Abstract
1. A significant proportion of plasma zinc exists complexed with amino acids. The effect of amino acids on the accumulation of radioactive zinc by rat erythrocytes was studied in vitro, to investigate the hypothesis that zinc might be transported into cells as an amino acid-zinc complex. 2. L-Histidine (500 microM-10 mM) stimulated 65Zn uptake; 50 mM-L-histidine gave a slight inhibition of uptake. D-Histidine (500 microM-10 mM) inhibited uptake in a dose-dependent manner. A non-zinc-binding amino acid, L-alanine, did not affect 65Zn uptake. 3. The effect of L-histidine was sodium dependent and temperature dependent, but was DIDS insensitive. These properties suggest that zinc is being transported as a zinc-histidine complex, utilizing an amino acid carrier system. Uptake of zinc in the presence of L-histidine differed from the previously described ionic mechanism, and may represent a physiological route of uptake. 4. L-Histidine stimulated efflux of 65Zn from pre-loaded cells. 5. The relevance of transport of a zinc-histidine complex is discussed with reference to histidinaemia, and as a significant zinc transport system in the presence of the very low ionic zinc concentrations found in plasma.
Full text
PDF


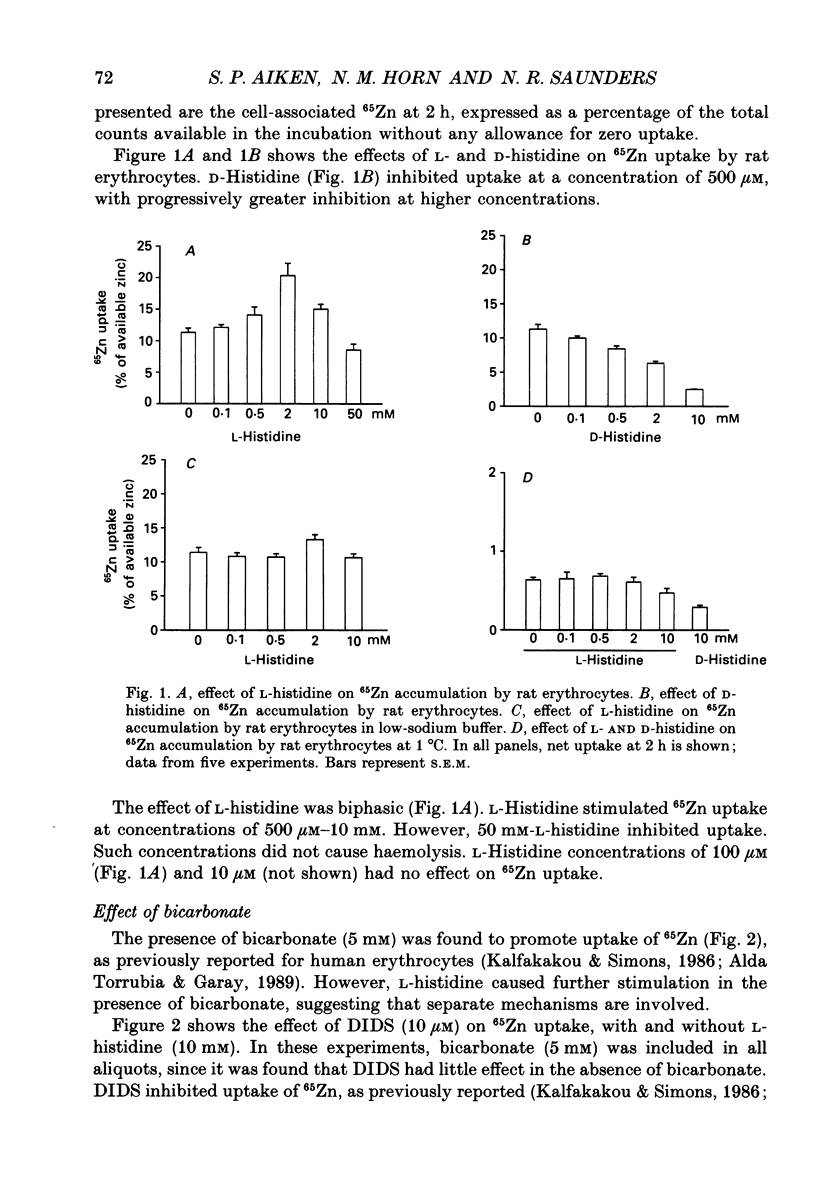





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
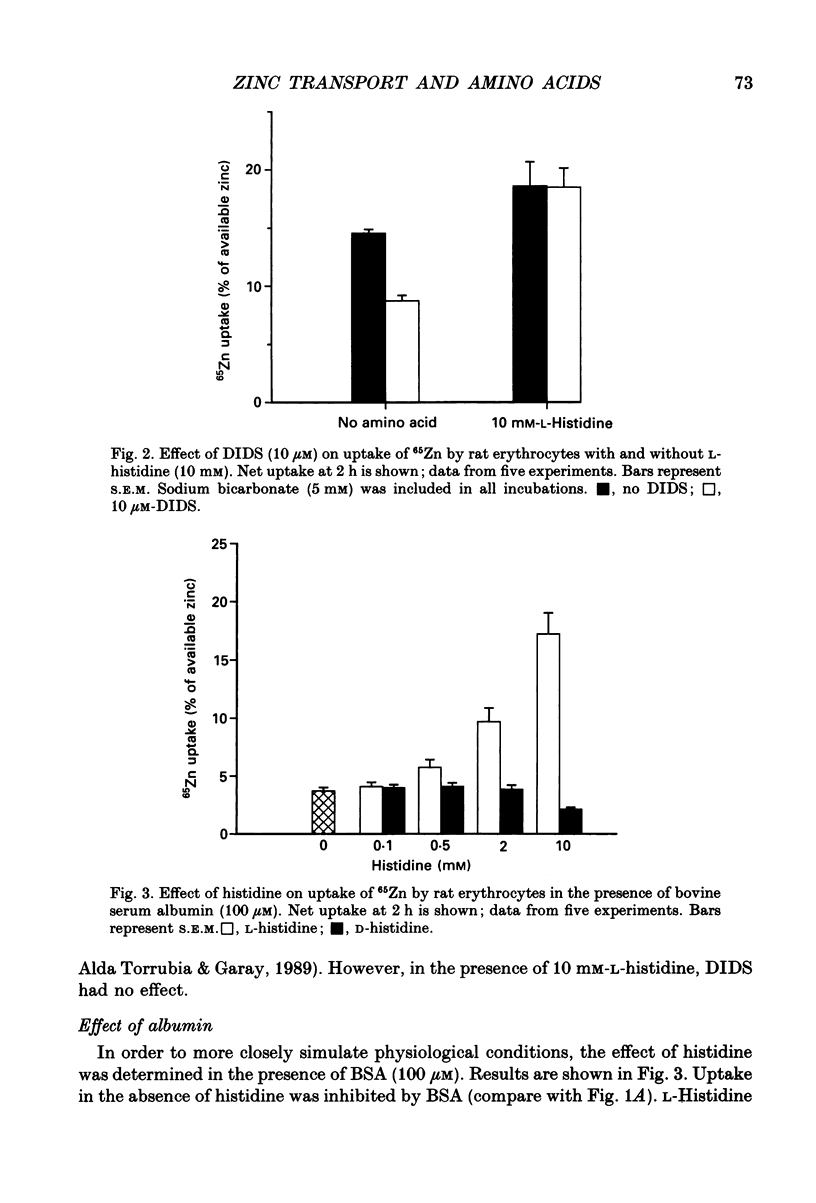
- Barker G. A., Ellory J. C. The identification of neutral amino acid transport systems. Exp Physiol. 1990 Jan;75(1):3–26. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1990.sp003382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARVER M. J. INFLUENCE OF PHENYLALANINE ADMINISTRATION ON THE FREE AMINO ACIDS OF BRAIN AND LIVER IN THE RAT. J Neurochem. 1965 Jan;12:45–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1965.tb10250.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
