Abstract
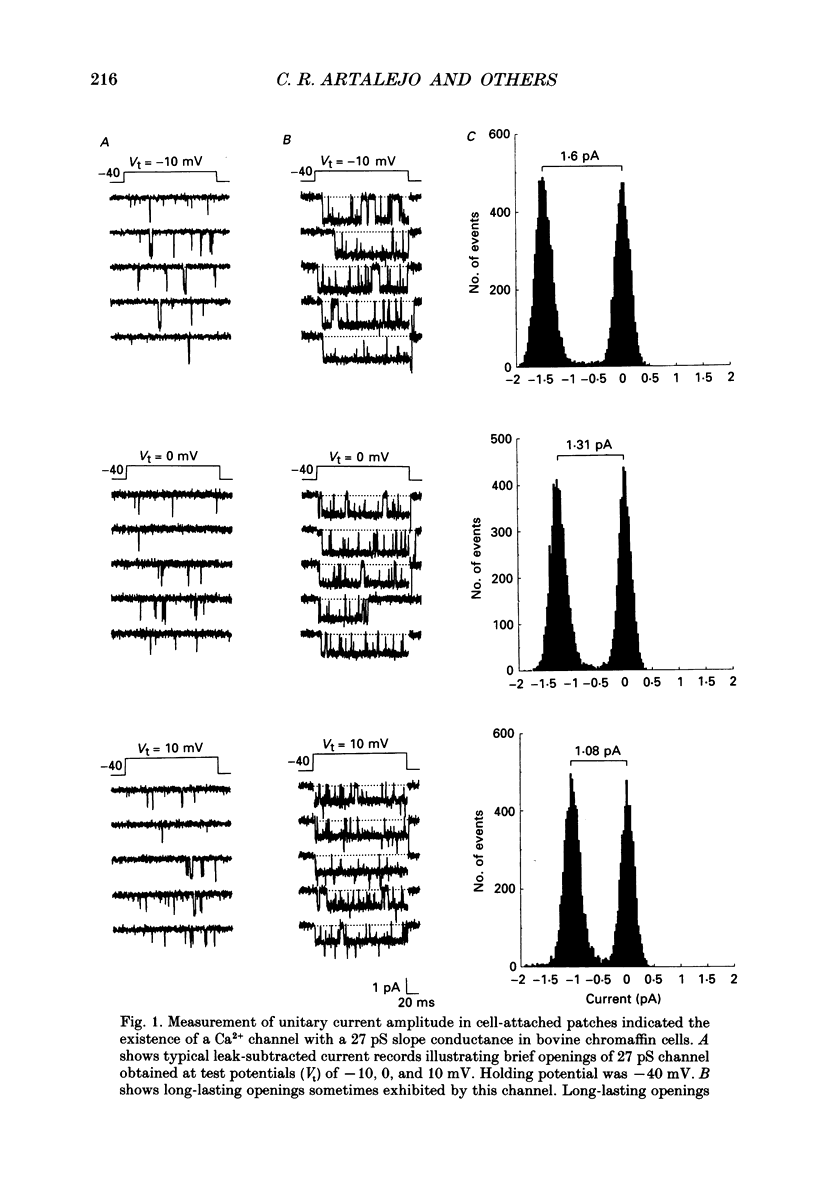
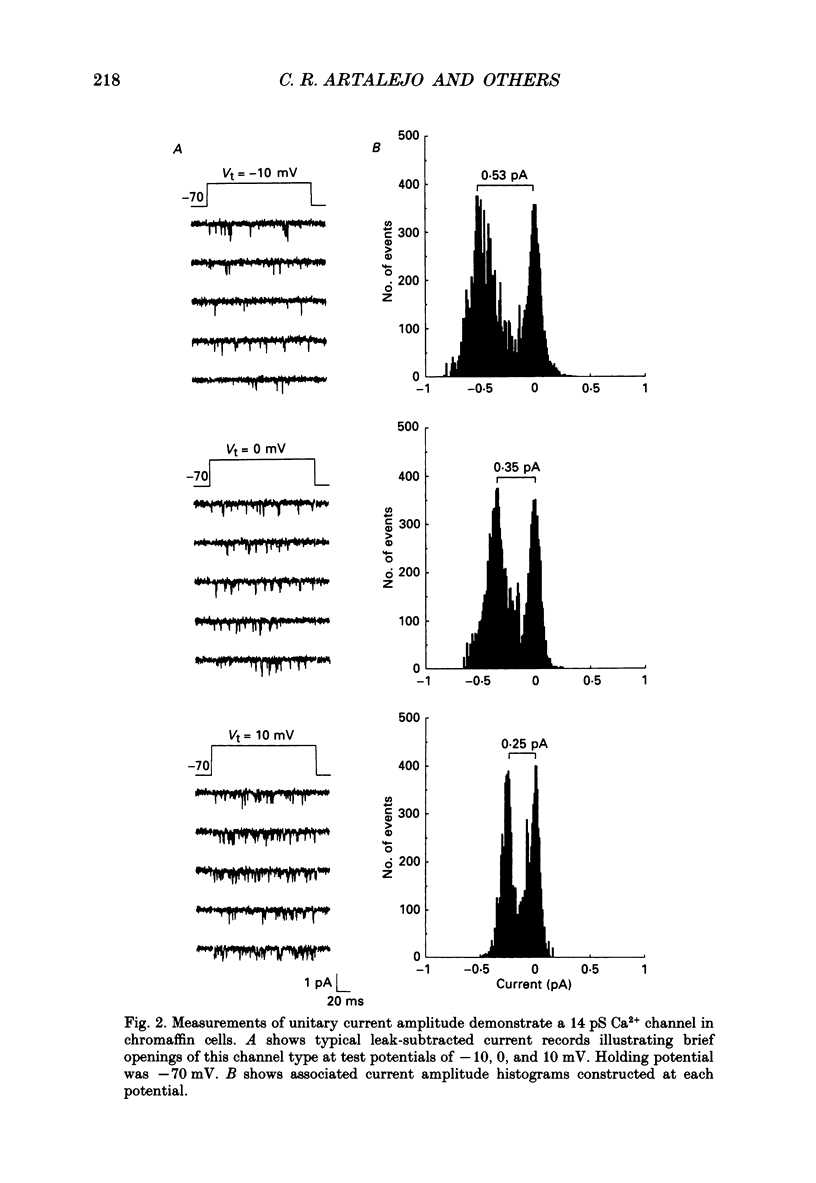
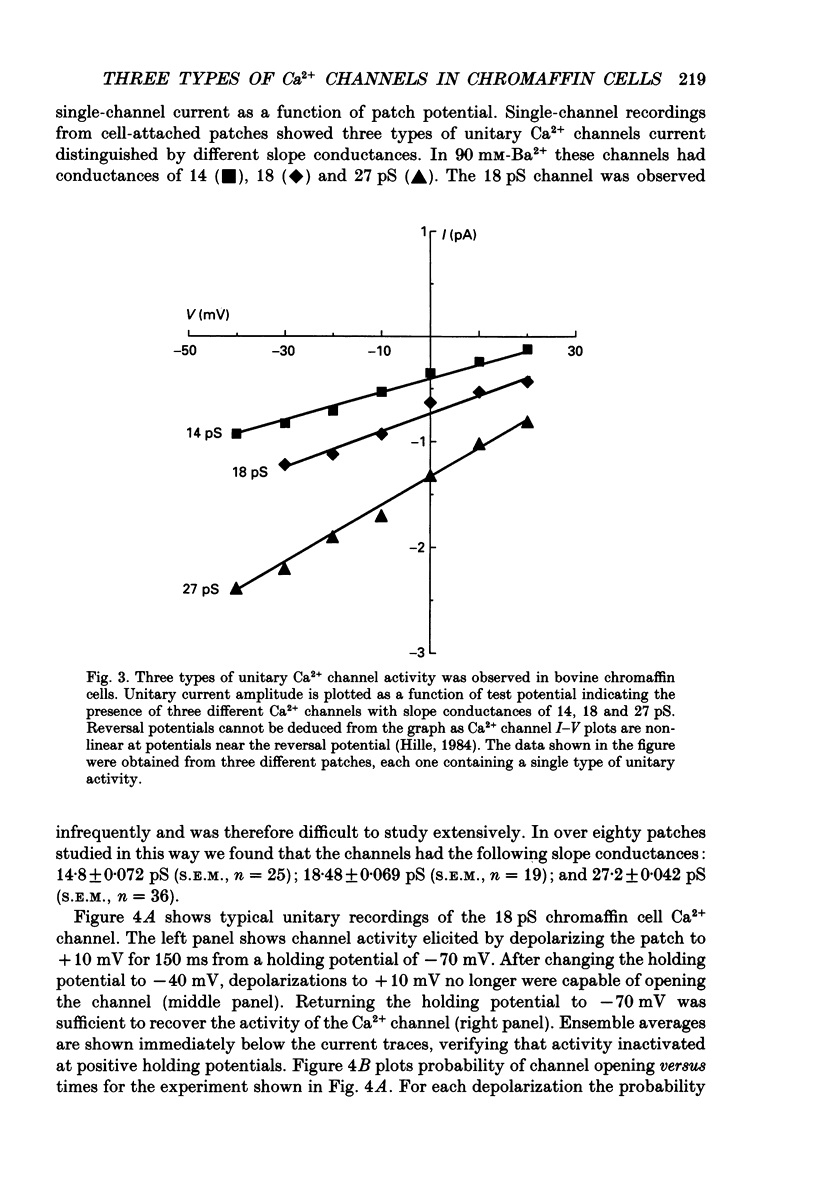
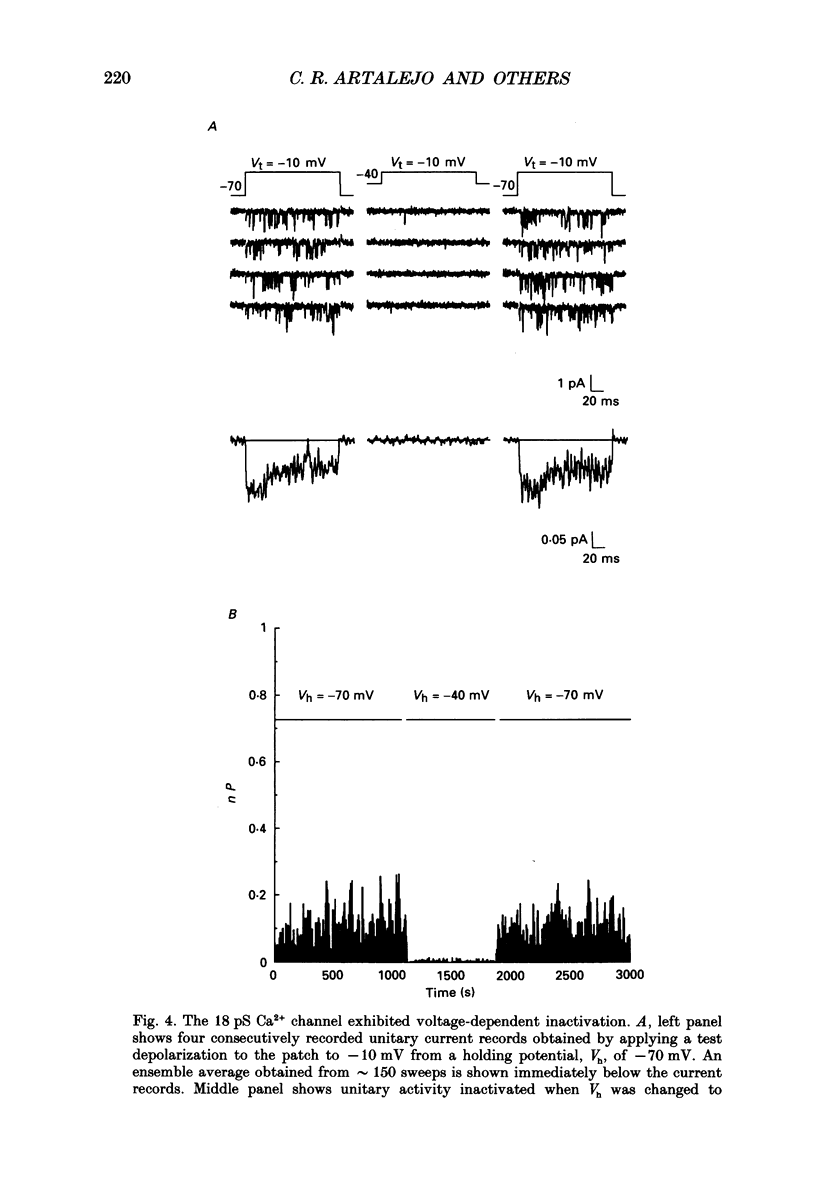
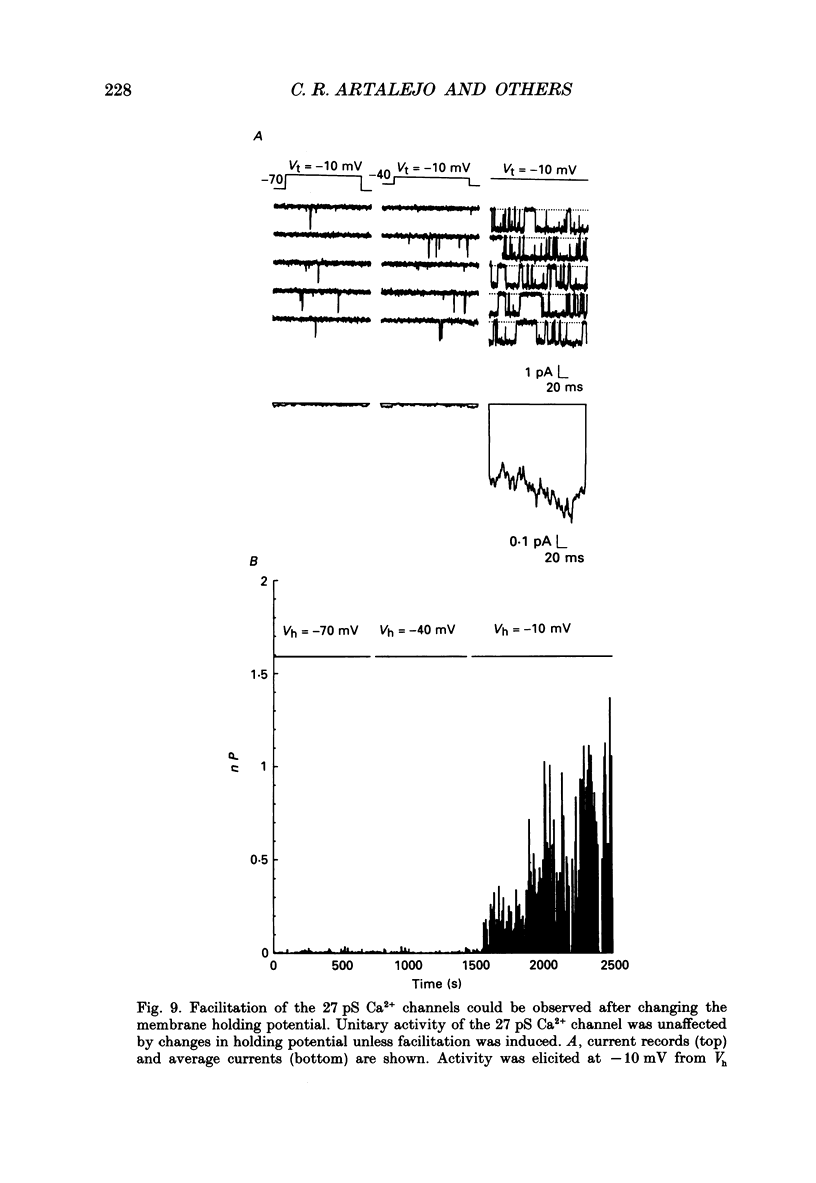
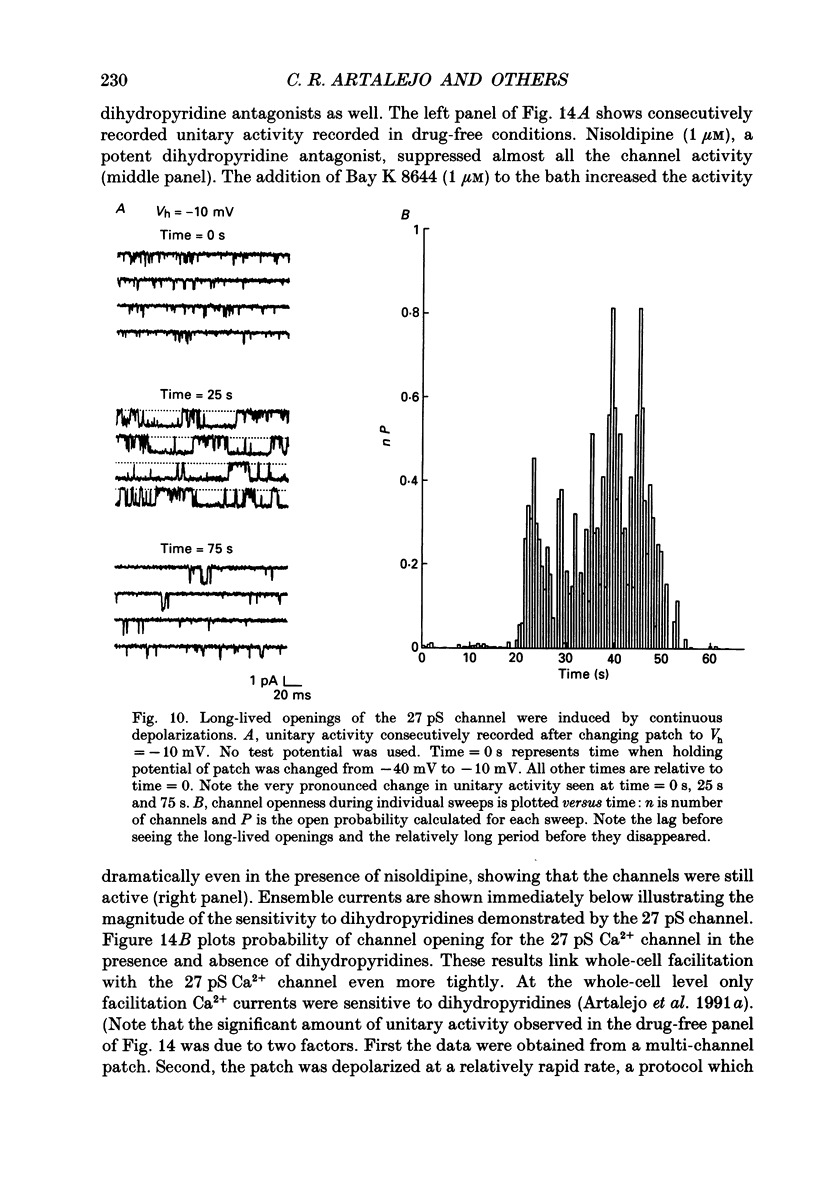
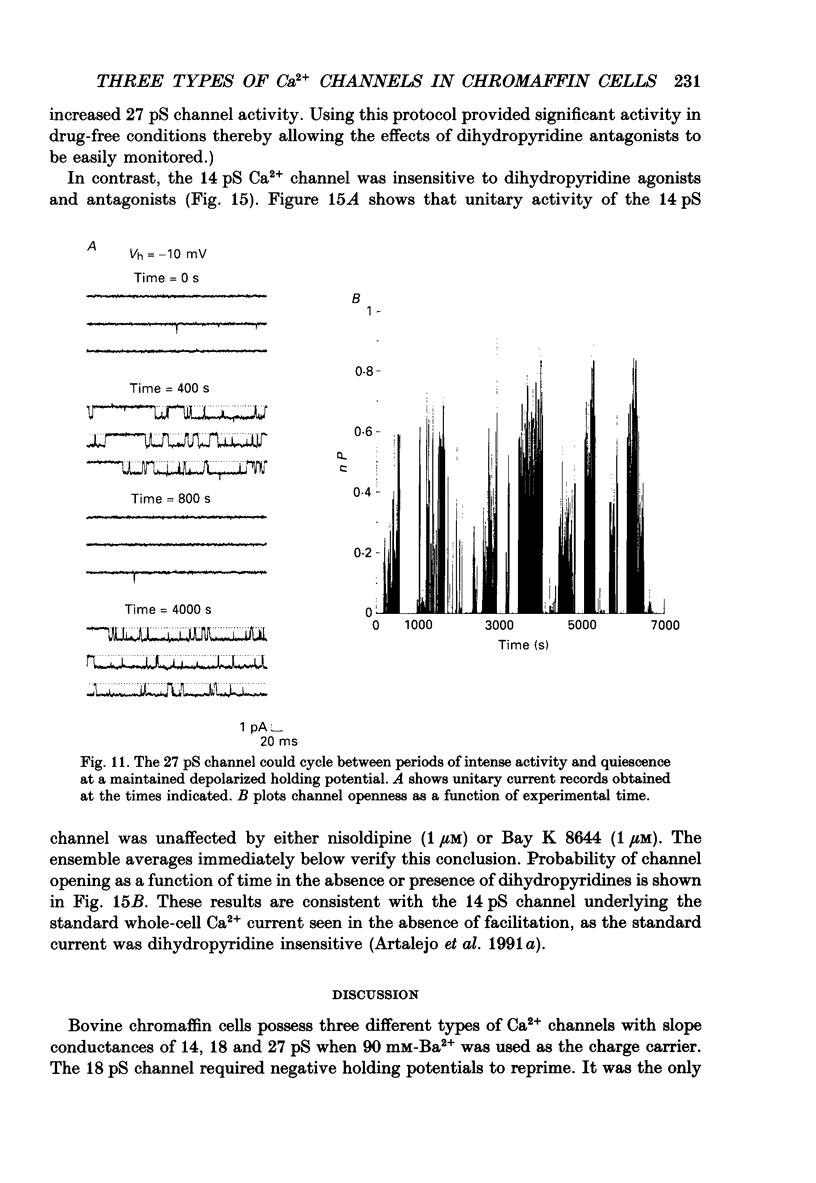
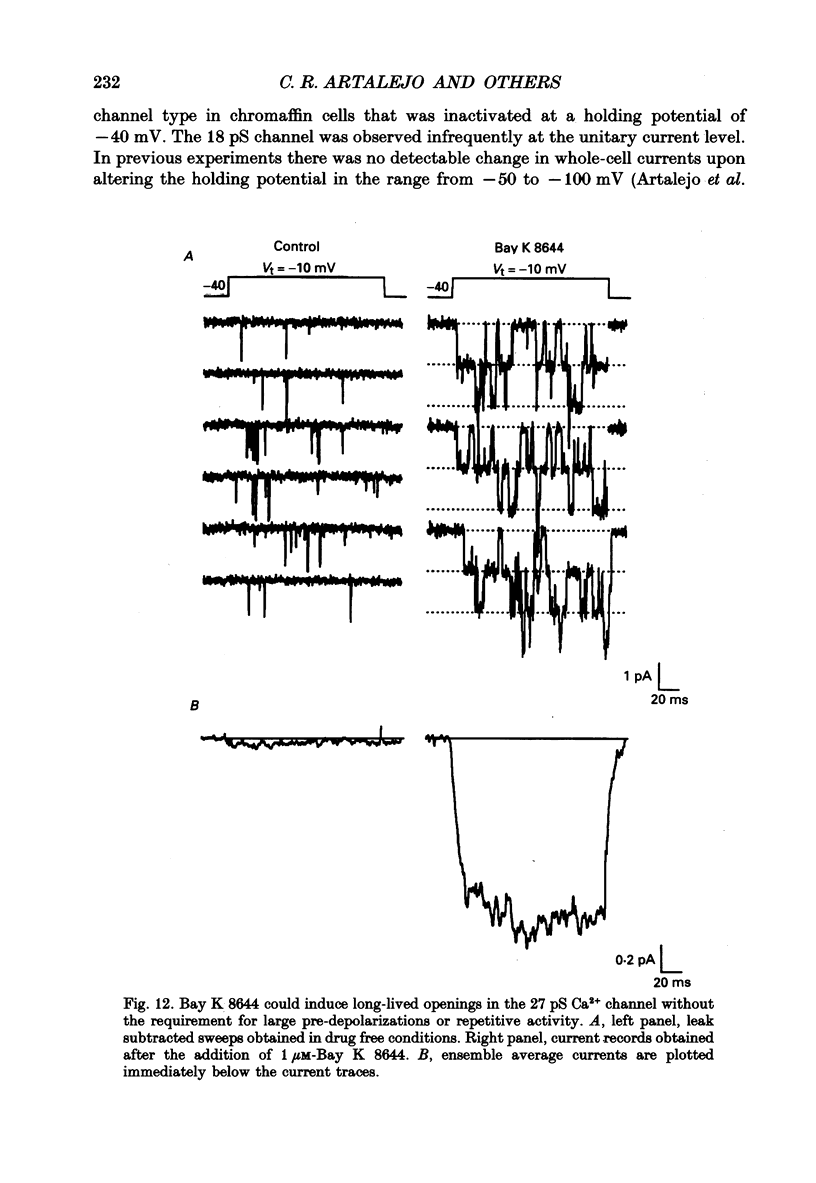
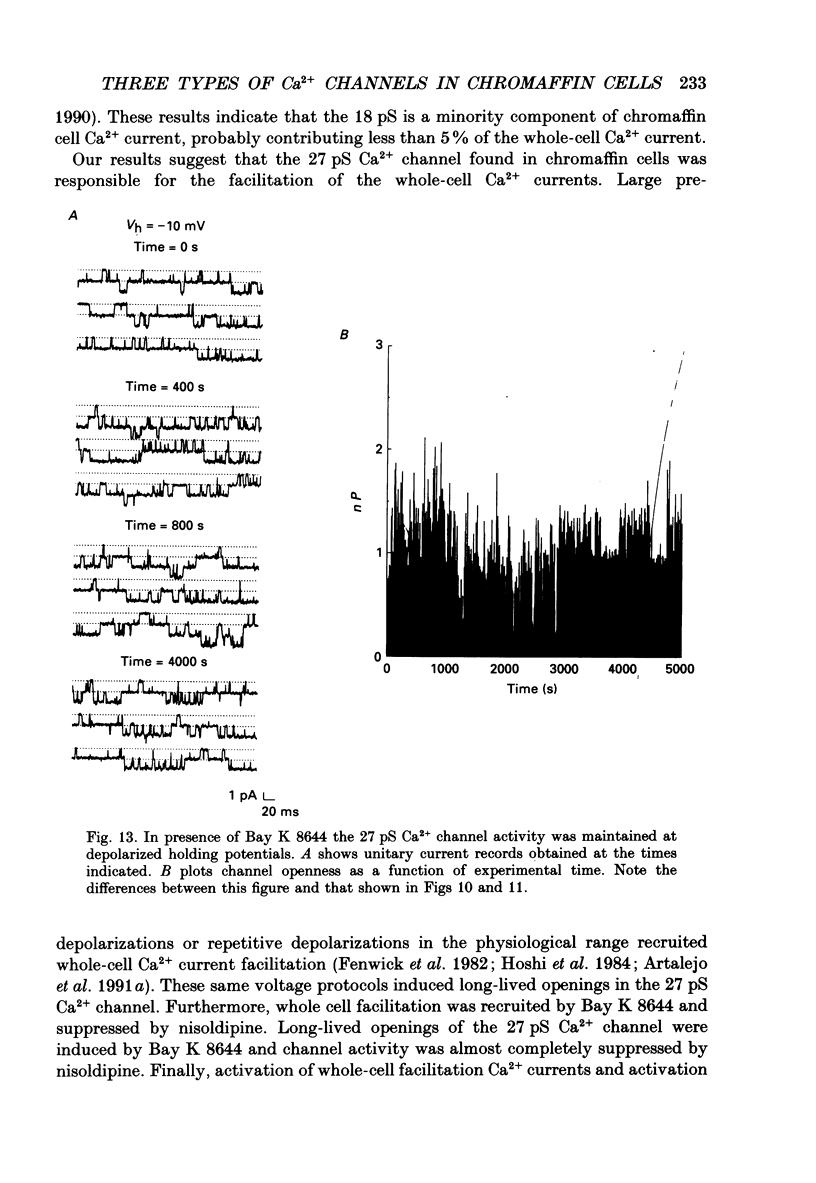
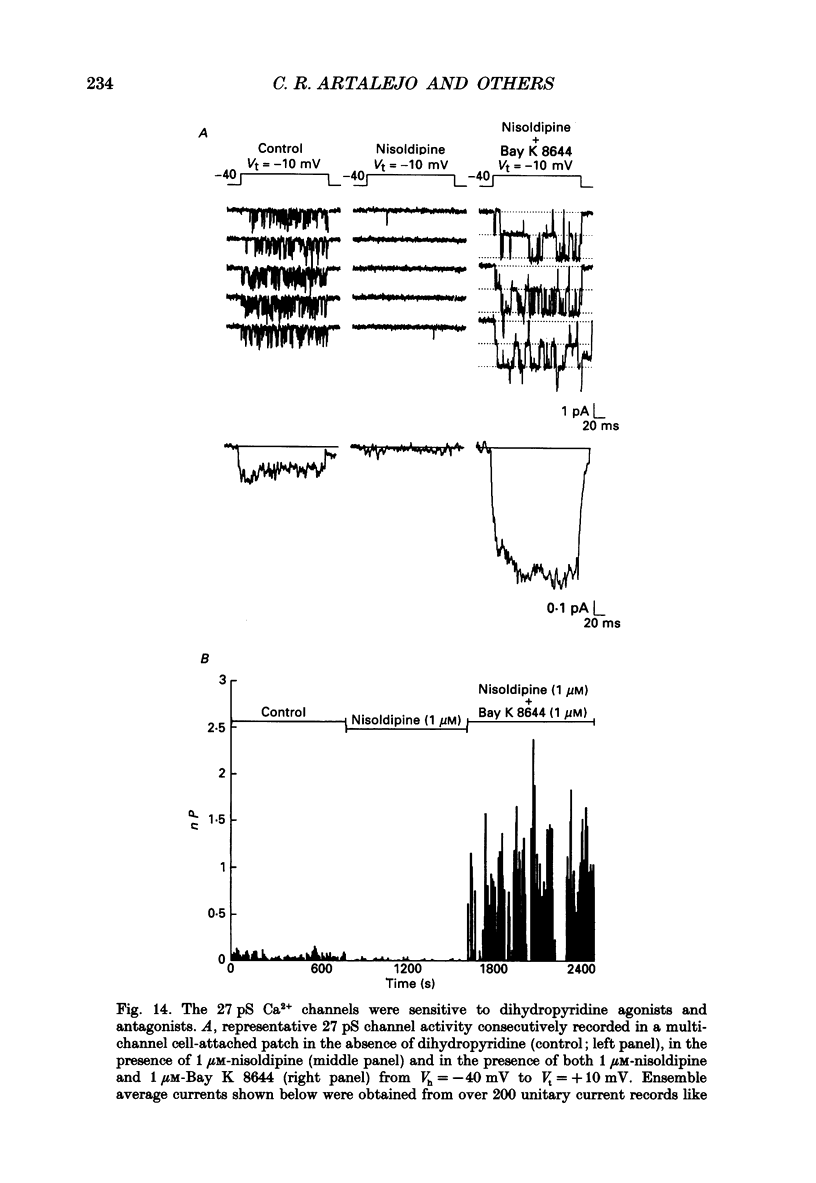
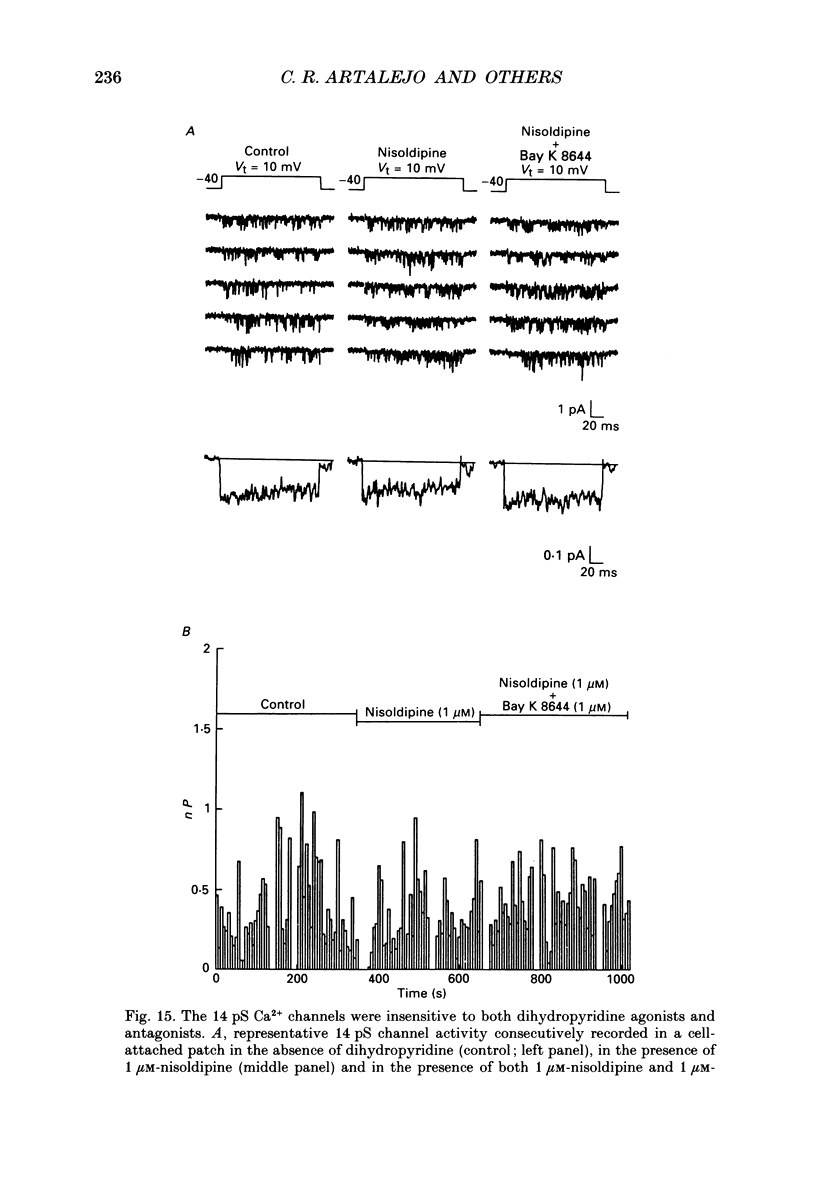
1. Cell-attached patch recordings from bovine chromaffin cells were performed with 90 mM-Ba2+ in the patch pipette and with isotonic potassium aspartate in the bathing solution to zero the membrane potential. Three different types of unitary Ca2+ channel activity could be distinguished in these recordings. 2. A 27 pS Ca2+ channel was distinguished by constructing amplitude histograms and measuring slope conductance. This channel activated over a broad range of potentials (depolarizations greater than -10 mV). 3. A second Ca2+ channel with a slope conductance of 14 pS could also be detected with amplitude histograms. This channel activated with depolarizations greater than -20 mV. 4. An 18 pS Ca2+ channel was observed infrequently indicating that this channel may carry only a small amount of the whole-cell current. This 18 pS channel was sensitive to changes in holding potential. Depolarizing the patch to +10 mV from a holding potential of -80 mV elicited