Abstract
1. Whole-cell membrane currents in voltage-clamped single isolated cells of longitudinal smooth muscle of guinea-pig ileum were studied at room temperature using patch pipettes filled with either high-K+ solution or high-Cs+ solution, to suppress K+ outward current, and containing 0.3 mM-EGTA. 2. In the presence of high-K+ solution in the pipette, membrane depolarization from the holding potential of -50 mV evoked an initial inward calcium current (ICa) followed by a large initial transient outward current and a sustained outward current with spontaneous oscillations superimposed. Prolonged depolarization above -20 mV produced a late transient outward current which reached a maximum (up to several nanoamps at +10 mV) within approximately 1 s and lasted several seconds. 3. The late outward current (ILTO) was voltage dependent and reversed at the EK (potassium equilibrium potential) in cells exposed to high-K+ external solution. It was blocked by TEA+ (tetraethylammonium) or Ba2+ applied externally (calculated Kd (dissociation constant) values were 0.67 and 4.43 mM, respectively) or by high-Cs+ solution perfusing the cell. The removal of extracellular Ca2+, application of Ca2+ channel blockers (3 mM-Co2+, 0.2 mM-Cd2+ or 1 microM-nifedipine) or perfusion of 5 mM-EGTA inside the cell also abolished the current. Thus, the current seems to be a Ca(2+)-activated K+ current. 4. There is a great discrepancy between the time course of the ICa and that of the late ILTO, which suggests that Ca2+ release from intracellular storage sites may contribute to the generation of the ILTO. 5. Bath application of caffeine (10 mM) during the development of ILTO enhanced the current. However, in the presence of caffeine ILTO was inhibited. Moderate inhibition of ICa by caffeine was also observed. 6. Ryanodine (5 microM) applied to the bathing solution completely inhibited ILTO within 3.5 min; however, it had no or little effect on the ICa. 7. Ruthenium Red (10 microM) completely blocked the ILTO and slightly and more slowly inhibited the ICa. 8. Increasing Mg2+ concentration in the pipette solution from 1 to 6 mM abolished the ILTO. 9. It was concluded that the ILTO was activated mainly by Ca2+ released from the intracellular storage sites following Ca2+ entry, presumably by a Ca(2+)-induced Ca2+ release mechanism.
Full text
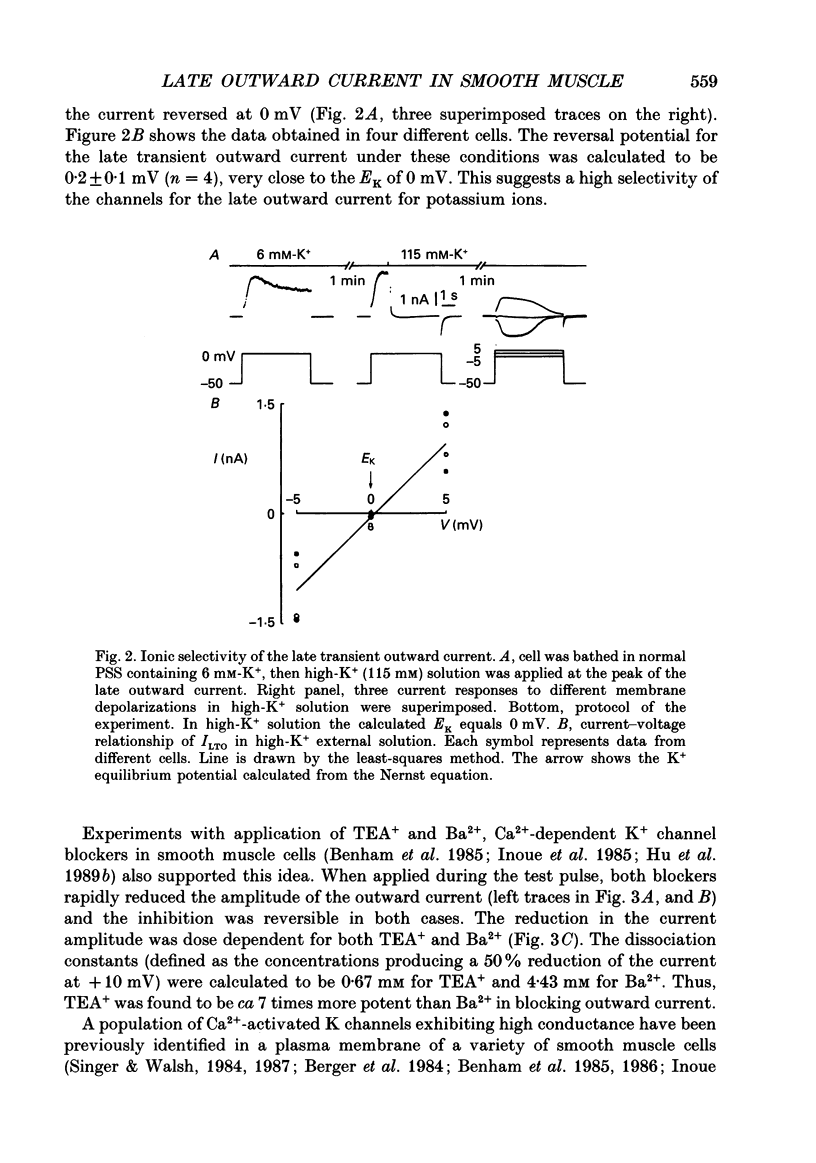
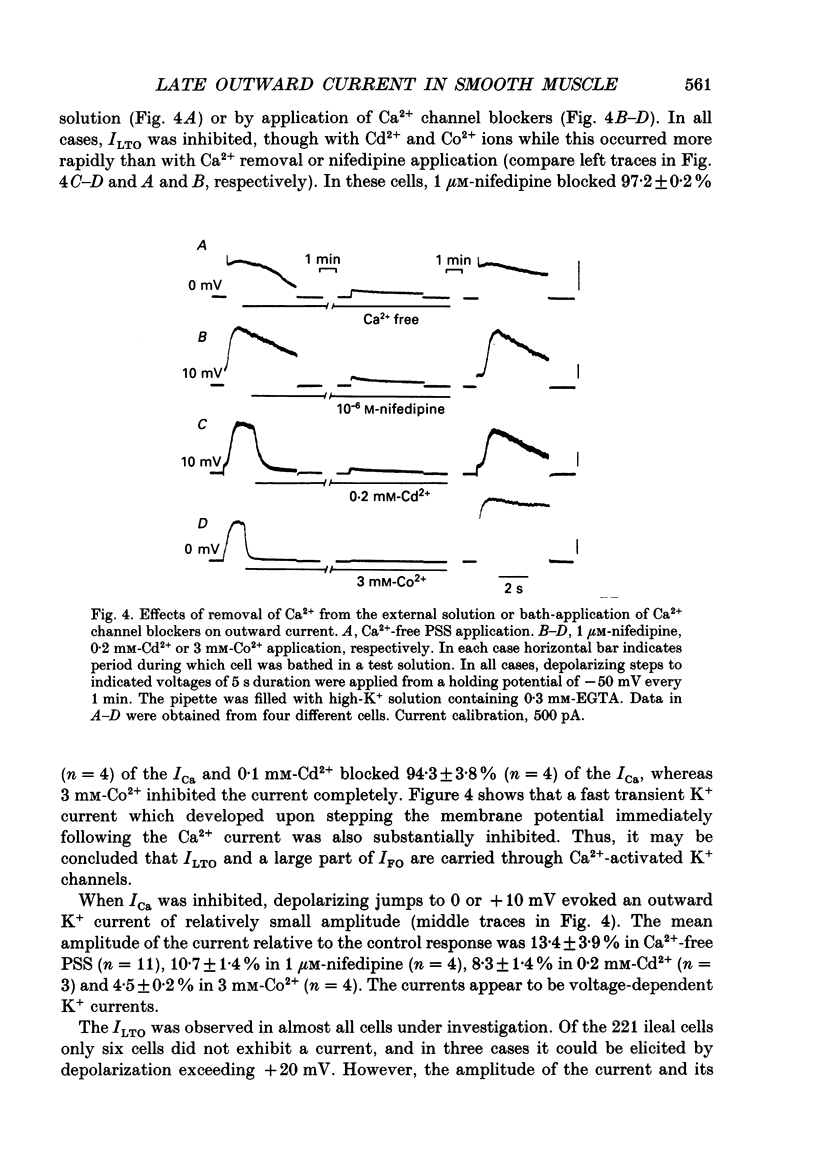
PDF
















Selected References
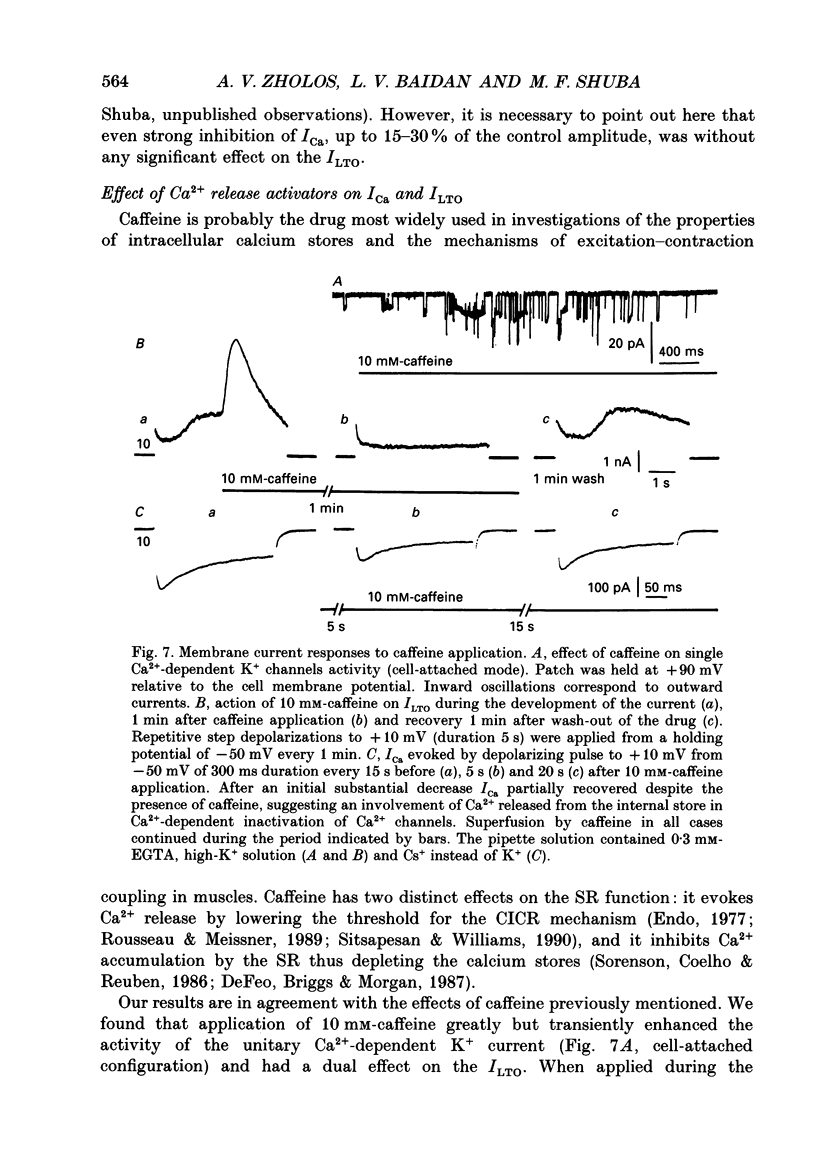
