Abstract
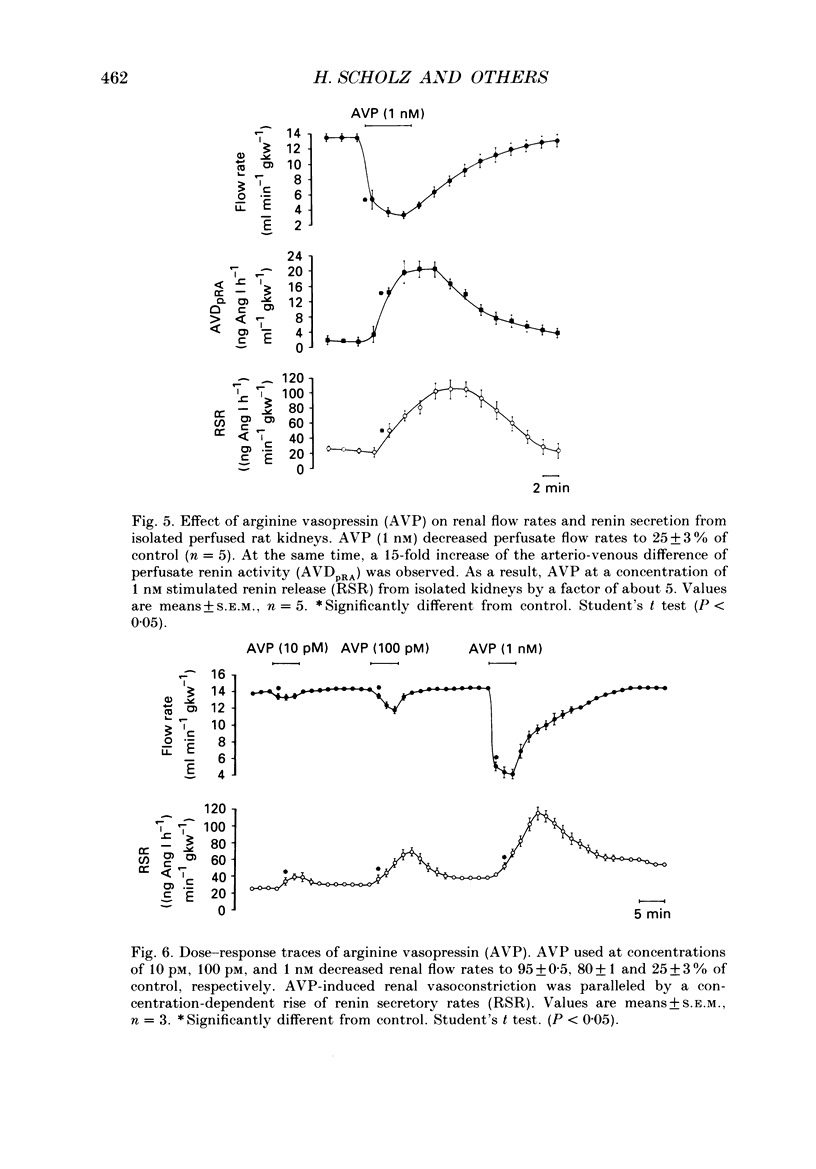
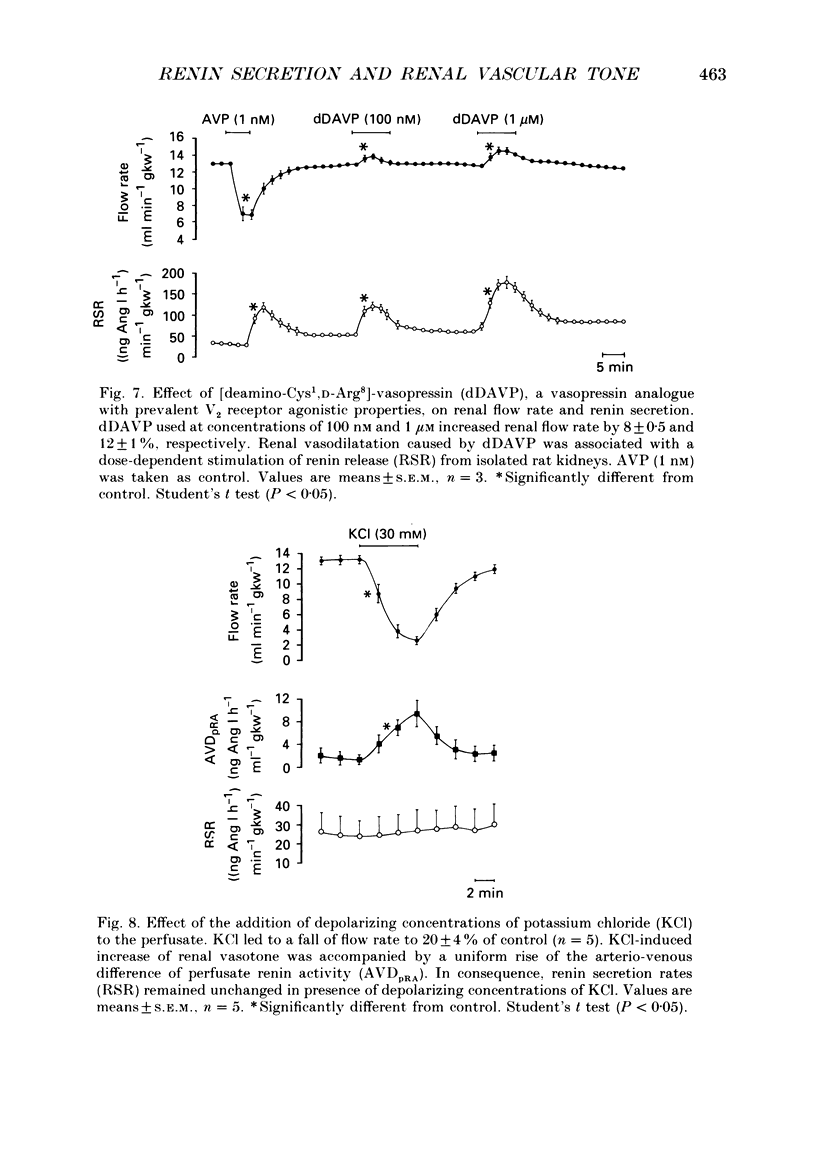
1. We have examined whether an increase of renal vascular resistance is generally accompanied by an inhibition of renin secretion. The effects of vasoconstriction produced by angiotensin II (Ang II), arginine-vasopressin (AVP), and potassium (KCl) depolarization on vascular resistance and on renin release from isolated rat kidneys perfused at constant pressure of 100 mmHg were investigated. 2. Histological examination performed on some representative kidneys revealed that the tubular lumina of all segments within the cortex were patent and the brush borders of the proximal tubules were well preserved. The renal vasculature and the juxtaglomerular region appeared to be morphologically intact. By immunocytochemistry, renin-positive cells were found exclusively in the wall of the afferent arterioles. 3. Basal flow rate through isolated kidneys was 14.5 +/- 2.0 ml min-1 (g kidney weight (gkw))-1 (mean +/- S.E.M., n = 10). Under control conditions renin secretory rates were in the range of 30-40 (ng Ang I h-1) min-1 gkw-1. 4. Ang II (100 pM) caused a decrease of renal flow rate to 42 +/- 2% of control which was accompanied by a reduction of renin secretion rates by a factor of 4. 5. AVP (10 pM to 1 nM) reduced renal perfusate flow in a dose-dependent fashion to a minimum of 25 +/- 3% of control. The vasoconstrictor effect of AVP was paralleled by a concentration-dependent increase of renin secretory rates reaching a factor of maximally 5 when AVP was used at a concentration of 1 nM. The stimulatory effect of AVP on renin release could be mimicked by [deamino-Cys1, D-Arg8]-vasopressin (dDAVP), a vasopressin analogue with prevalent V2 receptor agonistic properties. In the presence of dDAVP (100 nM, 1 microM) renal flow rate reversibly increased by 8 and 12% of control values, respectively. 6. Depolarizing concentrations of KCl (30 mM) decreased perfusate flow to 20 +/- 4% of control. The vasoconstrictor effect of KCl was paralleled by an increase of the arterio-venous difference of perfusate renin activity to such an extent that the rate of renin release remained unaltered. 7. Our findings suggest that there exists no general inverse relationship between renal arteriolar resistance and renin secretion. Our study, moreover, does not support a functional role of potential operated calcium channels in the control of renin secretion. Finally, we conclude that V2 receptors are present on juxtaglomerular epithelioid cell membranes and mediate the stimulatory effect of AVP on renin release from isolated rat kidneys.