robust unitary activity. Changing the patch holding potential to -40 mV while maintaining test depolarizations to +10 mV completely inactivated the 18 pS channel. Neither the 25 pS nor the 14 pS Ca2+ channels were affected by changes in holding potential in the range from -80 mV to -40 mV, indicating the 18 pS channel was a different type of channel. As the 18 pS channel was observed so infrequently, no detailed studies of it were possible. 5. Chromaffin cell Ca2+ currents exhibited facilitation. Large pre-depolarizations greatly augmented whole-cell currents observed in these cells. Whole-cell currents could double or triple after recruiting facilitation. The application of large pre-depolarizations altered the gating behaviour of the 27 pS Ca2+ channel manifested as dramatically increased channel opening probabilities measured during subsequent test pulses. Large pre-depolarizations induced unitary activity in the 27 pS Ca2+ channel similar to the long-lived openings exhibited by L-type Ca2+ channels in the presence of Bay K 8644. Large pre-depolarizations did not change the gating behaviour of the 14 pS Ca2+ channel. 6. Repetitive depolarizations in the physiological range could also induce facilitation. At the single-channel level facilitation was manifested as a striking increase in opening probability of the 27 pS Ca2+ channel. No effect of repetitive activity was observed on 14 pS channel gating. At the whole-cell level, repetitive depolarizations dramatically increased the current observed. 