Abstract
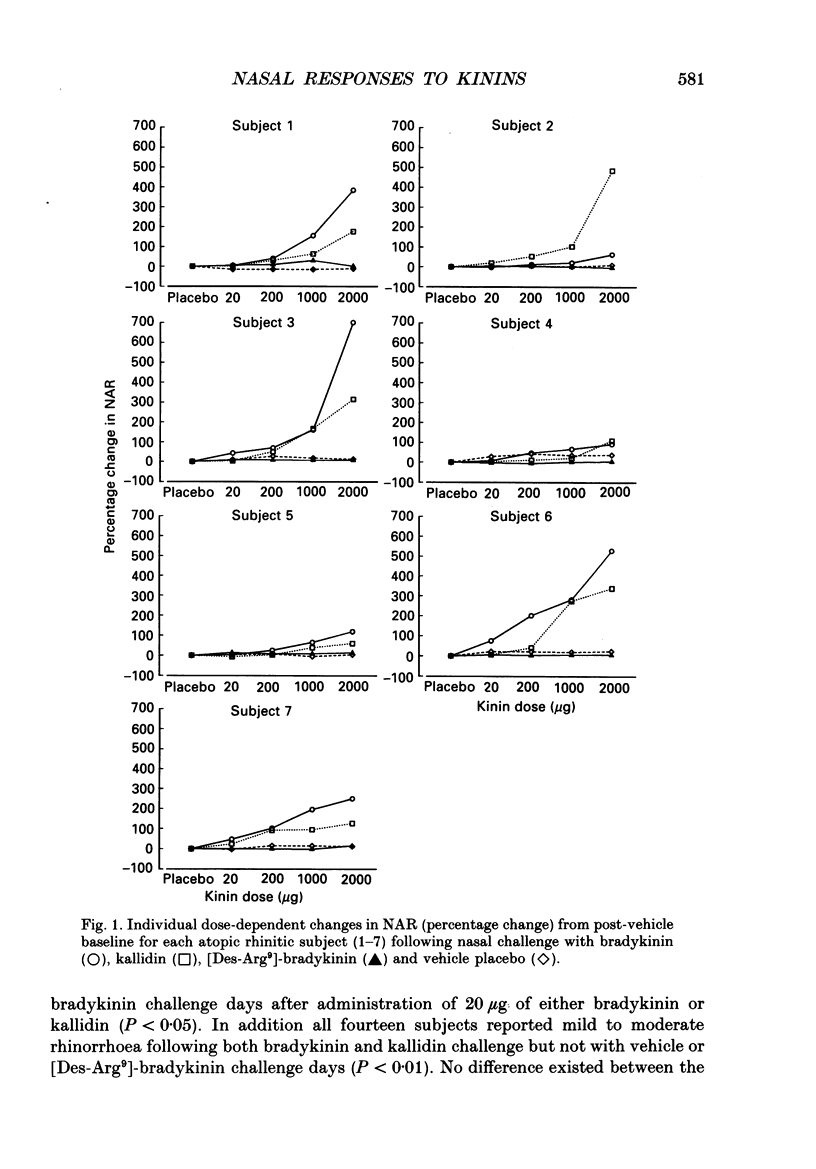
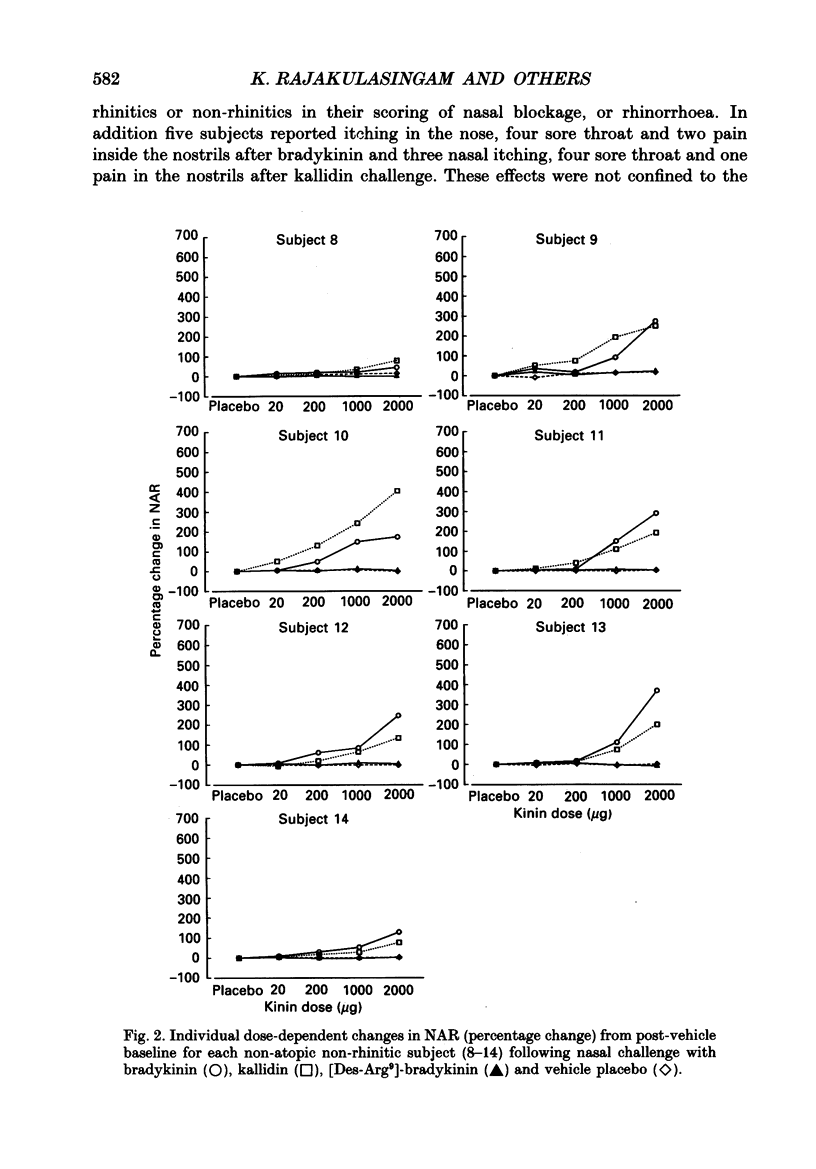
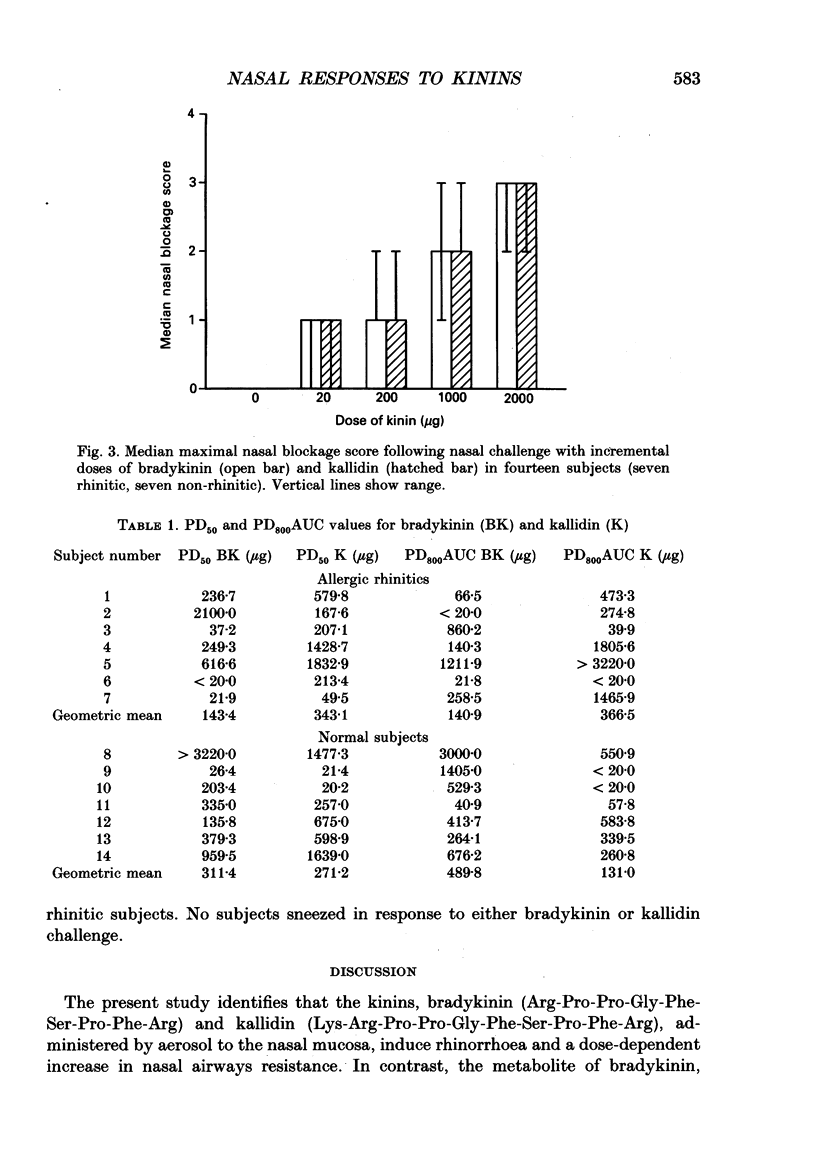
1. The structure-activity relationship of kinins within the nose has been investigated in atopic rhinitic (n = 7) and non-rhinitic (n = 7) subjects. On 4 separate days, each separated by a week, subjects randomly underwent nasal challenge with incremental doses of either the B1 agonist [Des-Arg9]-bradykinin, the B2 agonists kallidin or bradykinin, or vehicle placebo in a double-blind comparative study. The nasal response was monitored objectively by measurement of nasal airways resistance (NAR) by active posterior rhinomanometry and subjectively by symptom reporting of nasal blockage, rhinorrhoea, nasal itch and nasal pain. 2. The B2 agonists kallidin and bradykinin both induced a dose-dependent increase in NAR (P less than 0.001) and were associated with symptomatic reporting of nasal blockage (P less than 0.05), rhinorrhoea (P less than 0.01) and nasal discomfort (P less than 0.05) compared to placebo. In contrast the effects of the B1 agonist [Des-Arg9]-bradykinin on NAR and symptom reporting were indistinguishable from placebo. No difference could be identified in the nasal response to kallidin and bradykinin between rhinitic and non-rhinitic subjects and there was no evidence of B1 receptor upregulation in the disease state. For the whole group the provocative dose of agonist inducing a 50% increase in NAR (PD50) was 1.77 x 10(-4) mol for bradykinin and 2.86 x 10(-4) mol for kallidin (P greater than 0.05). 3. These findings identify that the nasal effects of kinins are mediated through B2 receptors and the advent of B2 receptor antagonists will permit a further evaluation of the role of kinins in rhinitis.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baraniuk J. N., Lundgren J. D., Mizoguchi H., Peden D., Gawin A., Merida M., Shelhamer J. H., Kaliner M. A. Bradykinin and respiratory mucous membranes. Analysis of bradykinin binding site distribution and secretory responses in vitro and in vivo. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Mar;141(3):706–714. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/141.3.706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrow S. E., Dollery C. T., Heavey D. J., Hickling N. E., Ritter J. M., Vial J. Effect of vasoactive peptides on prostacyclin synthesis in man. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Jan;87(1):243–247. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10177.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conklin B. R., Burch R. M., Steranka L. R., Axelrod J. Distinct bradykinin receptors mediate stimulation of prostaglandin synthesis by endothelial cells and fibroblasts. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Feb;244(2):646–649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossman D. C., Fuller R. W. Bradykinin induced wheal and flare is not mediated by histamine release or cyclooxygenase products. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1988 Jul;26(1):113–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1988.tb03375.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B., Roberts A. M., Coleridge H. M., Coleridge J. C. Reflex tracheal gland secretion evoked by stimulation of bronchial C-fibers in dogs. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982 Oct;53(4):985–991. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.53.4.985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deblois D., Bouthillier J., Marceau F. Effect of glucocorticoids, monokines and growth factors on the spontaneously developing responses of the rabbit isolated aorta to des-Arg9-bradykinin. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Apr;93(4):969–977. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11487.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devillier P., Renoux M., Giroud J. P., Regoli D. Peptides and histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Oct 29;117(1):89–96. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90475-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsch W., Ring J., Reimann H. J., Geiger R. Mediator studies in skin blister fluid from patients with dual skin reactions after intradermal allergen injection. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1982 Oct;70(4):236–242. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(82)90059-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drouin J. N., St-Pierre S. A., Regoli D. Receptors for bradykinin and kallidin. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1979 Apr;57(4):375–379. doi: 10.1139/y79-056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geppetti P., Maggi C. A., Perretti F., Frilli S., Manzini S. Simultaneous release by bradykinin of substance P- and calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactivities from capsaicin-sensitive structures in guinea-pig heart. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jun;94(2):288–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howarth P. H. Allergic rhinitis: a rational choice of treatment. Respir Med. 1989 May;83(3):179–188. doi: 10.1016/s0954-6111(89)80029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Iwata M., Ishizaka K. Release of histamine and arachidonate from mouse mast cells induced by glycosylation-enhancing factor and bradykinin. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1880–1887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leikauf G. D., Ueki I. F., Nadel J. A., Widdicombe J. H. Bradykinin stimulates Cl secretion and prostaglandin E2 release by canine tracheal epithelium. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jan;248(1 Pt 2):F48–F55. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.1.F48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marceau F., Lussier A., Regoli D., Giroud J. P. Pharmacology of kinins: their relevance to tissue injury and inflammation. Gen Pharmacol. 1983;14(2):209–229. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(83)90001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naclerio R. M., Proud D., Lichtenstein L. M., Kagey-Sobotka A., Hendley J. O., Sorrentino J., Gwaltney J. M. Kinins are generated during experimental rhinovirus colds. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jan;157(1):133–142. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.1.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polosa R., Phillips G. D., Lai C. K., Holgate S. T. Contribution of histamine and prostanoids to bronchoconstriction provoked by inhaled bradykinin in atopic asthma. Allergy. 1990 Apr;45(3):174–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1990.tb00480.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proud D., Reynolds C. J., Lacapra S., Kagey-Sobotka A., Lichtenstein L. M., Naclerio R. M. Nasal provocation with bradykinin induces symptoms of rhinitis and a sore throat. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Mar;137(3):613–616. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.3.613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proud D., Togias A., Naclerio R. M., Crush S. A., Norman P. S., Lichtenstein L. M. Kinins are generated in vivo following nasal airway challenge of allergic individuals with allergen. J Clin Invest. 