Abstract
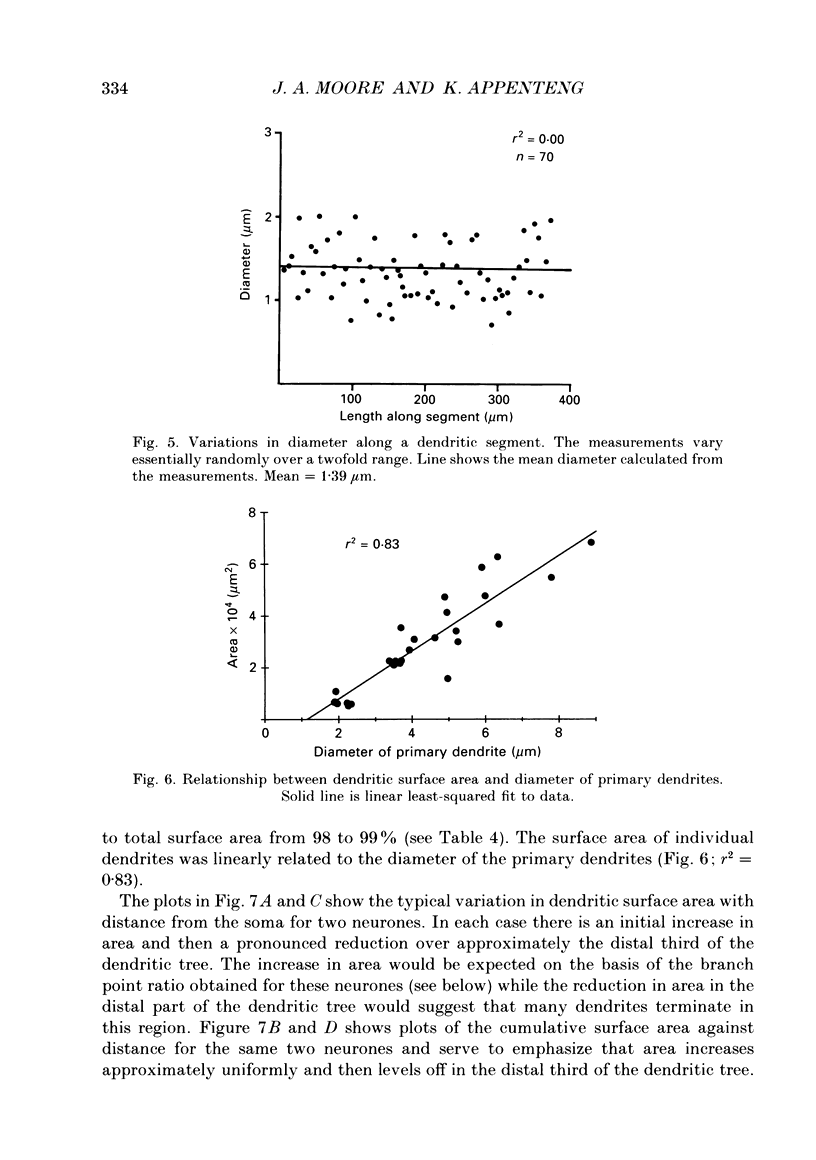
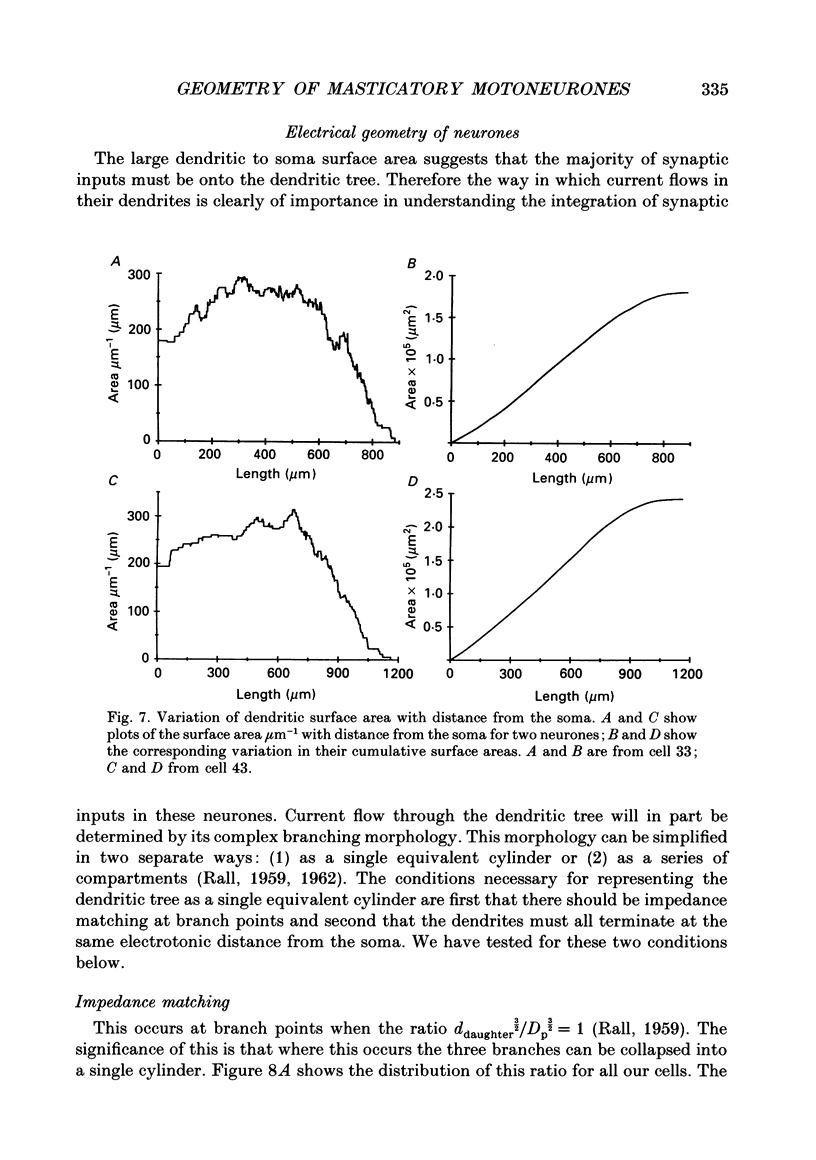
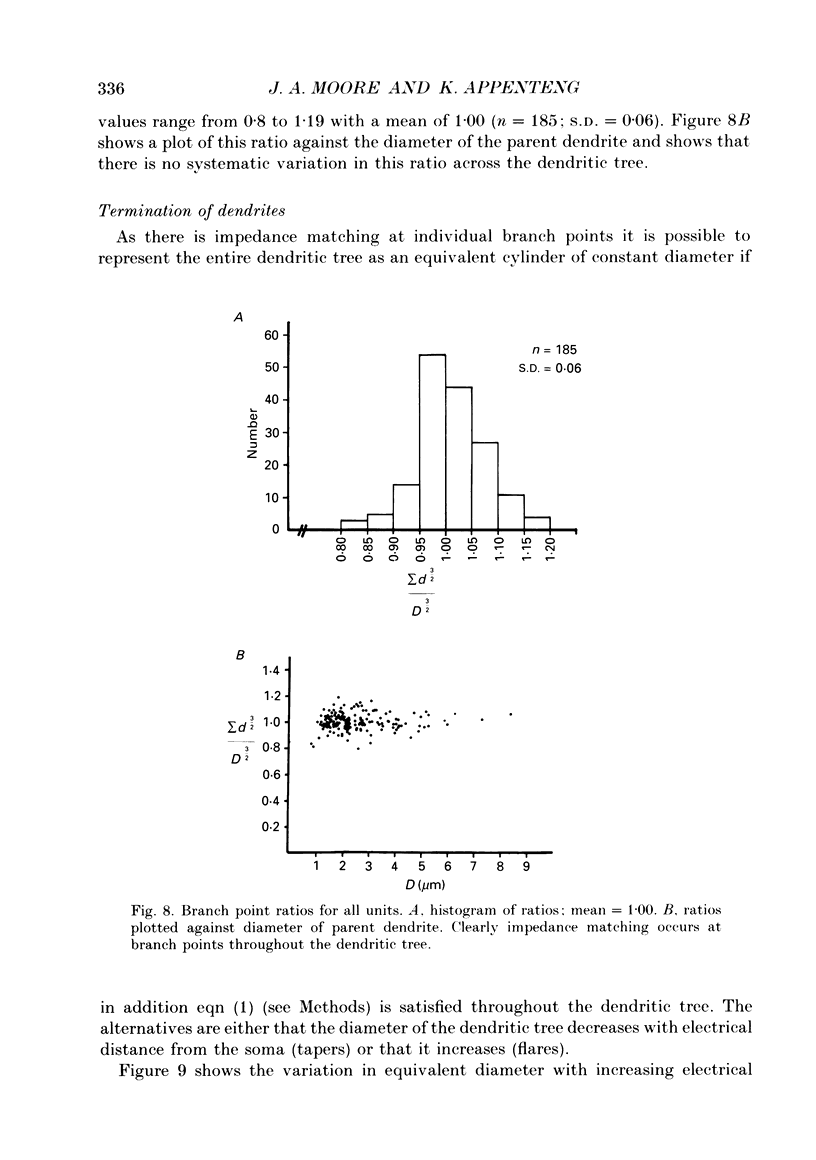
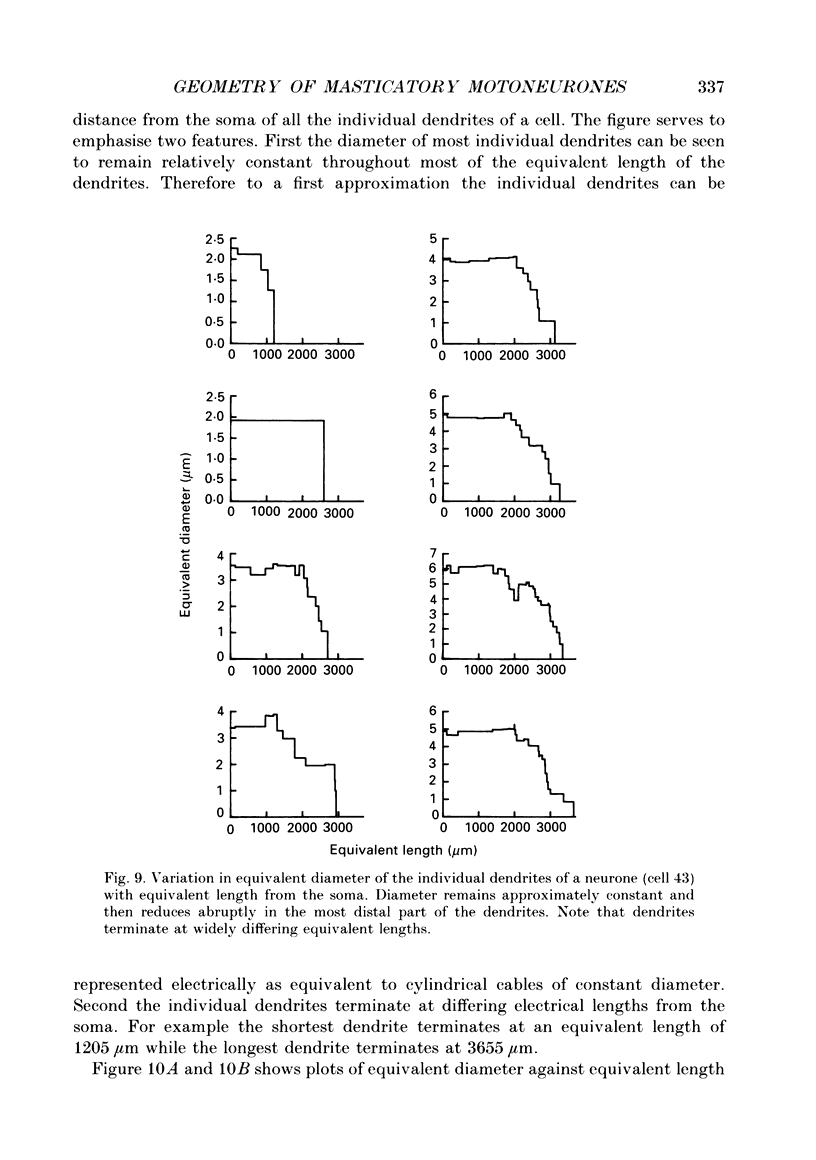
1. The aim of this work was to quantify both the morphology and electrical geometry of the dendritic trees of jaw-elevator motoneurones. To do this we have made intracellular recordings from identified motoneurones in anaesthetized rats, determined their membrane properties and then filled them with horseradish peroxidase by ionophoretic ejection. Four neurones were subsequently fully reconstructed and the lengths and diameters of all the dendritic segments measured. 2. The mean soma diameter was 25 microns and values of mean dendritic length for individual cells ranged from 514 to 773 microns. Dendrites branched on average 9.1 times to produce 10.2 end-terminations. Dendritic segments could be represented as constant diameter cylinders between branch points. Values of dendritic surface area ranged from 1.08 to 2.52 x 10(5) microns 2 and values of dendritic to total surface area from 98 to 99%. 3. At branch points the ratio of the summed diameters of the daughter dendrites to the 3/2 power against the parent dendrite to the 3/2 power was exactly 1.0. Therefore the individual branch points could be collapsed into a single cylinder. Furthermore for an individual dendrite the diameter of this cylinder remained constant with increasing electrical distance from the soma. Thus individual dendrites can be represented electrically as cylinders of constant diameter. 