7. Facilitation of 27 pS Ca2+ channel activity could be induced by changing the holding potential to a depolarized level (greater than or equal to -10 mV).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




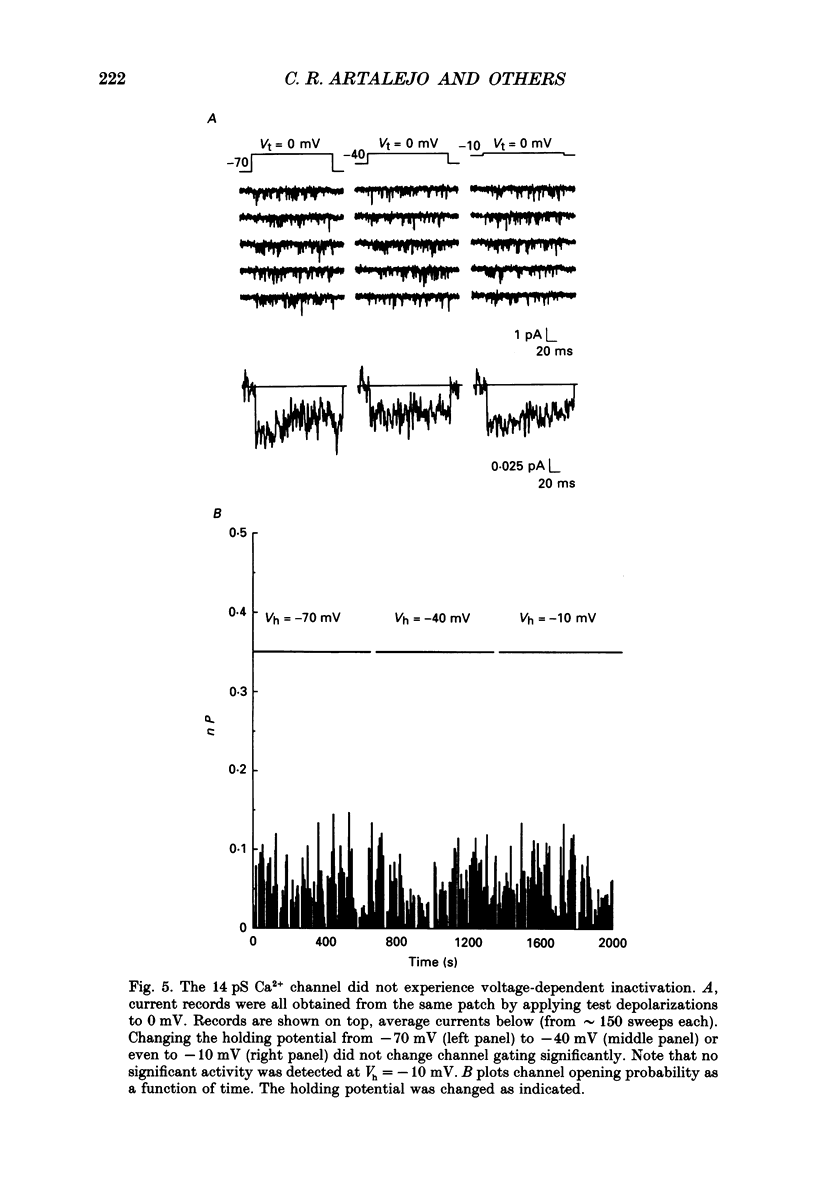
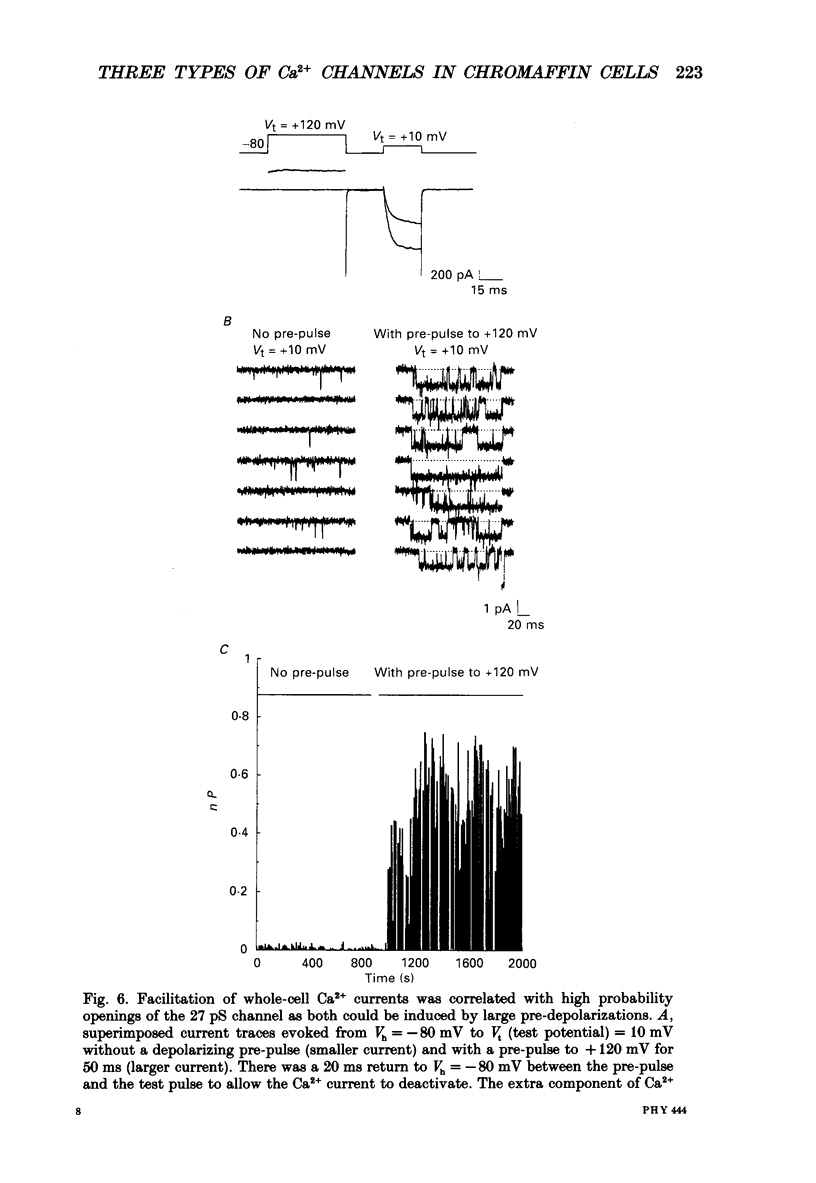

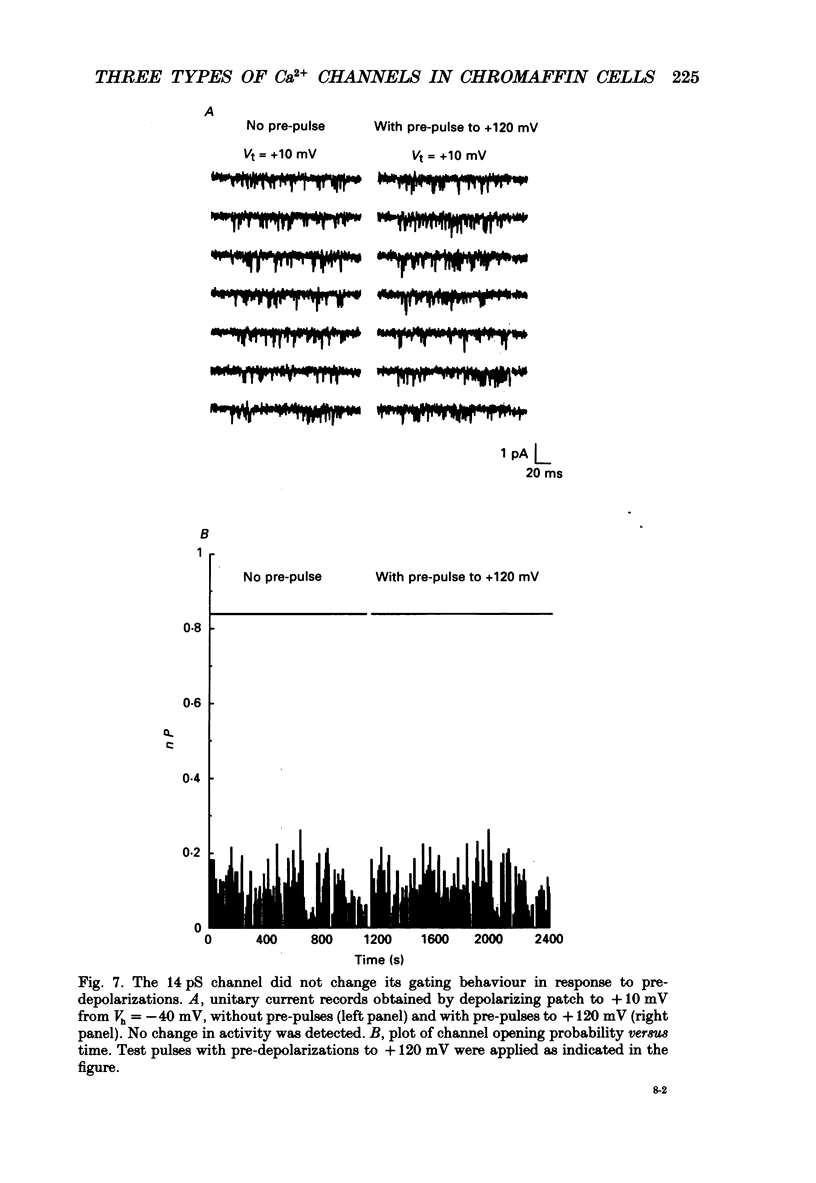
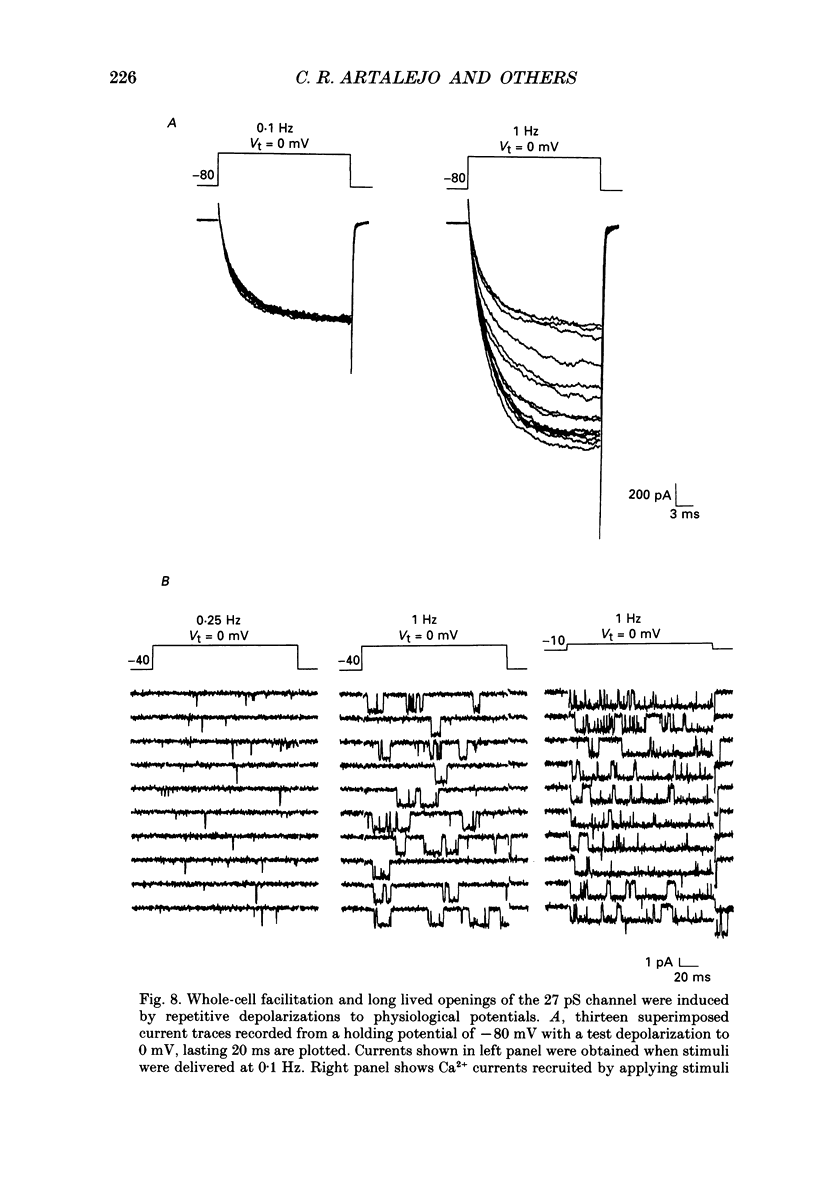







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Artalejo A. R., García A. G., Montiel C., Sánchez-García P. A dopaminergic receptor modulates catecholamine release from the cat adrenal gland. J Physiol. 1985 May;362:359–368. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artalejo C. R., Ariano M. A., Perlman R. L., Fox A. P. Activation of facilitation calcium channels in chromaffin cells by D1 dopamine receptors through a cAMP/protein kinase A-dependent mechanism. Nature. 1990 Nov 15;348(6298):239–242. doi: 10.1038/348239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artalejo C. R., Dahmer M. K., Perlman R. L., Fox A. P. Two types of Ca2+ currents are found in bovine chromaffin cells: facilitation is due to the recruitment of one type. J Physiol. 1991 Jan;432:681–707. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballesta J. J., Palmero M., Hidalgo M. J., Gutierrez L. M., Reig J. A., Viniegra S., Garcia A. G. Separate binding and functional sites for omega-conotoxin and nitrendipine suggest two types of calcium channels in bovine chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1989 Oct;53(4):1050–1056. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb07394.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P. Classes of calcium channels in vertebrate cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:367–384. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. Calcium channels. Gating for the physiologist. Nature. 1990 Nov 15;348(6298):192–193. doi: 10.1038/348192a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. C. The isolated bovine adrenomedullary chromaffin cell: a model of neuronal excitation-secretion. Endocrinology. 1977 Nov;101(5):1369–1378. doi: 10.1210/endo-101-5-1369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callewaert G., Hanbauer I., Morad M. Modulation of calcium channels in cardiac and neuronal cells by an endogenous peptide. Science. 1989 Feb 3;243(4891):663–666. doi: 10.1126/science.2536955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chern Y. J., Kim K. T., Slakey L. L., Westhead E. W. Adenosine receptors activate adenylate cyclase and enhance secretion from bovine adrenal chromaffin cells in the presence of forskolin. J Neurochem. 1988 May;50(5):1484–1493. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb03034.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. W., Rubin R. P. The mechanism of catecholamine release from the adrenal medulla and the role of calcium in stimulus-secretion coupling. J Physiol. 1963 Jul;167(2):288–310. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Fajdiga P. B., Howe N. B., Livett B. G. Functional and morphological characterization of isolated bovine adrenal medullary cells. J Cell Biol. 1978 Jan;76(1):12–30. doi: 10.1083/jcb.76.1.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Marty A., Neher E. Sodium and calcium channels in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:599–635. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox A. P., Nowycky M. C., Tsien R. W. Kinetic and pharmacological properties distinguishing three types of calcium currents in chick sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:149–172. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox A. P., Nowycky M. C., Tsien R. W. Single-channel recordings of three types of calcium channels in chick sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:173–200. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg A., Zinder O. Alpha- and beta-receptor control of catecholamine secretion from isolated adrenal medulla cells. Cell Tissue Res. 1982;226(3):655–665. doi: 10.1007/BF00214792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P., Lansman J. B., Tsien R. W. Different modes of Ca channel gating behaviour favoured by dihydropyridine Ca agonists and antagonists. Nature. 