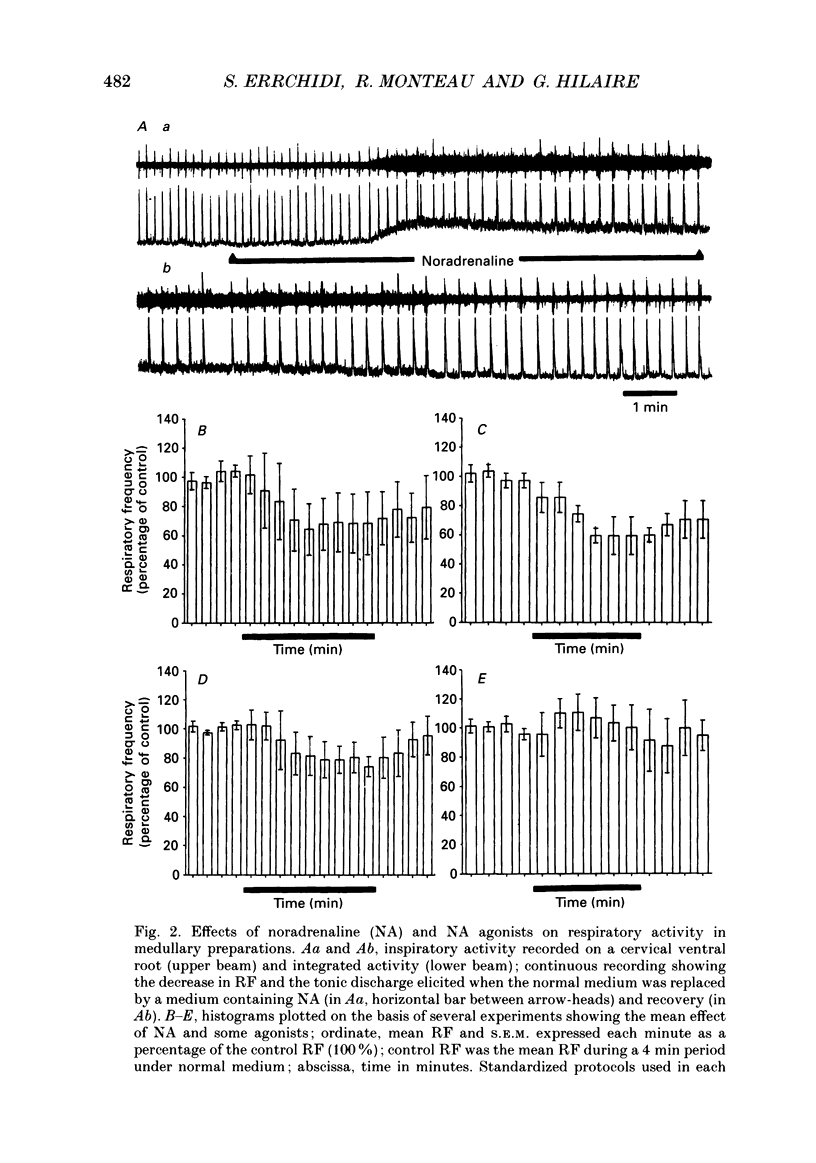
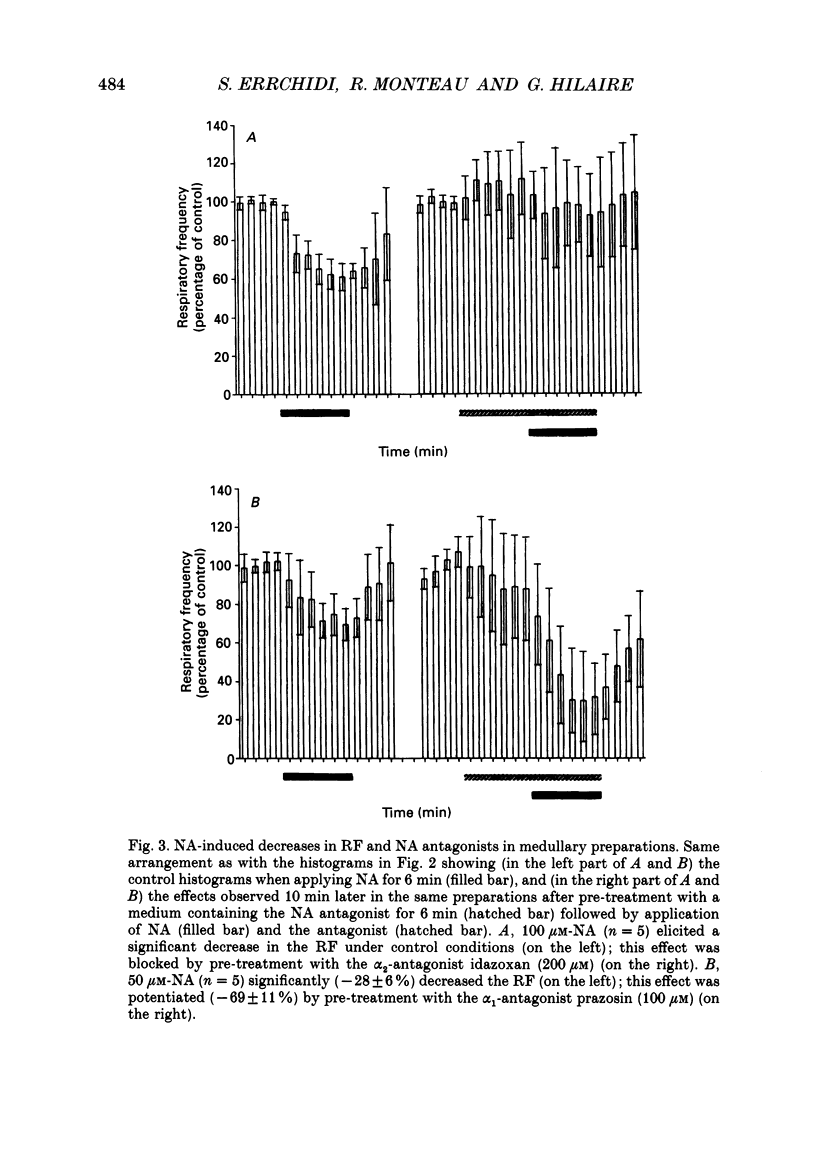
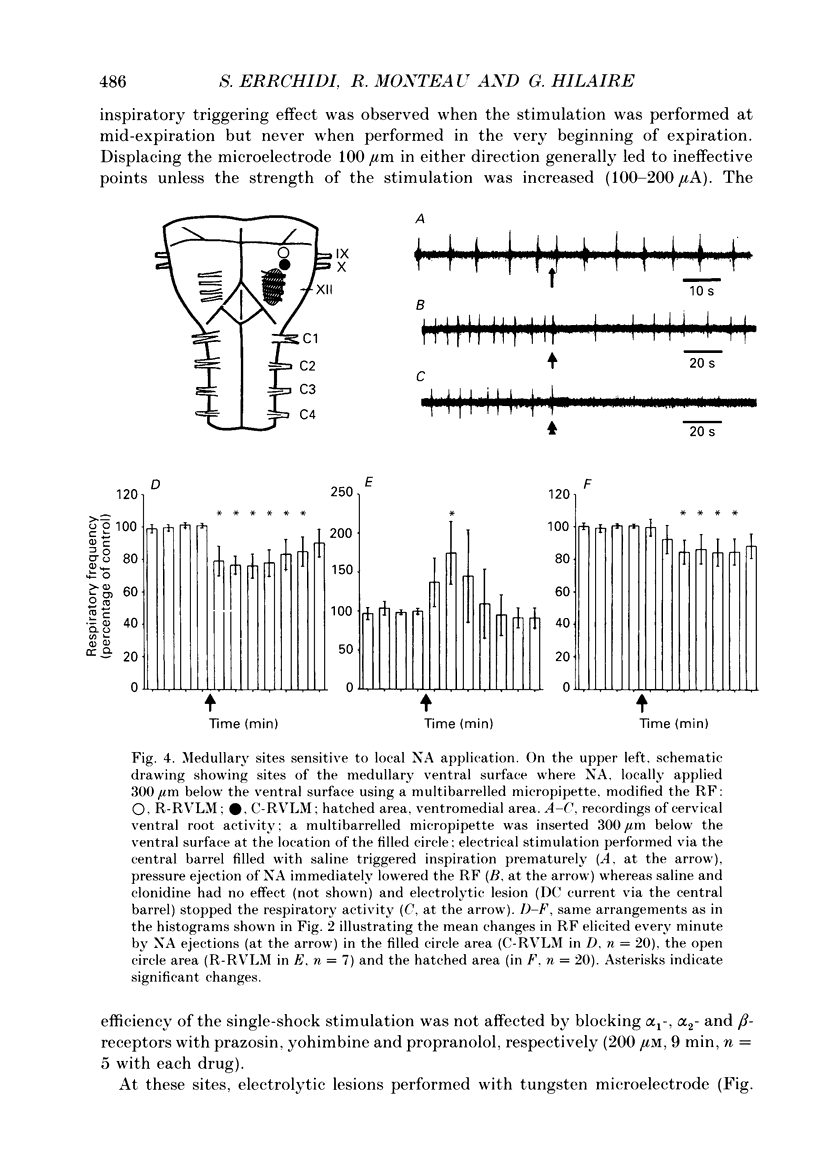
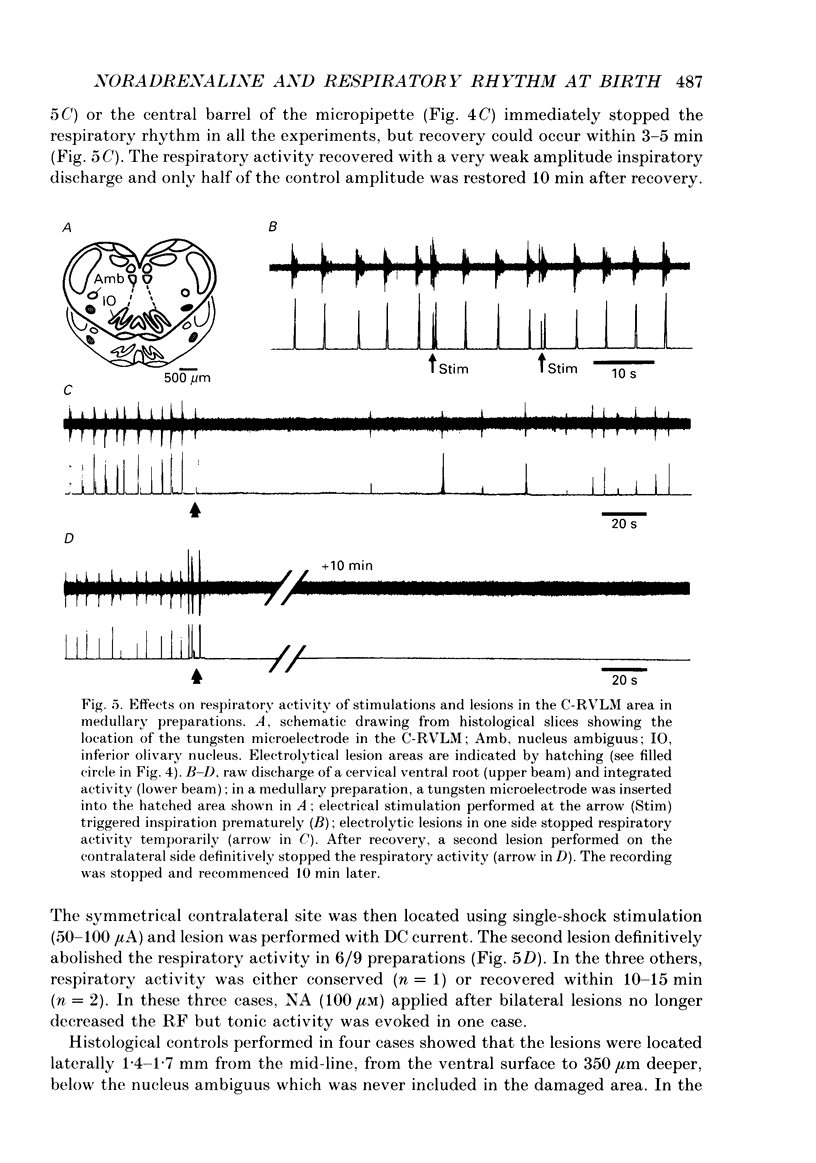
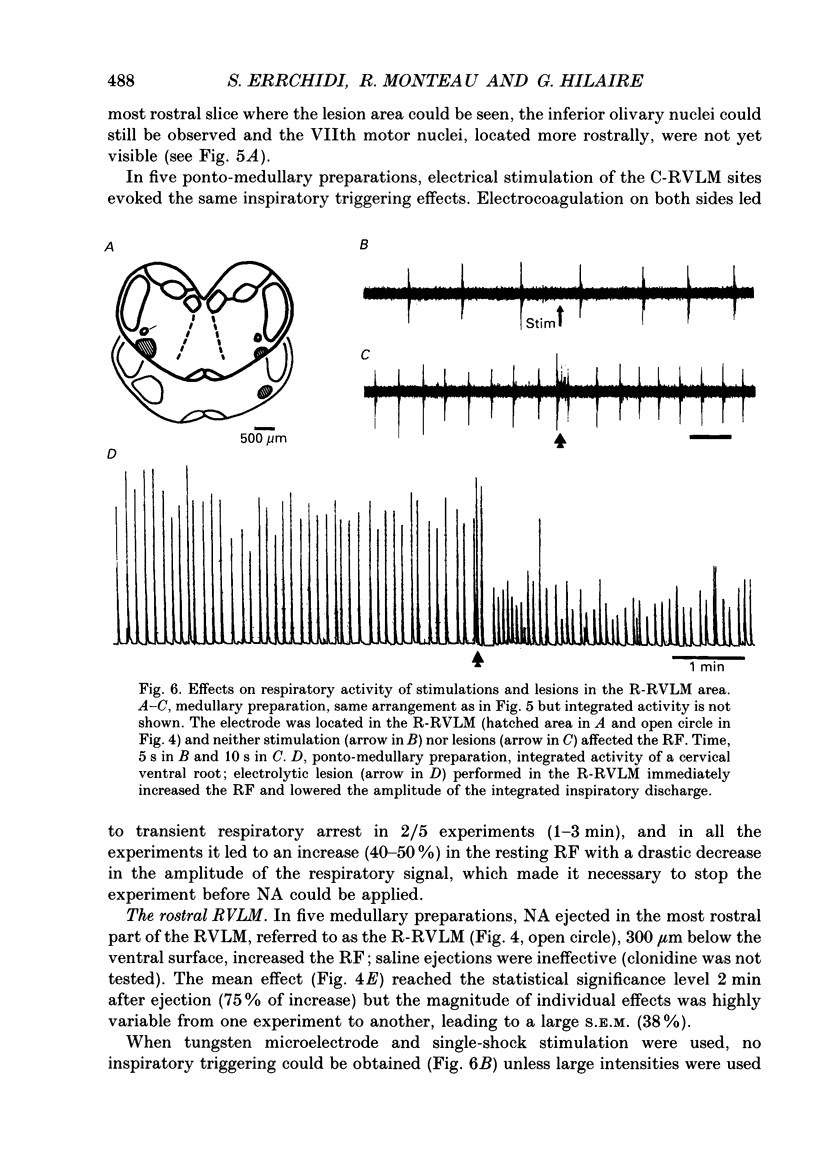
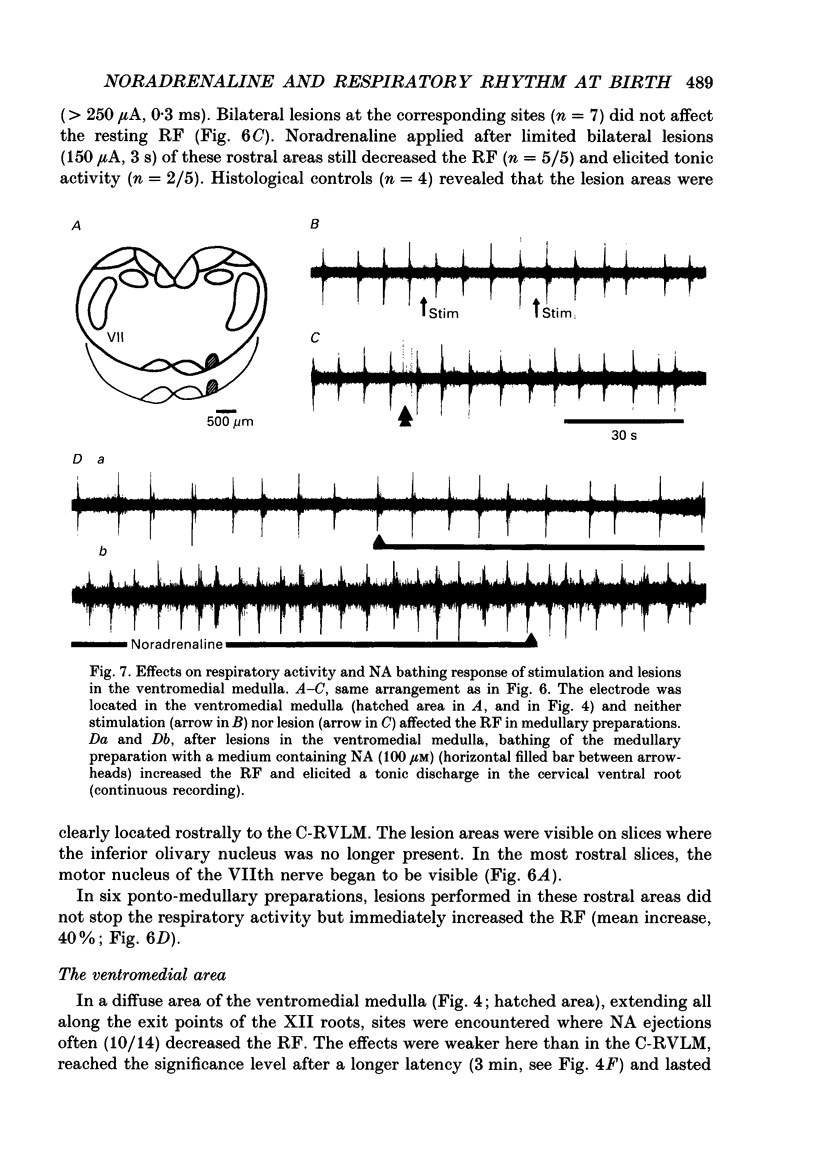
1. Superfused brain stem-spinal cord preparations of newborn rats, which continue to show a rhythmic respiratory activity in vitro, were used to analyse the mechanisms whereby the A5 noradrenergic area modulates the activity of the medullary respiratory rhythm generator in the newborn. 2. In preparations including the pons (ponto-medullary preparations), noradrenaline (NA, 25-100 microM) added to the bathing medium either increased (n = 29/50) or decreased (n = 21/50) the respiratory frequency and elicited a tonic discharge in the cervical ventral roots in 50% of the experiments. Double-bath experiments showed that the increases in respiratory frequency were due to NA acting on the pons, whereas the decreases in respiratory frequency were due to NA acting on the medulla. The NA-induced increases in respiratory frequency were attributed to inhibition of A5 neurons by NA and therefore to withdrawal of A5 inhibition on the medullary rhythm respiratory generator. The NA-induced decreases in respiratory frequency seemed to mimic the effects of endogenous NA on the A5 medullary targets. 3. Noradrenaline-induced tonic activity (i) could be induced after elimination of the pons but not on isolated spinal cord, (ii) could be elicited by alpha 1- but not alpha 2-agonists, (iii) could be blocked by alpha 1- but not alpha 2-antagonists. The tonic activity therefore originated from activation of alpha 1 receptors located in the medulla but its importance in respiratory function is doubtful. 