Abstract
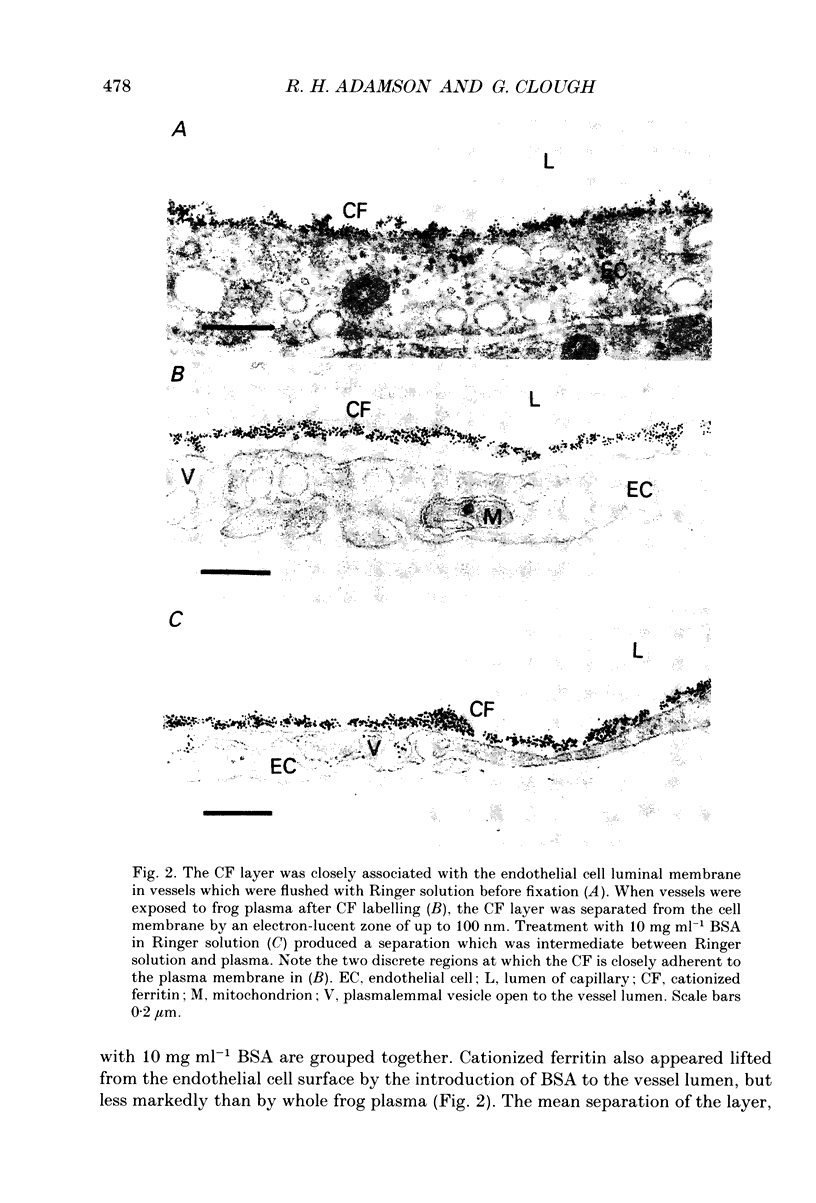
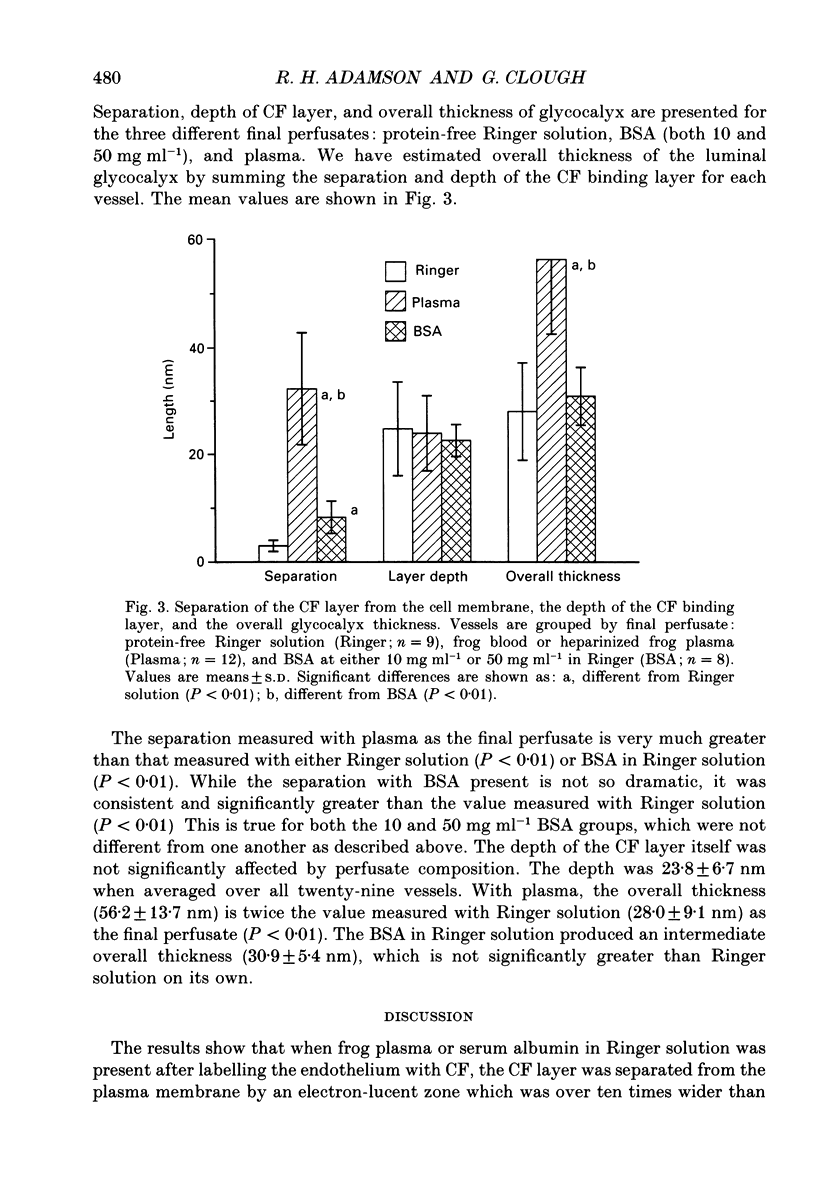
1. We have investigated the interaction of plasma proteins with the endothelial cell using cationized ferritin as a marker of the cell surface glycocalyx. 2. Single microvessels of the frog mesentery were sequentially perfused using glass micropipettes with solutions containing cationized ferritin (CF, 6.7 mg ml-1) in 0.10 M-NaCl and then with either frog plasma or bovine serum albumin (BSA; 50 or 10 mg ml-1), or protein-free Ringer solution, before suffusion fixation in 2.5% glutaraldehyde. 3. A layer of CF, usually two to four molecules thick, was associated with the luminal endothelial cell surface. In vessels post-flushed with protein-free Ringer solution the CF layer was closely adherent to all regions of the luminal endothelium, including the plasma membrane, vesicle diaphragms, coated pits and the entrances to clefts. However, when plasma was present during fixation the CF layer was separated from the cell surface by up to 100 nm over all regions. In vessels post-flushed with BSA the CF layer was also separated from the membrane but the effect was less striking. 4. The association of cationized ferritin with the endothelial cell surface was assessed quantitatively using electron micrographs of transverse sections (approximately 50 nm thick) of the perfused vessels, and expressed in terms of the depth of the layer of CF associated with the endothelial cell surface, its separation from the plasma membrane of the luminal endothelium, and the concentration of CF in the layer. The mean (+/- S.D.) separation in the presence of plasma, 32.3 +/- 10.5 nm (n = 12), was significantly greater (P less than 0.01) than that with either protein-free Ringer solution, 3.0 +/- 1.4 nm (n = 9), or BSA in Ringer solution, 8.3 +/- 3.0 nm (n = 8). The separation seen with BSA in Ringer was also significantly greater than that measured with a final Ringer solution perfusion (P less than 0.01). The effects of 10 and 50 mg ml-1 BSA were not different from one another. The total glycocalyx thickness, defined as the sum of the separation layer and depth of CF layer, with plasma present, 56.2 +/- 13.7 nm, was twice the value seen with Ringer solution, 28.0 +/- 9.1 nm (P less than 0.01), while the total thickness with BSA, 30.9 +/- 5.4 nm, was not different from the Ringer solution value.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson R. H. Permeability of frog mesenteric capillaries after partial pronase digestion of the endothelial glycocalyx. J Physiol. 1990 Sep;428:1–13. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin A. L., Winlove C. P. Effects of perfusate composition on binding of ruthenium red and gold colloid to glycocalyx of rabbit aortic endothelium. J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Mar;32(3):259–266. doi: 10.1177/32.3.6198357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Born G. V., Palinski W. Unusually high concentrations of sialic acids on the surface of vascular endothelia. Br J Exp Pathol. 