Abstract
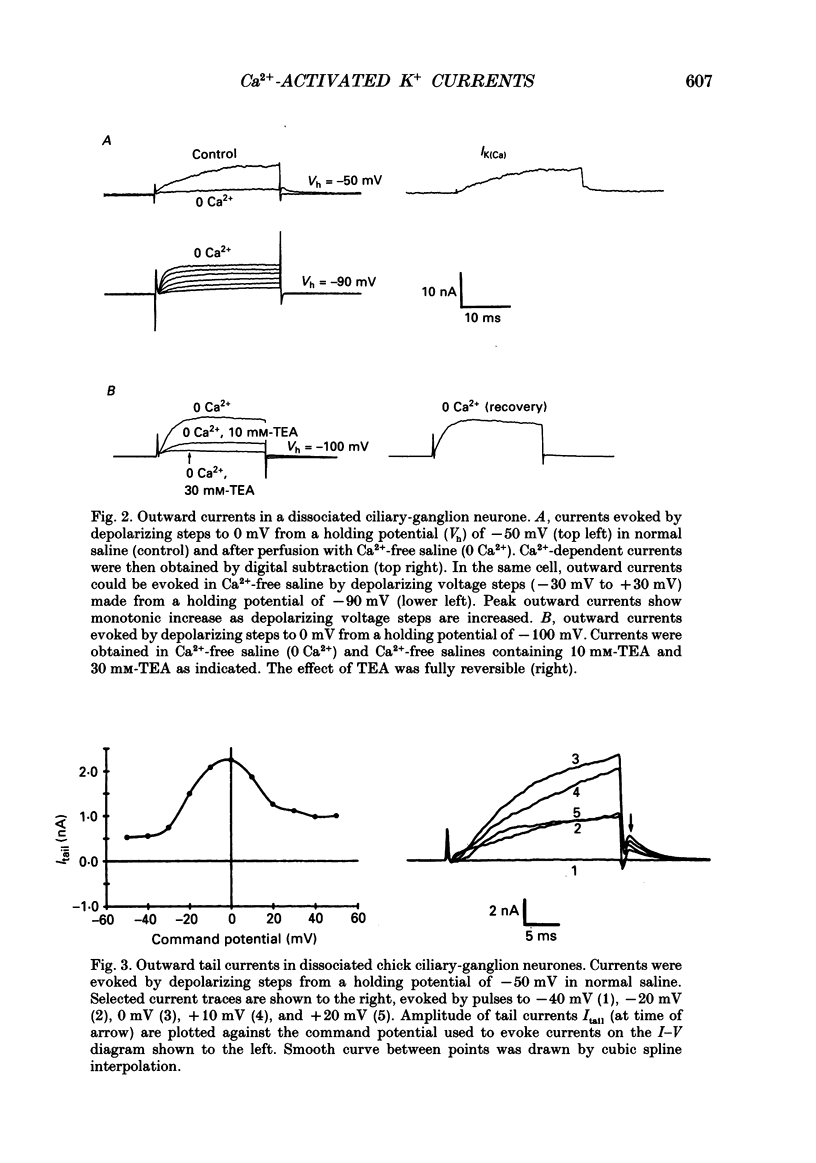
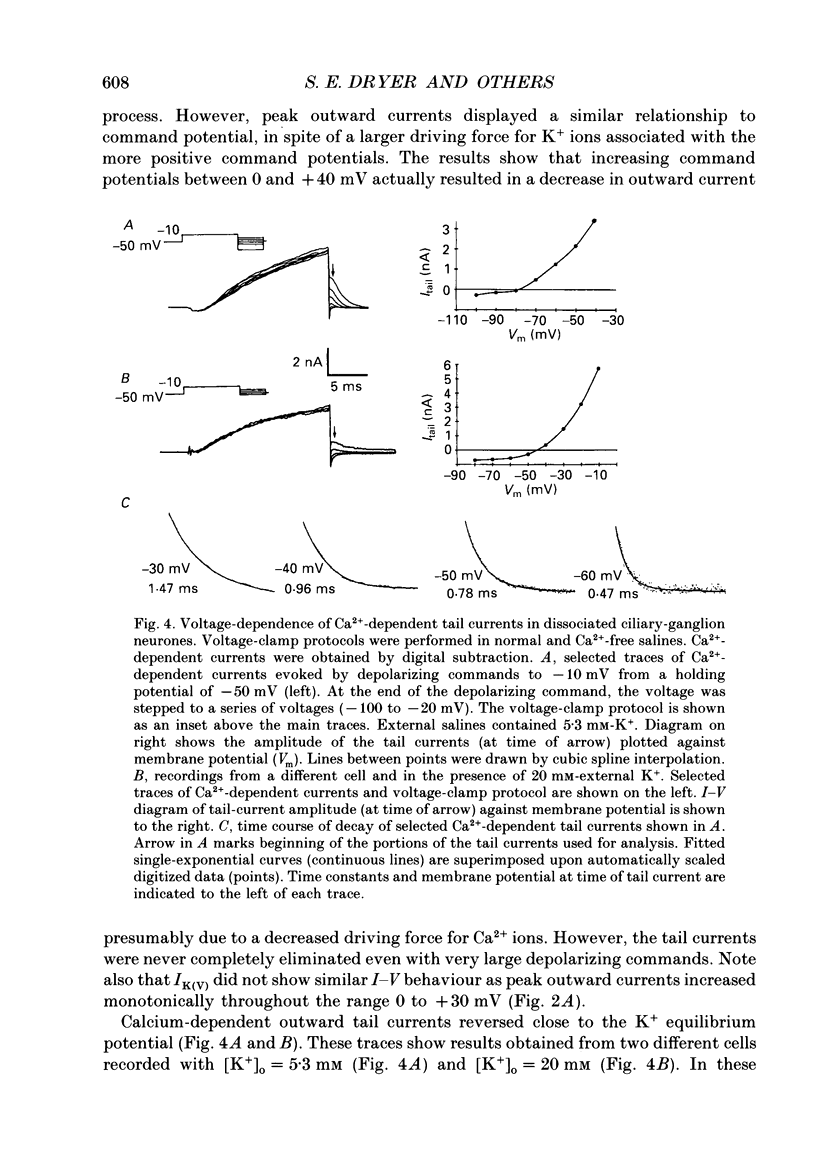
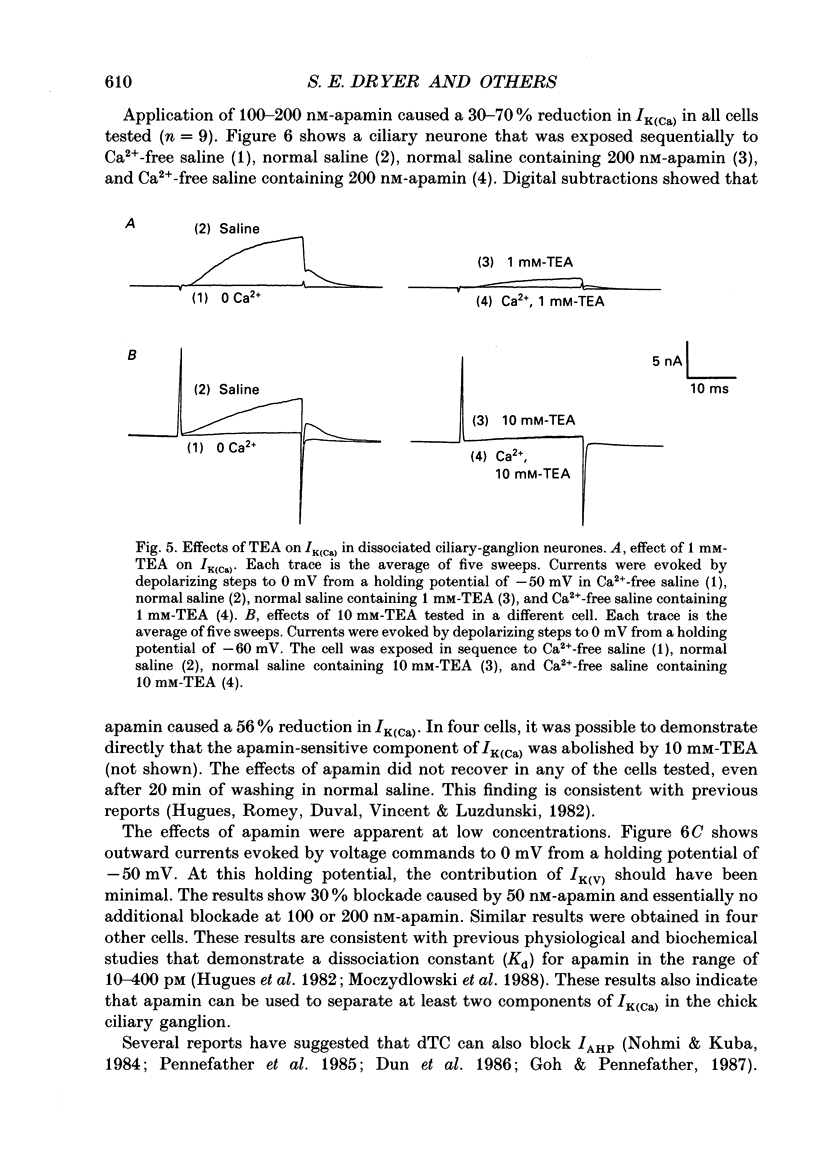
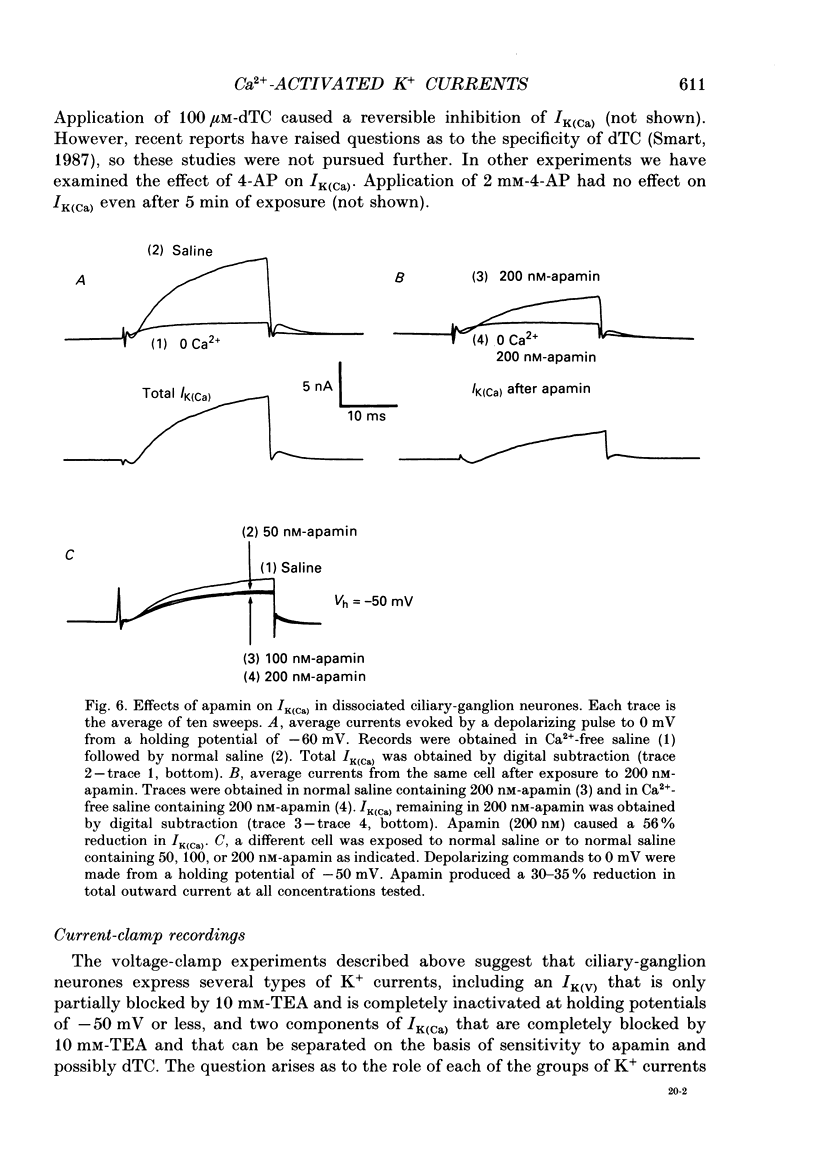
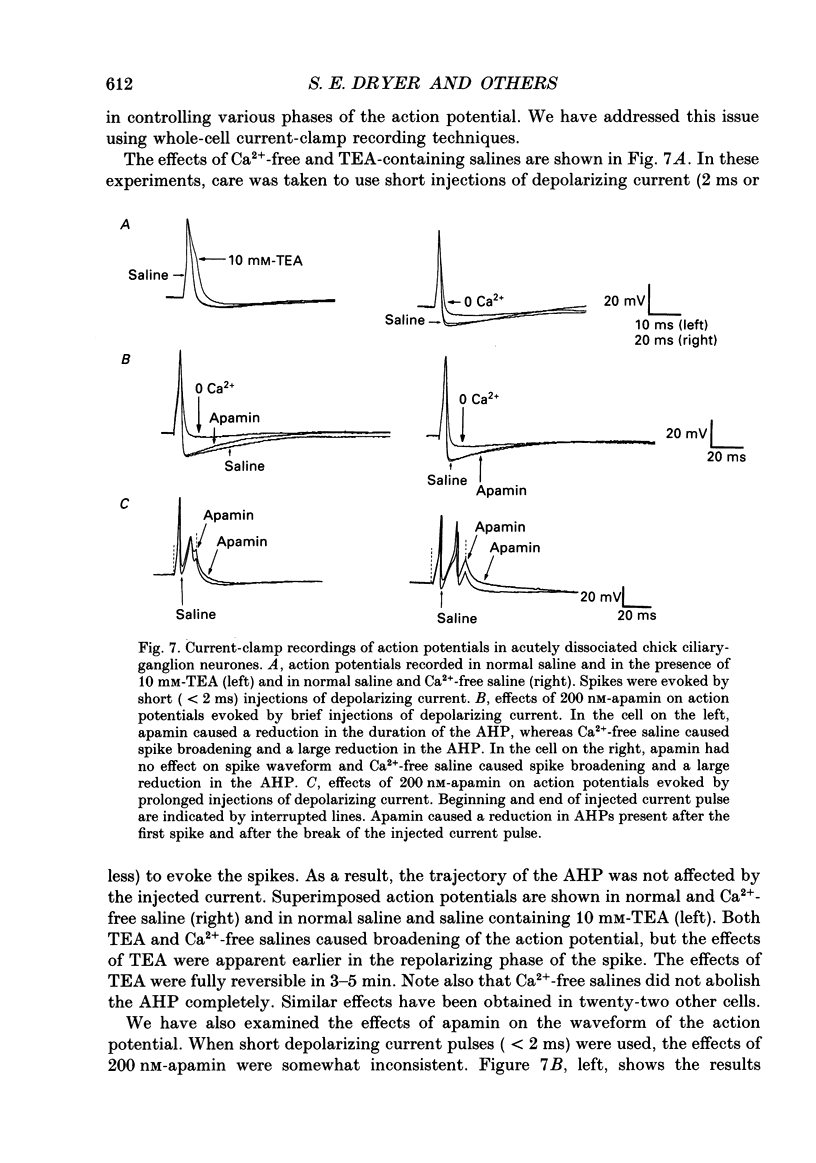
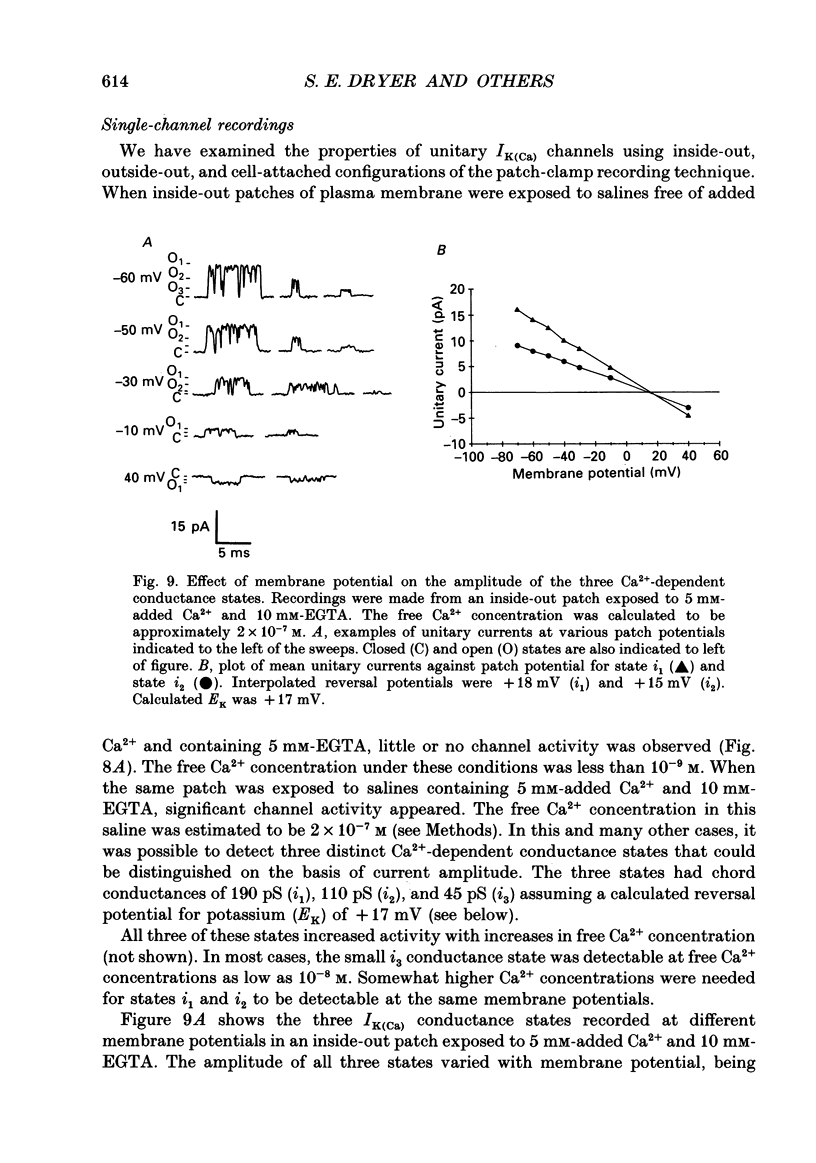
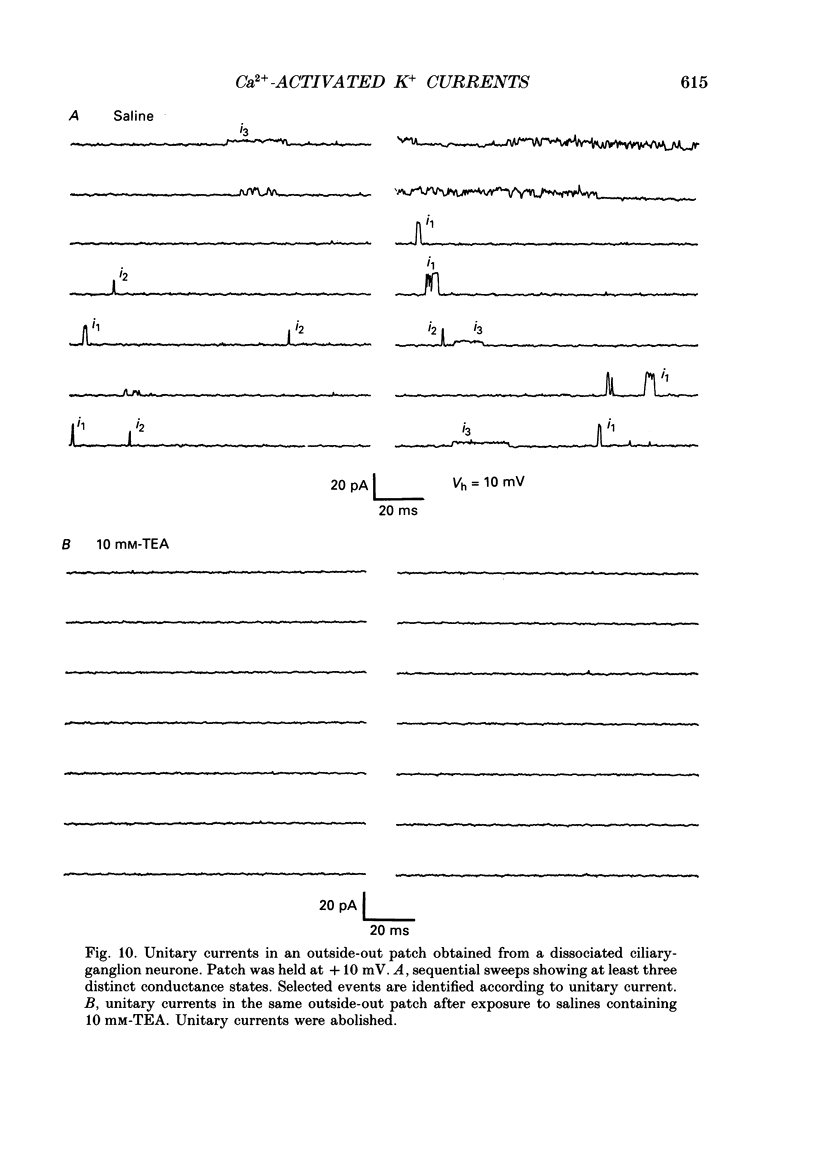
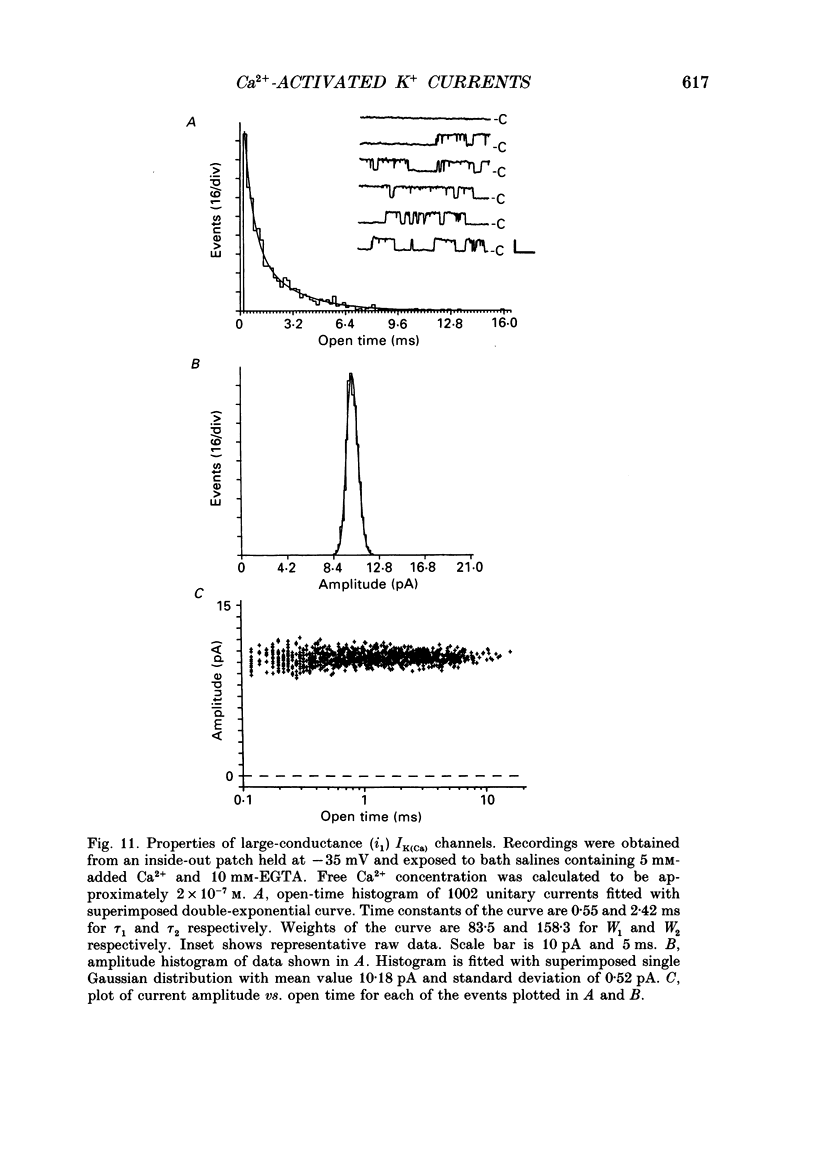
1. Whole-cell and single-channel recordings were used to characterize Ca(2+)-activated K+ channels (IK(Ca)) in acutely dissociated chick-ganglion neurones. 2. Application of depolarizing voltage steps resulted in outward currents that could be separated according to their dependence on external Ca2+ and/or holding potential. IK(Ca) was the only outward current that could be evoked from holding potentials of -50 mV or less. IK(Ca) was eliminated by bath application of Ca(2+)-free salines. A voltage-dependent outward current (IK(V)) could be evoked from more negative holding potentials in Ca(2+)-free salines. IK(V) was only partially blocked by as much as 30 mM-tetraethylammonium (TEA). 3. Tail currents associated with IK(Ca) reversed close to the K+ equilibrium potential (EK). IK(Ca) tail currents appeared sigmoidal, but the falling phase of the tail currents could be fitted with exponential curves that decayed faster at more negative membrane potentials. 4. IK(Ca) was blocked completely and reversibly by 10 mM-TEA. IK(Ca) was substantially reduced (80-90%) by as little as 1 mM-TEA. 5. Total IK(Ca) was reduced but not eliminated by saturating concentrations of apamin (200 nM). This blockade was not reversible with up to 30 min of washing. Application of 100 microM-d-tubocurare (dTC) also produced a partial blockade of total IK(Ca). 