Abstract
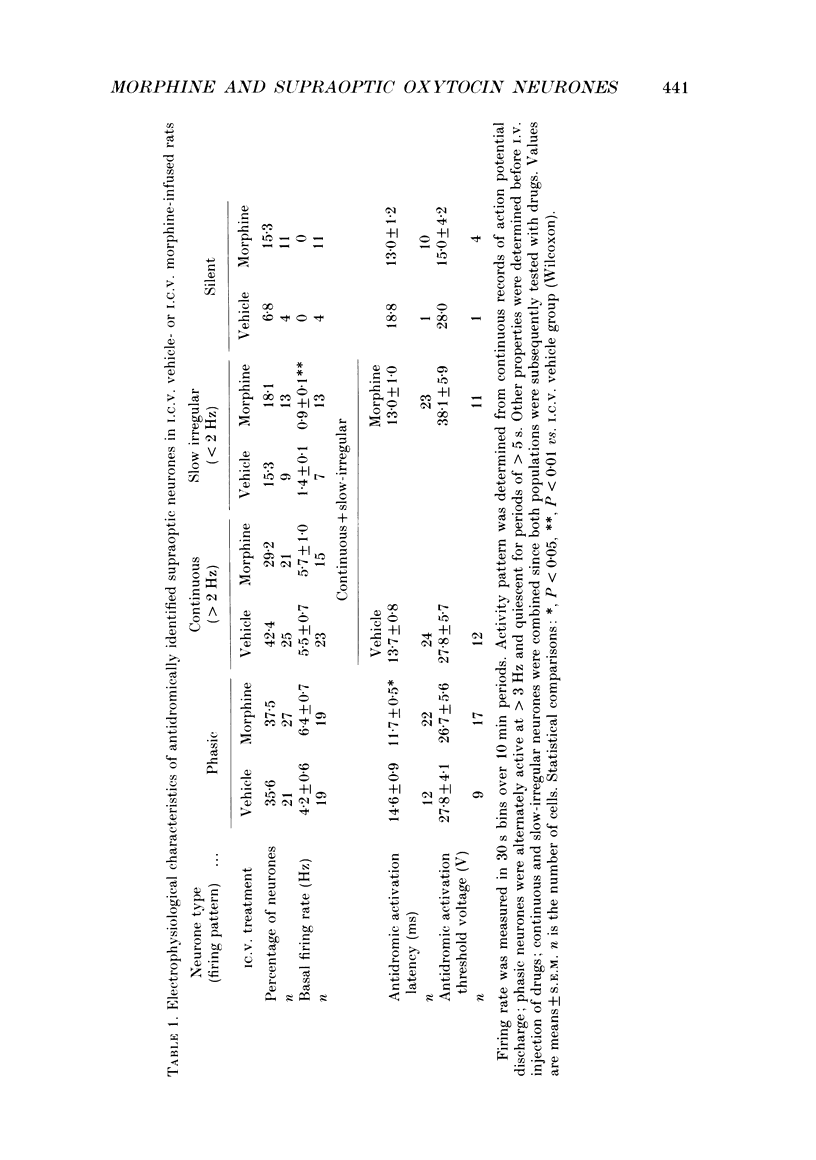
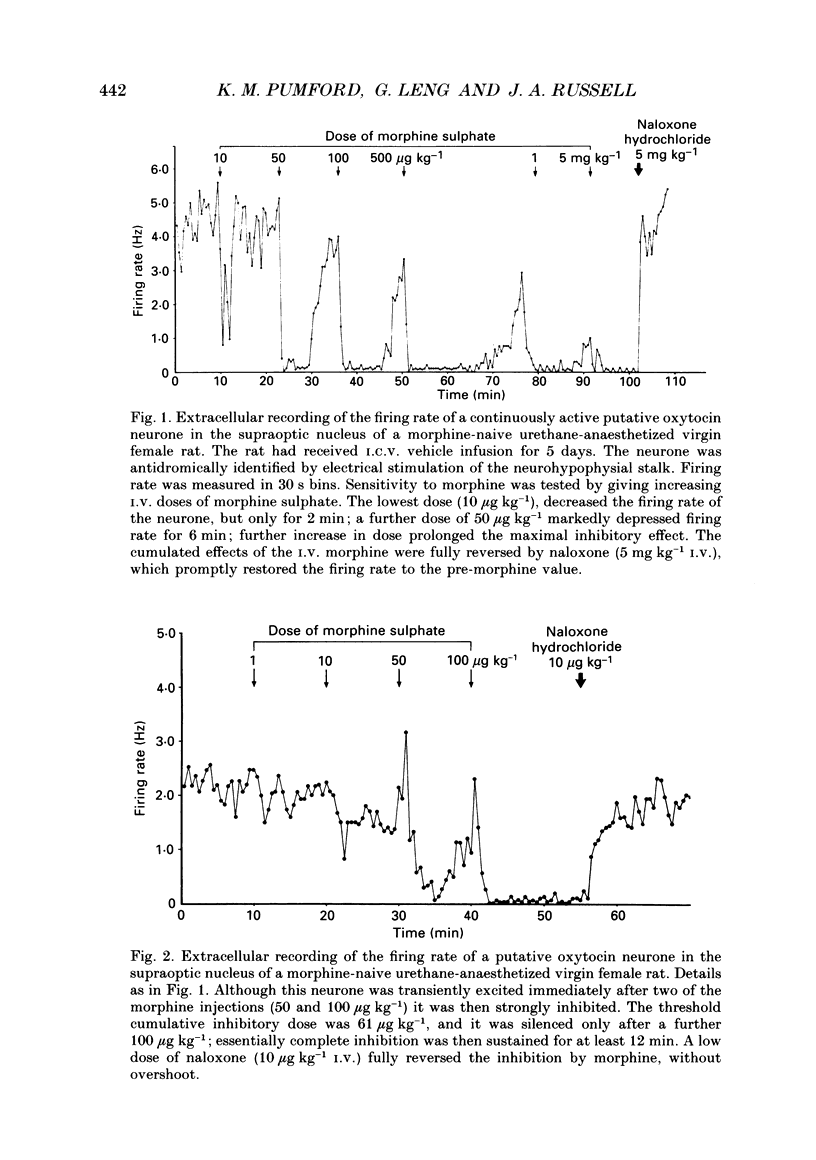
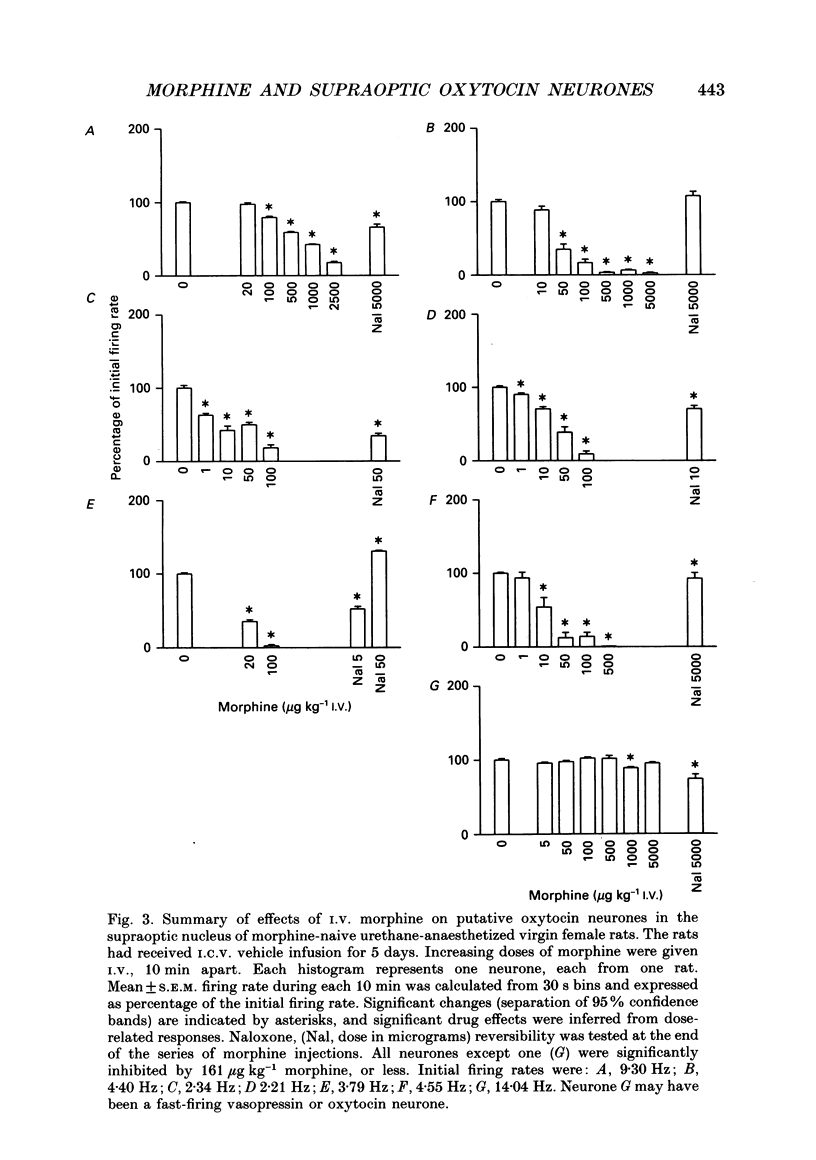
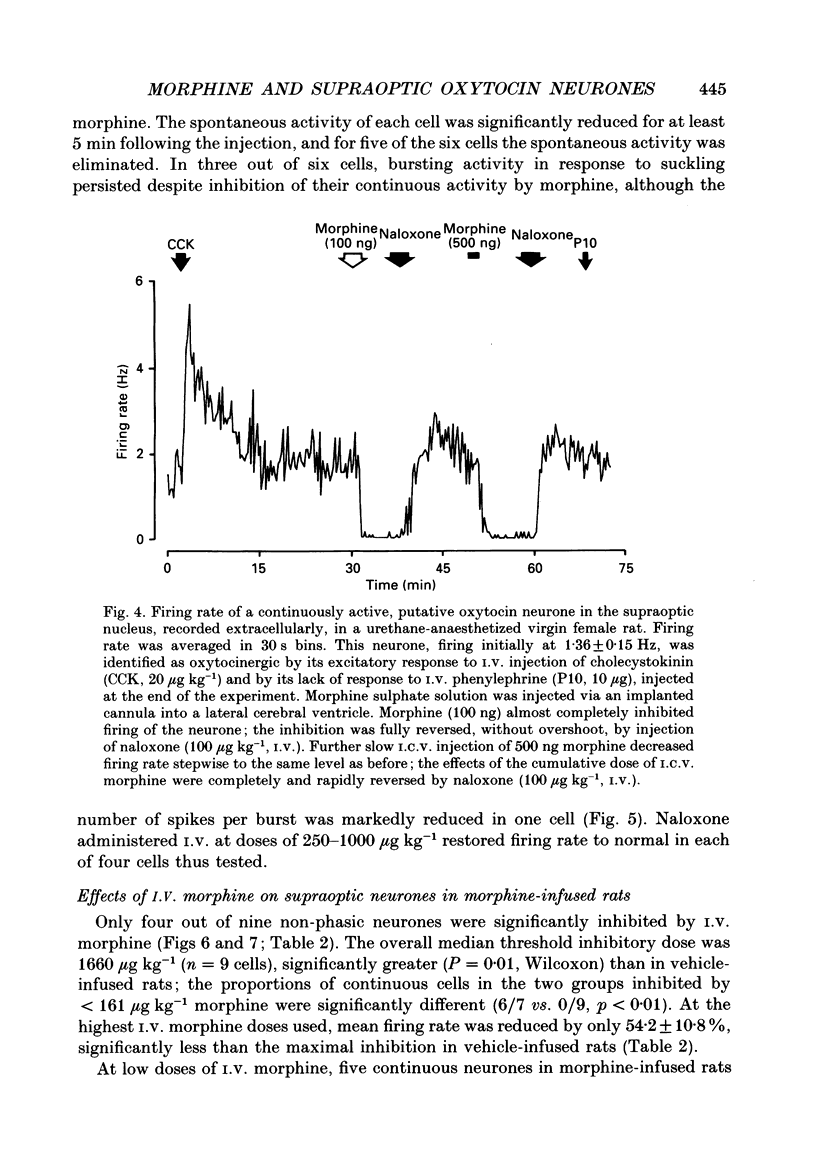
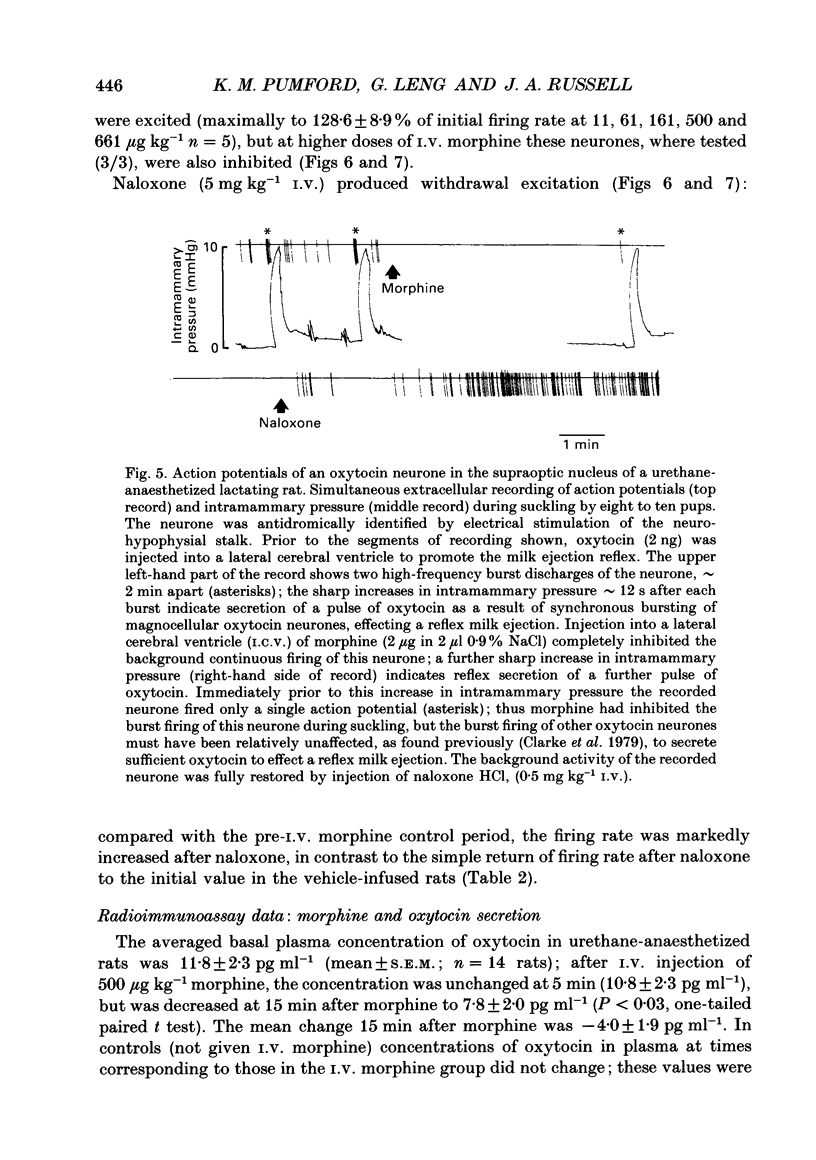
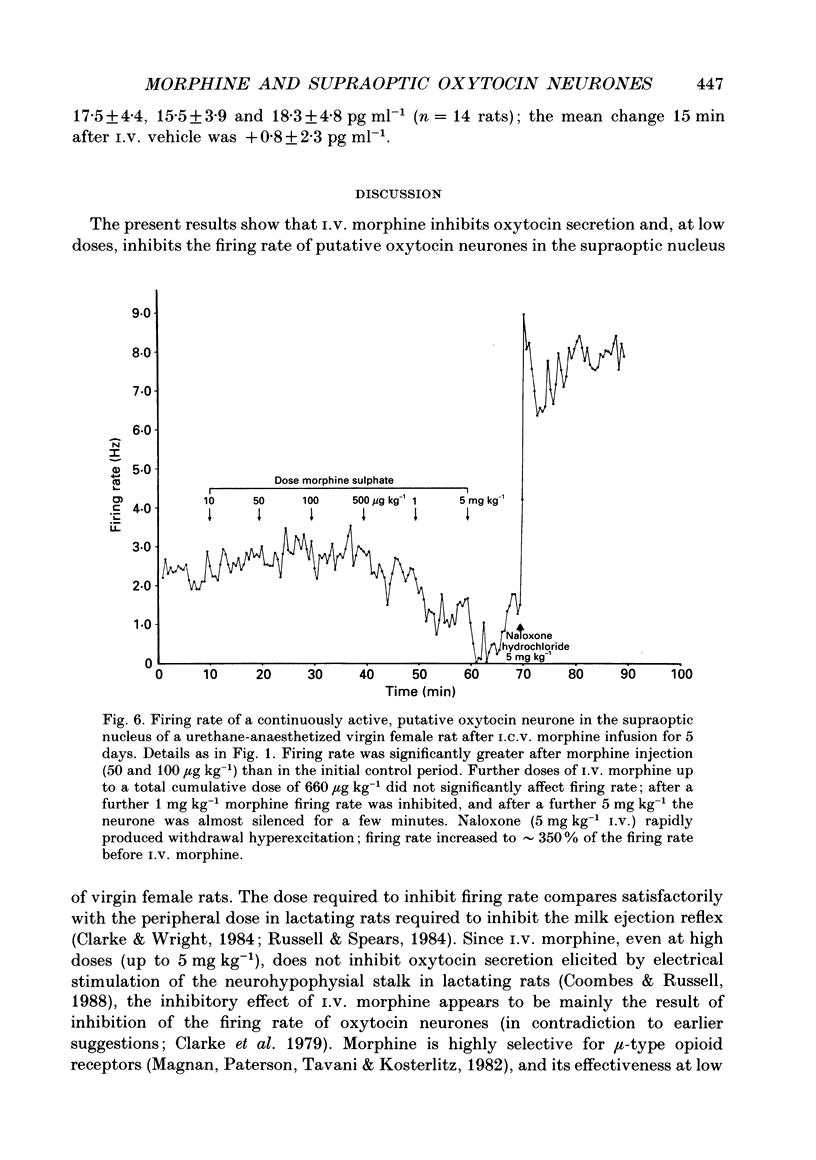
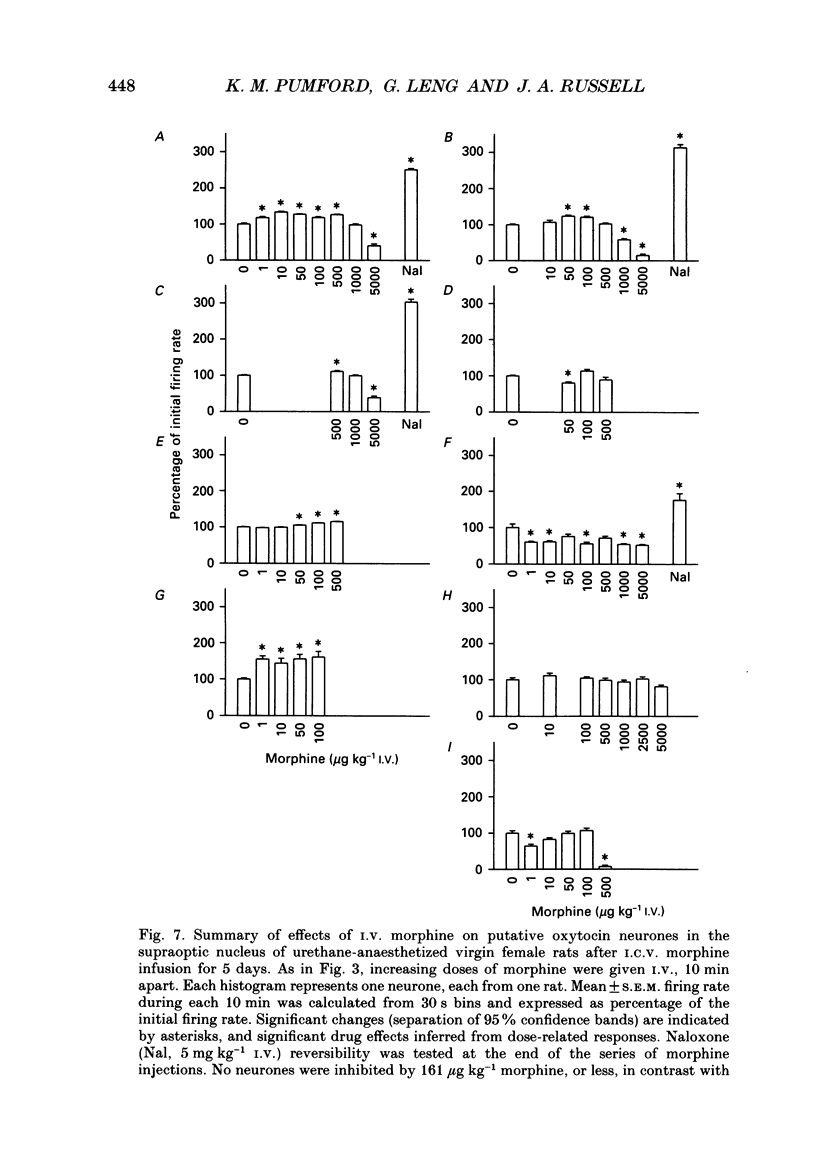
1. The effects of acute i.v. administration of morphine on putative oxytocin neurones of the supraoptic nucleus were studied in urethane-anaesthetized female rats which had been exposed to i.c.v. infusion of morphine (up to 50 micrograms h-1) or vehicle for 5 days. 2. In vehicle-infused rats, i.v. morphine inhibited the spontaneous activity of six out of seven putative oxytocin neurones. Increasing doses of morphine were given, from 1 microgram kg-1 to 5 mg kg-1. The median cumulative threshold dose to produce significant inhibition was 20 micrograms kg-1 (seven cells in six rats); six out of seven cells were inhibited at 161 micrograms kg-1. The highest doses tested inhibited by approximately 90% (excluding one unaffected cell). Inhibition was fully reversed by i.v. naloxone without overshoot, indicating a lack of acute dependence. 3. Injection of morphine i.c.v. inhibited firing at doses that were ineffective by i.v. injection and the effects of i.c.v. morphine were reversed by i.v. naloxone. 4. Acute morphine (500 micrograms kg-1 i.v.) reduced the plasma concentration of oxytocin, measured after 15 min by specific radioimmunoassay, by 34% (n = 14). 5. In lactating rats i.c.v. injection of morphine (1-2 micrograms) inhibited the activity of supraoptic neurones identified as oxytocinergic by their responses to suckling. 