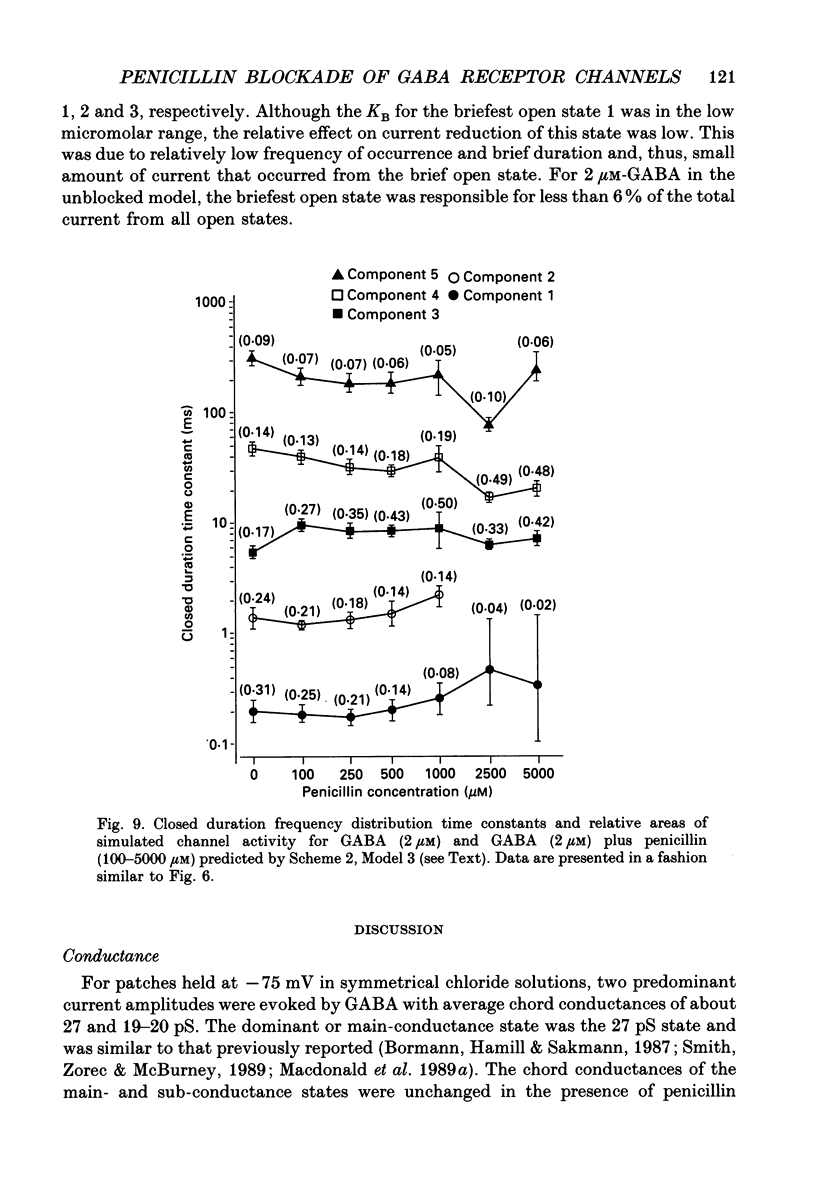
Abstract
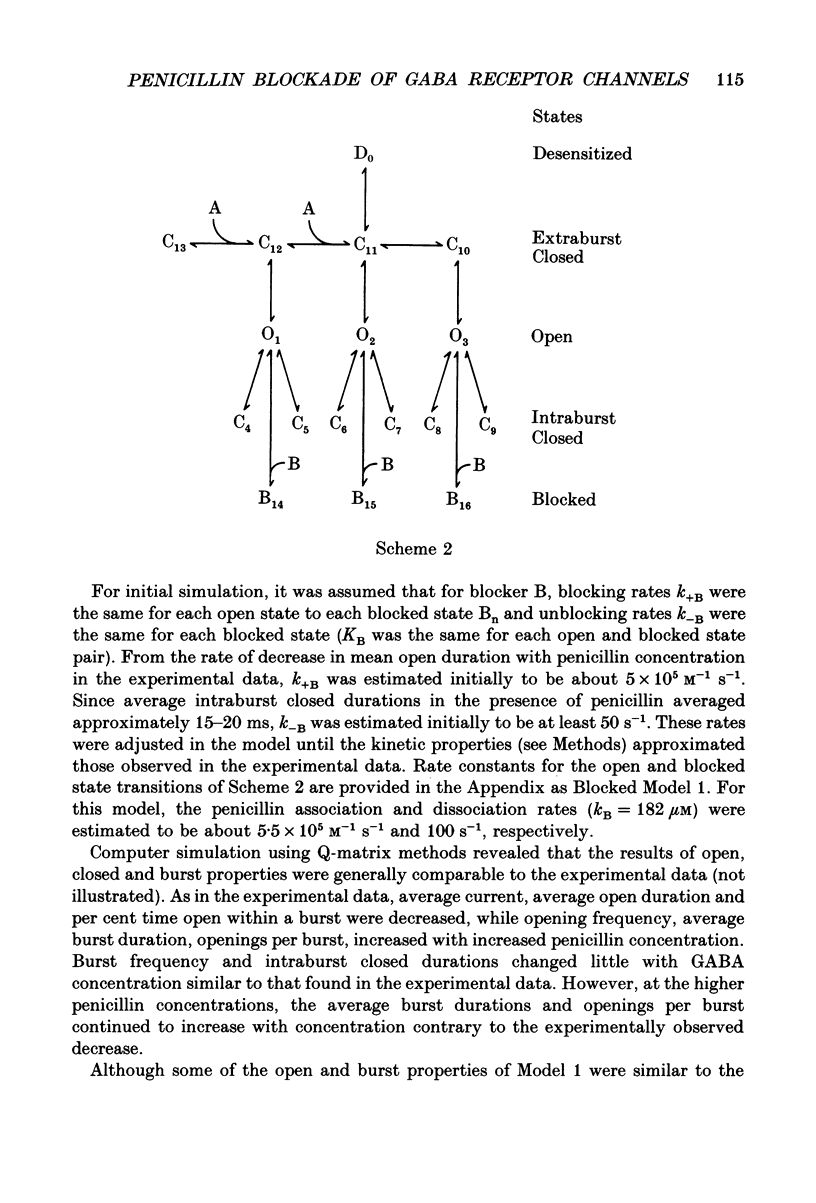
1. Reduction by penicillin of single gamma-aminobutyric acidA (GABAA) receptor currents from somata of mouse spinal cord neurones in culture was investigated using the excised outside-out patch-clamp recording technique. 2. GABA (2 microM) alone or with penicillin (100-5000 microM) applied by pressure ejection from micropipettes evoked inward currents when patches were voltage-clamped at -75 mV in symmetrical chloride solutions. Averaged GABA receptor currents were decreased in the presence of penicillin. 3. GABA receptor currents were recorded with at least two conductance states, a more frequent or main-conductance state of about 27 pS and a less frequent sub-conductance state of about 19-20 pS. The conductances of the two states were unchanged in the presence of penicillin. The kinetic properties of the main-conductance state were analysed and are summarized below. 4. Penicillin produced a concentration-dependent reduction of GABA receptor open properties by reduction of average GABA receptor channel open duration and an increase in channel opening frequency. 5. Penicillin shifted frequency histograms of GABA receptor channel open durations to shorter durations in a concentration-dependent manner. Three exponential functions were required to fit best the frequency histograms of open durations, suggesting that the channel had at least three open states. Penicillin produced a concentration-dependent reduction in the time constants obtained from the open duration frequency histograms. 6. Frequency histograms of GABA receptor channel closed durations could be fitted with five to seven exponential functions, suggesting that the channel had multiple closed states. In the presence of increased concentration of penicillin, there was a reduction in the relative frequency of brief gaps and the appearance of new closed time constants. 7. With increased penicillin concentration, GABA receptor channel burst frequency was unchanged, burst durations were increased, the number of openings per burst was increased and the per cent time open within a burst was decreased. 