6. Whole-cell current-clamp recordings showed that IK(Ca) contributed to the late phases of spike repolarization and was the dominant current flowing during the spike after-hyperpolarization (AHP). Application of 200 nM-apamin caused a reduction in the duration of the AHP. This reduction was best seen when multiple spikes were evoked by prolonged (20-50 ms) injections of depolarizing current. 7. Three distinct types of IK(Ca) channels could be observed in inside-out patches in the presence of free Ca2+ concentrations of 2 x 10(-7) M, but not in the presence of free Ca2+ at concentrations of less than 10(-9) M. These had unitary chord conductances of 190 pS (i1), 110 pS (i2), and 45 pS (i3) with [K+]o = 150 mM and [K+]i = 75 mM. Each of these three channels had distinct kinetic properties. The 45 pS channel was most sensitive to activation by Ca2+ and could be detected at free Ca2+ concentrations as low as 10(-8) M. 8. All three IK(Ca) channels could be observed in inside-out patches held at membrane potentials where IK(V) was fully inactivated. Application of 10 mM-TEA caused a complete block of IK(Ca) channels in outside-out patches.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
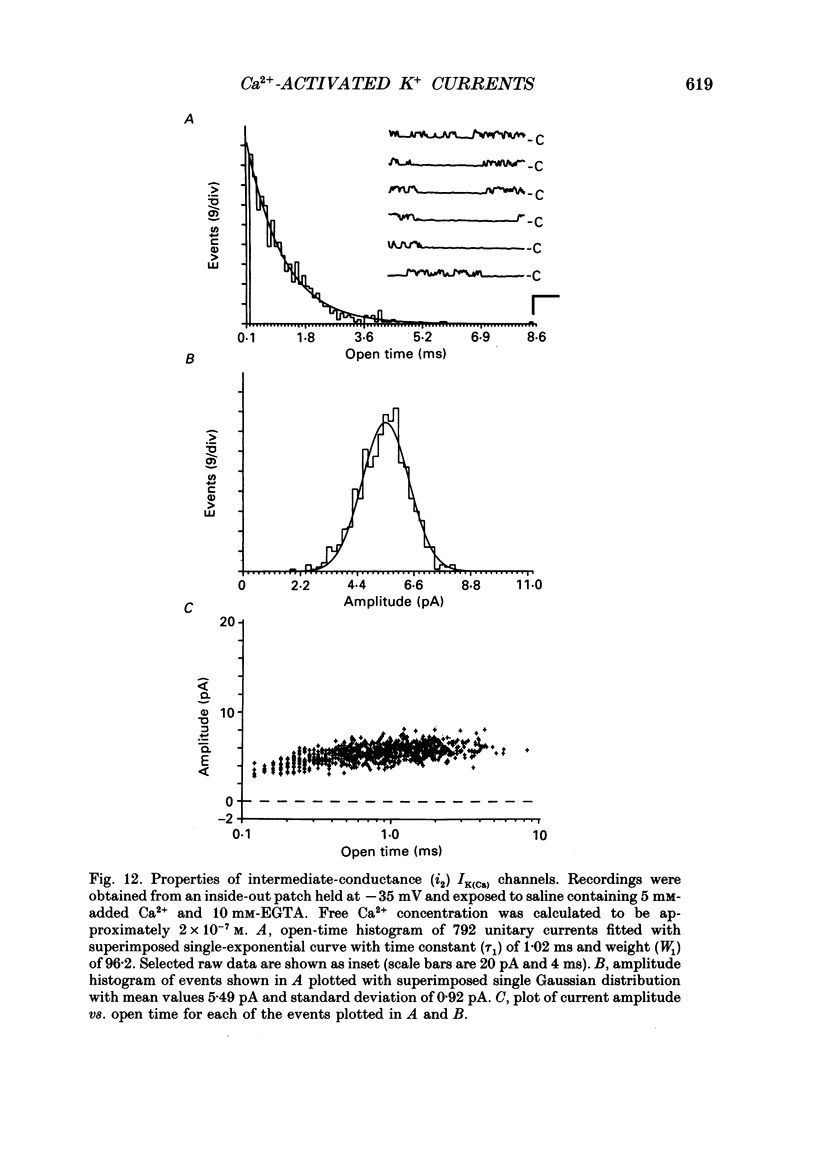
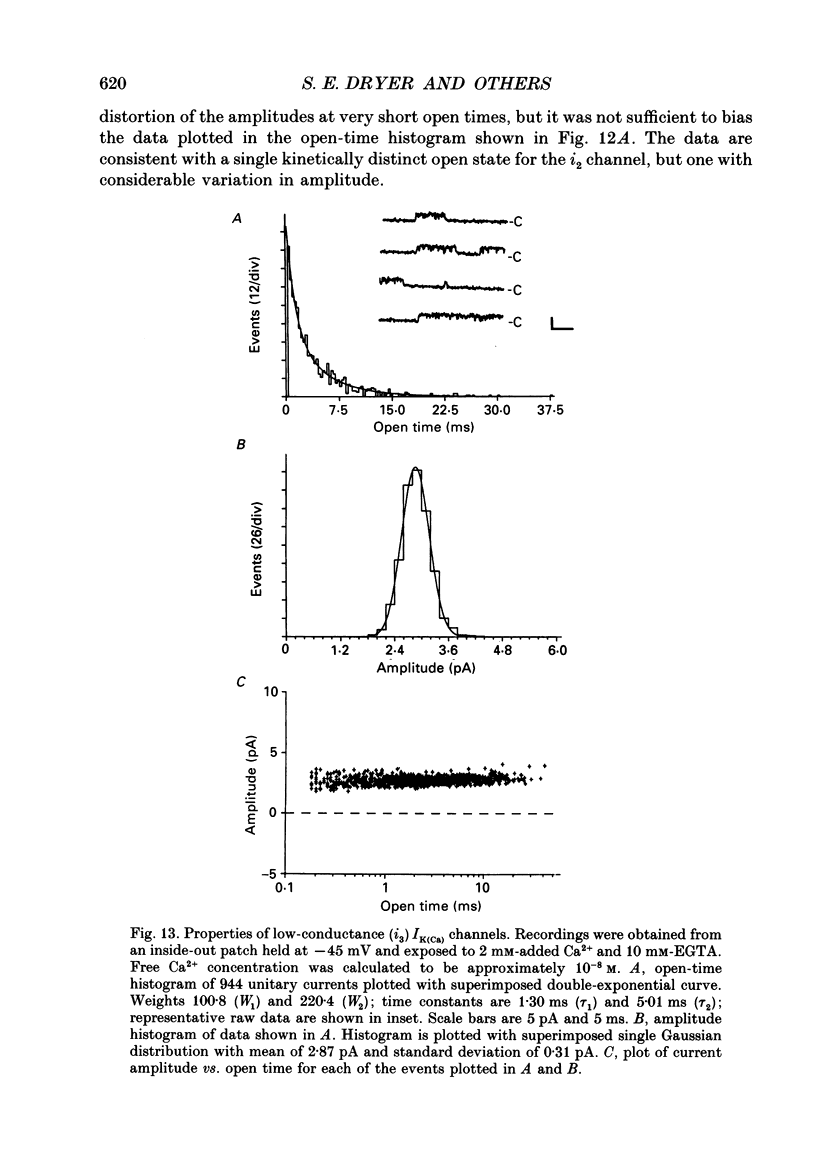
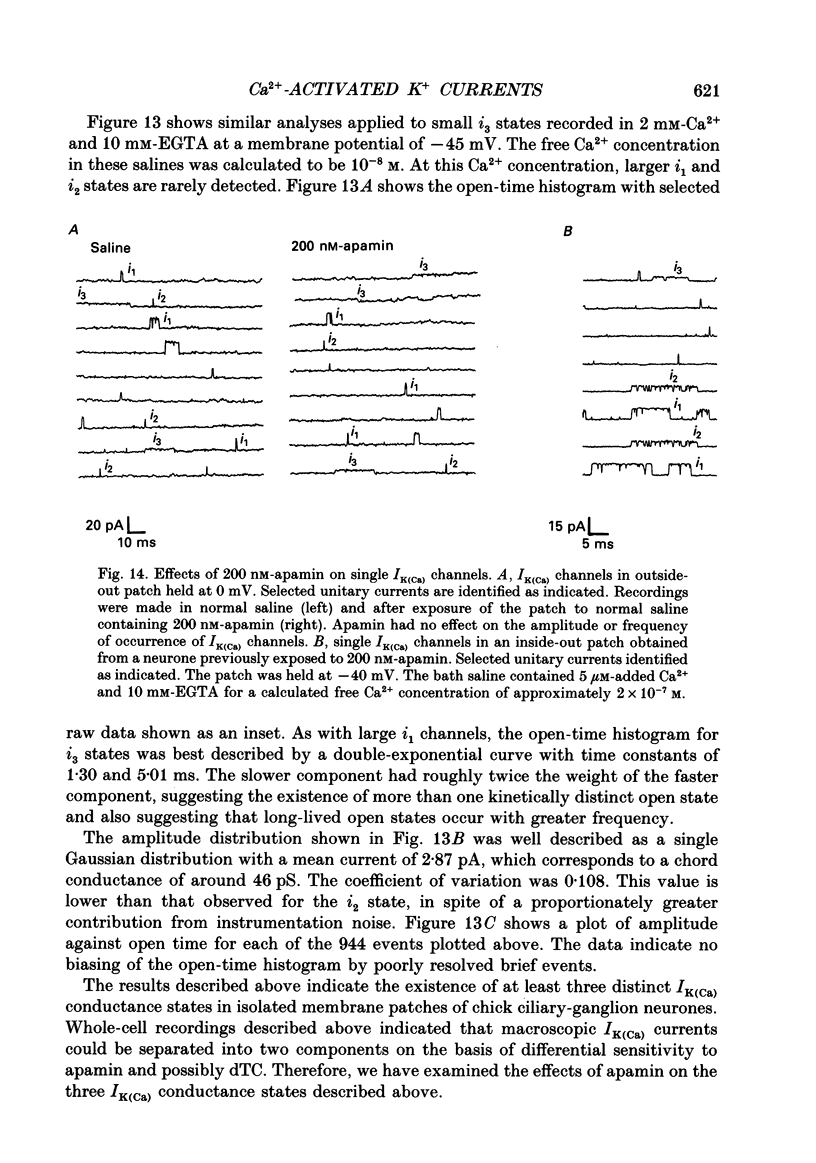
