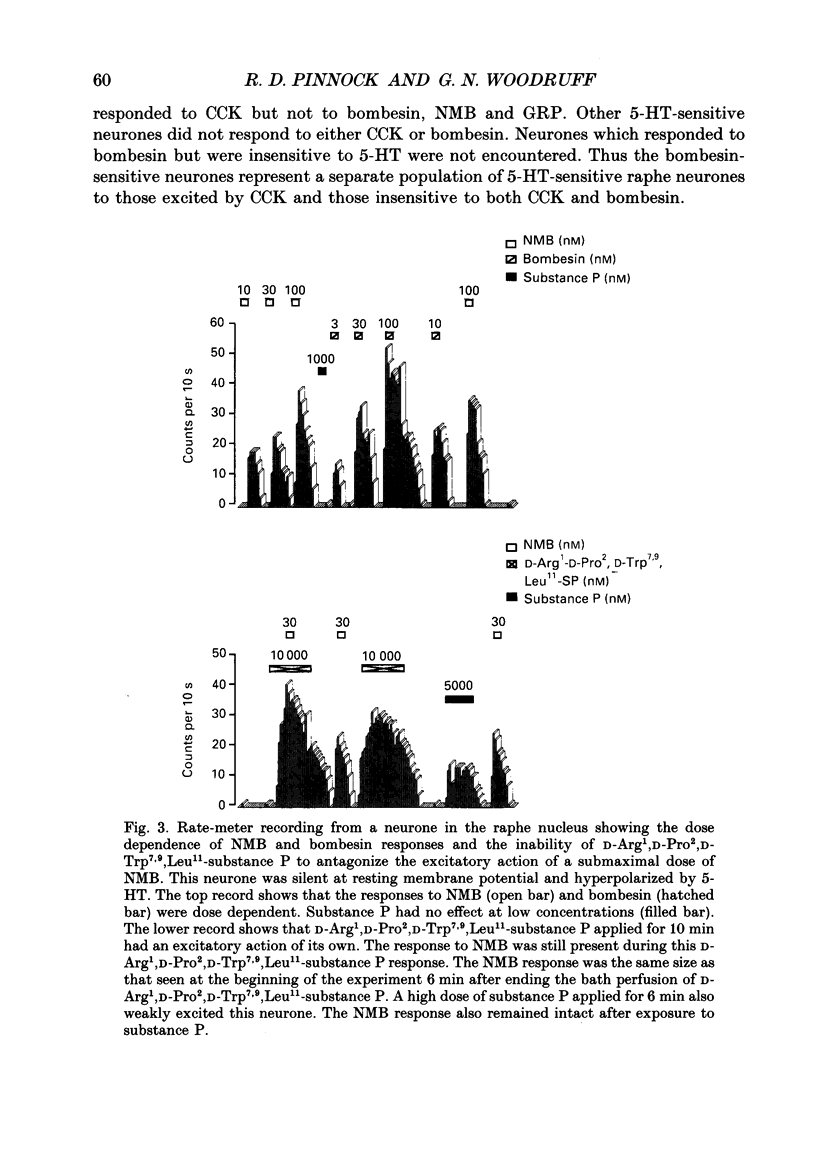
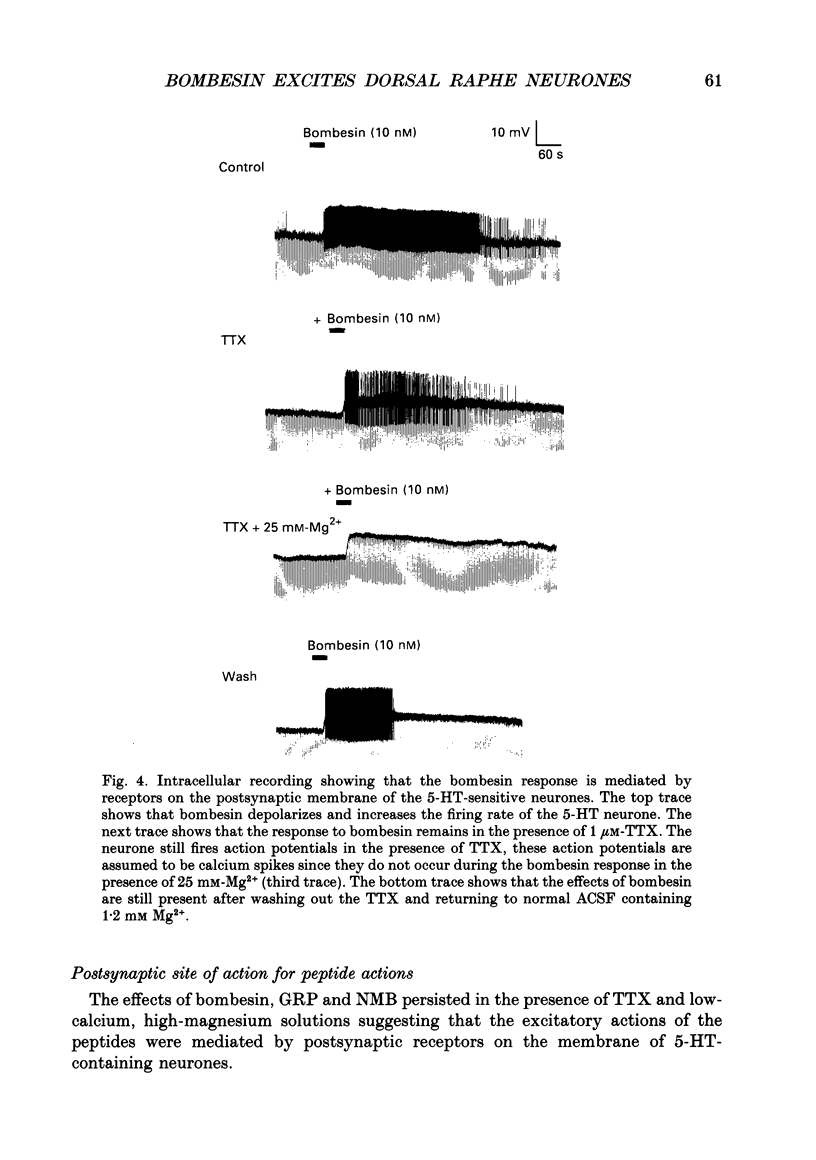
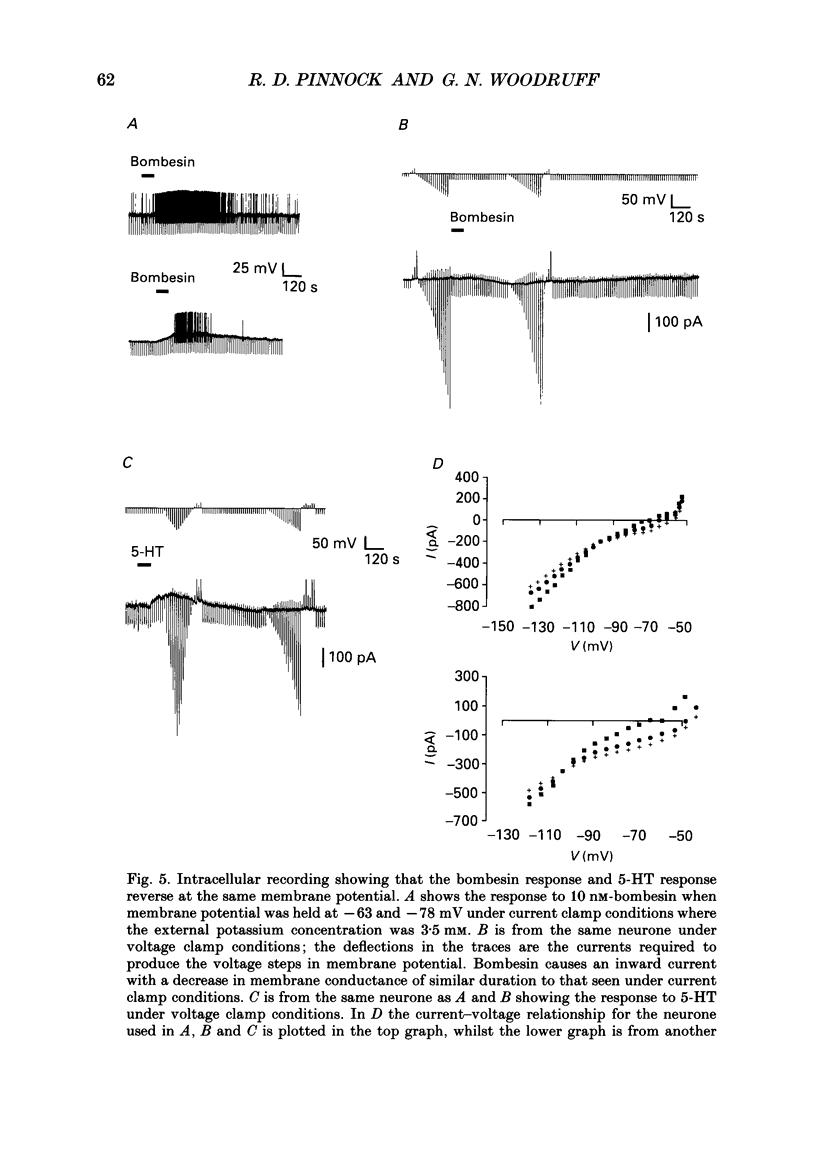
Abstract
1. The effects on dorsal raphe neurones of the peptides bombesin, gastrin-releasing peptide and neuromedin B were studied using intracellular recording techniques from slices of rat brain maintained in vitro. The peptides were added to the solutions perfusing the slices. 2. The peptides bombesin, gastrin-releasing peptide and neuromedin B depolarized neurones in the dorsal raphe nucleus. The same neurones were depolarized by phenylephrine and hyperpolarized by 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) but were insensitive to sulphated cholecystokinin octapeptide (CCK). 3. The responses to the peptides were not blocked by CCKA, CCKB and alpha 1-adrenoreceptor antagonists. 4. The response to the peptides persisted in the presence of tetrodotoxin (TTX) and low-calcium, high-magnesium-containing artificial cerebrospinal fluid (ACSF). 5. Under voltage clamp conditions the peptides caused a decrease in membrane conductance accompanied by an inward current. The reversal potential for the event was the same as that for 5-HT. 6. The results of the present study demonstrate that bombesin and the structurally related peptides gastrin-releasing peptide (GRP) and neuromedin B depolarized a subpopulation of raphe 5-HT neurones by acting on a postsynaptically located receptor linked to potassium channels.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aghajanian G. K. Modulation of a transient outward current in serotonergic neurones by alpha 1-adrenoceptors. Nature. 