8. The results suggested that penicillin produced simple open channel blockade of the GABA receptor channel. However, the experimental results also suggested that the association with and, perhaps, the dissociation of the blocker from its binding site were dependent upon the kinetic state of the open channel. Penicillin had faster association and slower dissociation rates when the channel was in unstable, brief open kinetic state than when the channel was in a more stable, longer open kinetic state. Possible models for penicillin reduction of single GABA receptor currents were simulated by computer and analysed.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF





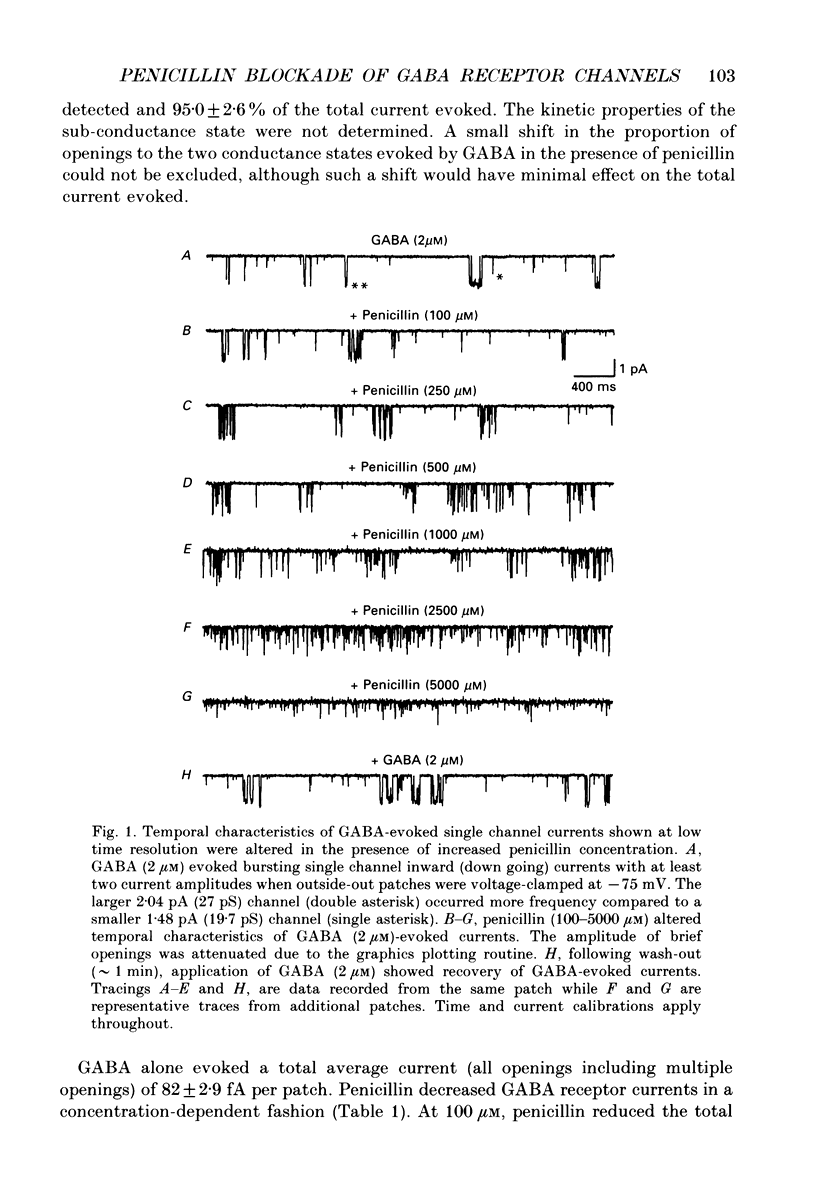
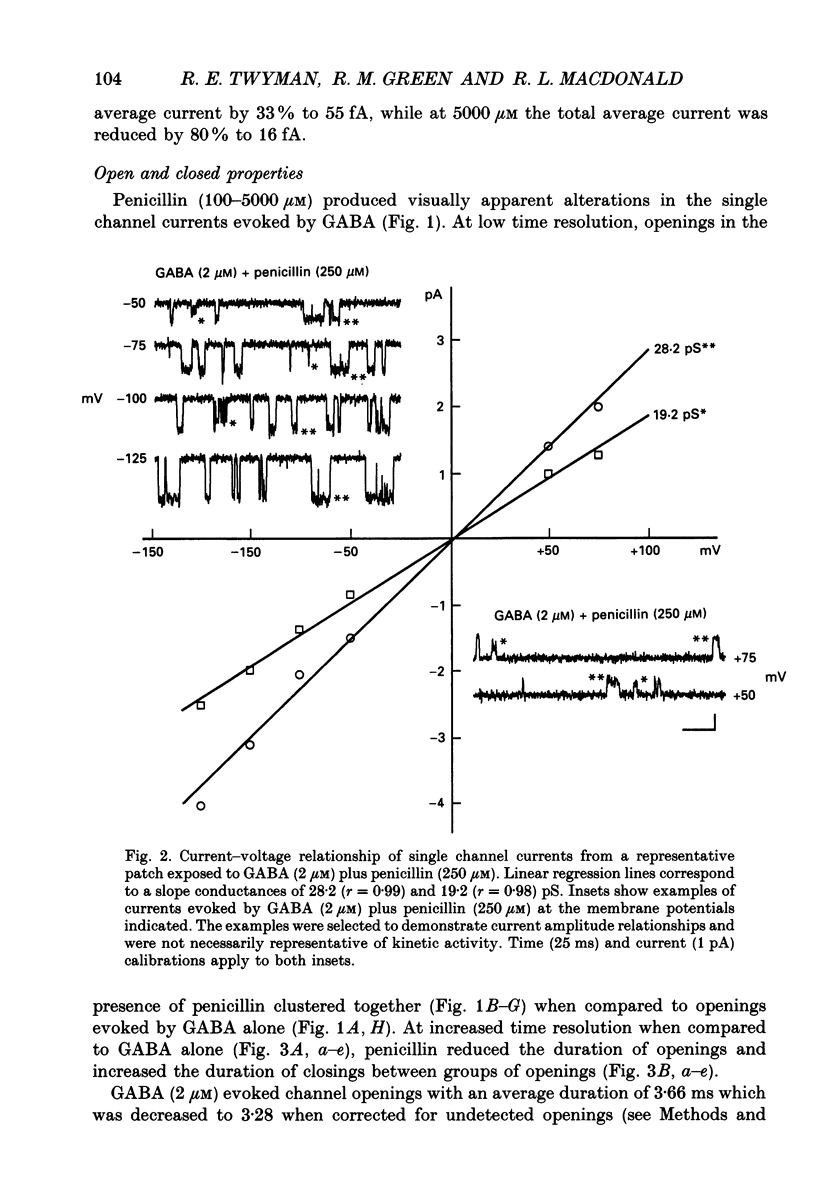
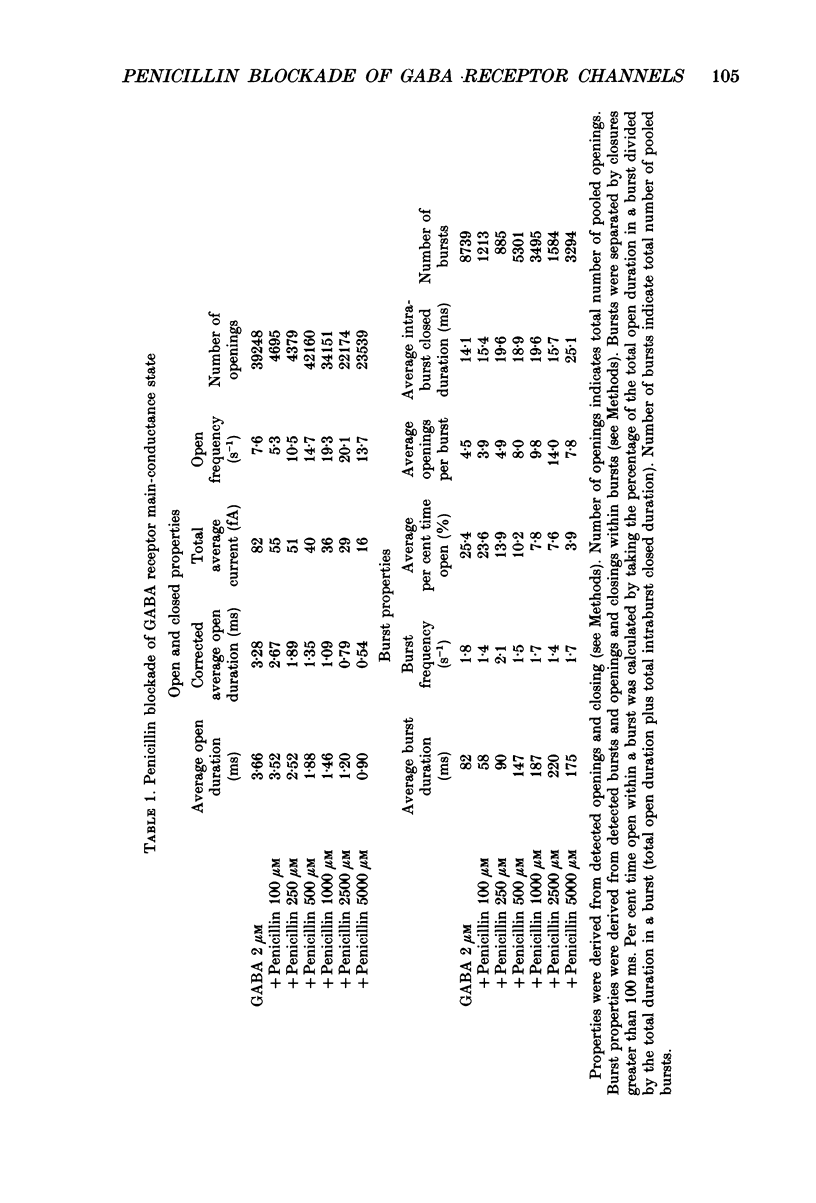
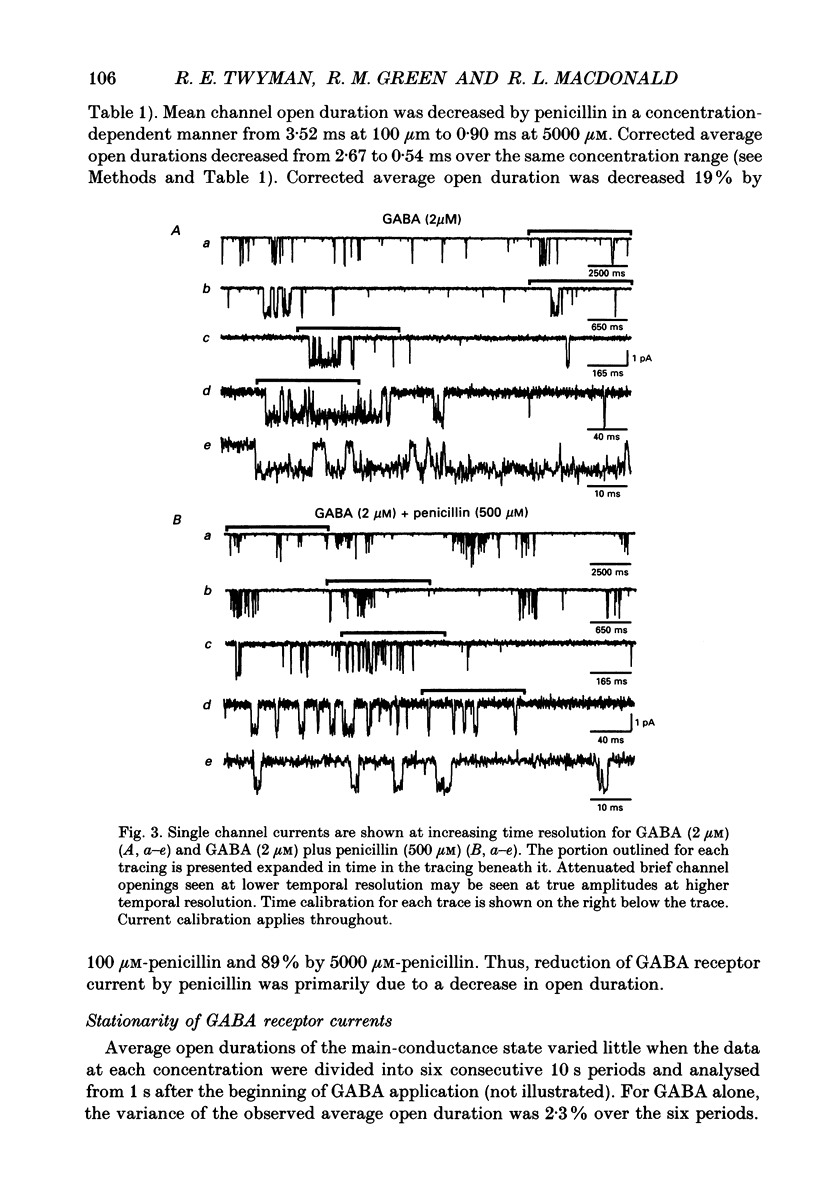











Selected References
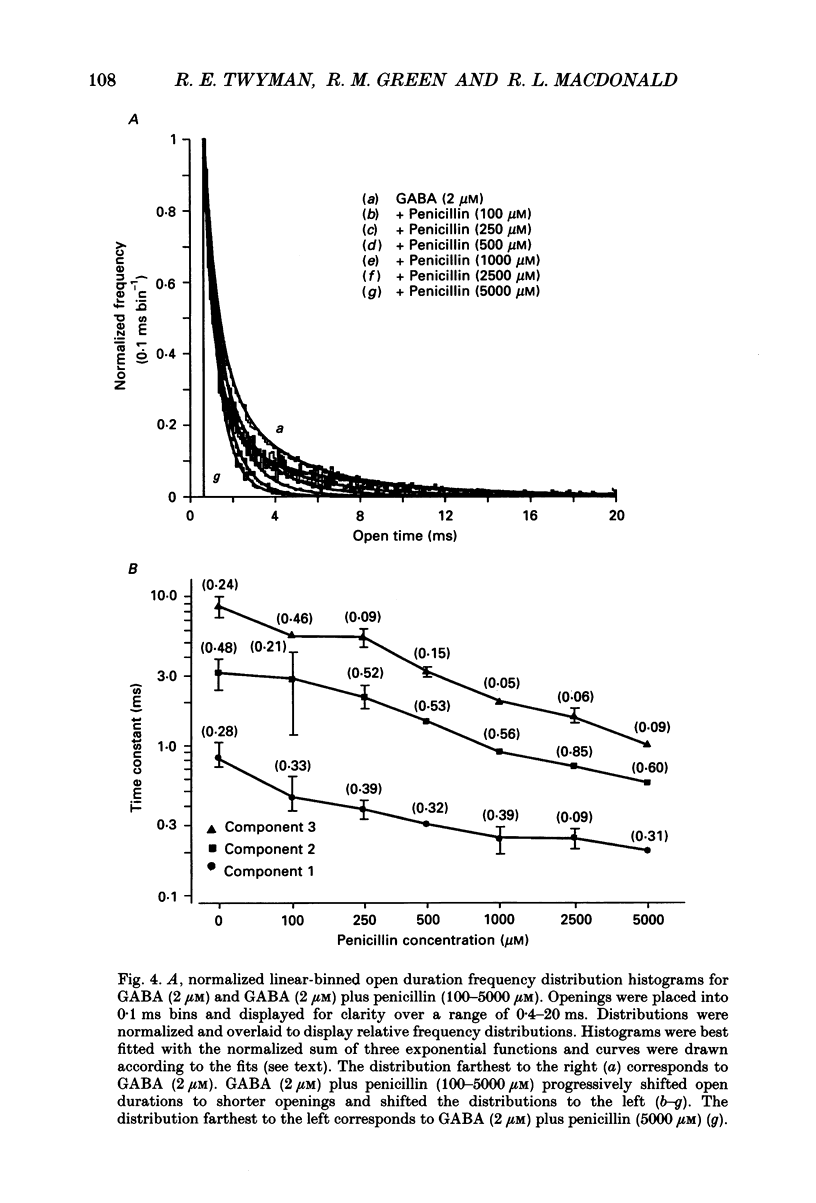
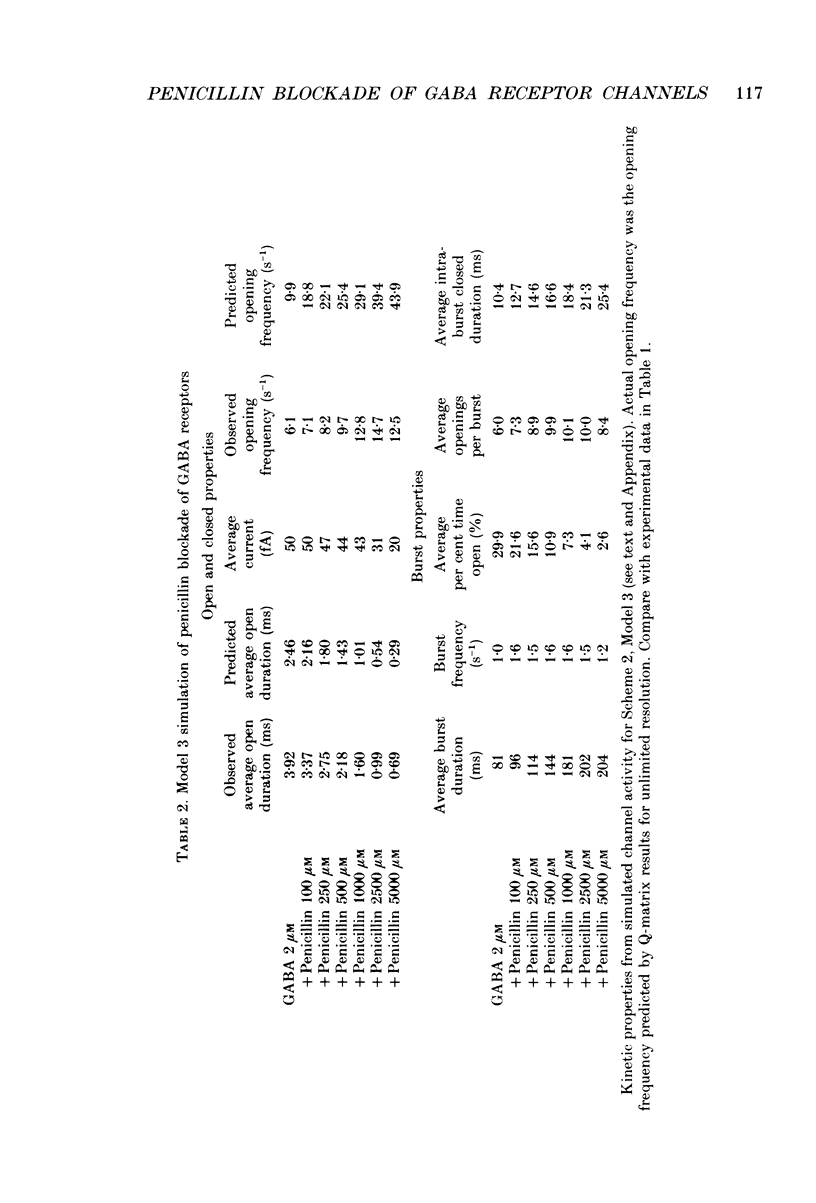
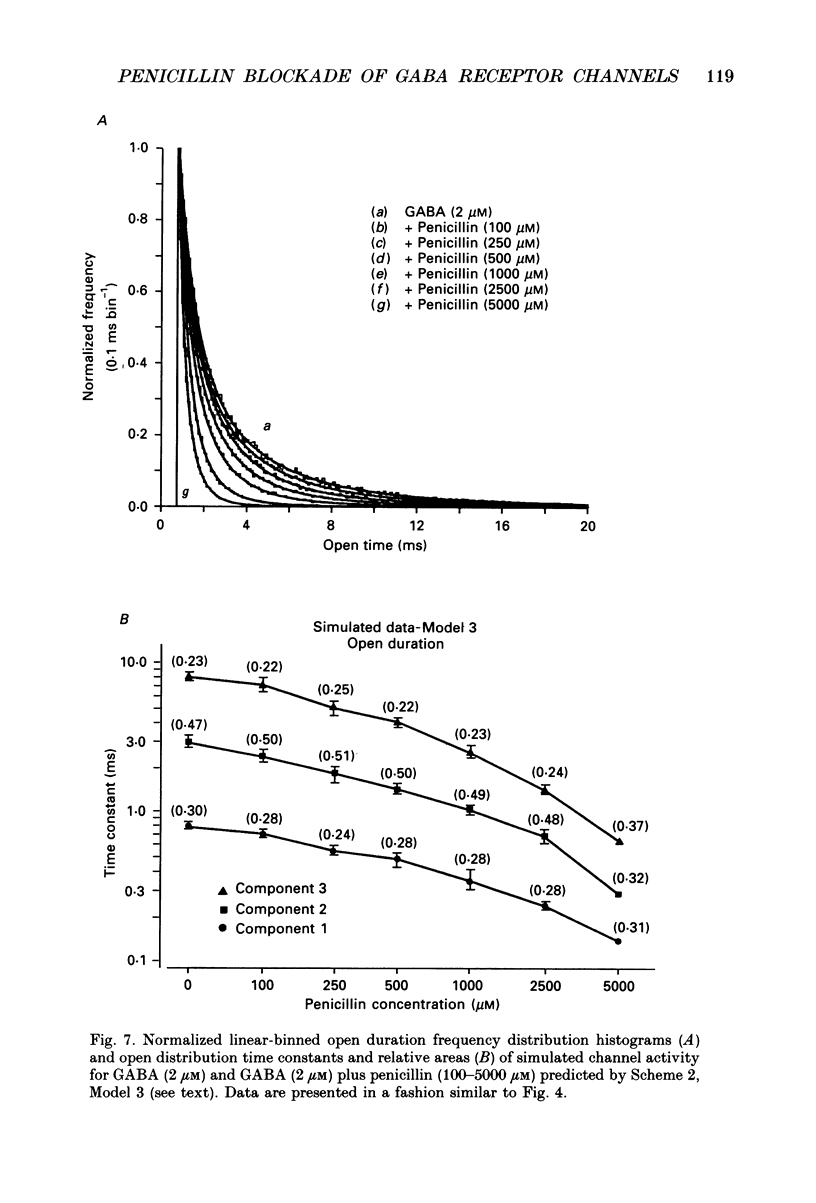
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
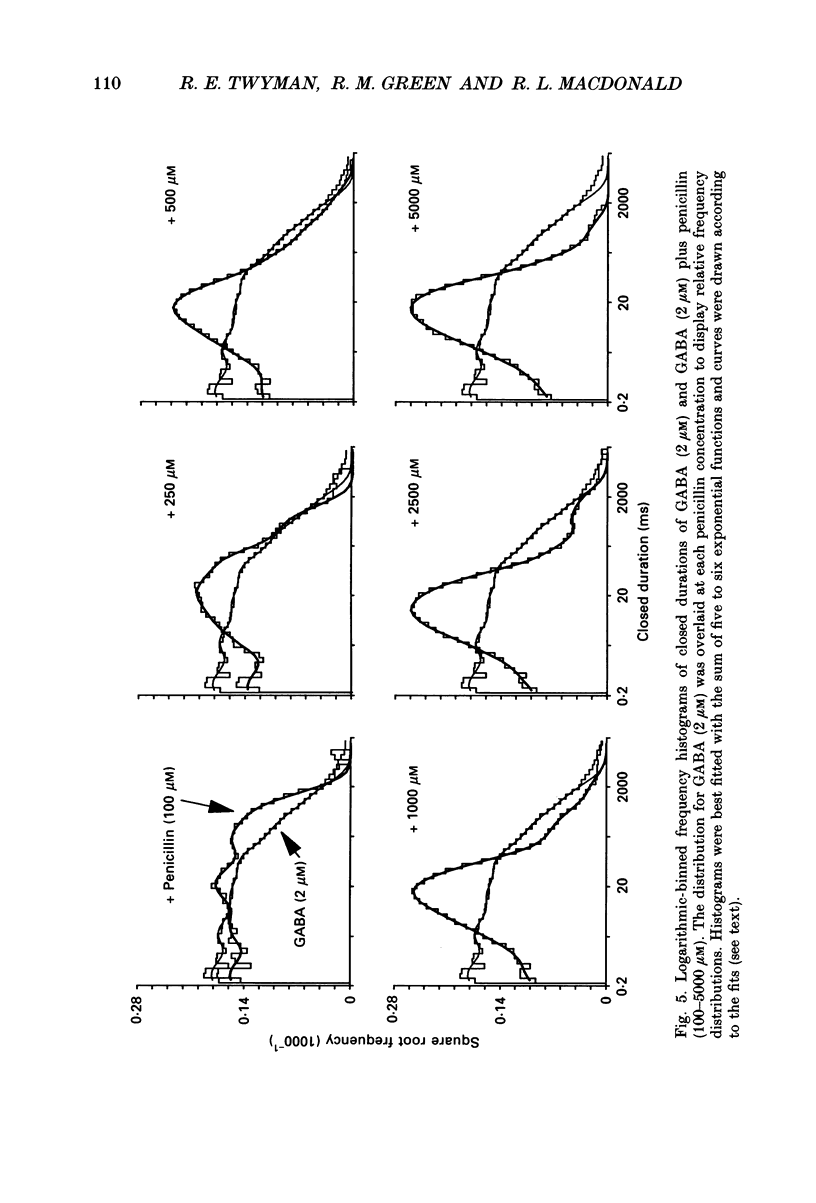
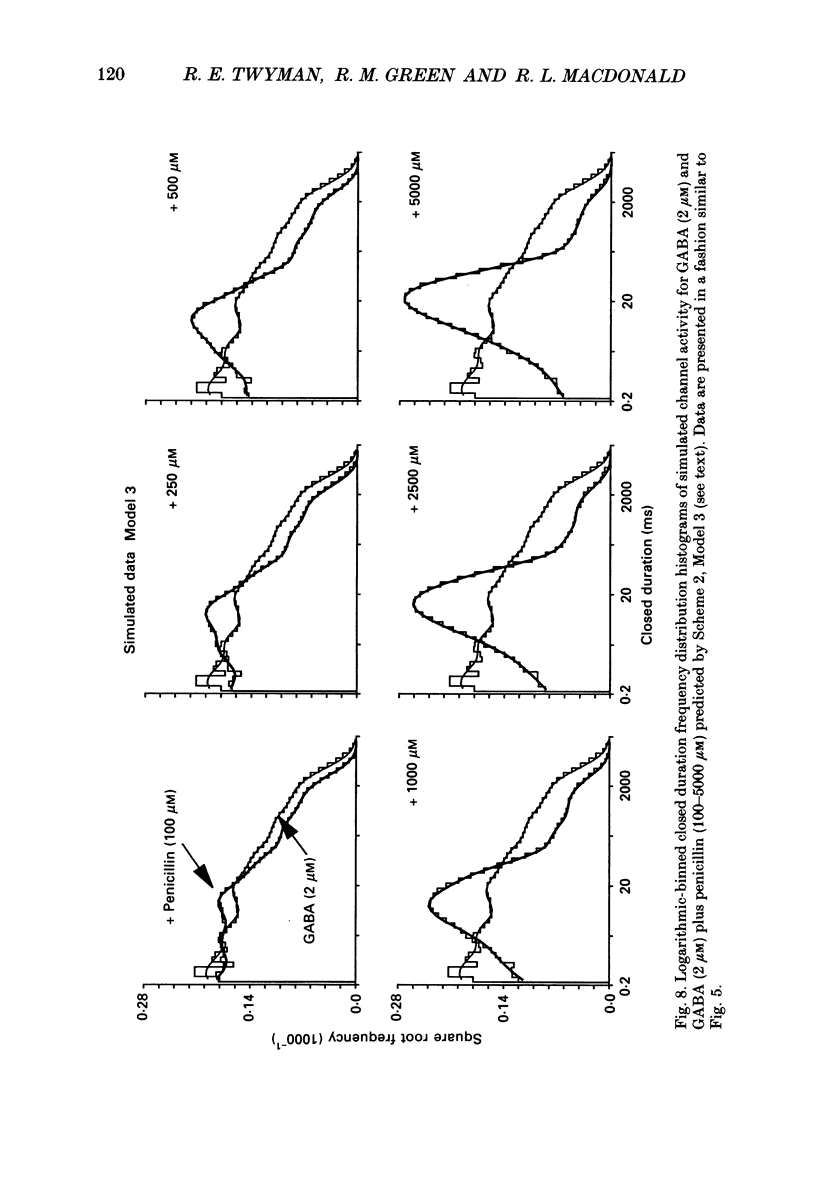
- Adams P. R. Drug blockade of open end-plate channels. J Physiol. 1976 Sep;260(3):531–552. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
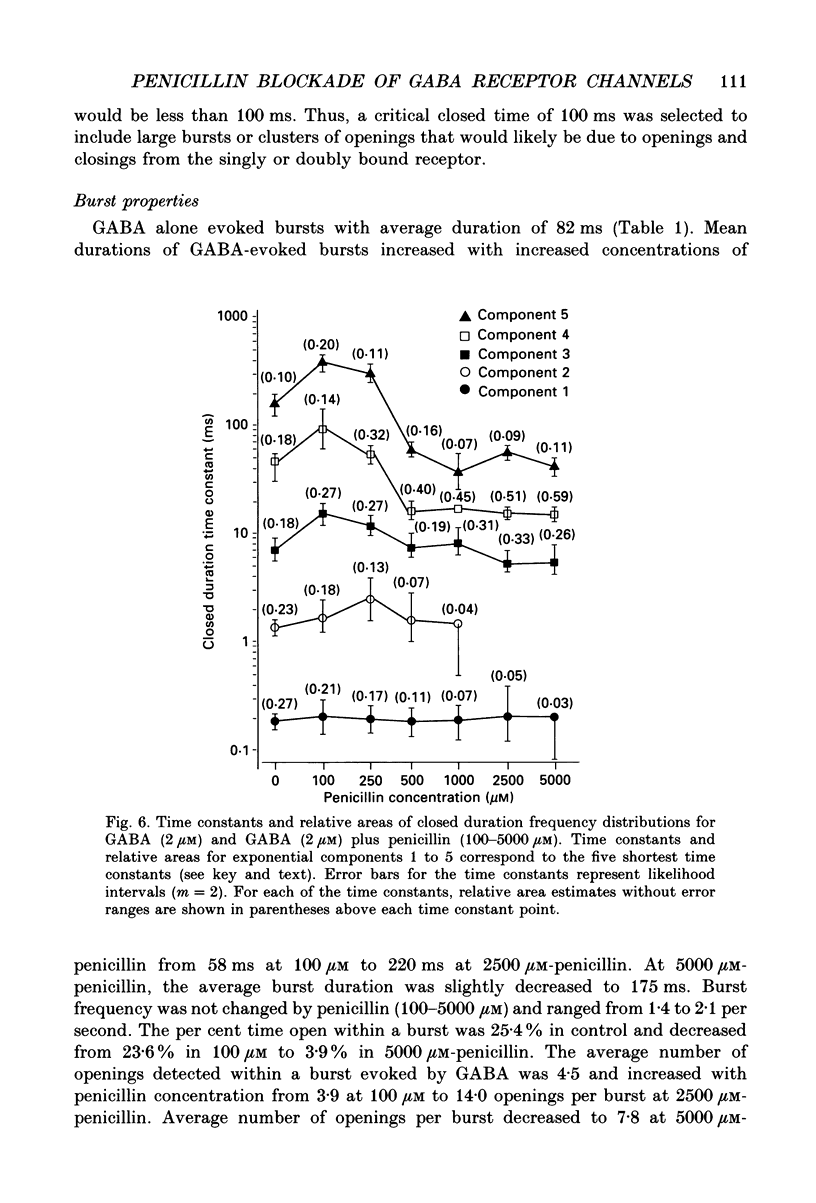
- Adams P. R. Voltage jump analysis of procaine action at frog end-plate. J Physiol. 1977 Jun;268(2):291–318. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akaike N., Inomata N., Tokutomi N. Contribution of chloride shifts to the fade of gamma-aminobutyric acid-gated currents in frog dorsal root ganglion cells. J Physiol. 1987 Oct;391:219–234. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ascher P., Nowak L. The role of divalent cations in the N-methyl-D-aspartate responses of mouse central neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1988 May;399:247–266. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatz A. L., Magleby K. L. Quantitative description of three modes of activity of fast chloride channels from rat skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1986 Sep;378:141–174. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bormann J., Hamill O. P., Sakmann B. Mechanism of anion permeation through channels gated by glycine and gamma-aminobutyric acid in mouse cultured spinal neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Apr;385:243–286. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cash D. J., Subbarao K. Desensitization of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor from rat brain: two distinguishable receptors on the same membrane. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 1;26(24):7556–7562. doi: 10.1021/bi00398a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Q. X., Stelzer A., Kay A. R., Wong R. K. GABAA receptor function is regulated by phosphorylation in acutely dissociated guinea-pig hippocampal neurones. J Physiol. 1990 Jan;420:207–221. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp017908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow P., Mathers D. Convulsant doses of penicillin shorten the lifetime of GABA-induced channels in cultured central neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Jul;88(3):541–547. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10234.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Hawkes A. G. On the stochastic properties of bursts of single ion channel openings and of clusters of bursts. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Dec 24;300(1098):1–59. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1982.0156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Hawkes A. G. On the stochastic properties of single ion channels. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Mar 6;211(1183):205–235. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1981.0003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Hawkes A. G. Relaxation and fluctuations of membrane currents that flow through drug-operated channels. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Nov 14;199(1135):231–262. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Mathie A., Powis D. A. Acetylcholine receptor channels and their block by clonidine in cultured bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1988 Aug;402:255–278. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Game C. J., Johnston G. A., McCulloch R. M., MacLachlan R. M. Convulsive action of penicillin. Brain Res. 1972 Aug 11;43(1):242–245. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90288-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidoff R. A. Penicillin and inhibition in the cat spinal cord. Brain Res. 1972 Oct 27;45(2):638–642. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90498-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidoff R. A. Penicillin and presynaptic inhibition in the amphibian spinal cord. Brain Res. 1972 Jan 14;36(1):218–222. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90778-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn P. F., Somjen G. G. Membrane resistance, monosynaptic EPSPs, and the epileptogenic action of penicillin in spinal motoneurons. Brain Res. 1977 Jun 17;128(3):569–574. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90184-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyenes M., Farrant M., Farb D. H. "Run-down" of gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptor function during whole-cell recording: a possible role for phosphorylation. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;34(6):719–723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochner B., Spira M. E., Werman R. Penicillin decreases chloride conductance in crustacean muscle: a model for the epileptic neuron. Brain Res. 1976 Apr 30;107(1):85–103. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90097-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Lange K. Estimating kinetic constants from single channel data. Biophys J. 1983 Aug;43(2):207–223. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84341-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R. Statistical methods for model discrimination. Applications to gating kinetics and permeation of the acetylcholine receptor channel. Biophys J. 1987 Feb;51(2):255–263. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83331-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao L. I., Crill W. E. Penicillin-induced segmental myoclonus. I. Motor responses and intracellular recording from motoneurons. Arch Neurol. 1972 Feb;26(2):156–161. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1972.00490080074008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The effect of procaine on the action of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):269–284. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn S. J., Horn R. Statistical discrimination of fractal and Markov models of single-channel gating. Biophys J. 1988 Nov;54(5):871–877. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83023-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Puil E., Werman R. Bicuculline, benzyl penicillin, and inhibitory amino acids in the spinal cord of the cat. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1977 Jun;55(3):670–680. doi: 10.1139/y77-091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald R. L., Rogers C. J., Twyman R. E. Barbiturate regulation of kinetic properties of the GABAA receptor channel of mouse spinal neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1989 Oct;417:483–500. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald R. L., Barker J. L. Pentylenetetrazol and penicillin are selective antagonists of GABA-mediated post-synaptic inhibition in cultured mammalian neurones. Nature. 1977 Jun 23;267(5613):720–721. doi: 10.1038/267720a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald R. L., Barker J. L. Specific antagonism of GABA-mediated postsynaptic inhibition in cultured mammalian spinal cord neurons: a common mode of convulsant action. Neurology. 1978 Apr;28(4):325–330. doi: 10.1212/wnl.28.4.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald R. L., Rogers C. J., Twyman R. E. Kinetic properties of the GABAA receptor main conductance state of mouse spinal cord neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1989 Mar;410:479–499. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBurney R. N., Barker J. L. GABA-induced conductance fluctuations in cultured spinal neurones. Nature. 1978 Aug 10;274(5671):596–597. doi: 10.1038/274596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McManus O. B., Blatz A. L., Magleby K. L. Sampling, log binning, fitting, and plotting durations of open and shut intervals from single channels and the effects of noise. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Nov;410(4-5):530–553. doi: 10.1007/BF00586537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McManus O. B., Magleby K. L. Kinetic time constants independent of previous single-channel activity suggest Markov gating for a large conductance Ca-activated K channel. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Dec;94(6):1037–1070. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.6.1037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer H., Prince D. Convulsant actions of penicillin: effects on inhibitory mechanisms. Brain Res. 1973 Apr 27;53(2):477–482. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90237-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishina M., Takai T., Imoto K., Noda M., Takahashi T., Numa S., Methfessel C., Sakmann B. Molecular distinction between fetal and adult forms of muscle acetylcholine receptor. Nature. 1986 May 22;321(6068):406–411. doi: 10.1038/321406a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Steinbach J. H. Local anaesthetics transiently block currents through single acetylcholine-receptor channels. J Physiol. 1978 Apr;277:153–176. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E. The charge carried by single-channel currents of rat cultured muscle cells in the presence of local anaesthetics. J Physiol. 1983 Jun;339:663–678. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak L., Bregestovski P., Ascher P., Herbet A., Prochiantz A. Magnesium gates glutamate-activated channels in mouse central neurones. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):462–465. doi: 10.1038/307462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickles H. G., Simmonds M. A. Antagonism by penicillin of gamma-aminobutyric acid depolarizations at presynaptic sites in rat olfactory cortex and cuneate nucleus in vitro. Neuropharmacology. 1980 Jan;19(1):35–38. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(80)90163-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter N. M., Twyman R. E., Uhler M. D., Macdonald R. L. Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase decreases GABAA receptor current in mouse spinal neurons. Neuron. 1990 Dec;5(6):789–796. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90338-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince D. A. The depolarization shift in "epileptic" neurons. Exp Neurol. 1968 Aug;21(4):467–485. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(68)90066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raichle M. E., Kutt H., Louis S., McDowell F. Neurotoxicity of intravenously administered penicillin G. Arch Neurol. 1971 Sep;25(3):232–239. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1971.00490030058006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakmann B., Methfessel C., Mishina M., Takahashi T., Takai T., Kurasaki M., Fukuda K., Numa S. Role of acetylcholine receptor subunits in gating of the channel. Nature. 1985 Dec 12;318(6046):538–543. doi: 10.1038/318538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakmann B., Patlak J., Neher E. Single acetylcholine-activated channels show burst-kinetics in presence of desensitizing concentrations of agonist. Nature. 1980 Jul 3;286(5768):71–73. doi: 10.1038/286071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield P. R., Darlison M. G., Fujita N., Burt D. R., Stephenson F. A., Rodriguez H., Rhee L. M., Ramachandran J., Reale V., Glencorse T. A. Sequence and functional expression of the GABA A receptor shows a ligand-gated receptor super-family. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):221–227. doi: 10.1038/328221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigworth F. J., Sine S. M. Data transformations for improved display and fitting of single-channel dwell time histograms. Biophys J. 1987 Dec;52(6):1047–1054. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83298-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. M., Zorec R., McBurney R. N. Conductance states activated by glycine and GABA in rat cultured spinal neurones. J Membr Biol. 1989 Apr;108(1):45–52. doi: 10.1007/BF01870424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twyman R. E., Macdonald R. L. Kinetic properties of the glycine receptor main- and sub-conductance states of mouse spinal cord neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1991 Apr;435:303–331. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twyman R. E., Rogers C. J., Macdonald R. L. Differential regulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor channels by diazepam and phenobarbital. Ann Neurol. 1989 Mar;25(3):213–220. doi: 10.1002/ana.410250302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twyman R. E., Rogers C. J., Macdonald R. L. Intraburst kinetic properties of the GABAA receptor main conductance state of mouse spinal cord neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1990 Apr;423:193–220. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twyman R. E., Rogers C. J., Macdonald R. L. Pentobarbital and picrotoxin have reciprocal actions on single GABAA receptor channels. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Jan 2;96(1):89–95. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90248-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss D. S., Magleby K. L. Gating scheme for single GABA-activated Cl- channels determined from stability plots, dwell-time distributions, and adjacent-interval durations. J Neurosci. 1989 Apr;9(4):1314–1324. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-04-01314.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhull A. M. Ionic blockage of sodium channels in nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Jun;61(6):687–708. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.6.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