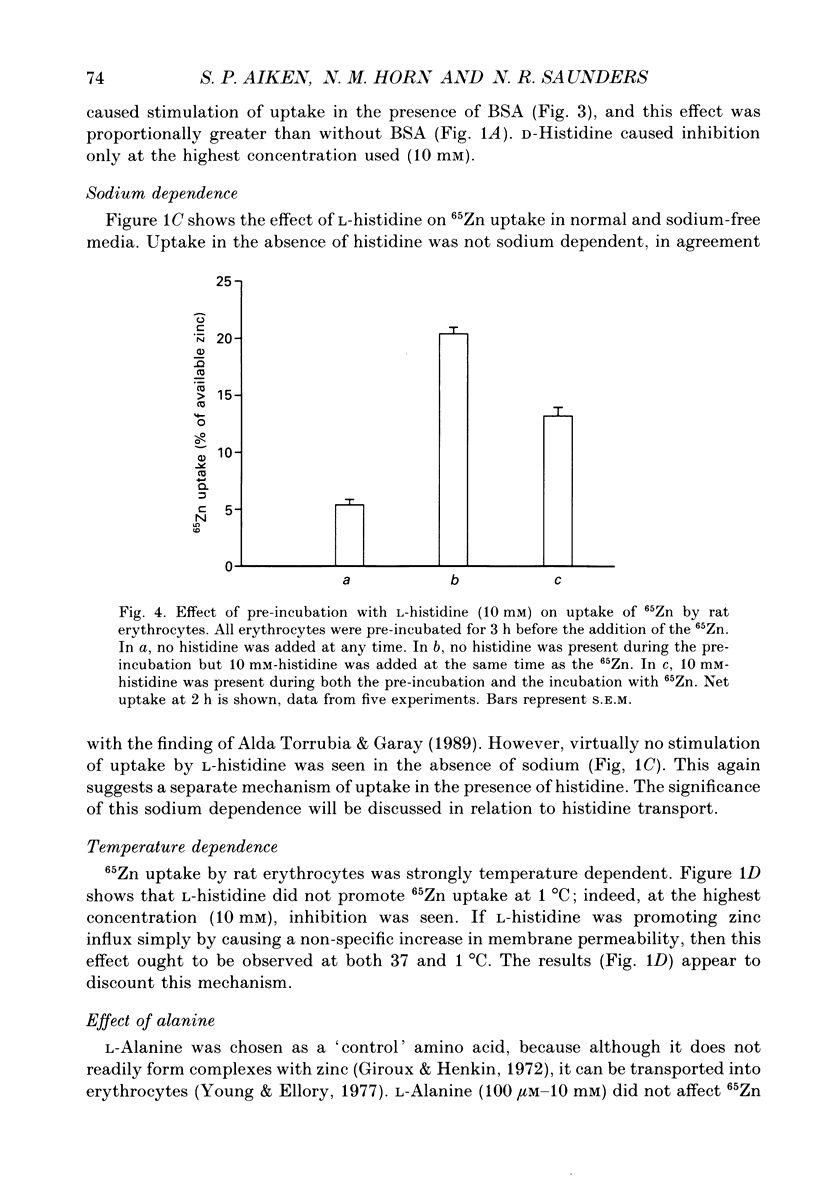
- CRAMPTON R. F., SMYTH D. H. The excretion of the enantiomorphs of aminoacids. J Physiol. 1953 Oct;122(1):1–10. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen H. N. Role of amino acid transport and countertransport in nutrition and metabolism. Physiol Rev. 1990 Jan;70(1):43–77. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
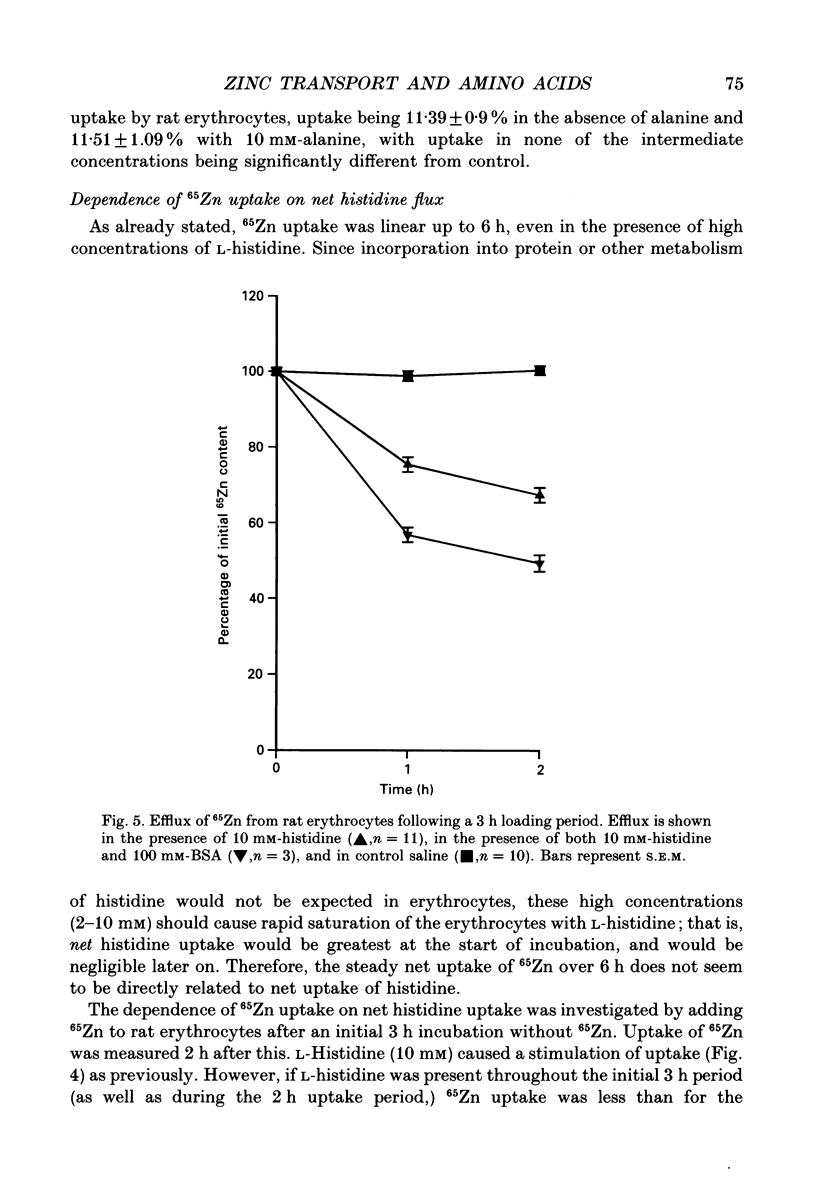
- Duchateau J., Hainaut K. Effects of immobilization on contractile properties, recruitment and firing rates of human motor units. J Physiol. 1990 Mar;422:55–65. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp017972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felipe A., Viñas O., Remesar X. Changes in glycine and leucine transport during red cell maturation in the rat. Biosci Rep. 1990 Apr;10(2):209–216. doi: 10.1007/BF01116580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foote J. W., Delves H. T. Albumin bound and alpha 2-macroglobulin bound zinc concentrations in the sera of healthy adults. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Sep;37(9):1050–1054. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.9.1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giroux E. L., Henkin R. I. Competition for zinc among serum albumin and amino acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jun 26;273(1):64–72. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90191-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkin R. I., Patten B. M., Re P. K., Bronzert D. A. A syndrome of acute zinc loss. Cerebellar dysfunction, mental changes, anorexia, and taste and smell dysfunction. Arch Neurol. 