- Adams P. R., Constanti A., Brown D. A., Clark R. B. Intracellular Ca2+ activates a fast voltage-sensitive K+ current in vertebrate sympathetic neurones. Nature. 1982 Apr 22;296(5859):746–749. doi: 10.1038/296746a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett J. N., Magleby K. L., Pallotta B. S. Properties of single calcium-activated potassium channels in cultured rat muscle. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:211–230. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatz A. L., Magleby K. L. Single apamin-blocked Ca-activated K+ channels of small conductance in cultured rat skeletal muscle. Nature. 1986 Oct 23;323(6090):718–720. doi: 10.1038/323718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourque C. W. Transient calcium-dependent potassium current in magnocellular neurosecretory cells of the rat supraoptic nucleus. J Physiol. 1988 Mar;397:331–347. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Higashida H. Voltage- and calcium-activated potassium currents in mouse neuroblastoma x rat glioma hybrid cells. J Physiol. 1988 Mar;397:149–165. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byerly L., Meech R., Moody W., Jr Rapidly activating hydrogen ion currents in perfused neurones of the snail, Lymnaea stagnalis. J Physiol. 1984 Jun;351:199–216. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capiod T., Ogden D. C. The properties of calcium-activated potassium ion channels in guinea-pig isolated hepatocytes. J Physiol. 1989 Feb;409:285–295. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassell J. F., McLachlan E. M. Two calcium-activated potassium conductances in a subpopulation of coeliac neurones of guinea-pig and rabbit. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:331–349. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castle N. A., Haylett D. G., Jenkinson D. H. Toxins in the characterization of potassium channels. Trends Neurosci. 1989 Feb;12(2):59–65. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(89)90137-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constanti A., Sim J. A. Calcium-dependent potassium conductance in guinea-pig olfactory cortex neurones in vitro. J Physiol. 1987 Jun;387:173–194. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitmer J. W., Eckert R. Two components of Ca-dependent potassium current in identified neurons of Aplysia californica. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Apr;403(4):353–359. doi: 10.1007/BF00589246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dryer S. E., Chiappinelli V. A. Properties of choroid and ciliary neurons in the avian ciliary ganglion and evidence for substance P as a neurotransmitter. J Neurosci. 1985 Oct;5(10):2654–2661. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-10-02654.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dryer S. E., Fujii J. T., Martin A. R. A Na+-activated K+ current in cultured brain stem neurones from chicks. J Physiol. 1989 Mar;410:283–296. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dryer S. E. Na(+)-activated K+ channels and voltage-evoked ionic currents in brain stem and parasympathetic neurones of the chick. J Physiol. 1991 Apr;435:513–532. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dun N. J., Jiang Z. G., Mo N. Tubocurarine suppresses slow calcium-dependent after-hyperpolarization in guinea-pig inferior mesenteric ganglion cells. J Physiol. 