Full text
PDF




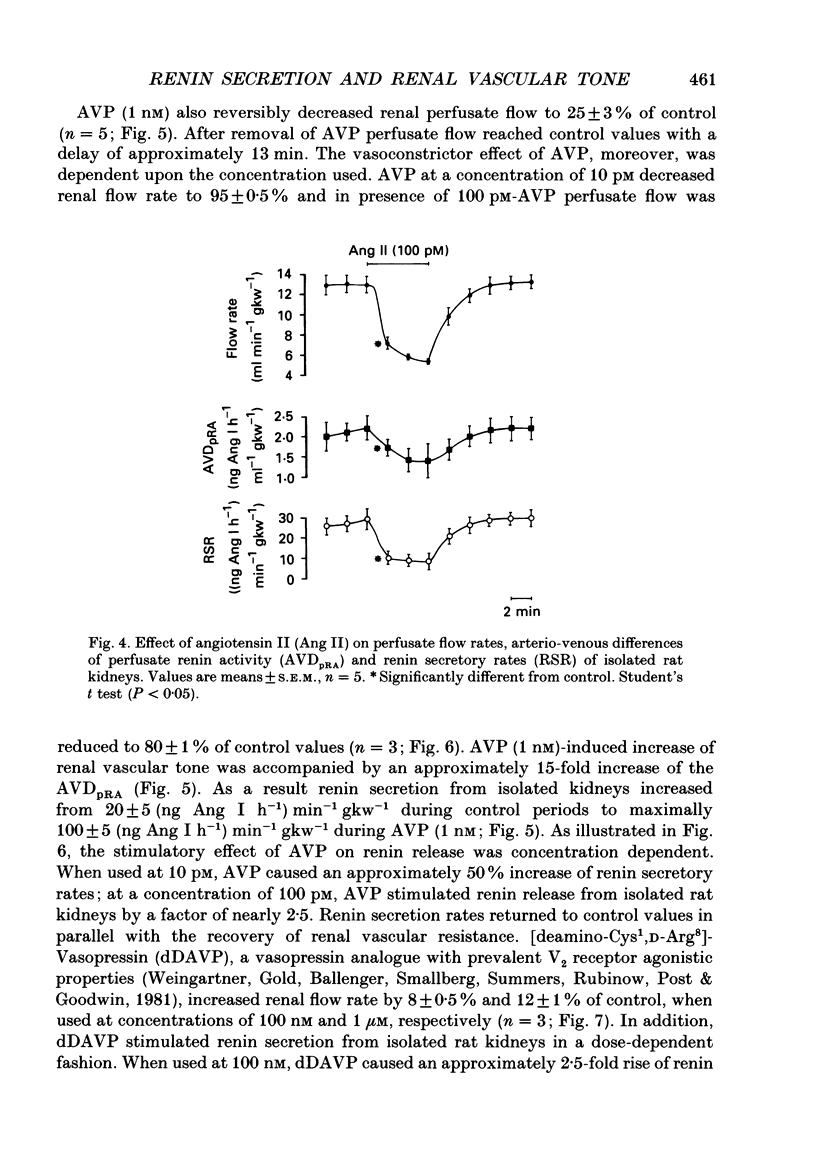





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bührle C. P., Scholz H., Hackenthal E., Nobiling R., Taugner R. Epithelioid cells: membrane potential changes induced by substances influencing renin secretion. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1986 Apr;45(1):37–47. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(86)90080-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caramelo C., Okada K., Tsai P., Schrier R. W. Phorbol esters and arginine vasopressin in vascular smooth muscle cell activation. Am J Physiol. 1989 May;256(5 Pt 2):F875–F881. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.5.F875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmines P. K., Navar L. G. Disparate effects of Ca channel blockade on afferent and efferent arteriolar responses to ANG II. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jun;256(6 Pt 2):F1015–F1020. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.6.F1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill P. C., Churchill M. C. Ca-dependence of the inhibitory effect of K-depolarization on renin secretion from rat kidney slices. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1982 Aug;258(2):300–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper C. L., Shaffer J. E., Malik K. U. Mechanism of action of angiotensin II and bradykinin on prostaglandin synthesis and vascular tone in the isolated rat kidney. Effect of Ca++ antagonists and calmodulin inhibitors. Circ Res. 1985 Jan;56(1):97–108. doi: 10.1161/01.res.56.1.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fray J. C., Lush D. J., Valentine A. N. Cellular mechanisms of renin secretion. Fed Proc. 1983 Dec;42(15):3150–3154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fray J. C. Mechanism by which renin secretion from perfused rat kidneys is stimulated by isoprenaline and inhibited by high perfusion pressure. J Physiol. 1980 Nov;308:1–13. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fray J. C. Stretch receptor control of renin release in perfused rat kidney: effect of high perfusate potassium. J Physiol. 1978 Sep;282:207–217. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackenthal E., Taugner R. Hormonal signals and intracellular messengers for renin secretion. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1986 Sep;47(1-2):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(86)90010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch A. T., Dzau V. J., Majzoub J. A., Creager M. A. Vasopressin-mediated forearm vasodilation in normal humans. Evidence for a vascular vasopressin V2 receptor. J Clin Invest. 1989 Aug;84(2):418–426. doi: 10.1172/JCI114182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karaki H., Weiss G. B. Calcium release in smooth muscle. Life Sci. 1988;42(2):111–122. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(88)90674-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konrads A., Hofbauer K. G., Werner U., Gross F. Effects of vasopressin and its deamino-D-arginine analogue on renin release in the isolated perfused rat kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1978 Oct 18;377(1):81–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00584378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz A. Cellular control of renin secretion. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1989;113:1–40. doi: 10.1007/BFb0032674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz A., Penner R. Angiotensin II induces oscillations of intracellular calcium and blocks anomalous inward rectifying potassium current in mouse renal juxtaglomerular cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3423–3427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz A., Pfeilschifter J., Hutter A., Bührle C., Nobiling R., Taugner R., Hackenthal E., Bauer C. Role of protein kinase C in inhibition of renin release caused by vasoconstrictors. Am J Physiol. 1986 Apr;250(4 Pt 1):C563–C571. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.250.4.C563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz A., Skott O., Chegini S., Penner R. Lack of direct evidence for a functional role of voltage-operated calcium channels in juxtaglomerular cells. Pflugers Arch. 1990 May;416(3):281–287. doi: 10.1007/BF00392064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liard J. F. Interaction between V1 and V2 effects in hemodynamic response to vasopressin in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1990 Feb;258(2 Pt 2):H482–H489. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.258.2.H482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loutzenhiser R., Hayashi K., Epstein M. Divergent effects of KCl-induced depolarization on afferent and efferent arterioles. Am J Physiol. 1989 Oct;257(4 Pt 2):F561–F564. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.257.4.F561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H., Kirk C. J., Billah M. M. Hormonal stimulation of phosphatidylinositol breakdown with particular reference to the hepatic effects of vasopressin. Biochem Soc Trans. 1979 Oct;7(5):861–865. doi: 10.1042/bst0070861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel F., Imbert-Teboul M., Chabardès D. Receptors to vasopressin and other hormones in the mammalian kidney. Kidney Int. 1987 Feb;31(2):512–520. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nobiling R., Münter K., Bührle C. P., Hackenthal E. Influence of pulsatile perfusion upon renin release from the isolated perfused rat kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Mar;415(6):713–717. doi: 10.1007/BF02584010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen H. The calcium messenger system (1). N Engl J Med. 1986 Apr 24;314(17):1094–1101. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198604243141707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen H. The calcium messenger system (2). N Engl J Med. 1986 May 1;314(18):1164–1170. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198605013141807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riegger G. A., Liebau G., Bauer E., Kochsiek K. Vasopressin and renin in high output heart failure of rats: hemodynamic effects of elevated plasma hormone levels. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1985 Jan-Feb;7(1):1–5. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198501000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rightsel W. A., Okamura T., Inagami T., Pitcock J. A., Takii Y., Brooks B., Brown P., Muirhead E. E. Juxtaglomerular cells grown as monolayer cell culture contain renin, angiotensin I-converting enzyme, and angiotensin I and II/III. Circ Res. 1982 Jun;50(6):822–829. doi: 10.1161/01.res.50.6.822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholz H., Kurtz A. Role of protein kinase C in renal vasoconstriction caused by angiotensin II. Am J Physiol. 1990 Sep;259(3 Pt 1):C421–C426. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.3.C421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schurek H. J., Alt J. M. Effect of albumin on the function of perfused rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jun;240(6):F569–F576. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.240.6.F569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J., Reid I. A. Role of the vasoconstrictor and antidiuretic activities of vasopressin in inhibition of renin secretion in conscious dogs. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jan;250(1 Pt 2):F92–F96. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.250.1.F92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takii Y., Figueiredo A. F., Inagami T. Application of immunochemical methods to the identification and characterization of rat kidney inactive renin. Hypertension. 1985 Mar-Apr;7(2):236–243. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.7.2.236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taugner R., Bührle C. P., Hackenthal E., Mannek E., Nobiling R. Morphology of the juxtaglomerular apparatus and secretory mechanisms. Contrib Nephrol. 1984;43:76–101. doi: 10.1159/000409945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita T. Ionic channels in smooth muscle studied with patch-clamp methods. Jpn J Physiol. 1988;38(1):1–18. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.38.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandongen R. Inhibition of renin secretion in the isolated rat kidney by antidiuretic hormone. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1975 Jul;49(1):73–76. doi: 10.1042/cs0490073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker B. R. Evidence for a vasodilatory effect of vasopressin in the conscious rat. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jul;251(1 Pt 2):H34–H39. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1986.251.1.H34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weingartner H., Gold P., Ballenger J. C., Smallberg S. A., Summers R., Rubinow D. R., Post R. M., Goodwin F. K. Effects of vasopressin on human memory functions. Science. 1981 Feb 6;211(4482):601–603. doi: 10.1126/science.7455701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]