Abstract
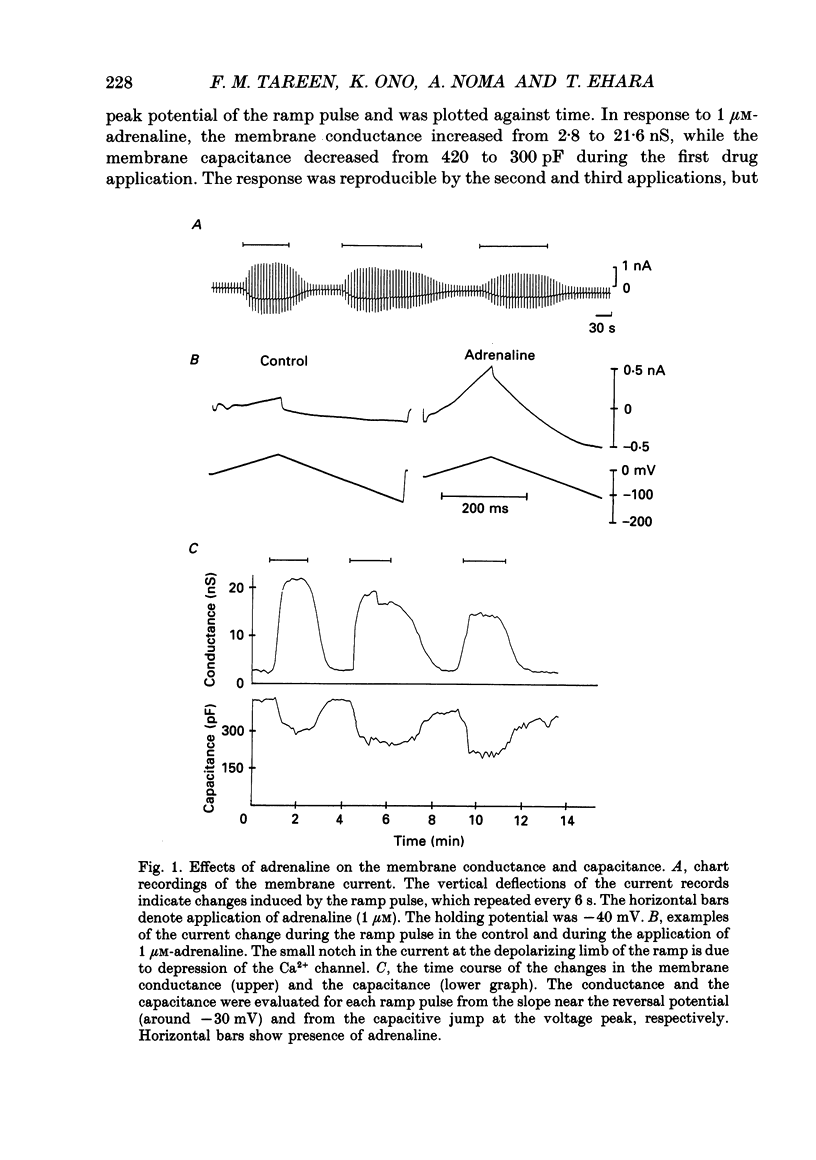
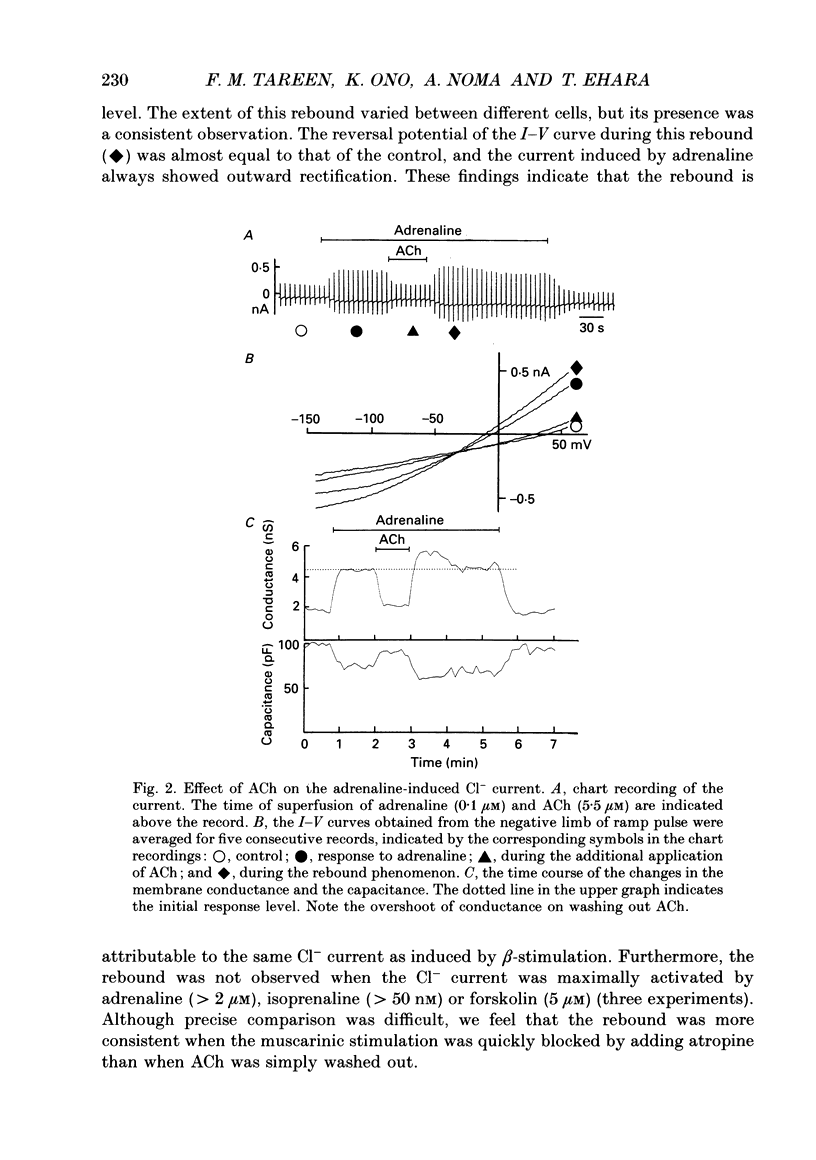
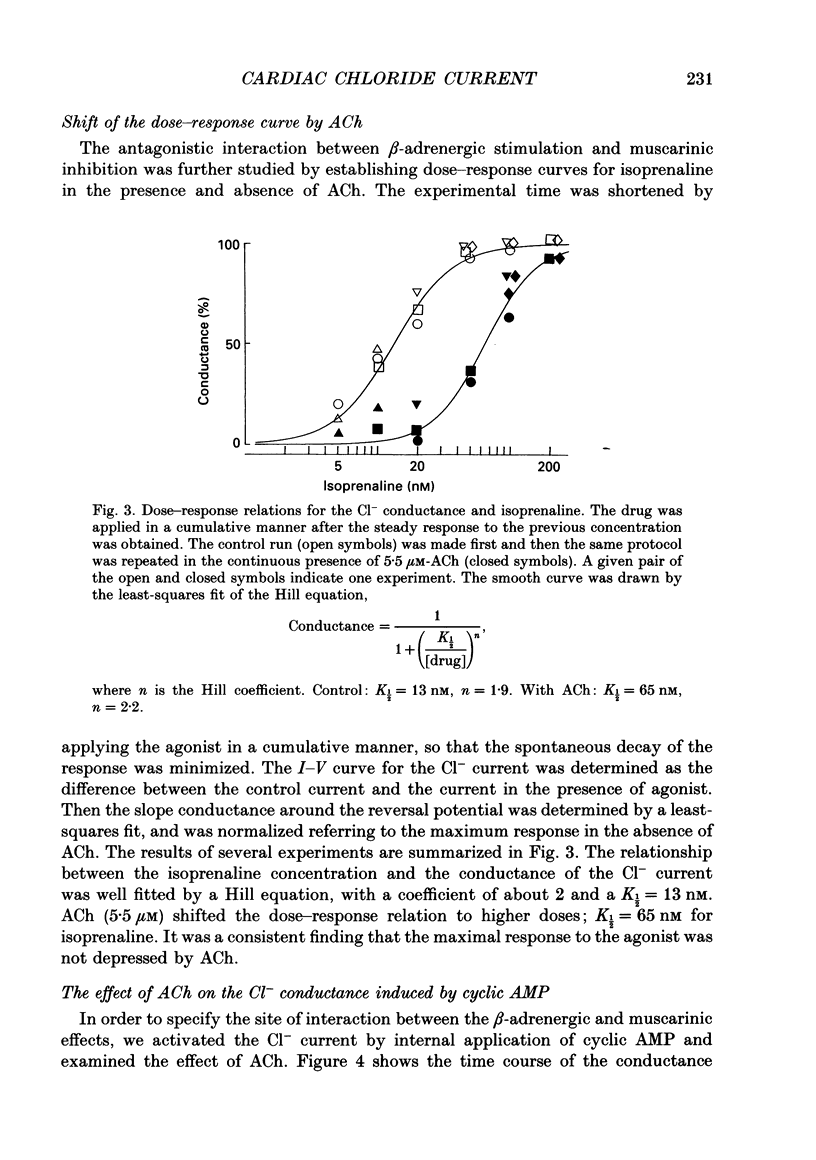
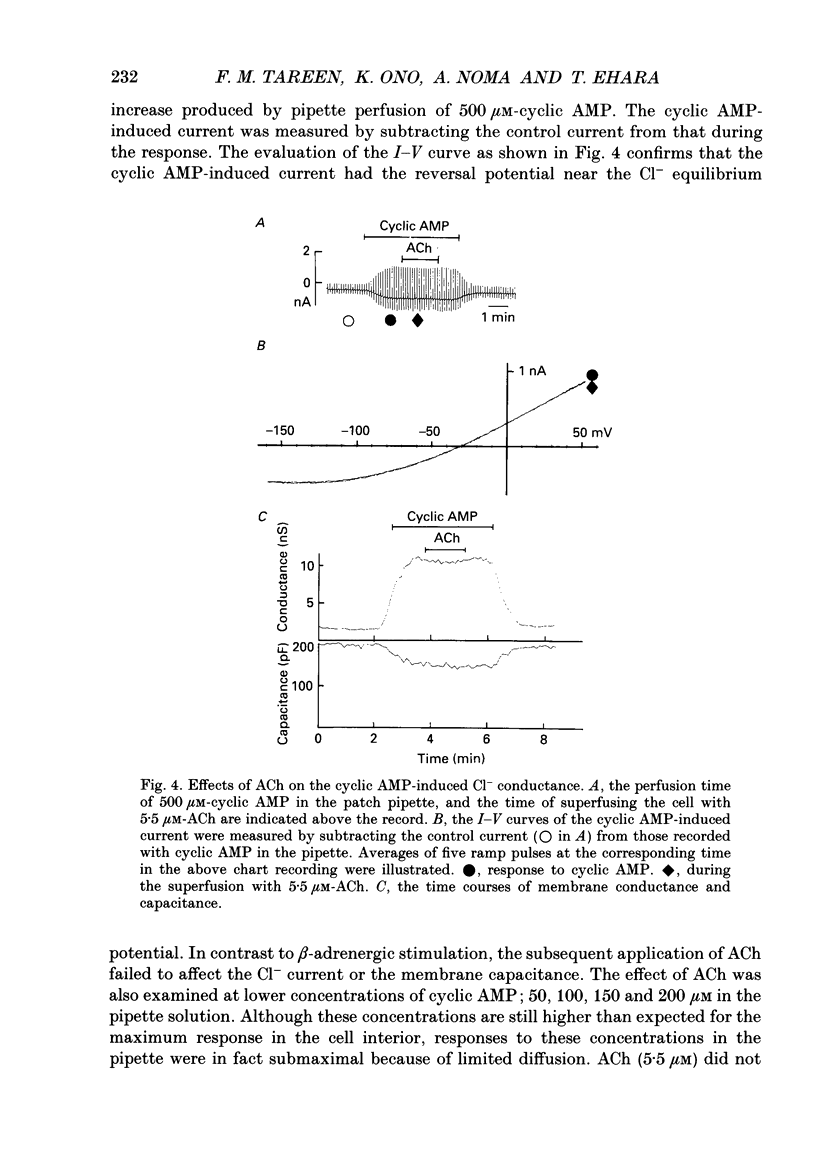
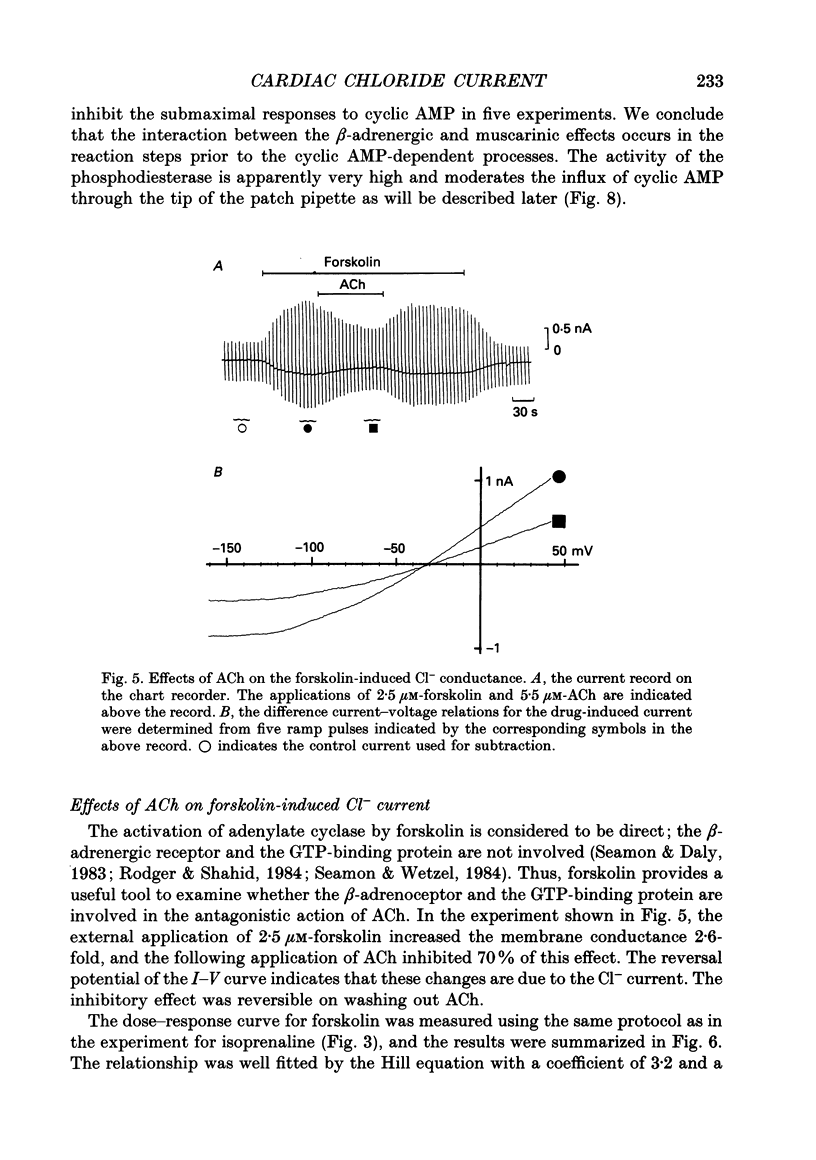
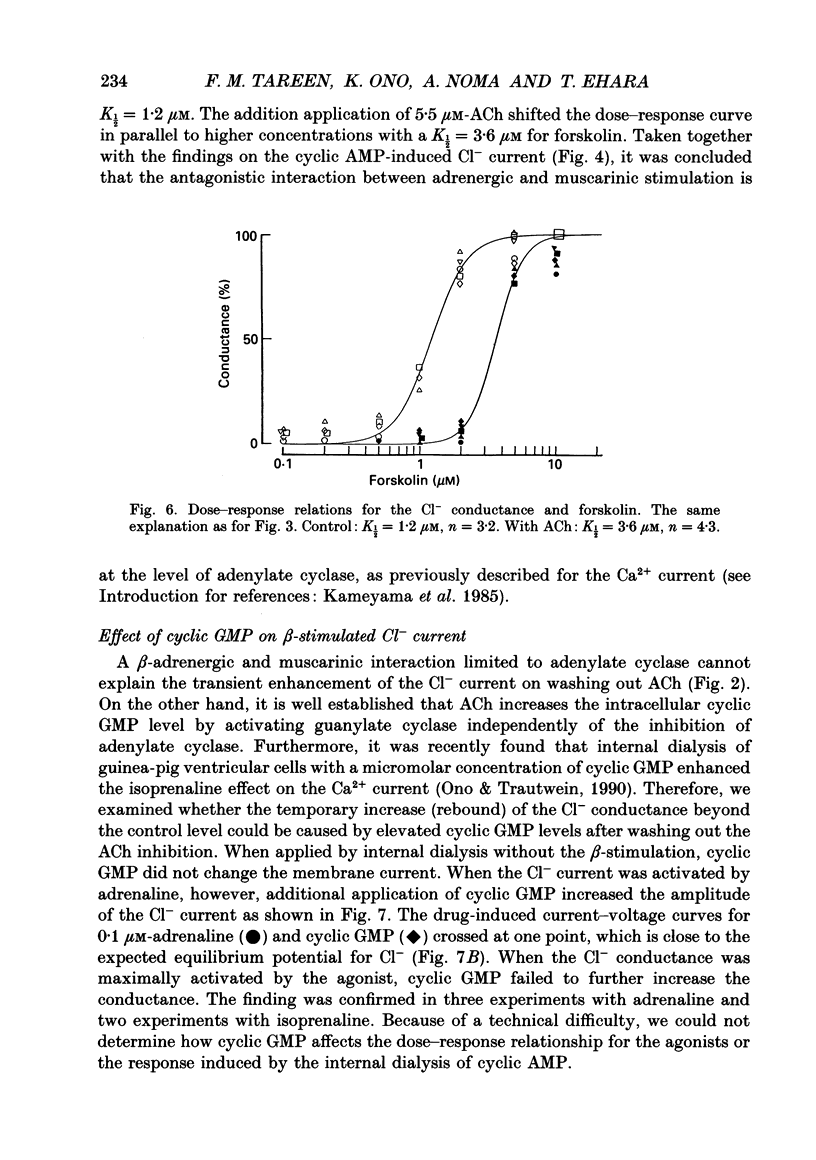
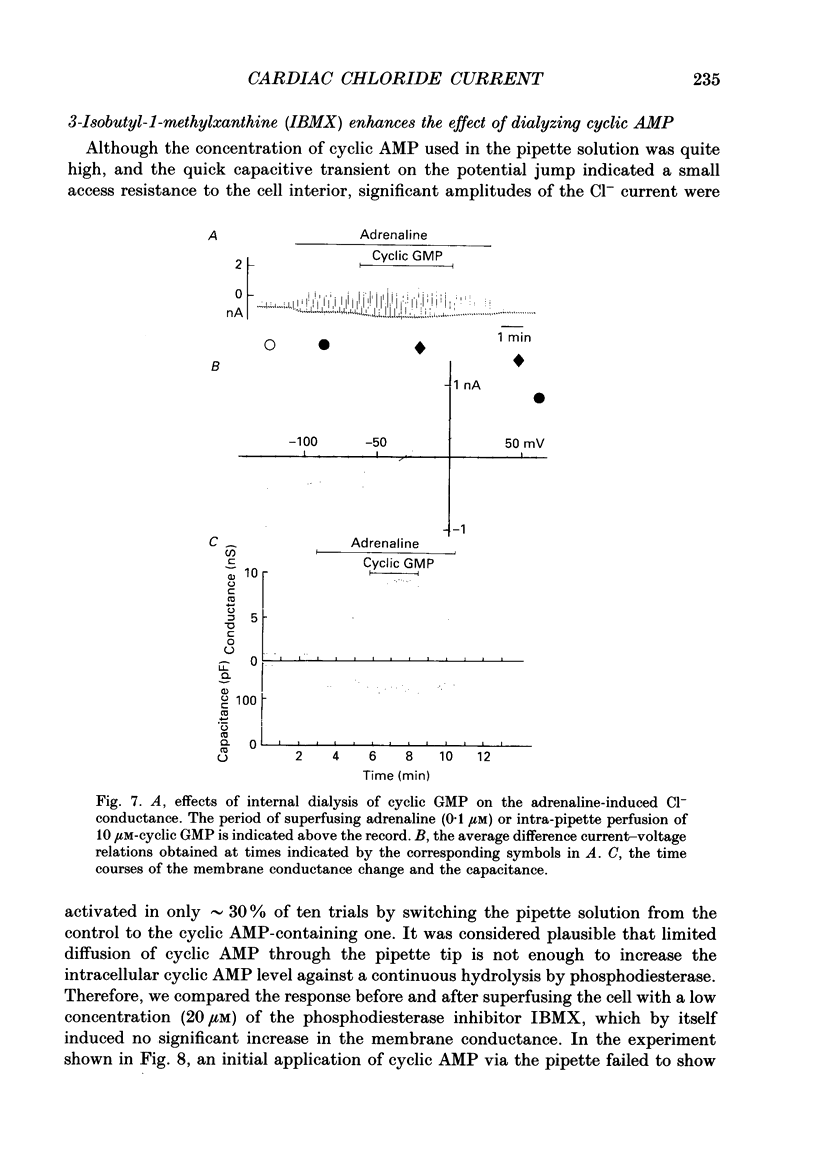
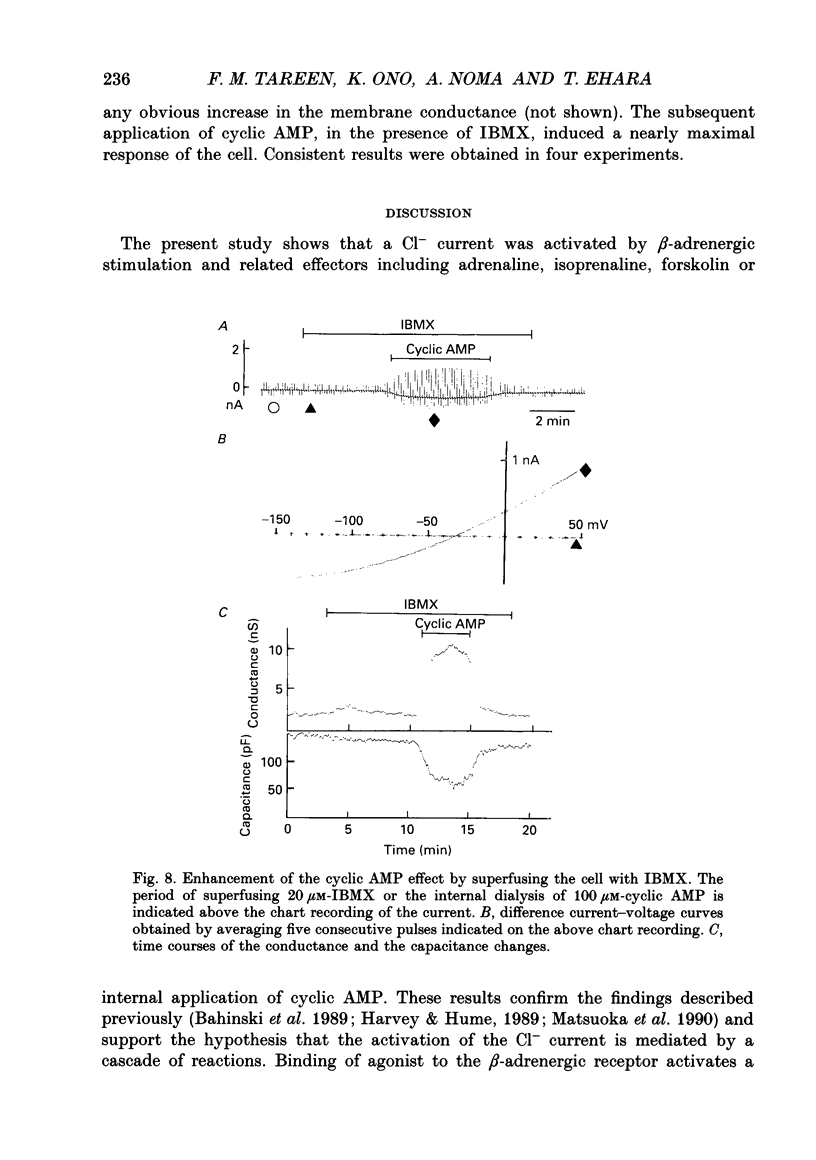
1. Single guinea-pig ventricular cells were voltage clamped using the patch clamp method combined with the pipette-perfusion technique. The voltage-dependent current systems were mostly blocked, and the background membrane conductance was measured by applying ramp pulses. 2. beta-Adrenergic effectors and related substances such as adrenaline, isoprenaline, forskolin or internal application of cyclic AMP induced a current component which showed a reversal potential near the expected Cl- equilibrium potential as well as an outward rectification in the I-V relation. It is suggested that the activation of this Cl- current was due to phosphorylation of the channel protein or related structure by the cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Coincidentally with the activation of the Cl- current, the membrane capacitance of the cell decreased reversibly. 3. Acetylcholine (ACh) depressed the responses induced by beta-adrenergic stimulation and forskolin, but failed to interfere with the one induced by cyclic AMP. 4. The dose dependence of the Cl- current activation by isoprenaline or forskolin was fitted by the Hill equation, with a coefficient of 1.9 and a half-maximum concentration K 1/2 = 13 nM for isoprenaline, and with a Hill coefficient of 3 and a K 1/2 = 1.2 microM for forskolin. In the presence of 5.5 microM-ACh the dose-response relation shifted to higher doses; K 1/2 was 65 nM for isoprenaline and 3.6 microM for forskolin. 