4. In medullary preparations (elimination of the pons by transection), the effects of NA agonists and antagonists on respiratory frequency were analysed. Significant decreases in respiratory frequency were induced by NA, adrenaline, phenylephrine and alpha-methyl-NA, but not by the agonists classified as alpha 2 (clonidine and guanfacine), alpha 1 (6-fluoro-NA) and beta (isoprenaline). Since yohimbine, idazoxan and piperoxane (alpha 2 antagonists) blocked the NA-induced decreases in respiratory frequency whereas prazosin (alpha 1-antagonist) did not, it is postulated that alpha 2-receptors may be involved in modulating respiratory frequency. 5. Stimulation, lesion and NA microejection experiments showed the complexity of the mechanisms mediating NA-induced changes in respiratory activity but suggested that the main site of NA action is located in the rostral ventrolateral medulla, where electrical stimulations triggered inspiration prematurely, lesions suppressed the NA-induced decrease in respiratory frequency, and localized application of NA led to an immediate decrease in the respiratory frequency.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF














Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrade R., Aghajanian G. K. Single cell activity in the noradrenergic A-5 region: responses to drugs and peripheral manipulations of blood pressure. Brain Res. 1982 Jun 17;242(1):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90502-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arata A., Onimaru H., Homma I. Respiration-related neurons in the ventral medulla of newborn rats in vitro. Brain Res Bull. 1990 Apr;24(4):599–604. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(90)90165-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benarroch E. E., Granata A. R., Ruggiero D. A., Park D. H., Reis D. J. Neurons of C1 area mediate cardiovascular responses initiated from ventral medullary surface. Am J Physiol. 1986 May;250(5 Pt 2):R932–R945. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1986.250.5.R932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolme P., Corrodi H., Fuxe K., Hökfelt T., Lidbrink P., Goldstein M. Possible involvement of central adrenaline neurons in vasomotor and respiratory control. Studies with clonidine and its interactions with piperoxane and yohimbine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1974 Sep;28(1):89–94. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(74)90116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolme P., Fuxe K. Pharmacological studies on a possible role of central noradrenaline neurons in respiratory control. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1973 Apr;25(4):351–352. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1973.tb10027.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bousquet P., Feldman J., Bloch R., Schwartz J. The nucleus reticularis lateralis: a region highly sensitive to clonidine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jan 29;69(3):389–392. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90490-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bousquet P., Feldman J., Schwartz J. Central cardiovascular effects of alpha adrenergic drugs: differences between catecholamines and imidazolines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Jul;230(1):232–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bousquet P., Feldman J. The blood pressure effects of alpha-adrenoceptor antagonists injected in the medullary site of action of clonidine: the nucleus reticularis lateralis. Life Sci. 1987 Mar 16;40(11):1045–1052. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90566-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrum C. E., Guyenet P. G. Afferent and efferent connections of the A5 noradrenergic cell group in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Jul 22;261(4):529–542. doi: 10.1002/cne.902610406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedarbaum J. M., Aghajanian G. K. Catecholamine receptors on locus coeruleus neurons: pharmacological characterization. Eur J Pharmacol. 1977 Aug 15;44(4):375–385. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(77)90312-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champagnat J., Denavit-Saubié M., Henry J. L., Leviel V. Catecholaminergic depressant effects on bulbar respiratory mechanisms. Brain Res. 1979 Jan 5;160(1):57–68. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90600-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiueh C. C., Zukowska-Grojec Z., Kirk K. L., Kopin I. J. 6-Fluorocatecholamines as false adrenergic neurotransmitters. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Jun;225(3):529–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denoroy L., Gay N., Gilly R., Tayot J., Pasquier B., Kopp N. Catecholamine synthesizing enzyme activity in brainstem areas from victims of sudden infant death syndrome. Neuropediatrics. 1987 Nov;18(4):187–190. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1052477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldridge F. L., Millhorn D. E. Central regulation of respiration by endogenous neurotransmitters and neuromodulators. Annu Rev Physiol. 1981;43:121–135. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.43.030181.001005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellenberger H. H., Feldman J. L. Subnuclear organization of the lateral tegmental field of the rat. I: Nucleus ambiguus and ventral respiratory group. J Comp Neurol. 1990 Apr 8;294(2):202–211. doi: 10.1002/cne.902940205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellenberger H. H., Feldman J. L., Zhan W. Z. Subnuclear organization of the lateral tegmental field of the rat. II: Catecholamine neurons and ventral respiratory group. J Comp Neurol. 1990 Apr 8;294(2):212–222. doi: 10.1002/cne.902940206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernsberger P., Giuliano R., Willette R. N., Reis D. J. Role of imidazole receptors in the vasodepressor response to clonidine analogs in the rostral ventrolateral medulla. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Apr;253(1):408–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errchidi S., Hilaire G., Monteau R. Permanent release of noradrenaline modulates respiratory frequency in the newborn rat: an in vitro study. J Physiol. 