1985 Jun 6;315(6019):501–503. doi: 10.1038/315501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baraban J. M., Aghajanian G. K. Noradrenergic innervation of serotonergic neurons in the dorsal raphe: demonstration by electron microscopic autoradiography. Brain Res. 1981 Jan 5;204(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90646-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boden P. R., Woodruff G. N., Pinnock R. D. Pharmacology of a cholecystokinin receptor on 5-hydroxytryptamine neurones in the dorsal raphe of the rat brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;102(3):635–638. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12225.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreifuss J. J., Raggenbass M. Tachykinins and bombesin excite non-pyramidal neurones in rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1986 Oct;379:417–428. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erspamer V., Erspamer G. F., Inselvini M., Negri L. Occurrence of bombesin and alytesin in extracts of the skin of three European discoglossid frogs and pharmacological actions of bombesin on extravascular smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Jun;45(2):333–348. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb08087.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gmerek D. E., Cowan A. Role of opioid receptors in bombesin-induced grooming. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;525:291–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb38614.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halfpenny P. R., Horwell D. C., Hughes J., Hunter J. C., Rees D. C. Highly selective kappa-opioid analgesics. 3. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of novel N-[2-(1-pyrrolidinyl)-4- or -5-substituted-cyclohexyl]arylacetamide derivatives. J Med Chem. 1990 Jan;33(1):286–291. doi: 10.1021/jm00163a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J., Boden P., Costall B., Domeney A., Kelly E., Horwell D. C., Hunter J. C., Pinnock R. D., Woodruff G. N. Development of a class of selective cholecystokinin type B receptor antagonists having potent anxiolytic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6728–6732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo K., Mitchell J. A., de Nucci G., Vane J. R. Simultaneous measurement of endothelium-derived relaxing factor by bioassay and guanylate cyclase stimulation. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Oct;98(2):630–636. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12637.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan Z. Z., Colmers W. F., Williams J. T. 5-HT-mediated synaptic potentials in the dorsal raphe nucleus: interactions with excitatory amino acid and GABA neurotransmission. J Neurophysiol. 1989 Aug;62(2):481–486. doi: 10.1152/jn.1989.62.2.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philpott H. G., Petersen O. H. Separate activation sites for cholecystokinin and bombesin on pancreatic acini: an electrophysiological study employing a competitive antagonist for the action of CCK. Pflugers Arch. 1979 Nov;382(3):263–267. doi: 10.1007/BF00583711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spindel E. R., Chin W. W., Price J., Rees L. H., Besser G. M., Habener J. F. Cloning and characterization of cDNAs encoding human gastrin-releasing peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5699–5703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. T., Colmers W. F., Pan Z. Z. Voltage- and ligand-activated inwardly rectifying currents in dorsal raphe neurons in vitro. J Neurosci. 1988 Sep;8(9):3499–3506. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-09-03499.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura M., Higashi H. 5-Hydroxytryptamine mediates inhibitory postsynaptic potentials in rat dorsal raphe neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Jan 7;53(1):69–74. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90099-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


