Abstract
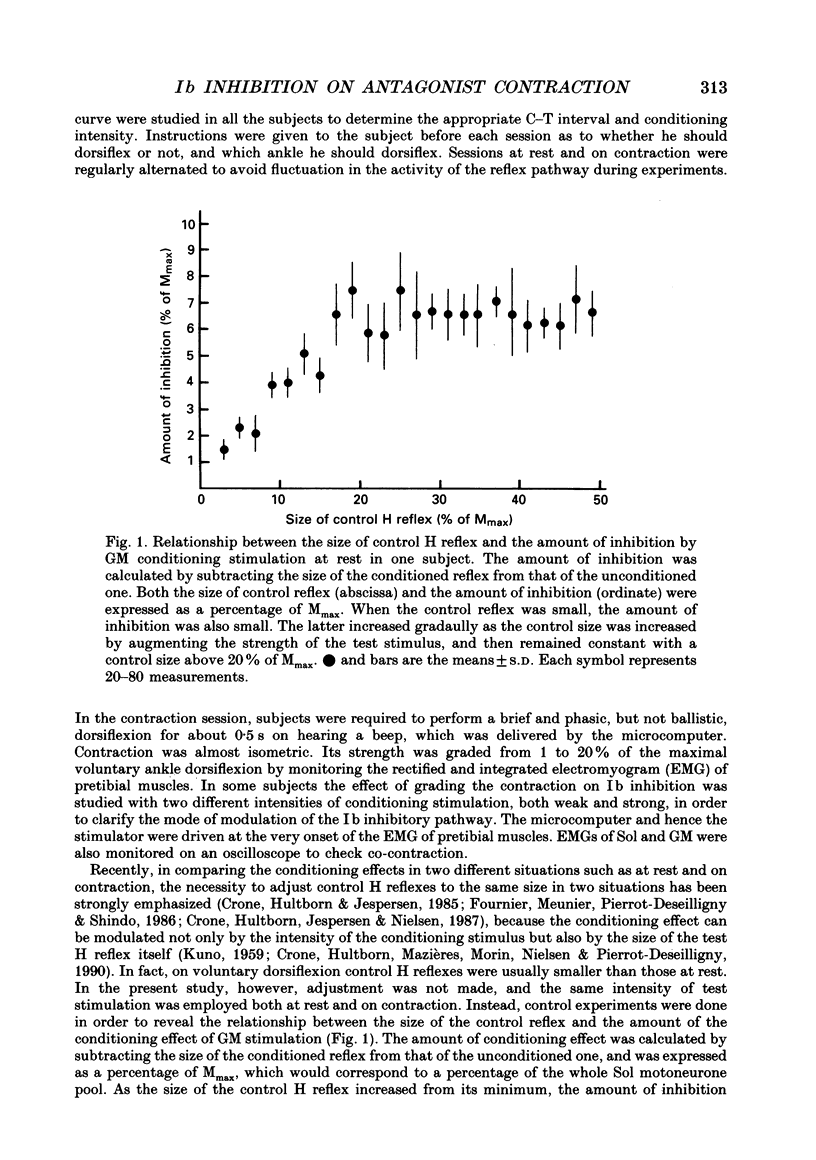
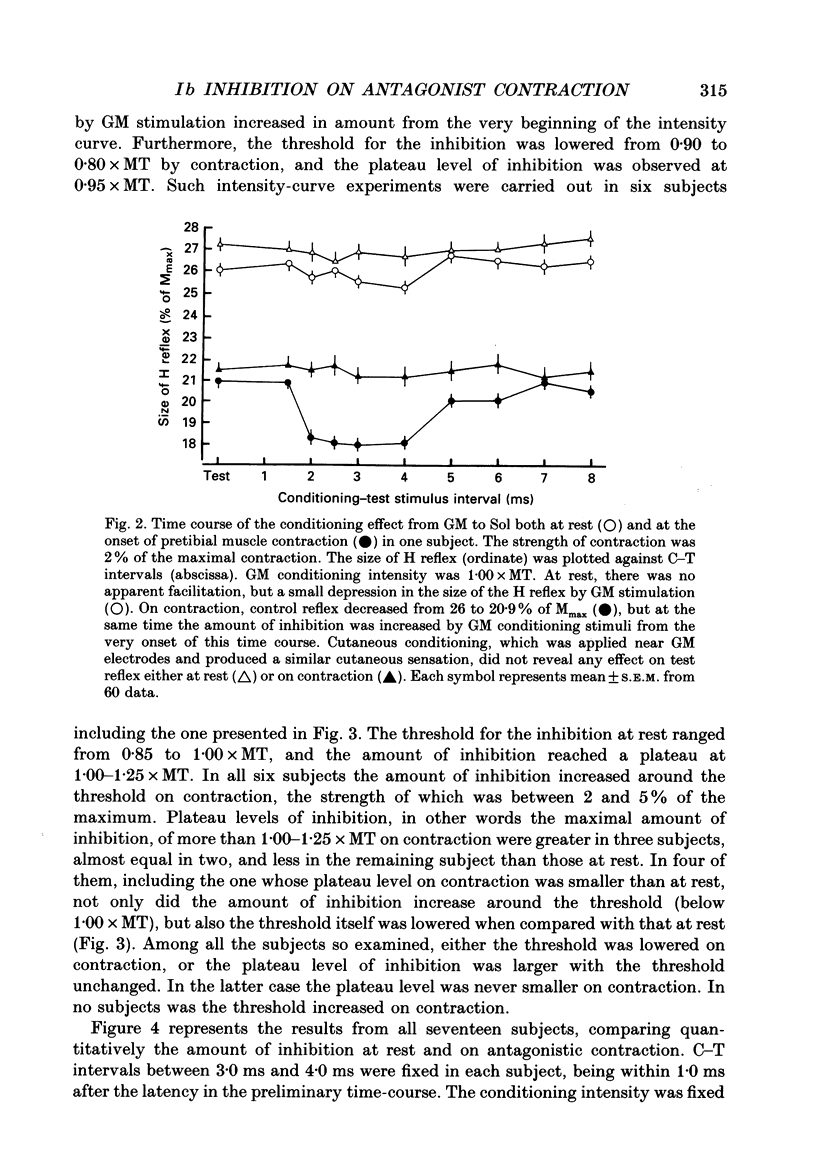
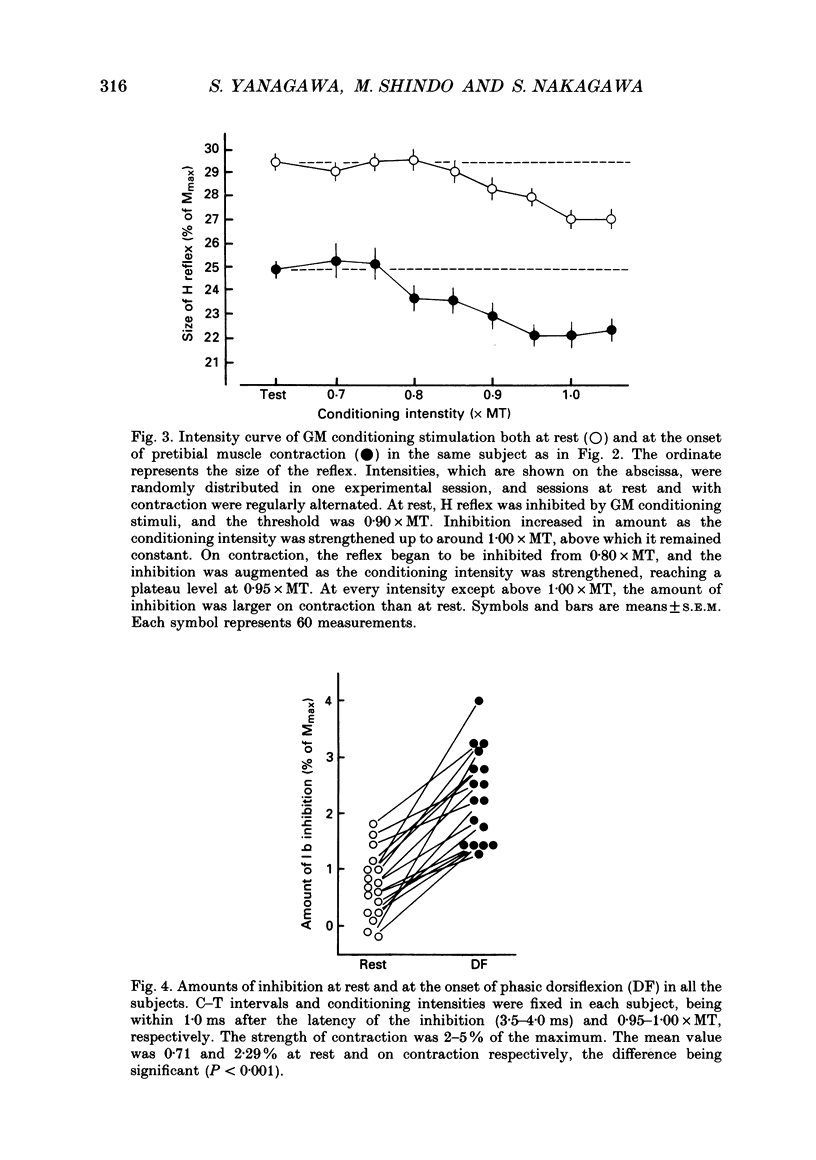
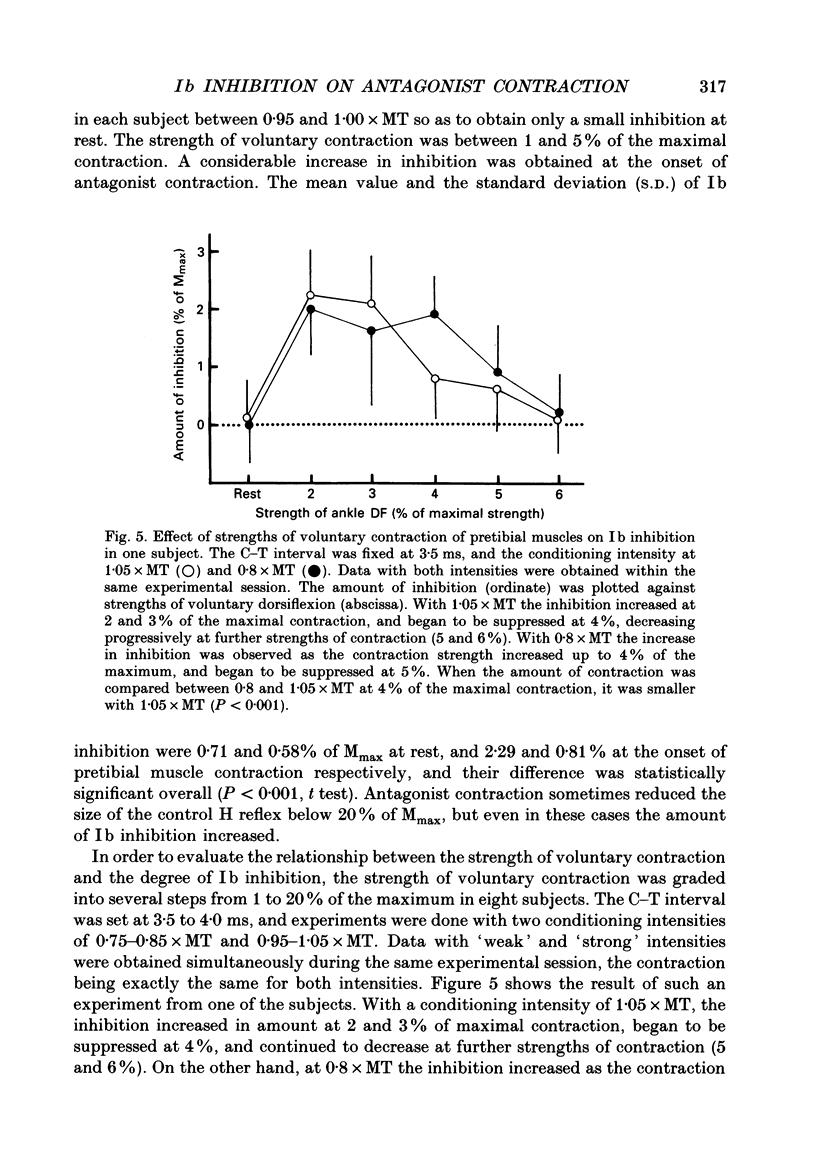
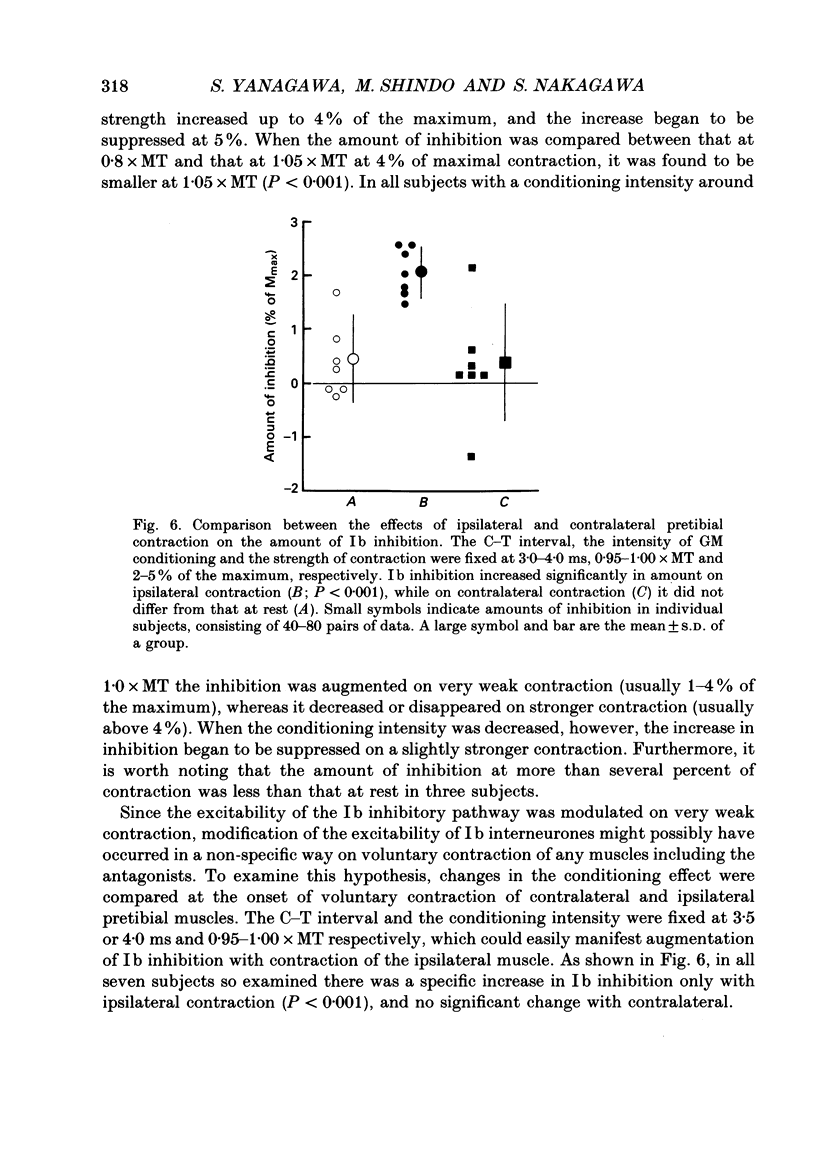
1. Ib inhibition from gastrocnemius medialis (GM) muscle to soleus (Sol) muscle was studied at rest and at the onset of phasic voluntary contraction of antagonistic pretibial muscles in seventeen normal subjects. 2. In twelve out of seventeen subjects there was inhibition of Sol H reflex by GM conditioning stimulation at rest with a latency of 1.5-3.0 ms and a threshold of 0.85-1.00 times the motor threshold (MT). The amount of inhibition at 0.95-1.05 x MT, which was calculated by subtracting the size of the conditioned reflex from that of the unconditioned one, ranged from 0.8 to 5.6% of the maximal M-response or 2.9-18.3% of control H reflex. This inhibition was ascribed to Ib inhibition, taking into account its latency and threshold. 3. On weak pretibial contraction the inhibition either increased in amount or newly appeared in all the subjects. When the strength of voluntary contraction was graded from 1 to 20% of the maximum, the increment in the amount of inhibition decreased or almost disappeared at strengths of more than several per cent. These facts imply that at least some of the Ib interneurones are facilitated to fire by descending commands alone without peripheral Ib impulses. Contralateral ankle dorsiflexion did not modify the inhibition. 