Abstract
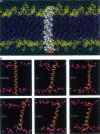
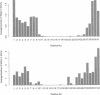
To probe the fundamentals of membrane/protein interactions, all-atom multi-nanosecond molecular dynamics simulations were conducted on a single transmembrane poly(32)alanine helix in a fully solvated dimyristoyphosphatidylcholine (DMPC) bilayer. The central 12 residues, which interact only with the lipid hydrocarbon chains, maintained a very stable helical structure. Helical regions extended beyond these central 12 residues, but interactions with the lipid fatty-acyl ester linkages, the lipid headgroups, and water molecules made the helix less stable in this region. The C and N termini, exposed largely to water, existed as random coils. As a whole, the helix tilted substantially, from perpendicular to the bilayer plane (0 degree) to a 30 degrees tilt. The helix experienced a bend at its middle, and the two halves of the helix at times assumed substantially different tilts. Frequent hydrogen bonding, of up to 0.7 ns in duration, occurred between peptide and lipid molecules. This resulted in correlated translational diffusion between the helix and a few lipid molecules. Because of the large variation in lipid conformation, the lipid environment of the peptide was not well defined in terms of "annular" lipids and on average consisted of 18 lipid molecules. When compared with a "neat" bilayer without peptide, no significant difference was seen in the bilayer thickness, lipid conformations or diffusion, or headgroup orientation. However, the lipid hydrocarbon chain order parameters showed a significant decrease in order, especially in those methylene groups closest to the headgroup.
Full text
PDF

















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bassolino-Klimas D., Alper H. E., Stouch T. R. Solute diffusion in lipid bilayer membranes: an atomic level study by molecular dynamics simulation. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 30;32(47):12624–12637. doi: 10.1021/bi00210a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büldt G., Wohlgemuth R. The headgroup conformation of phospholipids in membranes. J Membr Biol. 1981 Feb 15;58(2):81–100. doi: 10.1007/BF01870972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challou N., Goormaghtigh E., Cabiaux V., Conrath K., Ruysschaert J. M. Sequence and structure of the membrane-associated peptide of glycophorin A. Biochemistry. 1994 Jun 7;33(22):6902–6910. doi: 10.1021/bi00188a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu S. W., Clark M., Balaji V., Subramaniam S., Scott H. L., Jakobsson E. Incorporation of surface tension into molecular dynamics simulation of an interface: a fluid phase lipid bilayer membrane. Biophys J. 1995 Oct;69(4):1230–1245. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80005-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daggett V., Kollman P. A., Kuntz I. D. A molecular dynamics simulation of polyalanine: an analysis of equilibrium motions and helix-coil transitions. Biopolymers. 1991 Aug;31(9):1115–1134. doi: 10.1002/bip.360310911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daggett V., Levitt M. Molecular dynamics simulations of helix denaturation. J Mol Biol. 1992 Feb 20;223(4):1121–1138. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90264-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damodaran K. V., Merz K. M., Jr, Gaber B. P. Structure and dynamics of the dilauroylphosphatidylethanolamine lipid bilayer. Biochemistry. 1992 Aug 25;31(33):7656–7664. doi: 10.1021/bi00148a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dauber-Osguthorpe P., Roberts V. A., Osguthorpe D. J., Wolff J., Genest M., Hagler A. T. Structure and energetics of ligand binding to proteins: Escherichia coli dihydrofolate reductase-trimethoprim, a drug-receptor system. Proteins. 1988;4(1):31–47. doi: 10.1002/prot.340040106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edholm O., Johansson J. Lipid bilayer polypeptide interactions studied by molecular dynamics simulation. Eur Biophys J. 1987;14(4):203–209. doi: 10.1007/BF00256353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Essex J. W., Hann M. M., Richards W. G. Molecular dynamics simulation of a hydrated phospholipid bilayer. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1994 May 28;344(1309):239–260. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1994.0064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feller S. E., Pastor R. W. On simulating lipid bilayers with an applied surface tension: periodic boundary conditions and undulations. Biophys J. 1996 Sep;71(3):1350–1355. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79337-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawrisch K., Ruston D., Zimmerberg J., Parsegian V. A., Rand R. P., Fuller N. Membrane dipole potentials, hydration forces, and the ordering of water at membrane surfaces. Biophys J. 1992 May;61(5):1213–1223. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81931-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu W., Lazo N. D., Cross T. A. Tryptophan dynamics and structural refinement in a lipid bilayer environment: solid state NMR of the gramicidin channel. Biochemistry. 1995 Oct 31;34(43):14138–14146. doi: 10.1021/bi00043a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang P., Perez J. J., Loew G. H. Molecular dynamics simulations of phospholipid bilayers. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1994 Apr;11(5):927–956. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1994.10508045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson K. Lateral diffusion in membranes. Cell Motil. 1983;3(5-6):367–373. doi: 10.1002/cm.970030504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killian J. A. Gramicidin and gramicidin-lipid interactions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Dec 11;1113(3-4):391–425. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(92)90008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killian J. A., de Jong A. M., Bijvelt J., Verkleij A. J., de Kruijff B. Induction of non-bilayer lipid structures by functional signal peptides. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):815–819. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08178.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitson D. H., Avbelj F., Moult J., Nguyen D. T., Mertz J. E., Hadzi D., Hagler A. T. On achieving better than 1-A accuracy in a simulation of a large protein: Streptomyces griseus protease A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):8920–8924. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.8920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs H., Mark A. E., Johansson J., van Gunsteren W. F. The effect of environment on the stability of an integral membrane helix: molecular dynamics simulations of surfactant protein C in chloroform, methanol and water. J Mol Biol. 1995 Apr 7;247(4):808–822. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(05)80156-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S. C., Deber C. M. A measure of helical propensity for amino acids in membrane environments. Nat Struct Biol. 1994 Jun;1(6):368–373. doi: 10.1038/nsb0694-368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loncharich R. J., Brooks B. R. The effects of truncating long-range forces on protein dynamics. Proteins. 1989;6(1):32–45. doi: 10.1002/prot.340060104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miick S. M., Casteel K. M., Millhauser G. L. Experimental molecular dynamics of an alanine-based helical peptide determined by spin label electron spin resonance. Biochemistry. 1993 Aug 10;32(31):8014–8021. doi: 10.1021/bi00082a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milik M., Skolnick J. Insertion of peptide chains into lipid membranes: an off-lattice Monte Carlo dynamics model. Proteins. 1993 Jan;15(1):10–25. doi: 10.1002/prot.340150104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F. Area/lipid of bilayers from NMR. Biophys J. 1993 May;64(5):1476–1481. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81514-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F., Zhang R., Tristram-Nagle S., Sun W., Petrache H. I., Suter R. M. X-ray structure determination of fully hydrated L alpha phase dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine bilayers. Biophys J. 1996 Mar;70(3):1419–1431. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79701-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastor R. W., Venable R. M., Karplus M. Model for the structure of the lipid bilayer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):892–896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pink D. A., Ramadurai K. S., Powell J. R. Computer simulation of lipid diffusion in a two-component bilayer. The effect of adsorbing macromolecules. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jun 5;1148(2):197–208. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(93)90130-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pleiss J., Jähnig F. Collective vibrations of an alpha-helix. A molecular dynamics study. Biophys J. 1991 Apr;59(4):795–804. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82292-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pleiss J., Jähnig F. Conformational transition of an alpha-helix studied by molecular dynamics. Eur Biophys J. 1992;21(1):63–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00195445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber H., Steinhauser O. Taming cut-off induced artifacts in molecular dynamics studies of solvated polypeptides. The reaction field method. J Mol Biol. 1992 Dec 5;228(3):909–923. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90874-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H. L. Monte Carlo calculations of order parameter profiles in models of lipid-protein interactions in bilayers. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 7;25(20):6122–6126. doi: 10.1021/bi00368a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig A., Seelig J. Effect of a single cis double bond on the structures of a phospholipid bilayer. Biochemistry. 1977 Jan 11;16(1):45–50. doi: 10.1021/bi00620a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig A., Seelig J. The dynamic structure of fatty acyl chains in a phospholipid bilayer measured by deuterium magnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1974 Nov 5;13(23):4839–4845. doi: 10.1021/bi00720a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig J., Gally G. U., Wohlgemuth R. Orientation and flexibility of the choline head group in phosphatidylcholine bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jun 2;467(2):109–119. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90188-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig J., Nebel S., Ganz P., Bruns C. Electrostatic and nonpolar peptide-membrane interactions. Lipid binding and functional properties of somatostatin analogues of charge z = +1 to z = +3. Biochemistry. 