1985 Oct;66(5):543–549. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundgaard M., Frøkjaer-Jensen J. Functional aspects of the ultrastructure of terminal blood vessels: a qualitative study on consecutive segments of the frog mesenteric microvasculature. Microvasc Res. 1982 Jan;23(1):1–30. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(82)90028-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundgaard M. The three-dimensional organization of tight junctions in a capillary endothelium revealed by serial-section electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1984 Jul;88(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(84)90177-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clough G., Michel C. C. The role of vesicles in the transport of ferritin through frog endothelium. J Physiol. 1981 Jun;315:127–142. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clough G. The steady-state transport of cationized ferritin by endothelial cell vesicles. J Physiol. 1982 Jul;328:389–401. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry F. E., Michel C. C. A fiber matrix model of capillary permeability. Microvasc Res. 1980 Jul;20(1):96–99. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(80)90024-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry F. E., Rutledge J. C., Lenz J. F. Modulation of microvessel wall charge by plasma glycoprotein orosomucoid. Am J Physiol. 1989 Nov;257(5 Pt 2):H1354–H1359. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.257.5.H1354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desjardins C., Duling B. R. Heparinase treatment suggests a role for the endothelial cell glycocalyx in regulation of capillary hematocrit. Am J Physiol. 1990 Mar;258(3 Pt 2):H647–H654. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.258.3.H647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haraldsson B., Rippe B. Orosomucoid as one of the serum components contributing to normal capillary permselectivity in rat skeletal muscle. Acta Physiol Scand. 1987 Jan;129(1):127–135. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1987.tb08047.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley V. H., Curry F. E. Albumin modulation of capillary permeability: test of an adsorption mechanism. Am J Physiol. 1985 Feb;248(2 Pt 2):H264–H273. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1985.248.2.H264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loudon M. F., Michel C. C., White I. F. The labelling of vesicles in frog endothelial cells with ferritin. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:97–112. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft J. H. Fine structures of capillary and endocapillary layer as revealed by ruthenium red. Fed Proc. 1966 Nov-Dec;25(6):1773–1783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann G. E. Alterations of myocardial capillary permeability by albumin in the isolated, perfused rabbit heart. J Physiol. 