4. Soleus muscle H reflex was not modulated at all by cutaneous stimulation instead of GM stimulation at rest, nor was it affected by cutaneous stimulation on ipsilateral antagonistic contraction. 5. It is concluded that activity in the Ib inhibitory pathway is facilitated at the onset of antagonistic voluntary contraction. This suggests that control of the Ib inhibitory pathway may be utilized in ordinary voluntary movement, and is presumably beneficial for smooth execution of movement.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brink E., Harrison P. J., Jankowska E., McCrea D. A., Skoog B. Post-synaptic potentials in a population of motoneurones following activity of single interneurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1983 Oct;343:341–359. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brink E., Jankowska E., McCrea D. A., Skoog B. Inhibitory interactions between interneurones in reflex pathways from group Ia and group Ib afferents in the cat. J Physiol. 1983 Oct;343:361–373. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavallari P., Fournier E., Katz R., Malmgren K., Pierrot-Deseilligny E., Shindo M. Cutaneous facilitation of transmission in Ib reflex pathways in the human upper limb. Exp Brain Res. 1985;60(1):197–199. doi: 10.1007/BF00237033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crone C., Hultborn H., Jespersen B., Nielsen J. Reciprocal Ia inhibition between ankle flexors and extensors in man. J Physiol. 1987 Aug;389:163–185. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crone C., Hultborn H., Jespersen B. Reciprocal Ia inhibition from the peroneal nerve to soleus motoneurones with special reference to the size of the test reflex. Exp Brain Res. 1985;59(2):418–422. doi: 10.1007/BF00230924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crone C., Hultborn H., Mazières L., Morin C., Nielsen J., Pierrot-Deseilligny E. Sensitivity of monosynaptic test reflexes to facilitation and inhibition as a function of the test reflex size: a study in man and the cat. Exp Brain Res. 1990;81(1):35–45. doi: 10.1007/BF00230098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. Supraspinal control of interneurones mediating spinal reflexes. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;147:565–584. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier E., Katz R., Pierrot-Deseilligny E. A re-evaluation of the pattern of group I fibre projections in the human lower limb on using randomly alternated stimulations. Exp Brain Res. 1984;56(1):193–195. doi: 10.1007/BF00237457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier E., Katz R., Pierrot-Deseilligny E. Descending control of reflex pathways in the production of voluntary isolated movements in man. Brain Res. 1983 Dec 12;288(1-2):375–377. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90122-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier E., Meunier S., Pierrot-Deseilligny E., Shindo M. Evidence for interneuronally mediated Ia excitatory effects to human quadriceps motoneurones. J Physiol. 1986 Aug;377:143–169. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison P. J., Jankowska E. Sources of input to interneurones mediating group I non-reciprocal inhibition of motoneurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1985 Apr;361:379–401. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hongo T., Jankowska E., Lundberg A. The rubrospinal tract. II. Facilitation of interneuronal transmission in reflex paths to motoneurones. Exp Brain Res. 1969;7(4):365–391. doi: 10.1007/BF00237321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNO M. Excitability following antidromic activation in spinal motoneurones supplying red muscles. J Physiol. 1959 Dec;149:374–393. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAPORTE Y., LLOYD D. P. C. Nature and significance of the reflex connections established by large afferent fibers of muscular origin. Am J Physiol. 1952 Jun;169(3):609–621. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1952.169.3.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg A., Malmgren K., Schomburg E. D. Cutaneous facilitation of transmission in reflex pathways from Ib afferents to motoneurones. J Physiol. 1977 Mar;265(3):763–780. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierrot-Deseilligny E., Bergego C., Katz R., Morin C. Cutaneous depression of Ib reflex pathways to motoneurones in man. Exp Brain Res. 1981;42(3-4):351–361. doi: 10.1007/BF00237500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierrot-Deseilligny E., Bergego C., Katz R. Reversal in cutaneous of Ib pathways during human voluntary contraction. Brain Res. 1982 Feb 11;233(2):400–403. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)91213-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierrot-Deseilligny E., Katz R., Morin C. Evidence of Ib inhibition in human subjects. Brain Res. 1979 Apr 20;166(1):176–179. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90660-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierrot-Deseilligny E., Morin C., Bergego C., Tankov N. Pattern of group I fibre projections from ankle flexor and extensor muscles in man. Exp Brain Res. 1981;42(3-4):337–350. doi: 10.1007/BF00237499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