1993 Sep 21;32(37):9714–9721. doi: 10.1021/bi00088a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperotto M. M., Mouritsen O. G. Monte Carlo simulation studies of lipid order parameter profiles near integral membrane proteins. Biophys J. 1991 Feb;59(2):261–270. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82219-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tu K., Tobias D. J., Blasie J. K., Klein M. L. Molecular dynamics investigation of the structure of a fully hydrated gel-phase dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine bilayer. Biophys J. 1996 Feb;70(2):595–608. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79623-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Buuren A. R., Berendsen H. J. Molecular dynamics simulation of the stability of a 22-residue alpha-helix in water and 30% trifluoroethanol. Biopolymers. 1993 Aug;33(8):1159–1166. doi: 10.1002/bip.360330802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaz W. L., Almeida P. F. Microscopic versus macroscopic diffusion in one-component fluid phase lipid bilayer membranes. Biophys J. 1991 Dec;60(6):1553–1554. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82190-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venable R. M., Zhang Y., Hardy B. J., Pastor R. W. Molecular dynamics simulations of a lipid bilayer and of hexadecane: an investigation of membrane fluidity. Science. 1993 Oct 8;262(5131):223–226. doi: 10.1126/science.8211140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel H., Nilsson L., Rigler R., Voges K. P., Jung G. Structural fluctuations of a helical polypeptide traversing a lipid bilayer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5067–5071. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt T. C., Killian J. A., De Kruijff B. Structure and dynamics of the acyl chain of a transmembrane polypeptide. Biochemistry. 1994 Mar 1;33(8):2063–2070. doi: 10.1021/bi00174a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. S., Schulz G. E. Structure of porin refined at 1.8 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1992 Sep 20;227(2):493–509. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90903-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener M. C., King G. I., White S. H. Structure of a fluid dioleoylphosphatidylcholine bilayer determined by joint refinement of x-ray and neutron diffraction data. I. Scaling of neutron data and the distributions of double bonds and water. Biophys J. 1991 Sep;60(3):568–576. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82086-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener M. C., White S. H. Structure of a fluid dioleoylphosphatidylcholine bilayer determined by joint refinement of x-ray and neutron diffraction data. III. Complete structure. Biophys J. 1992 Feb;61(2):434–447. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81849-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener M. C., White S. H. Transbilayer distribution of bromine in fluid bilayers containing a specifically brominated analogue of dioleoylphosphatidylcholine. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 16;30(28):6997–7008. doi: 10.1021/bi00242a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. A., Pohorille A. Molecular dynamics of a water-lipid bilayer interface. J Am Chem Soc. 1994;116(4):1490–1501. doi: 10.1021/ja00083a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolf T. B., Roux B. Structure, energetics, and dynamics of lipid-protein interactions: A molecular dynamics study of the gramicidin A channel in a DMPC bilayer. Proteins. 1996 Jan;24(1):92–114. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0134(199601)24:1<92::AID-PROT7>3.0.CO;2-Q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xing J., Scott H. L. Monte Carlo studies of lipid chains and gramicidin A in a model membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Nov 30;165(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91025-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeates T. O., Komiya H., Chirino A., Rees D. C., Allen J. P., Feher G. Structure of the reaction center from Rhodobacter sphaeroides R-26 and 2.4.1: protein-cofactor (bacteriochlorophyll, bacteriopheophytin, and carotenoid) interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7993–7997. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. P., Lewis R. N., Henry G. D., Sykes B. D., Hodges R. S., McElhaney R. N. Peptide models of helical hydrophobic transmembrane segments of membrane proteins. 1. Studies of the conformation, intrabilayer orientation, and amide hydrogen exchangeability of Ac-K2-(LA)12-K2-amide. Biochemistry. 1995 Feb 21;34(7):2348–2361. doi: 10.1021/bi00007a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. P., Lewis R. N., Hodges R. S., McElhaney R. N. Peptide models of helical hydrophobic transmembrane segments of membrane proteins. 2. Differential scanning calorimetric and FTIR spectroscopic studies of the interaction of Ac-K2-(LA)12-K2-amide with phosphatidylcholine bilayers. Biochemistry. 1995 Feb 21;34(7):2362–2371. doi: 10.1021/bi00007a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jongh H. H., Goormaghtigh E., Killian J. A. Analysis of circular dichroism spectra of oriented protein-lipid complexes: toward a general application. Biochemistry. 1994 Dec 6;33(48):14521–14528. doi: 10.1021/bi00252a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]