Abstract
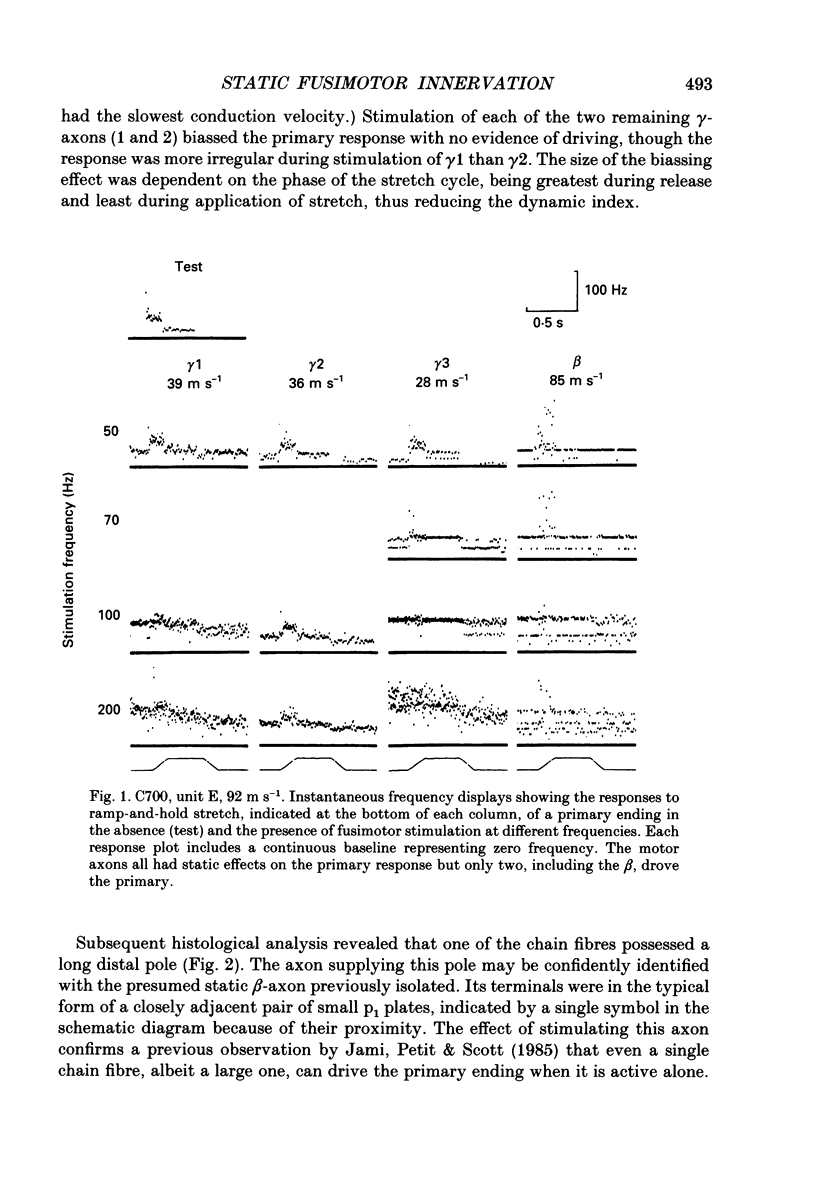
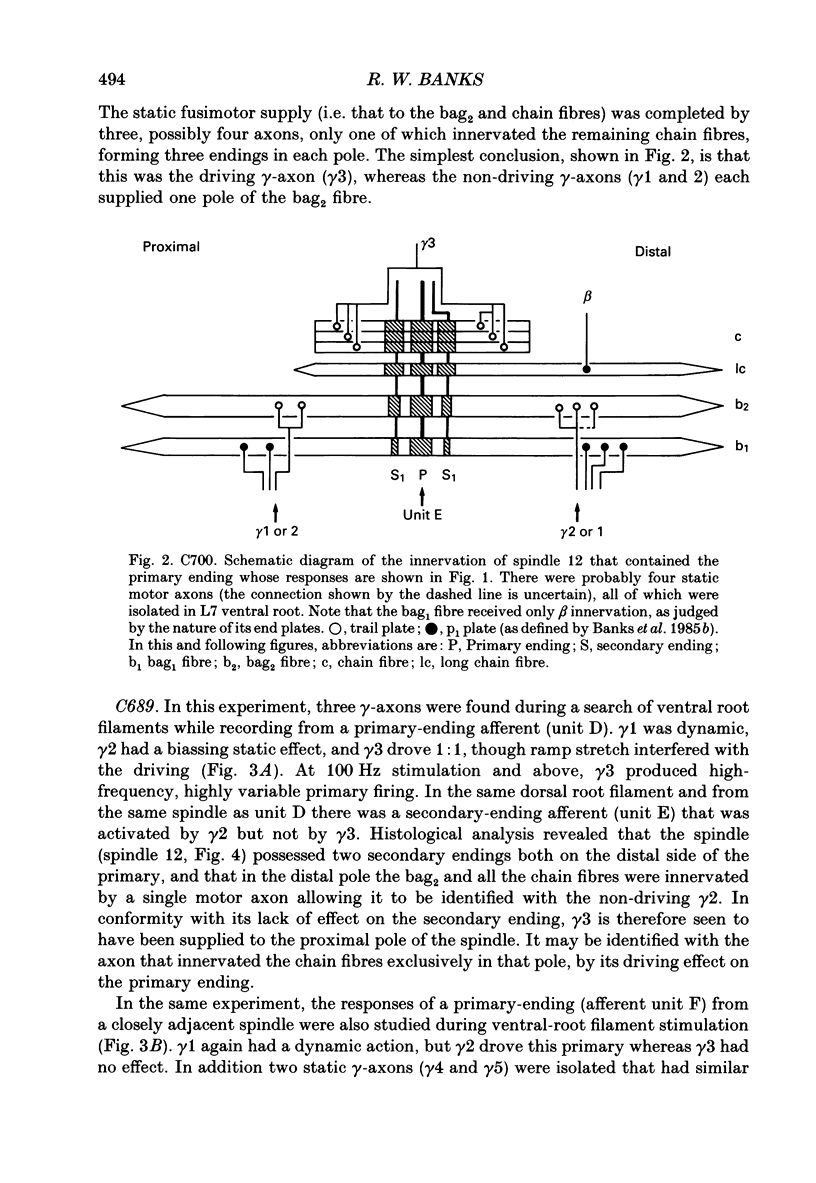
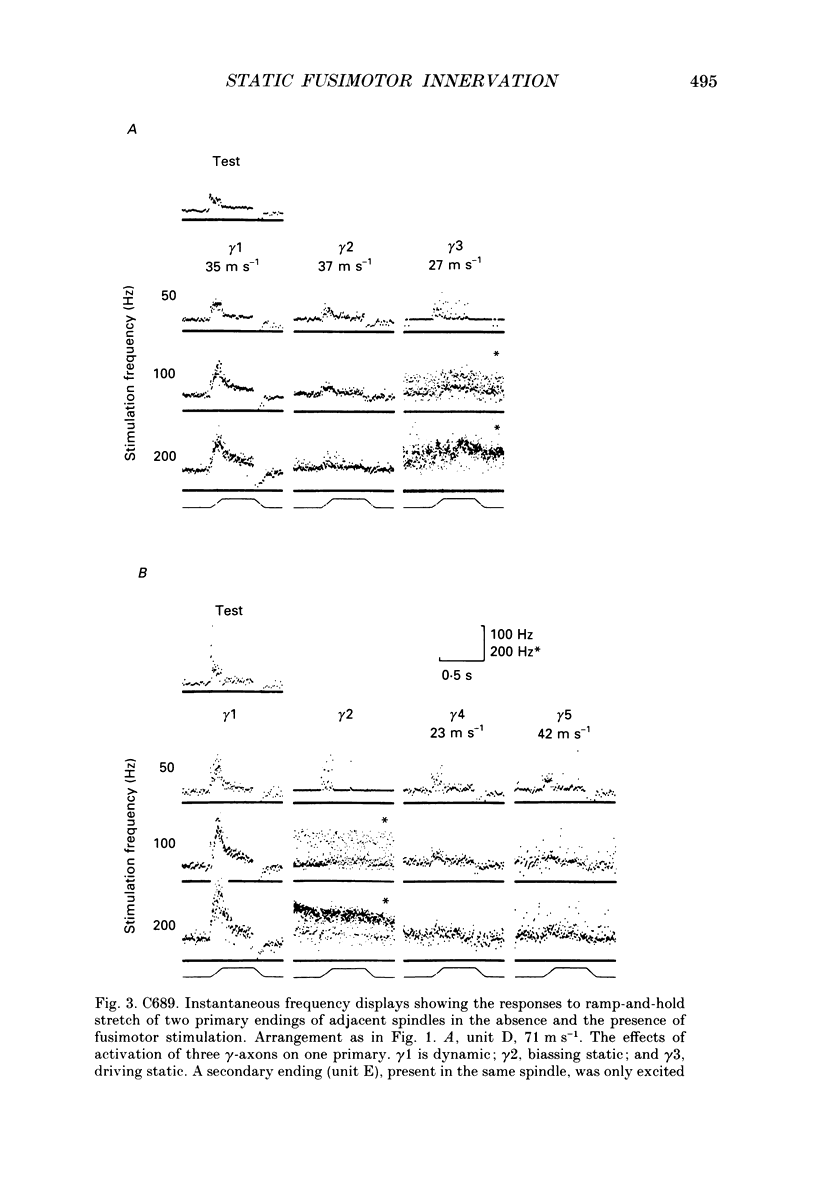
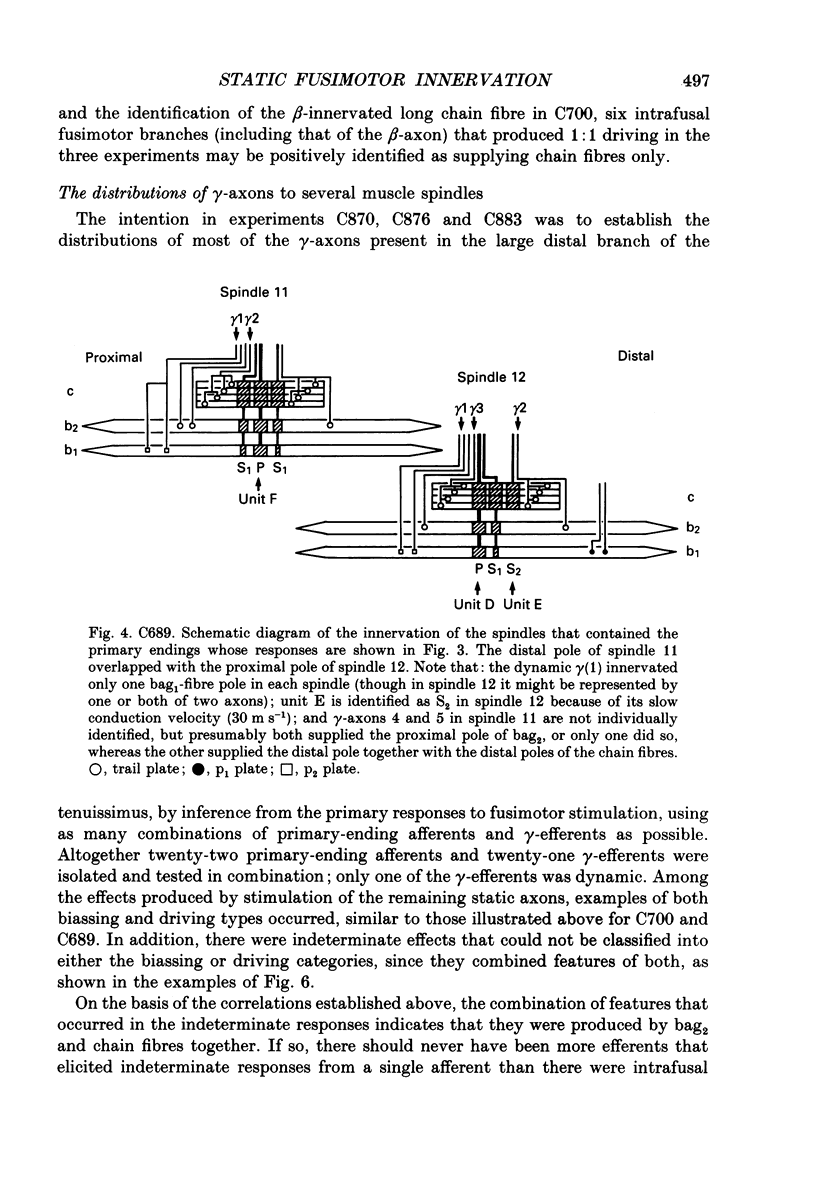
1. The distribution of static gamma-axons within and among muscle spindles of the tenuissimus muscle has been studied in the anaesthetized cat, on the basis of the effects on the responses of primary endings when bag2 or chain fibres or both are activated by static gamma-stimulation. 2. Locations of spindles were marked for subsequent histological analysis using teased, silver-impregnated preparations. 3. Static effects were classified into: (i) biassing; (ii) driving; or (iii) indeterminate categories. 4. Critical correlations established that the biassing type was produced by bag2 activity, either alone or in combination with chain fibres, whereas the driving type was produced by chain fibres active alone. Indirect evidence suggested that indeterminate effects were produced by bag2 and chain fibres active together. 5. The static gamma-axons showed some differential distribution according to their conduction velocities: faster-conducting axons were likely to be more widely distributed among spindles but less likely to innervate chain fibres alone than were more slowly conducting axons. 6. The results are discussed in terms of their possible functional and developmental significance.
Full text
PDF














Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arbuthnott E. R., Ballard K. J., Boyd I. A., Gladden M. H., Sutherland F. I. The ultrastructure of cat fusimotor endings and their relationship to foci of sarcomere convergence in intrafusal fibres. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:285–309. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN M. C., CROWE A., MATTHEWS P. B. OBSERVATIONS ON THE FUSIMOTOR FIBRES OF THE TIBIALIS POSTERIOR MUSCLE OF THE CAT. J Physiol. 1965 Mar;177:140–159. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks R. W. A histological study of the motor innervation of the cat's muscle spindle. J Anat. 1981 Dec;133(Pt 4):571–591. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks R. W., Barker D., Stacey M. J. Form and classification of motor endings in mammalian muscle spindles. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985 Aug 22;225(1239):195–212. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1985.0058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks R. W., Barker D., Stacey M. J. Form and distribution of sensory terminals in cat hindlimb muscle spindles. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Nov 4;299(1096):329–364. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1982.0136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks R. W. Observations on the primary sensory ending of tenuissimus muscle spindles in the cat. Cell Tissue Res. 1986;246(2):309–319. doi: 10.1007/BF00215893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Emonet-Dénand F., Harker D. W., Jami L., Laporte Y. Distribution of fusimotor axons to intrafusal muscle fibres in cat tenuissimus spindles as determined by the glycogen-depletion method. J Physiol. 1976 Sep;261(1):49–69. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Emonet-Dénand F., Harker D. W., Jami L., Laporte Y. Types of intra- and extrafusal muscle fibre innervated by dynamic skeleto-fusimotor axons in cat peroneus brevis and tenuissimus muscles, as determined by the glycogen-depletion method. J Physiol. 1977 Apr;266(3):713–726. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Emonet-Dénand F., Laporte Y., Proske U., Stacey M. J. Morphological identification and intrafusal distribution of the endings of static fusimotor axons in the cat. J Physiol. 1973 Apr;230(2):405–427. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Scott J. J., Stacey M. J. Sensory reinnervation of cat peroneus brevis muscle spindles after nerve crush. Brain Res. 1985 Apr 29;333(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd I. A., Gladden M. H., McWilliam P. N., Ward J. Control of dynamic and static nuclear bag fibres and nuclear chain fibres by gamma and beta axons in isolated cat muscle spindels. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(1):133–162. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd I. A. The response of fast and slow nuclear bag fibres and nuclear chain fibres in isolated cat muscle spindles to fusimotor stimulation, and the effect of intrafusal contraction on the sensory endings. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1976 Jul;61(3):203–254. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1976.sp002354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd I. A. Two types of static gamma-axon in cat muscle spindles. Q J Exp Physiol. 1986 Apr;71(2):307–327. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1986.sp002987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretag A. H. Synthetic interstitial fluid for isolated mammalian tissue. Life Sci. 1969 Mar 1;8(5):319–329. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(69)90283-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. C., Butler R. G. Studies on the site of termination of static and dynamic fusimotor fibres within muscle spindles of the tenuissimus muscle of the cat. J Physiol. 1973 Sep;233(3):553–573. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROWE A., MATTHEWS P. B. THE EFFECTS OF STIMULATION OF STATIC AND DYNAMIC FUSIMOTOR FIBRES ON THE RESPONSE TO STRETCHING OF THE PRIMARY ENDINGS OF MUSCLE SPINDLES. J Physiol. 1964 Oct;174:109–131. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emonet-Dénand F., Jami L., Laporte Y. Skeleto-fusimotor axons in the hind-limb muscles of the cat. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(1):153–166. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emonet-Dénand F., Laporte Y., Matthews P. B., Petit J. On the subdivision of static and dynamic fusimotor actions on the primary ending of the cat muscle spindle. J Physiol. 1977 Jul;268(3):827–861. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink B. R. Interstitial fluid. Nature. 1984 Mar 1;308(5954):20–20. doi: 10.1038/308020b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gioux M., Petit J., Proske U. Slowing of the discharge of secondary endings of cat muscle spindles during fusimotor stimulation. Exp Brain Res. 1990;83(1):164–171. doi: 10.1007/BF00232205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladden M. H., McWilliam P. N. The activity of intrafusal muscle fibres during cortical stimulation in the cat [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(2):28P–29P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladden M. H., McWilliam P. N. The activity of intrafusal muscle fibres in anaesthetized, decerebrate and spinal cats [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(2):49P–50P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladden M. H. Structural features relative to the function of intrafusal muscle fibres in the cat. Prog Brain Res. 1976;44:51–59. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)60722-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harker D. W., Jami L., Laporte Y., Petit J. Fast-conducting skeletofusimotor axons supplying intrafusal chain fibers in the cat peroneus tertius muscle. J Neurophysiol. 1977 Jul;40(4):791–799. doi: 10.1152/jn.1977.40.4.791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jami L., Lan-Couton D., Malmgren K., Petit J. "Fast" and "slow" skeleto-fusimotor innervation in cat tenuissimus spindles; a study with the glycogen-depletion method. Acta Physiol Scand. 1978 Jul;103(3):284–298. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1978.tb06216.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jami L., Lan-Couton D., Malmgren K., Petit J. Histophysiological observations on fast skeleto-fusimotor axons. Brain Res. 1979 Mar 23;164:53–59. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucera J., Hammar K., Meek B. Ultrastructure of dynamic and static skeletofusimotor endings in a cat muscle spindle. Cell Tissue Res. 1984;238(1):151–158. doi: 10.1007/BF00215156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucera J. Histochemical study of long nuclear chain fibers in the cat muscle spindle. Anat Rec. 1980 Dec;198(4):567–580. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091980403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucera J. Histological identification of (static) skeletofusimotor innervation to a cat muscle spindle. Brain Res. 1984 Mar 5;294(2):390–395. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91057-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucera J., Hughes R. Histological study of motor innervation to long nuclear chain intrafusal fibers in the muscle spindle of the cat. Cell Tissue Res. 1983;228(3):535–547. doi: 10.1007/BF00211474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucera J. Ultrastructure of extrafusal and intrafusal terminals of a (dynamic) skeletofusimotor axon in cat tenuissimus muscle. Brain Res. 1984 Apr 23;298(1):181–186. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91166-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucera J., Walro J. M. Factors that determine the form of neuromuscular junctions of intrafusal fibers in the cat. Am J Anat. 1986 May;176(1):97–117. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001760108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev-Tov A., Pratt C. A., Burke R. E. The motor-unit population of the cat tenuissimus muscle. J Neurophysiol. 1988 Apr;59(4):1128–1142. doi: 10.1152/jn.1988.59.4.1128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milburn A. Stages in the development of cat muscle spindles. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1984 Aug;82:177–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wand P., Schwarz M. Two types of cat static fusimotor neurones under separate central control? Neurosci Lett. 1985 Jul 4;58(1):145–149. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90344-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