6. In seventeen rats infused with i.c.v. morphine the initial firing rate of twenty-eight spontaneously active, non-phasic neurones was significantly less, by 24%, than thirty-four similar cells in control rats, indicating incomplete tolerance to i.c.v. morphine. Morphine (up to 161 micrograms kg-1 given i.v.) inhibited none of nine active non-phasic neurones (P less than 0.01 compared to control rats), but at higher doses inhibited four of nine cells; the overall median threshold cumulative dose (1660 micrograms kg-1) was significantly greater than in vehicle-infused controls, indicating tolerance to i.v. morphine. In contrast with control rats, some cells (5/9) were modestly excited by low doses of morphine. Naloxone (5 mg kg-1 i.v.) produced withdrawal excitation: the firing rate of putative oxytocin neurones increased to approximately 260% of the pre-i.v. morphine value, indicating dependence in mechanisms regulating the firing rate of these neurones. 7. In morphine-infused rats, the basal firing rate of nineteen phasically active, putative vasopressin supraoptic neurones was not different in nineteen phasic cells in controls (6.4 +/- 0.7 vs. 4.2 +/- 0.6 Hz). 8. Thus morphine potently inhibits the firing of magnocellular oxytocin neurones in the female rat, inhibiting oxytocin secretion. Morphine tolerance and dependence develop during i.c.v. infusion of morphine for 5 days. Similar tolerance to and dependence upon endogenous opioids during pregnancy may be important in the preparation of oxytocin neurones for parturition.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bicknell R. J., Leng G., Lincoln D. W., Russell J. A. Naloxone excites oxytocin neurones in the supraoptic nucleus of lactating rats after chronic morphine treatment. J Physiol. 1988 Feb;396:297–317. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady L. S., Herkenham M., Long J. B., Rothman R. B. Chronic morphine increases mu-opiate receptor binding in rat brain: a quantitative autoradiographic study. Brain Res. 1989 Jan 16;477(1-2):382–386. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91432-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buranarugsa P., Hubbard J. I. The neuronal organization of the rat subfornical organ in vitro and a test of the osmo- and morphine-receptor hypotheses. J Physiol. 