4. However dendrites of a given neurone terminated at different electrical distances from the soma. The equivalent-cylinder diameter of the combined dendritic tree remained constant over the proximal half and then showed a pronounced reduction over the distal half. The reduction in equivalent diameter could be ascribed to the termination of dendrites at differing electrical distances from the soma. Therefore the complete dendritic tree of these motoneurones is best represented as a cylinder over the proximal half of their electrical length but as a cone over the distal half.
Full text
PDF




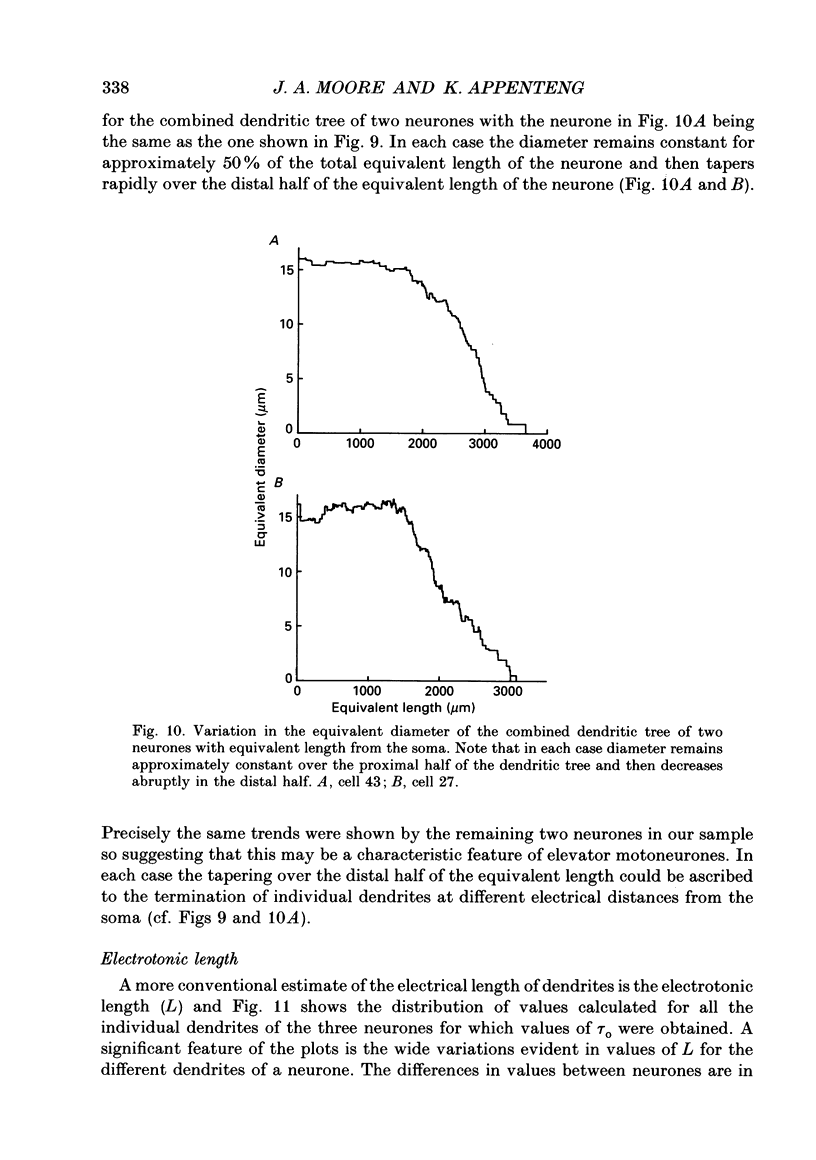
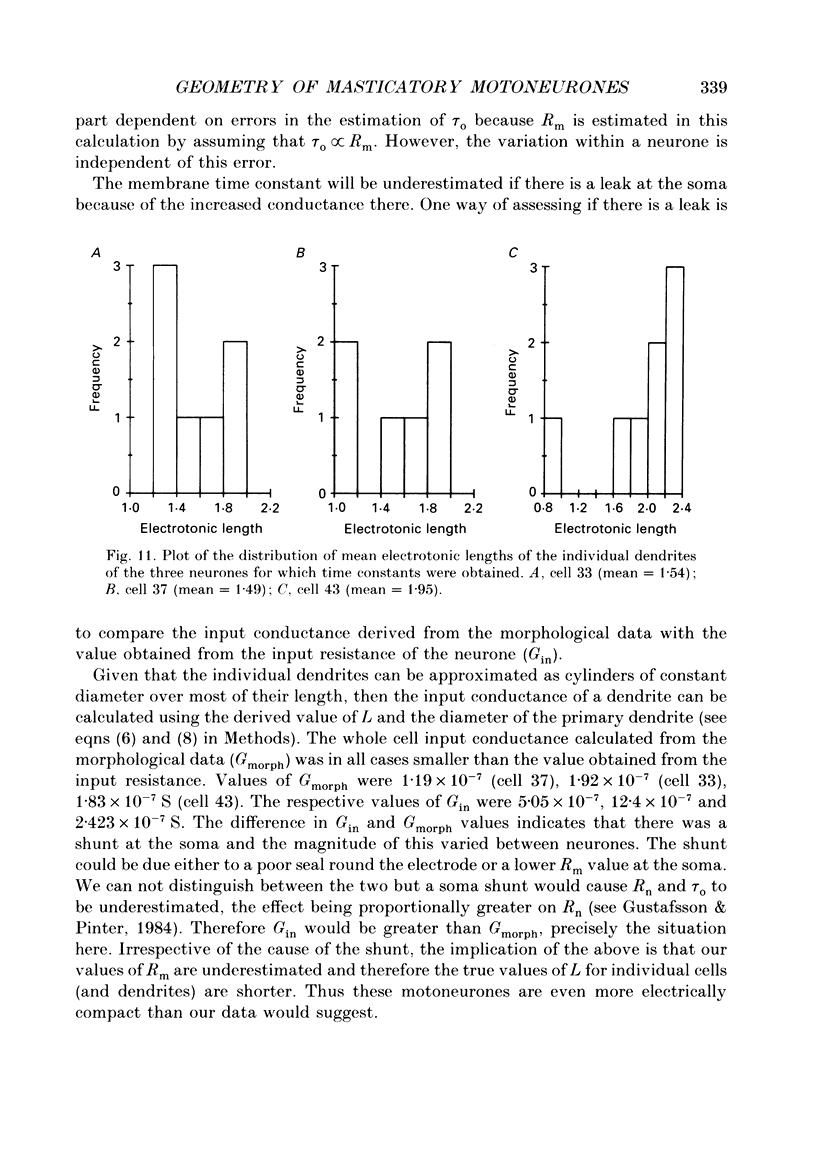




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appenteng K., Donga R., Williams R. G. Morphological and electrophysiological determination of the projections of jaw-elevator muscle spindle afferents in rats. J Physiol. 1985 Dec;369:93–113. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appenteng K., Girdlestone D. Transneuronal transport of wheat germ agglutinin-conjugated horseradish peroxidase into trigeminal interneurones of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Apr 15;258(3):387–396. doi: 10.1002/cne.902580307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomfield S. A., Hamos J. E., Sherman S. M. Passive cable properties and morphological correlates of neurones in the lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat. J Physiol. 1987 Feb;383:653–692. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bras H., Gogan P., Tyc-Dumont S. The dendrites of single brain-stem motoneurons intracellularly labelled with horseradish peroxidase in the cat. Morphological and electrical differences. Neuroscience. 1987 Sep;22(3):947–970. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)92972-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron W. E., Averill D. B., Berger A. J. Quantitative analysis of the dendrites of cat phrenic motoneurons stained intracellularly with horseradish peroxidase. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Jan 1;231(1):91–101. doi: 10.1002/cne.902310108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Redman S. J. Cable properties of cat spinal motoneurones measured by combining voltage clamp, current clamp and intracellular staining. J Physiol. 1989 Feb;409:63–87. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullheim S., Fleshman J. W., Glenn L. L., Burke R. E. Membrane area and dendritic structure in type-identified triceps surae alpha motoneurons. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Jan 1;255(1):68–81. doi: 10.1002/cne.902550106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durand J., Durand-Arczynska W., Wankmiller D. Coupling of active sodium transport to oxidative metabolism in the rabbit distal colon. J Physiol. 1988 Feb;396:55–64. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egger M. D., Egger L. D. Quantitative morphological analysis of spinal motoneurons. Brain Res. 1982 Dec 16;253(1-2):19–30. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90669-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleshman J. W., Segev I., Burke R. B. Electrotonic architecture of type-identified alpha-motoneurons in the cat spinal cord. J Neurophysiol. 1988 Jul;60(1):60–85. doi: 10.1152/jn.1988.60.1.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Pinter M. J. Relations among passive electrical properties of lumbar alpha-motoneurones of the cat. J Physiol. 1984 Nov;356:401–431. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack J. J., Redman S. J. An electrical description of the motoneurone, and its application to the analysis of synaptic potentials. J Physiol. 1971 Jun;215(2):321–352. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack J. J., Redman S. J. The propagation of transient potentials in some linear cable structures. J Physiol. 1971 Jun;215(2):283–320. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E. Further indications for enhancement of retrograde transneuronal transport of WGA-HRP by synaptic activity. Brain Res. 1985 Aug 26;341(2):403–408. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91084-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J., Appenteng K. The membrane properties and firing characteristics of rat jaw-elevator motoneurones. J Physiol. 1990 Apr;423:137–153. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALL W. Branching dendritic trees and motoneuron membrane resistivity. Exp Neurol. 1959 Nov;1:491–527. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(59)90046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALL W. Theory of physiological properties of dendrites. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1962 Mar 2;96:1071–1092. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1962.tb54120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall W., Burke R. E., Smith T. G., Nelson P. G., Frank K. Dendritic location of synapses and possible mechanisms for the monosynaptic EPSP in motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1967 Sep;30(5):1169–1193. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.5.1169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redman S., Walmsley B. The time course of synaptic potentials evoked in cat spinal motoneurones at identified group Ia synapses. J Physiol. 1983 Oct;343:117–133. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rokx J. T., van Willigen J. D., Jüch P. J. Distribution of innervating neurons of masticatory muscle spindles in the rat: an HRP study. Exp Neurol. 1985 Jun;88(3):562–569. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(85)90071-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose P. K., Keirstead S. A., Vanner S. J. A quantitative analysis of the geometry of cat motoneurons innervating neck and shoulder muscles. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Sep 1;239(1):89–107. doi: 10.1002/cne.902390108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schierwagen A., Grantyn R. Quantitative morphological analysis of deep superior colliculus neurons stained intracellularly with HRP in the cat. J Hirnforsch. 1986;27(6):611–623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner D. A., Schwartzkroin P. A. Electrical characteristics of dendrites and dendritic spines in intracellularly stained CA3 and dentate hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci. 1983 Nov;3(11):2381–2394. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-11-02381.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner D. A., Schwartzkroin P. A. Steady-state electrotonic analysis of intracellularly stained hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1980 Jul;44(1):184–199. doi: 10.1152/jn.1980.44.1.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulfhake B., Kellerth J. O. A quantitative light microscopic study of the dendrites of cat spinal alpha-motoneurons after intracellular staining with horseradish peroxidase. J Comp Neurol. 1981 Nov 10;202(4):571–583. doi: 10.1002/cne.902020409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulfhake B., Kellerth J. O. A quantitative morphological study of HRP-labelled cat alpha-motoneurones supplying different hindlimb muscles. Brain Res. 1983 Mar 28;264(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida A., Tsuru K., Mitsuhiro Y., Otani K., Shigenaga Y. Morphology of masticatory motoneurons stained intracellularly with horseradish peroxidase. Brain Res. 1987 Jul 28;416(2):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90925-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