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaronson P. I., Benham C. D. Alterations in [Ca2+]i mediated by sodium-calcium exchange in smooth muscle cells isolated from the guinea-pig ureter. J Physiol. 1989 Sep;416:1–18. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baró I., Escande D. A long lasting Ca2+-activated outward current in guinea-pig atrial myocytes. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Oct;415(1):63–71. doi: 10.1007/BF00373142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. D., Bolton T. B., Lang R. J., Takewaki T. Calcium-activated potassium channels in single smooth muscle cells of rabbit jejunum and guinea-pig mesenteric artery. J Physiol. 1986 Feb;371:45–67. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. D., Bolton T. B., Lang R. J., Takewaki T. The mechanism of action of Ba2+ and TEA on single Ca2+-activated K+ -channels in arterial and intestinal smooth muscle cell membranes. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Feb;403(2):120–127. doi: 10.1007/BF00584088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. D., Bolton T. B. Spontaneous transient outward currents in single visceral and vascular smooth muscle cells of the rabbit. J Physiol. 1986 Dec;381:385–406. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger W., Grygorcyk R., Schwarz W. Single K+ channels in membrane evaginations of smooth muscle cells. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Sep;402(1):18–23. doi: 10.1007/BF00584826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton T. B., Lim S. P. Properties of calcium stores and transient outward currents in single smooth muscle cells of rabbit intestine. J Physiol. 1989 Feb;409:385–401. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFeo T. T., Briggs G. M., Morgan K. G. Ca2+ signals obtained with multiple indicators in mammalian vascular muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1987 Dec;253(6 Pt 2):H1456–H1461. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1987.253.6.H1456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo M. Calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Physiol Rev. 1977 Jan;57(1):71–108. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escande D., Coulombe A., Faivre J. F., Deroubaix E., Coraboeuf E. Two types of transient outward currents in adult human atrial cells. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jan;252(1 Pt 2):H142–H148. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1987.252.1.H142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraoka M., Kawano S. Calcium-sensitive and insensitive transient outward current in rabbit ventricular myocytes. J Physiol. 1989 Mar;410:187–212. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisada T., Kurachi Y., Sugimoto T. Properties of membrane currents in isolated smooth muscle cells from guinea-pig trachea. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Apr;416(1-2):151–161. doi: 10.1007/BF00370237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisayama T., Takayanagi I. Ryanodine: its possible mechanism of action in the caffeine-sensitive calcium store of smooth muscle. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Sep;412(4):376–381. doi: 10.1007/BF01907555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. L., Yamamoto Y., Kao C. Y. Permeation, selectivity, and blockade of the Ca2+-activated potassium channel of the guinea pig taenia coli myocyte. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Nov;94(5):849–862. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.5.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. L., Yamamoto Y., Kao C. Y. The Ca2+-activated K+ channel and its functional roles in smooth muscle cells of guinea pig taenia coli. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Nov;94(5):833–847. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.5.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. D., Hering S., Bolton T. B. The action of caffeine on inward barium current through voltage-dependent calcium channels in single rabbit ear artery cells. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Jun;416(4):462–466. doi: 10.1007/BF00370755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang K. S., van Breemen C. Ryanodine modulation of 45Ca efflux and tension in rabbit aortic smooth muscle. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Apr;408(4):343–350. doi: 10.1007/BF00581127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino M., Kobayashi T., Endo M. Use of ryanodine for functional removal of the calcium store in smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Apr 15;152(1):417–422. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80730-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imaizumi Y., Muraki K., Watanabe M. Ionic currents in single smooth muscle cells from the ureter of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1989 Apr;411:131–159. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue R., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. Two Ca-dependent K-channels classified by the application of tetraethylammonium distribute to smooth muscle membranes of the rabbit portal vein. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Oct;405(3):173–179. doi: 10.1007/BF00582557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanmura Y., Missiaen L., Raeymaekers L., Casteels R. Ryanodine reduces the amount of calcium in intracellular stores of smooth-muscle cells of the rabbit ear artery. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Dec;413(2):153–159. doi: 10.1007/BF00582525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon J. L., Sutko J. L. Calcium- and voltage-activated plateau currents of cardiac Purkinje fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Jun;89(6):921–958. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.6.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo K., Mitchell J. A., de Nucci G., Vane J. R. Simultaneous measurement of endothelium-derived relaxing factor by bioassay and guanylate cyclase stimulation. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Oct;98(2):630–636. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12637.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G. Intracellular perfusion of nerve cells and its effects on membrane currents. Physiol Rev. 1984 Apr;64(2):435–454. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.2.435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kume H., Takai A., Tokuno H., Tomita T. Regulation of Ca2+-dependent K+-channel activity in tracheal myocytes by phosphorylation. Nature. 1989 Sep 14;341(6238):152–154. doi: 10.1038/341152a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maylie J., Morad M. A transient outward current related to calcium release and development of tension in elephant seal atrial fibres. J Physiol. 1984 Dec;357:267–292. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann J. D., Welsh M. J. Calcium-activated potassium channels in canine airway smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1986 Mar;372:113–127. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasri-Sebdani M., Traoré F., Cognard C., Potreau D., Poindessault J. P., Raymond G. The depressing effect of tetracaine and ryanodine on the slow outward current correlated with that of contraction in voltage-clamped frog muscle fibres. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Apr;416(1-2):106–112. doi: 10.1007/BF00370230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohya Y., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. Cellular calcium regulates outward currents in rabbit intestinal smooth muscle cell. Am J Physiol. 1987 Apr;252(4 Pt 1):C401–C410. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.252.4.C401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacaud P., Loirand G., Mironneau C., Mironneau J. Opposing effects of noradrenaline on the two classes of voltage-dependent calcium channels of single vascular smooth muscle cells in short-term primary culture. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Nov;410(4-5):557–559. doi: 10.1007/BF00586539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau E., Meissner G. Single cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-release channel: activation by caffeine. Am J Physiol. 1989 Feb;256(2 Pt 2):H328–H333. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.256.2.H328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau E., Smith J. S., Meissner G. Ryanodine modifies conductance and gating behavior of single Ca2+ release channel. Am J Physiol. 1987 Sep;253(3 Pt 1):C364–C368. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.3.C364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadoshima J., Akaike N., Kanaide H., Nakamura M. Cyclic AMP modulates Ca-activated K channel in cultured smooth muscle cells of rat aortas. Am J Physiol. 1988 Oct;255(4 Pt 2):H754–H759. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1988.255.4.H754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai T., Terada K., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. Ryanodine inhibits the Ca-dependent K current after depletion of Ca stored in smooth muscle cells of the rabbit ileal longitudinal muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;95(4):1089–1100. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11743.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer J. J., Walsh J. V., Jr Characterization of calcium-activated potassium channels in single smooth muscle cells using the patch-clamp technique. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Feb;408(2):98–111. doi: 10.1007/BF00581337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer J. J., Walsh J. V. Large conductance ca-activated k channels in smooth muscle cell membrane: reduction in unitary currents due to internal na ions. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):68–70. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(84)84112-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitsapesan R., Williams A. J. Mechanisms of caffeine activation of single calcium-release channels of sheep cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Physiol. 1990 Apr;423:425–439. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Imagawa T., Ma J., Fill M., Campbell K. P., Coronado R. Purified ryanodine receptor from rabbit skeletal muscle is the calcium-release channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Jul;92(1):1–26. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorenson M. M., Coelho H. S., Reuben J. P. Caffeine inhibition of calcium accumulation by the sarcoplasmic reticulum in mammalian skinned fibers. J Membr Biol. 1986;90(3):219–230. doi: 10.1007/BF01870128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. V., Jr, Singer J. J. Voltage clamp of single freshly dissociated smooth muscle cells: current-voltage relationships for three currents. Pflugers Arch. 1981 May;390(2):207–210. doi: 10.1007/BF00590209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