1984 Oct 11;311(5986):538–544. doi: 10.1038/311538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirning L. D., Fox A. P., McCleskey E. W., Olivera B. M., Thayer S. A., Miller R. J., Tsien R. W. Dominant role of N-type Ca2+ channels in evoked release of norepinephrine from sympathetic neurons. Science. 1988 Jan 1;239(4835):57–61. doi: 10.1126/science.2447647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi T., Rothlein J., Smith S. J. Facilitation of Ca2+-channel currents in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5871–5875. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi T., Smith S. J. Large depolarization induces long openings of voltage-dependent calcium channels in adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurosci. 1987 Feb;7(2):571–580. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-02-00571.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokubun S., Reuter H. Dihydropyridine derivatives prolong the open state of Ca channels in cultured cardiac cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4824–4827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester H. A., Snutch T. P., Leonard J. P., Nargeot J., Dascal N., Curtis B. M., Davidson N. Expression of mRNA encoding voltage-dependent Ca channels in Xenopus oocytes. Review and progress report. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;560:174–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb24094.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R. R., Sugimori M., Cherksey B. Voltage-dependent calcium conductances in mammalian neurons. The P channel. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;560:103–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb24084.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marriott D., Adams M., Boarder M. R. Effect of forskolin and prostaglandin E1 on stimulus secretion coupling in cultured bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1988 Feb;50(2):616–623. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb02955.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita K., Dohi T., Kitayama S., Koyama Y., Tsujimoto A. Enhancement of stimulation-evoked catecholamine release from cultured bovine adrenal chromaffin cells by forskolin. J Neurochem. 1987 Jan;48(1):243–247. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb13154.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowycky M. C., Fox A. P., Tsien R. W. Long-opening mode of gating of neuronal calcium channels and its promotion by the dihydropyridine calcium agonist Bay K 8644. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):2178–2182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.2178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowycky M. C., Fox A. P., Tsien R. W. Three types of neuronal calcium channel with different calcium agonist sensitivity. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):440–443. doi: 10.1038/316440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietrobon D., Hess P. Novel mechanism of voltage-dependent gating in L-type calcium channels. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):651–655. doi: 10.1038/346651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosario L. M., Soria B., Feuerstein G., Pollard H. B. Voltage-sensitive calcium flux into bovine chromaffin cells occurs through dihydropyridine-sensitive and dihydropyridine- and omega-conotoxin-insensitive pathways. Neuroscience. 1989;29(3):735–747. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90145-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Lipscombe D., Madison D. V., Bley K. R., Fox A. P. Multiple types of neuronal calcium channels and their selective modulation. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Oct;11(10):431–438. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90194-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S. P. Vasoactive intestinal peptide elevates cyclic AMP levels and potentiates secretion in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Neuropeptides. 1988 Jan;11(1):17–21. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(88)90023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