1983 Nov;72(5):1678–1685. doi: 10.1172/JCI111127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rangachari P. K., McWade D., Donoff B. Luminal receptors for bradykinin on the canine tracheal epithelium: functional subtyping. Regul Pept. 1988 Jun;21(3-4):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(88)90006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Barabé J. Pharmacology of bradykinin and related kinins. Pharmacol Rev. 1980 Mar;32(1):1–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Marceau F., Barabé J. De novo formation of vascular receptors for bradykinin. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1978 Aug;56(4):674–677. doi: 10.1139/y78-109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis M. L., Okino L., Rocha e Silva M. Comparative pharmacological actions of bradykinin and related kinins of larger molecular weights. Biochem Pharmacol. 1971 Nov;20(11):2935–2946. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(71)90096-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saria A., Martling C. R., Yan Z., Theodorsson-Norheim E., Gamse R., Lundberg J. M. Release of multiple tachykinins from capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerves in the lung by bradykinin, histamine, dimethylphenyl piperazinium, and vagal nerve stimulation. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Jun;137(6):1330–1335. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.6.1330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. L., Kagey-Sobotka A., Bleecker E. R., Traystman R., Kaplan A. P., Gralnick H., Valentine M. D., Permutt S., Lichtenstein L. M. Physiologic manifestations of human anaphylaxis. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):1072–1080. doi: 10.1172/JCI109936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson C., Andersson M., Persson C. G., Venge P., Alkner U., Pipkorn U. Albumin, bradykinins, and eosinophil cationic protein on the nasal mucosal surface in patients with hay fever during natural allergen exposure. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1990 May;85(5):828–833. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(90)90064-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN ARMAN C. G., MILLER L. M. Close similarity and minor differences between bradykinin and kallidin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1961 Mar;131:366–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