1990 Oct;429:497–510. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman J. E., Aghajanian G. K. Idazoxan (RX 781094) selectively antagonizes alpha 2-adrenoceptors on rat central neurons. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Oct 15;105(3-4):265–272. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90618-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda A., Nabekura J., Ito C., Plata-Salamán C. R., Oomura Y. Developmentally different onset of alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenergic responses in the neonatal rat dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus in vitro. Brain Res. 1989 Jul 31;493(2):357–361. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91170-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyenet P. G. Baroreceptor-mediated inhibition of A5 noradrenergic neurons. Brain Res. 1984 Jun 11;303(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90207-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyenet P. G., Darnall R. A., Riley T. A. Rostral ventrolateral medulla and sympathorespiratory integration in rats. Am J Physiol. 1990 Nov;259(5 Pt 2):R1063–R1074. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1990.259.5.R1063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselton J. R., Guyenet P. G. Central respiratory modulation of medullary sympathoexcitatory neurons in rat. Am J Physiol. 1989 Mar;256(3 Pt 2):R739–R750. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1989.256.3.R739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilaire G., Monteau R., Errchidi S. Possible modulation of the medullary respiratory rhythm generator by the noradrenergic A5 area: an in vitro study in the newborn rat. Brain Res. 1989 Apr 24;485(2):325–332. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90577-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrott B., Louis W. J., Summers R. J. [3H]-guanfacine: a radioligand that selectively labels high affinity alpha2-adrenoceptor sites in homogenates of rat brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Feb;75(2):401–408. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb08801.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kattwinkel J., Mars H., Fanaroff A. A., Klaus M. H. Urinary biogenic amines in idiopathic apnea of prematurity. J Pediatr. 1976 Jun;88(6):1003–1006. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)81063-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler J. P., Jean A. Effect of catecholamines on the swallowing reflex after pressure microinjections into the lateral solitary complex of the medulla oblongata. Brain Res. 1986 Oct 29;386(1-2):69–77. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90142-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millhorn D. E., Eldridge F. L. Role of ventrolateral medulla in regulation of respiratory and cardiovascular systems. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Oct;61(4):1249–1263. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.61.4.1249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monteau R., Errchidi S., Gauthier P., Hilaire G., Rega P. Pneumotaxic centre and apneustic breathing: interspecies differences between rat and cat. Neurosci Lett. 1989 May 8;99(3):311–316. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90465-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monteau R., Morin D., Hennequin S., Hilaire G. Differential effects of serotonin on respiratory activity of hypoglossal and cervical motoneurons: an in vitro study on the newborn rat. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Mar 26;111(1-2):127–132. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90356-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monteau R., Morin D., Hilaire G. Acetylcholine and central chemosensitivity: in vitro study in the newborn rat. Respir Physiol. 1990 Aug;81(2):241–253. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(90)90049-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin D., Hennequin S., Monteau R., Hilaire G. Serotonergic influences on central respiratory activity: an in vitro study in the newborn rat. Brain Res. 1990 Dec 10;535(2):281–287. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91611-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin D., Monteau R., Hilaire G. Serotonin and cervical respiratory motoneurones: intracellular study in the newborn rat brainstem-spinal cord preparation. Exp Brain Res. 1991;84(1):229–232. doi: 10.1007/BF00231779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison S. F., Milner T. A., Reis D. J. Reticulospinal vasomotor neurons of the rat rostral ventrolateral medulla: relationship to sympathetic nerve activity and the C1 adrenergic cell group. J Neurosci. 1988 Apr;8(4):1286–1301. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-04-01286.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss I. R., Inman J. G. Neurochemicals and respiratory control during development. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Jul;67(1):1–13. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.67.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata Y., Martin C. B., Jr, Miyake K., Socol M., Druzin M. Effect of catecholamine on fetal breathing activity in rhesus monkeys. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1981 Apr 15;139(8):942–947. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(81)90964-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onimaru H., Arata A., Homma I. Localization of respiratory rhythm-generating neurons in the medulla of brainstem-spinal cord preparations from newborn rats. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Jul 22;78(2):151–155. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90624-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onimaru H., Homma I. Respiratory rhythm generator neurons in medulla of brainstem-spinal cord preparation from newborn rat. Brain Res. 1987 Feb 17;403(2):380–384. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90080-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. C., Feldman J. L. In vitro brainstem-spinal cord preparations for study of motor systems for mammalian respiration and locomotion. J Neurosci Methods. 1987 Oct;21(2-4):321–333. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(87)90126-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. C., Greer J. J., Liu G. S., Feldman J. L. Neural mechanisms generating respiratory pattern in mammalian brain stem-spinal cord in vitro. I. Spatiotemporal patterns of motor and medullary neuron activity. J Neurophysiol. 1990 Oct;64(4):1149–1169. doi: 10.1152/jn.1990.64.4.1149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. C., Morrison D. E., Ellenberger H. H., Otto M. R., Feldman J. L. Brainstem projections to the major respiratory neuron populations in the medulla of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1989 Mar 1;281(1):69–96. doi: 10.1002/cne.902810107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun M. K., Hackett J. T., Guyenet P. G. Sympathoexcitatory neurons of rostral ventrolateral medulla exhibit pacemaker properties in the presence of a glutamate-receptor antagonist. Brain Res. 1988 Jan 12;438(1-2):23–40. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91320-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun M. K., Young B. S., Hackett J. T., Guyenet P. G. Reticulospinal pacemaker neurons of the rat rostral ventrolateral medulla with putative sympathoexcitatory function: an intracellular study in vitro. Brain Res. 1988 Mar 1;442(2):229–239. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91508-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzue T. Respiratory rhythm generation in the in vitro brain stem-spinal cord preparation of the neonatal rat. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:173–183. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