5. Washing out ACh in the presence of isoprenaline frequently caused transient overshoots of the response. When a saturating concentration of isoprenaline was used, this rebound was not observed. 6. The internal application of cyclic GMP enhanced the response of the Cl- current induced by isoprenaline or adrenaline. 7. When cyclic AMP was applied internally, the response was small in most cells. When the cell was superfused with 20 microM-IBMX (3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine), the Cl- current was consistently induced by the application of cyclic AMP. It is suggested that phosphodiesterase activity strongly buffered the influx of cyclic AMP through the patch pipette tip. 8. We suggest that the compensatory interaction between the beta-adrenergic stimulation and the muscarinic inhibition is at the membrane level, most probably via GTP-binding proteins in activating adenylate cyclase.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bahinski A., Nairn A. C., Greengard P., Gadsby D. C. Chloride conductance regulated by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase in cardiac myocytes. Nature. 1989 Aug 31;340(6236):718–721. doi: 10.1038/340718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biegon R. L., Epstein P. M., Pappano A. J. Muscarinic antagonism of the effects of phosphodiesterase inhibitor (methylisobutylxanthine) in embryonic chick ventricle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Nov;215(2):348–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooker G. Dissociation of cyclic GMP from the negative inotropic action of carbachol in guinea pig atria. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1977 Dec;3(6):407–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmeliet E., Mubagwa K. Characterization of the acetylcholine-induced potassium current in rabbit cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1986 Feb;371:219–237. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly J. W. Forskolin, adenylate cyclase, and cell physiology: an overview. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1984;17:81–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D. The cardiac hyperpolarizing-activated current, if. Origins and developments. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1985;46(3):163–183. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(85)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D., Tromba C. Muscarinic control of the hyperpolarization-activated current (if) in rabbit sino-atrial node myocytes. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:493–510. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J., Ten Eick R. E., Trapani A. J. Are increases in cyclic GMP levels responsible for the negative inotropic effects of acetylcholine in the heart? Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Dec 7;79(3):912–918. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91197-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan T. M., Noble D., Noble S. J., Powell T., Twist V. W., Yamaoka K. On the mechanism of isoprenaline- and forskolin-induced depolarization of single guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. J Physiol. 1988 Jun;400:299–320. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehara T., Ishihara K. Anion channels activated by adrenaline in cardiac myocytes. Nature. 1990 Sep 20;347(6290):284–286. doi: 10.1038/347284a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endoh M., Maruyama M., Iijima T. Attenuation of muscarinic cholinergic inhibition by islet-activating protein in the heart. Am J Physiol. 1985 Aug;249(2 Pt 2):H309–H320. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1985.249.2.H309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endoh M. The time course of changes in cyclic nucleotide levels during cholinergic inhibition of positive inotropic actions of isoprenaline and theophylline in the isolated canine ventricular myocardium. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980 Jun;312(2):175–182. doi: 10.1007/BF00569727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischmeister R., Hartzell H. C. Cyclic guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate regulates the calcium current in single cells from frog ventricle. J Physiol. 1987 Jun;387:453–472. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischmeister R., Hartzell H. C. Mechanism of action of acetylcholine on calcium current in single cells from frog ventricle. J Physiol. 1986 Jul;376:183–202. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischmeister R., Shrier A. Interactive effects of isoprenaline, forskolin and acetylcholine on Ca2+ current in frog ventricular myocytes. J Physiol. 1989 Oct;417:213–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flitney F. W., Singh J. Evidence that cyclic GMP may regulate cyclic AMP metabolism in the isolated frog ventricle. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1981 Nov;13(11):963–979. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(81)90472-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadsby D. C. Beta-adrenoceptor agonists increase membrane K+ conductance in cardiac Purkinje fibres. Nature. 1983 Dec 15;306(5944):691–693. doi: 10.1038/306691a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George W. J., Polson J. B., O'Toole A. G., Goldberg N. D. Elevation of guanosine 3',5'-cyclic phosphate in rat heart after perfusion with acetylcholine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):398–403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock A. A., DeLean A. L., Lefkowitz R. J. Quantitative resolution of beta-adrenergic receptor subtypes by selective ligand binding: application of a computerized model fitting technique. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Jul;16(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell H. C. Distribution of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors and presynaptic nerve terminals in amphibian heart. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jul;86(1):6–20. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.1.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell H. C., Fischmeister R. Effect of forskolin and acetylcholine on calcium current in single isolated cardiac myocytes. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Nov;32(5):639–645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell H. C., Fischmeister R. Opposite effects of cyclic GMP and cyclic AMP on Ca2+ current in single heart cells. Nature. 1986 Sep 18;323(6085):273–275. doi: 10.1038/323273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. D., Hume J. R. Autonomic regulation of a chloride current in heart. Science. 1989 May 26;244(4907):983–985. doi: 10.1126/science.2543073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hescheler J., Kameyama M., Trautwein W. On the mechanism of muscarinic inhibition of the cardiac Ca current. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Aug;407(2):182–189. doi: 10.1007/BF00580674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisatome I., Kiyosue T., Imanishi S., Arita M. Isoproterenol inhibits residual fast channel via stimulation of beta-adrenoceptors in guinea-pig ventricular muscle. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1985 Jul;17(7):657–665. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2828(85)80065-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg G., Klockner U. Calcium tolerant ventricular myocytes prepared by preincubation in a "KB medium". Pflugers Arch. 1982 Oct;395(1):6–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00584963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameyama M., Hescheler J., Hofmann F., Trautwein W. Modulation of Ca current during the phosphorylation cycle in the guinea pig heart. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Aug;407(2):123–128. doi: 10.1007/BF00580662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameyama M., Hofmann F., Trautwein W. On the mechanism of beta-adrenergic regulation of the Ca channel in the guinea-pig heart. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Oct;405(3):285–293. doi: 10.1007/BF00582573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi R. C., Alloatti G., Fischmeister R. Cyclic GMP regulates the Ca-channel current in guinea pig ventricular myocytes. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Apr;413(6):685–687. doi: 10.1007/BF00581823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linden J., Hollen C. E., Patel A. The mechanism by which adenosine and cholinergic agents reduce contractility in rat myocardium. Correlation with cyclic adenosine monophosphate and receptor densities. Circ Res. 1985 May;56(5):728–735. doi: 10.1161/01.res.56.5.728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka S., Ehara T., Noma A. Chloride-sensitive nature of the adrenaline-induced current in guinea-pig cardiac myocytes. J Physiol. 1990 Jun;425:579–598. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAfee D. A., Whiting G. J., Siegel B. Neurotransmitter and cyclic nucleotide modulation of frog cardiac contractility. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1978 Aug;10(8):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(78)90405-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Clapham D. E. Roles of G protein subunits in transmembrane signalling. Nature. 1988 May 12;333(6169):129–134. doi: 10.1038/333129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell T., Terrar D. A., Twist V. W. Electrical properties of individual cells isolated from adult rat ventricular myocardium. J Physiol. 1980 May;302:131–153. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H. Calcium channel modulation by neurotransmitters, enzymes and drugs. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):569–574. doi: 10.1038/301569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodger I. W., Shahid M. Forskolin, cyclic nucleotides and positive inotropism in isolated papillary muscles of the rabbit. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Jan;81(1):151–159. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10755.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert B., VanDongen A. M., Kirsch G. E., Brown A. M. Beta-adrenergic inhibition of cardiac sodium channels by dual G-protein pathways. Science. 1989 Aug 4;245(4917):516–519. doi: 10.1126/science.2547248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seamon K. B., Wetzel B. Interaction of forskolin with dually regulated adenylate cyclase. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1984;17:91–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soejima M., Noma A. Mode of regulation of the ACh-sensitive K-channel by the muscarinic receptor in rabbit atrial cells. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Apr;400(4):424–431. doi: 10.1007/BF00587544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Bean B. P., Hess P., Lansman J. B., Nilius B., Nowycky M. C. Mechanisms of calcium channel modulation by beta-adrenergic agents and dihydropyridine calcium agonists. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1986 Jul;18(7):691–710. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2828(86)80941-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe A. M., Besch H. R., Jr Interaction between cyclic adenosine monophosphate and cyclic gunaosine monophosphate in guinea pig ventricular myocardium. Circ Res. 1975 Sep;37(3):309–317. doi: 10.1161/01.res.37.3.309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


