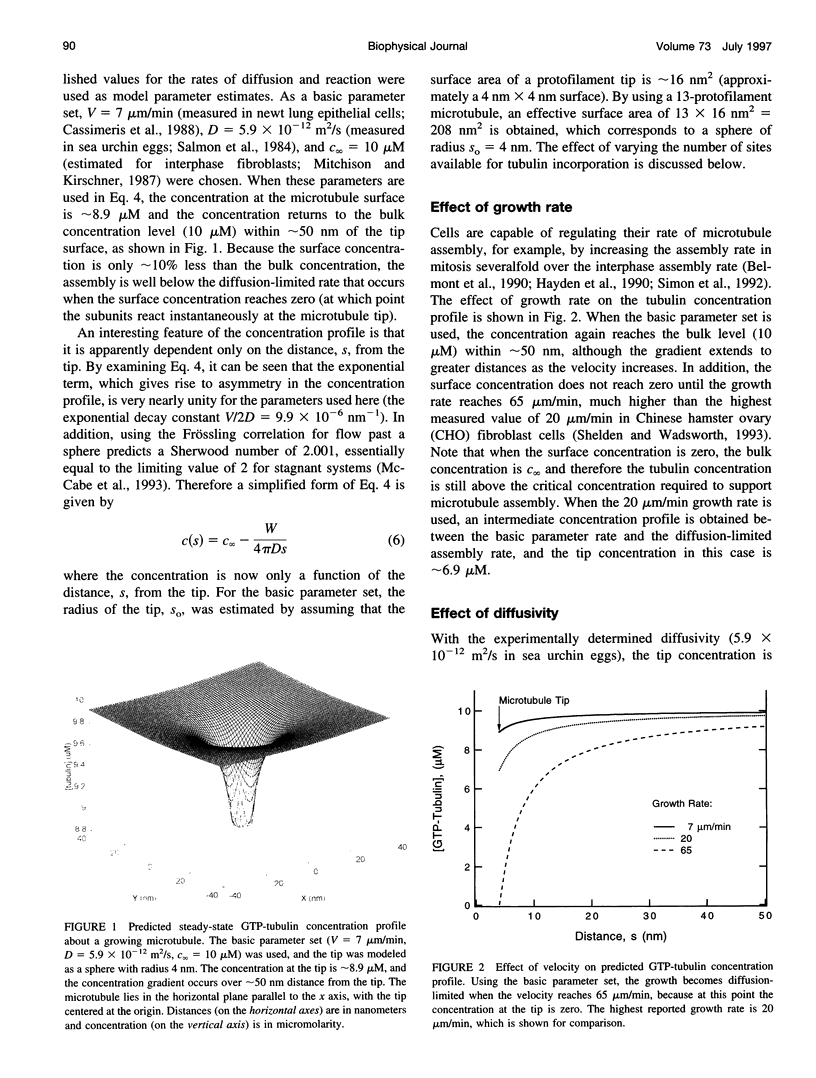
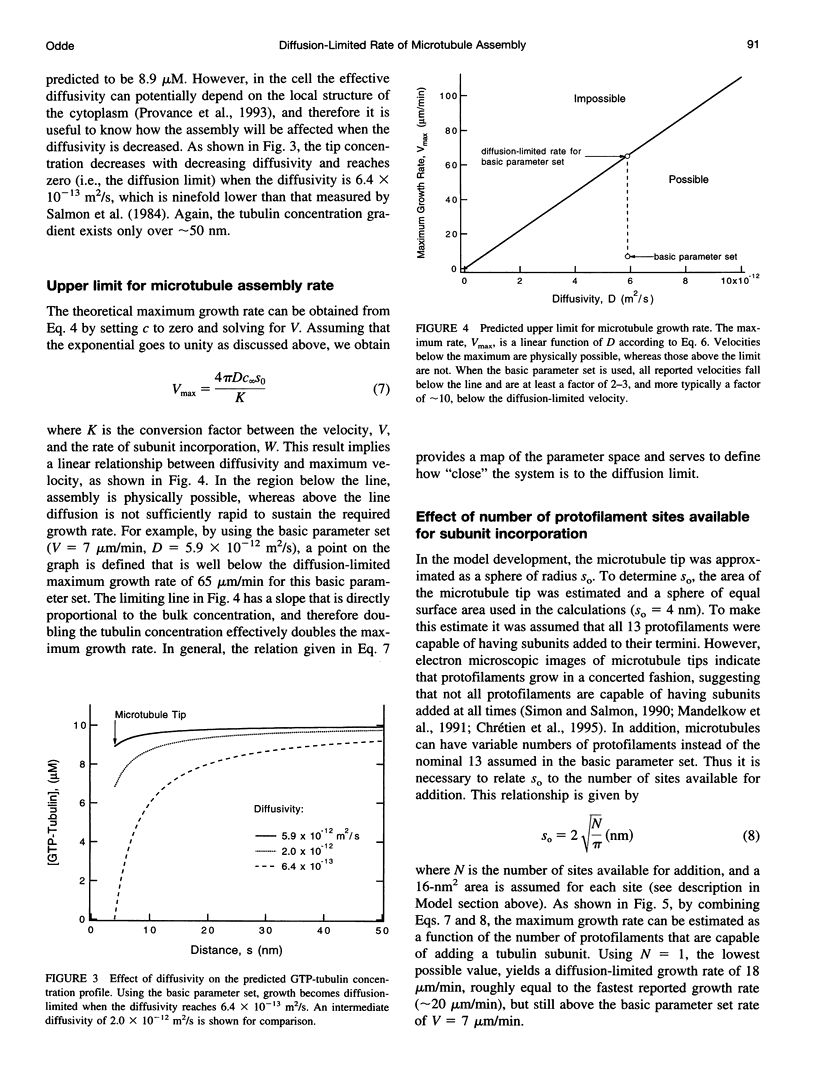
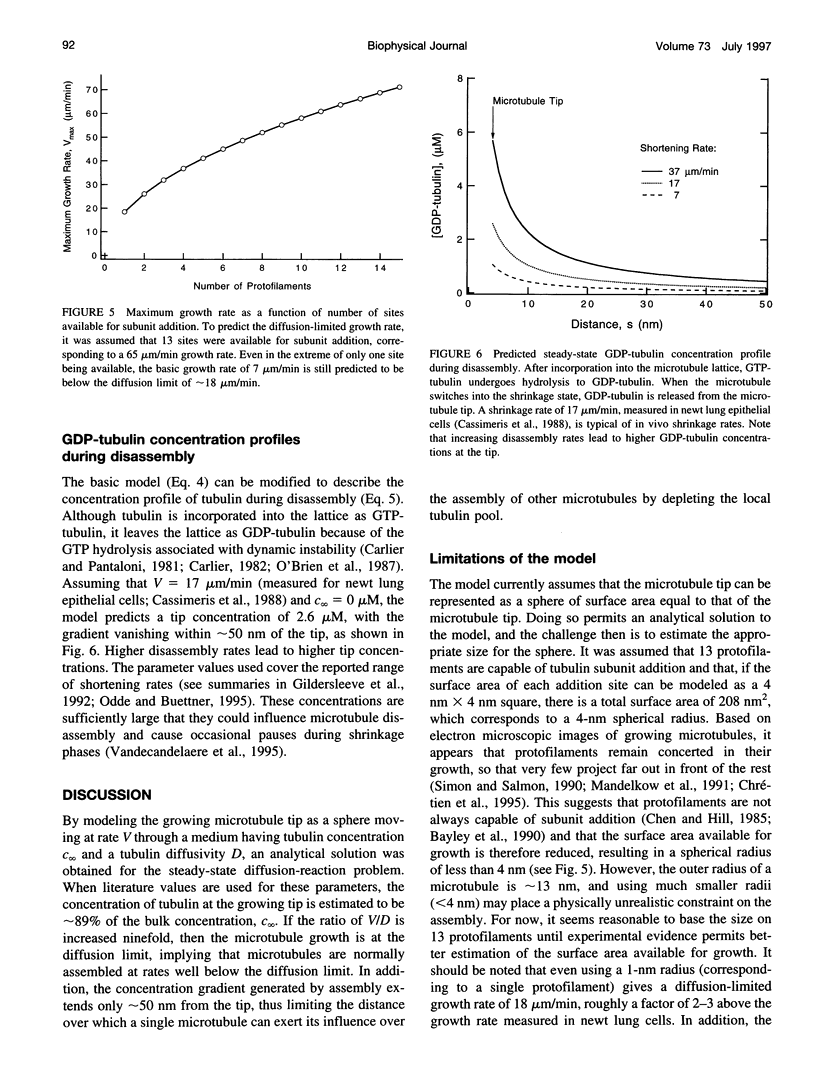
Abstract
Microtubule assembly is a complex process with individual microtubules alternating stochastically between extended periods of assembly and disassembly, a phenomenon known as dynamic instability. Since the discovery of dynamic instability, molecular models of assembly have generally assumed that tubulin incorporation into the microtubule lattice is primarily reaction-limited. Recently this assumption has been challenged and the importance of diffusion in microtubule assembly dynamics asserted on the basis of scaling arguments, with tubulin gradients predicted to extend over length scales exceeding a cell diameter, approximately 50 microns. To assess whether individual microtubules in vivo assemble at diffusion-limited rates and to predict the theoretical upper limit on the assembly rate, a steady-state mean-field model for the concentration of tubulin about a growing microtubule tip was developed. Using published parameter values for microtubule assembly in vivo (growth rate = 7 microns/min, diffusivity = 6 x 10(-12) m2/s, tubulin concentration = 10 microM), the model predicted that the tubulin concentration at the microtubule tip was approximately 89% of the concentration far from the tip, indicating that microtubule self-assembly is not diffusion-limited. Furthermore, the gradients extended less than approximately 50 nm (the equivalent of about two microtubule diameters) from the microtubule tip, a distance much less than a cell diameter. In addition, a general relation was developed to predict the diffusion-limited assembly rate from the diffusivity and bulk tubulin concentration. Using this relation, it was estimated that the maximum theoretical assembly rate is approximately 65 microns/min, above which tubulin can no longer diffuse rapidly enough to support faster growth.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayley P. M., Schilstra M. J., Martin S. R. A simple formulation of microtubule dynamics: quantitative implications of the dynamic instability of microtubule populations in vivo and in vitro. J Cell Sci. 1989 Jun;93(Pt 2):241–254. doi: 10.1242/jcs.93.2.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayley P. M., Schilstra M. J., Martin S. R. Microtubule dynamic instability: numerical simulation of microtubule transition properties using a Lateral Cap model. J Cell Sci. 1990 Jan;95(Pt 1):33–48. doi: 10.1242/jcs.95.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayley P. M. What makes microtubules dynamic? J Cell Sci. 1990 Mar;95(Pt 3):329–334. doi: 10.1242/jcs.95.3.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayley P. Why microtubules grow and shrink. Nature. 1993 May 27;363(6427):309–309. doi: 10.1038/363309a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belmont L. D., Hyman A. A., Sawin K. E., Mitchison T. J. Real-time visualization of cell cycle-dependent changes in microtubule dynamics in cytoplasmic extracts. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):579–589. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90022-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ze'ev A., Farmer S. R., Penman S. Mechanisms of regulating tubulin synthesis in cultured mammalian cells. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):319–325. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlier M. F. Guanosine-5'-triphosphate hydrolysis and tubulin polymerization. Review article. Mol Cell Biochem. 1982 Sep 3;47(2):97–113. doi: 10.1007/BF00234410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlier M. F. Nucleotide hydrolysis in cytoskeletal assembly. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;3(1):12–17. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90160-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlier M. F., Pantaloni D. Kinetic analysis of guanosine 5'-triphosphate hydrolysis associated with tubulin polymerization. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 31;20(7):1918–1924. doi: 10.1021/bi00510a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassimeris L., Pryer N. K., Salmon E. D. Real-time observations of microtubule dynamic instability in living cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2223–2231. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassimeris L. Regulation of microtubule dynamic instability. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1993;26(4):275–281. doi: 10.1002/cm.970260402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. D., Hill T. L. Monte Carlo study of the GTP cap in a five-start helix model of a microtubule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1131–1135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrétien D., Fuller S. D., Karsenti E. Structure of growing microtubule ends: two-dimensional sheets close into tubes at variable rates. J Cell Biol. 1995 Jun;129(5):1311–1328. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.5.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., Sherline P., Kirschner M. W. Unpolymerized tubulin modulates the level of tubulin mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):537–546. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dogterom M., Maggs A. C., Leibler S. Diffusion and formation of microtubule asters: physical processes versus biochemical regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jul 18;92(15):6683–6688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.15.6683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dogterom M, Leibler S. Physical aspects of the growth and regulation of microtubule structures. Phys Rev Lett. 1993 Mar 1;70(9):1347–1350. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.70.1347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson H. P., O'Brien E. T. Microtubule dynamic instability and GTP hydrolysis. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1992;21:145–166. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.21.060192.001045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fygenson DK, Braun E, Libchaber A. Phase diagram of microtubules. Phys Rev E Stat Phys Plasmas Fluids Relat Interdiscip Topics. 1994 Aug;50(2):1579–1588. doi: 10.1103/physreve.50.1579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gildersleeve R. F., Cross A. R., Cullen K. E., Fagen A. P., Williams R. C., Jr Microtubules grow and shorten at intrinsically variable rates. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):7995–8006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gliksman N. R., Skibbens R. V., Salmon E. D. How the transition frequencies of microtubule dynamic instability (nucleation, catastrophe, and rescue) regulate microtubule dynamics in interphase and mitosis: analysis using a Monte Carlo computer simulation. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Oct;4(10):1035–1050. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.10.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Garay M. L., Cabral F. alpha-Tubulin limits its own synthesis: evidence for a mechanism involving translational repression. J Cell Biol. 1996 Dec;135(6 Pt 1):1525–1534. doi: 10.1083/jcb.135.6.1525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayden J. H., Bowser S. S., Rieder C. L. Kinetochores capture astral microtubules during chromosome attachment to the mitotic spindle: direct visualization in live newt lung cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1039–1045. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz S. B. Taxol (paclitaxel): mechanisms of action. Ann Oncol. 1994;5 (Suppl 6):S3–S6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson K., Wojcieszyn J. The translational mobility of substances within the cytoplasmic matrix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6747–6751. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luby-Phelps K., Taylor D. L., Lanni F. Probing the structure of cytoplasm. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;102(6):2015–2022. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.6.2015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandelkow E. M., Mandelkow E., Milligan R. A. Microtubule dynamics and microtubule caps: a time-resolved cryo-electron microscopy study. J Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;114(5):977–991. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.5.977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. R., Schilstra M. J., Bayley P. M. Dynamic instability of microtubules: Monte Carlo simulation and application to different types of microtubule lattice. Biophys J. 1993 Aug;65(2):578–596. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81091-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison T. J., Kirschner M. W. Some thoughts on the partitioning of tubulin between monomer and polymer under conditions of dynamic instability. Cell Biophys. 1987 Dec;11:35–55. doi: 10.1007/BF02797111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison T., Kirschner M. Dynamic instability of microtubule growth. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):237–242. doi: 10.1038/312237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison T., Kirschner M. Microtubule assembly nucleated by isolated centrosomes. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):232–237. doi: 10.1038/312232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northrup S. H., Erickson H. P. Kinetics of protein-protein association explained by Brownian dynamics computer simulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3338–3342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien E. T., Voter W. A., Erickson H. P. GTP hydrolysis during microtubule assembly. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 30;26(13):4148–4156. doi: 10.1021/bi00387a061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odde D. J., Buettner H. M. Time series characterization of simulated microtubule dynamics in the nerve growth cone. Ann Biomed Eng. 1995 May-Jun;23(3):268–286. doi: 10.1007/BF02584428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odde D. J., Cassimeris L., Buettner H. M. Kinetics of microtubule catastrophe assessed by probabilistic analysis. Biophys J. 1995 Sep;69(3):796–802. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)79953-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provance D. W., Jr, McDowall A., Marko M., Luby-Phelps K. Cytoarchitecture of size-excluding compartments in living cells. J Cell Sci. 1993 Oct;106(Pt 2):565–577. doi: 10.1242/jcs.106.2.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieder C. L. The formation, structure, and composition of the mammalian kinetochore and kinetochore fiber. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;79:1–58. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61672-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowinsky E. K., Wright M., Monsarrat B., Donehower R. C. Clinical pharmacology and metabolism of Taxol (paclitaxel): update 1993. Ann Oncol. 1994;5 (Suppl 6):S7–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabry J., O'Connor T. P., Kirschner M. W. Axonal transport of tubulin in Ti1 pioneer neurons in situ. Neuron. 1995 Jun;14(6):1247–1256. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90271-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon E. D., Saxton W. M., Leslie R. J., Karow M. L., McIntosh J. R. Diffusion coefficient of fluorescein-labeled tubulin in the cytoplasm of embryonic cells of a sea urchin: video image analysis of fluorescence redistribution after photobleaching. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2157–2164. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze E., Kirschner M. New features of microtubule behaviour observed in vivo. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):356–359. doi: 10.1038/334356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelden E., Wadsworth P. Observation and quantification of individual microtubule behavior in vivo: microtubule dynamics are cell-type specific. J Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;120(4):935–945. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.4.