1981;319:311–323. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason J. C., Curry F. E., Michel C. C. The effects of proteins upon the filtration coefficient of individually perfused frog mesenteric capillaries. Microvasc Res. 1977 Mar;13(2):185–202. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(77)90084-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason J. C., Curry F. E., White I. F., Michel C. C. The ultrastructure of frog mesenteric capillaries of known filtration coefficient. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1979 Jul;64(3):217–224. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1979.sp002474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel C. C., Phillips M. E. The effects of bovine serum albumin and a form of cationised ferritin upon the molecular selectivity of the walls of single frog capillaries. Microvasc Res. 1985 Mar;29(2):190–203. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(85)90016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milici A. J., Watrous N. E., Stukenbrok H., Palade G. E. Transcytosis of albumin in capillary endothelium. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2603–2612. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneeberger E. E., Hamelin M. Interaction of serum proteins with lung endothelial glycocalyx: its effect on endothelial permeability. Am J Physiol. 1984 Aug;247(2 Pt 2):H206–H217. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1984.247.2.H206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnitzer J. E., Carley W. W., Palade G. E. Albumin interacts specifically with a 60-kDa microvascular endothelial glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6773–6777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnitzer J. E., Carley W. W., Palade G. E. Specific albumin binding to microvascular endothelium in culture. Am J Physiol. 1988 Mar;254(3 Pt 2):H425–H437. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1988.254.3.H425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simionescu N., Simionescu M., Palade G. E. Differentiated microdomains on the luminal surface of the capillary endothelium. I. Preferential distribution of anionic sites. J Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;90(3):605–613. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.3.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner M. R., Clough G., Michel C. C. The effects of cationised ferritin and native ferritin upon the filtration coefficient of single frog capillaries. Evidence that proteins in the endothelial cell coat influence permeability. Microvasc Res. 1983 Mar;25(2):205–222. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(83)90016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson P. D. Effects of blood-free and protein-free perfusion on CFC in the isolated cat hindlimb. Am J Physiol. 1983 Dec;245(6):H911–H919. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1983.245.6.H911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]