1975 Nov;32(11):745–751. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1975.00490530067006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hundal H. S., Rennie M. J., Watt P. W. Characteristics of L-glutamine transport in perfused rat skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;393:283–305. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa M., Saito H., Morishita H., Ito T., Kato T., Wada Y. Development of histidinemic patients: follow-up study of five cases with neuropsychological symptoms. Acta Paediatr Jpn. 1987 Jun;29(3):444–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-200x.1987.tb00343.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilberg M. S., Handlogten M. E., Christensen H. N. Characteristics of an amino acid transport system in rat liver for glutamine, asparagine, histidine, and closely related analogs. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):4011–4019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magneson G. R., Puvathingal J. M., Ray W. J., Jr The concentrations of free Mg2+ and free Zn2+ in equine blood plasma. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):11140–11148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oelshlegel F. J., Jr, Brewer G. J., Knutsen C., Prasad A. S., Schoomaker E. B. Studies on the interaction of zinc with human hemoglobin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Aug;163(2):742–748. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90536-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldendorf W. H. Brain uptake of radiolabeled amino acids, amines, and hexoses after arterial injection. Am J Physiol. 1971 Dec;221(6):1629–1639. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.6.1629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldendorf W. H. Stereospecificity of blood-brain barrier permeability to amino acids. Am J Physiol. 1973 Apr;224(4):967–969. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.4.967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardridge W. M., Jefferson L. S. Liver uptake of amino acids and carbohydrates during a single circulatory passage. Am J Physiol. 1975 Apr;228(4):1155–1161. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.4.1155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIVARAMA SASTRY K., VISWANATHAN L., RAMAIAH A., SARMA P. S. Studies on the binding of 65Zn by equine erythrocytes in vitro. Biochem J. 1960 Mar;74:561–567. doi: 10.1042/bj0740561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrubia J. O., Garay R. Evidence for a major route for zinc uptake in human red blood cells: [Zn(HCO3)2Cl]- influx through the [Cl-/HCO3-] anion exchanger. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Feb;138(2):316–322. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041380214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wensink J., Molenaar A. J., Woroniecka U. D., Van den Hamer C. J. Zinc uptake into synaptosomes. J Neurochem. 1988 Mar;50(3):782–789. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb02982.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Ellory J. C., Tucker E. M. Amino acid transport defect in glutathione-deficient sheep erythrocytes. Nature. 1975 Mar 13;254(5496):156–157. doi: 10.1038/254156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