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J. R., Parsons S. F., Salmon E. D. Buffer conditions and non-tubulin factors critically affect the microtubule dynamic instability of sea urchin egg tubulin. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1992;21(1):1–14. doi: 10.1002/cm.970210102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J. R., Salmon E. D. The structure of microtubule ends during the elongation and shortening phases of dynamic instability examined by negative-stain electron microscopy. J Cell Sci. 1990 Aug;96(Pt 4):571–582. doi: 10.1242/jcs.96.4.571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skibbens R. V., Skeen V. P., Salmon E. D. Directional instability of kinetochore motility during chromosome congression and segregation in mitotic newt lung cells: a push-pull mechanism. J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;122(4):859–875. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.4.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabony J. Morphological bifurcations involving reaction-diffusion processes during microtubule formation. Science. 1994 Apr 8;264(5156):245–248. doi: 10.1126/science.8146654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandecandelaere A., Martin S. R., Bayley P. M. Regulation of microtubule dynamic instability by tubulin-GDP. Biochemistry. 1995 Jan 31;34(4):1332–1343. doi: 10.1021/bi00004a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasquez R. J., Gard D. L., Cassimeris L. XMAP from Xenopus eggs promotes rapid plus end assembly of microtubules and rapid microtubule polymer turnover. J Cell Biol. 1994 Nov;127(4):985–993. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.4.985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verde F., Dogterom M., Stelzer E., Karsenti E., Leibler S. Control of microtubule dynamics and length by cyclin A- and cyclin B-dependent kinases in Xenopus egg extracts. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(5):1097–1108. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.5.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. A., O'Brien E. T., Pryer N. K., Soboeiro M. F., Voter W. A., Erickson H. P., Salmon E. D. Dynamic instability of individual microtubules analyzed by video light microscopy: rate constants and transition frequencies. J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;107(4):1437–1448. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.4.1437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Spooner B. S., Wessells N. K. Ultrastructure and function of growth cones and axons of cultured nerve cells. J Cell Biol. 1971 Jun;49(3):614–635. doi: 10.1083/jcb.49.3.614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman S. B., Minton A. P. Macromolecular crowding: biochemical, biophysical, and physiological consequences. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1993;22:27–65. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.22.060193.000331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]