1986 Jun;375:499–514. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein M. L., Davis J. P., Gellman L. E., Lamb J. R., Dahl J. L. Cholinergic neurons of the chicken ciliary ganglion contain somatostatin. Neuroscience. 1988 Jun;25(3):1053–1060. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90058-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farley J., Rudy B. Multiple types of voltage-dependent Ca2+-activated K+ channels of large conductance in rat brain synaptosomal membranes. Biophys J. 1988 Jun;53(6):919–934. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83173-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner P. I. Single-channel recordings of three K+-selective currents in cultured chick ciliary ganglion neurons. J Neurosci. 1986 Jul;6(7):2106–2116. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-07-02106.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goh J. W., Pennefather P. S. Pharmacological and physiological properties of the after-hyperpolarization current of bullfrog ganglion neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:315–330. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermann A., Erxleben C. Charybdotoxin selectively blocks small Ca-activated K channels in Aplysia neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Jul;90(1):27–47. doi: 10.1085/jgp.90.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugues M., Romey G., Duval D., Vincent J. P., Lazdunski M. Apamin as a selective blocker of the calcium-dependent potassium channel in neuroblastoma cells: voltage-clamp and biochemical characterization of the toxin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1308–1312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster B., Adams P. R. Calcium-dependent current generating the afterhyperpolarization of hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1986 Jun;55(6):1268–1282. doi: 10.1152/jn.1986.55.6.1268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster B., Nicoll R. A. Properties of two calcium-activated hyperpolarizations in rat hippocampal neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Aug;389:187–203. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster B., Pennefather P. Potassium currents evoked by brief depolarizations in bull-frog sympathetic ganglion cells. J Physiol. 1987 Jun;387:519–548. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre R., Oberhauser A., Labarca P., Alvarez O. Varieties of calcium-activated potassium channels. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:385–399. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.002125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN A. R., PILAR G. DUAL MODE OF SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION IN THE AVIAN CILIARY GANGLION. J Physiol. 1963 Sep;168:443–463. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Pallotta B. S. Calcium dependence of open and shut interval distributions from calcium-activated potassium channels in cultured rat muscle. J Physiol. 1983 Nov;344:585–604. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty A. Ca-dependent K channels with large unitary conductance in chromaffin cell membranes. Nature. 1981 Jun 11;291(5815):497–500. doi: 10.1038/291497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marwitt R., Pilar G., Weakly J. N. Characterization of two ganglion cell populations in avian ciliary ganglia. Brain Res. 1971 Jan 22;25(2):317–334. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90441-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W., Standen N. B. Potassium activation in Helix aspersa neurones under voltage clamp: a component mediated by calcium influx. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):211–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C., Moczydlowski E., Latorre R., Phillips M. Charybdotoxin, a protein inhibitor of single Ca2+-activated K+ channels from mammalian skeletal muscle. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):316–318. doi: 10.1038/313316a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nohmi M., Kuba K. (+)-Tubocurarine blocks the Ca2+-dependent K+-channel of the bullfrog sympathetic ganglion cell. Brain Res. 1984 May 28;301(1):146–148. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90412-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennefather P., Lancaster B., Adams P. R., Nicoll R. A. Two distinct Ca-dependent K currents in bullfrog sympathetic ganglion cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):3040–3044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.3040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhart P. H., Chung S., Levitan I. B. A family of calcium-dependent potassium channels from rat brain. Neuron. 1989 Jan;2(1):1031–1041. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90227-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribera A. B., Spitzer N. C. Both barium and calcium activate neuronal potassium currents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6577–6581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwindt P. C., Spain W. J., Foehring R. C., Stafstrom C. E., Chubb M. C., Crill W. E. Multiple potassium conductances and their functions in neurons from cat sensorimotor cortex in vitro. J Neurophysiol. 1988 Feb;59(2):424–449. doi: 10.1152/jn.1988.59.2.424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M., Barker J. L. Rat hippocampal neurons in culture: potassium conductances. J Neurophysiol. 1984 Jun;51(6):1409–1433. doi: 10.1152/jn.1984.51.6.1409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smart T. G. Single calcium-activated potassium channels recorded from cultured rat sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Aug;389:337–360. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhardt R., Zucker R., Schatten G. Intracellular calcium release at fertilization in the sea urchin egg. Dev Biol. 1977 Jul 1;58(1):185–196. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90084-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. H. Three pharmacologically distinct potassium channels in molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(2):465–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