1979 Jun;291:101–116. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie M. J., Williams J. T., North R. A. Cellular mechanisms of opioid tolerance: studies in single brain neurons. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Nov;32(5):633–638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke G., Wood P., Merrick L., Lincoln D. W. Opiate inhibition of peptide release from the neurohumoral terminals of hypothalamic neurones. Nature. 1979 Dec 13;282(5740):746–748. doi: 10.1038/282746a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke G., Wright D. M. A comparison of analgesia and suppression of oxytocin release by opiates. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Nov;83(3):799–806. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16235.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crain S. M., Shen K. F. Opioids can evoke direct receptor-mediated excitatory effects on sensory neurons. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Feb;11(2):77–81. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90322-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyball R. E., Leng G. Regulation of the milk ejection reflex in the rat. J Physiol. 1986 Nov;380:239–256. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. G., Olley J. E. Comparison of the oxytocin response to water-deprivation, hyperosmolarity and administration of morphine or naltrexone in lactating and virgin female rats. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Nov 22;94(1-2):177–181. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90291-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund-Mercier M. J., Richard P. Electrophysiological evidence for facilitatory control of oxytocin neurones by oxytocin during suckling in the rat. J Physiol. 1984 Jul;352:447–466. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giagnoni G., Casiraghi L., Basilico L., Pecora N., Mennuni L., Parolaro D., Colleoni M., Gori E. Cerebral extract from morphine-tolerant rats shows antiopiate properties in guinea pig ileum bioassay. Pharmacol Res Commun. 1988 Apr;20(4):307–322. doi: 10.1016/s0031-6989(88)80067-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grell S., Christensen J. D., Fjalland B. The influence of morphine and naloxone on plasma oxytocin concentration in the rat. Pharmacol Toxicol. 1988 Oct;63(4):274–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1988.tb00953.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris M. C. Effects of chemoreceptor and baroreceptor stimulation on the discharge of hypothalamic supraoptic neurones in rats. J Endocrinol. 1979 Jul;82(1):115–125. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0820115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herkenham M., Rice K. C., Jacobson A. E., Rothman R. B. Opiate receptors in rat pituitary are confined to the neural lobe and are exclusively kappa. Brain Res. 1986 Sep 24;382(2):365–371. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi T., Honda K., Fukuoka T., Negoro H., Wakabayashi K. Release of oxytocin during suckling and parturition in the rat. J Endocrinol. 1985 Jun;105(3):339–346. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1050339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. M., Duggan A. W. Dependence in the absence of tolerance to morphine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Jan 27;97(3-4):305–308. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90465-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juss T. S., Wakerley J. B. Mesencephalic areas controlling pulsatile oxytocin release in the suckled rat. J Endocrinol. 1981 Nov;91(2):233–244. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0910233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W. The Wellcome Foundation lecture, 1982. Opioid peptides and their receptors. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985 Jul 22;225(1238):27–40. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1985.0048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leng G., Mansfield S., Bicknell R. J., Blackburn R. E., Brown D., Chapman C., Dyer R. G., Hollingsworth S., Shibuki K., Yates J. O. Endogenous opioid actions and effects of environmental disturbance on parturition and oxytocin secretion in rats. J Reprod Fertil. 1988 Sep;84(1):345–356. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0840345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leng G., Russell J. A., Grossmann R. Sensitivity of magnocellular oxytocin neurones to opioid antagonists in rats treated chronically with intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) morphine. Brain Res. 1989 Apr 10;484(1-2):290–296. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90372-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lincoln D. W., Wakerley J. B. Electrophysiological evidence for the activation of supraoptic neurones during the release of oxytocin. J Physiol. 1974 Oct;242(2):533–554. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh H. H., Tao P. L., Smith A. P. Role of receptor regulation in opioid tolerance mechanisms. Synapse. 1988;2(4):457–462. doi: 10.1002/syn.890020414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnan J., Paterson S. J., Tavani A., Kosterlitz H. W. The binding spectrum of narcotic analgesic drugs with different agonist and antagonist properties. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1982 Jun;319(3):197–205. doi: 10.1007/BF00495865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour A., Khachaturian H., Lewis M. E., Akil H., Watson S. J. Anatomy of CNS opioid receptors. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Jul;11(7):308–314. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocchetti I., Costa E. Down regulation of hypothalamic proopiomelanocortin system during morphine tolerance. Clin Neuropharmacol. 1986;9 (Suppl 4):125–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulain D. A., Wakerley J. B. Electrophysiology of hypothalamic magnocellular neurones secreting oxytocin and vasopressin. Neuroscience. 1982 Apr;7(4):773–808. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90044-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayner V. C., Robinson I. C., Russell J. A. Chronic intracerebroventricular morphine and lactation in rats: dependence and tolerance in relation to oxytocin neurones. J Physiol. 1988 Feb;396:319–347. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renaud L. P., Tang M., McCann M. J., Stricker E. M., Verbalis J. G. Cholecystokinin and gastric distension activate oxytocinergic cells in rat hypothalamus. Am J Physiol. 1987 Oct;253(4 Pt 2):R661–R665. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1987.253.4.R661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. A., Blackburn R. E., Leng G. The role of the AV3V region in the control of magnocellular oxytocin neurons. Brain Res Bull. 1988 Jun;20(6):803–810. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(88)90095-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. A., Blackburn R. E., Leng G. The role of the AV3V region in the control of magnocellular oxytocin neurons. Brain Res Bull. 1988 Jun;20(6):803–810. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(88)90095-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. A., Gosden R. G., Humphreys E. M., Cutting R., Fitzsimons N., Johnston V., Liddle S., Scott S., Stirland J. A. Interruption of parturition in rats by morphine: a result of inhibition of oxytocin secretion. J Endocrinol. 1989 Jun;121(3):521–536. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1210521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEPHENSON R. P. A modification of receptor theory. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1956 Dec;11(4):379–393. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1956.tb00006.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidl E., Schulz R. Selective opiate tolerance in the guinea-pig ileum is not associated with selective dependence. Life Sci. 1983;33 (Suppl 1):357–360. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90516-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharif N. A., Hughes J. Discrete mapping of brain Mu and delta opioid receptors using selective peptides: quantitative autoradiography, species differences and comparison with kappa receptors. Peptides. 1989 May-Jun;10(3):499–522. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(89)90135-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuki K., Leng G., Way S. Effects of naloxone and of intraperitoneal hypertonic saline upon oxytocin release and upon supraoptic neuronal activity. Neurosci Lett. 1988 May 16;88(1):75–80. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90318-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summy-Long J. Y., Miller D. S., Rosella-Dampman L. M., Hartman R. D., Emmert S. E. A functional role for opioid peptides in the differential secretion of vasopressin and oxytocin. Brain Res. 1984 Sep 10;309(2):362–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner B. E., Coombes J. E., Pumford K. M., Russell J. A. Opioid receptor subtypes in the supraoptic nucleus and posterior pituitary gland of morphine-tolerant rats. Neuroscience. 1990;37(3):635–645. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90095-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner B. E., Kawata M., Russell J. A. Does acute, intense stimulation of oxytocin neurones in the supraoptic nucleus increase their content of oxytocin mRNA? Brain Res. 1989 Jun 12;489(2):283–290. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90861-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Portoghese P. S., Takemori A. E. Irreversible binding of [3H]beta-funaltrexamine to brain slices of morphine-tolerant and -dependent mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 May 10;149(3):205–212. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90650-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempel A., Habas J., Paredes W., Barr G. A. Morphine-induced downregulation of mu-opioid receptors in neonatal rat brain. Brain Res. 1988 Jun 1;469(1-2):129–133. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(88)90176-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakerley J. B., Noble R., Clarke G. Effects of morphine and D-Ala, D-Leu enkephalin on the electrical activity of supraoptic neurosecretory cells in vitro. Neuroscience. 1983 Sep;10(1):73–81. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werling L. L., McMahon P. N., Cox B. M. Selective changes in mu opioid receptor properties induced by chronic morphine exposure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6393–6397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitnall M. H., Gainer H., Cox B. M., Molineaux C. J. Dynorphin-A-(1-8) is contained within vasopressin neurosecretory vesicles in rat pituitary. Science. 1983 Dec 9;222(4628):1137–1139. doi: 10.1126/science.6648526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao B. G., Chapman C., Bicknell R. J. Opioid-noradrenergic interactions in the neurohypophysis. I. Differential opioid receptor regulation of oxytocin, vasopressin, and noradrenaline release. Neuroendocrinology. 1988 Jul;48(1):16–24. doi: 10.1159/000124984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


