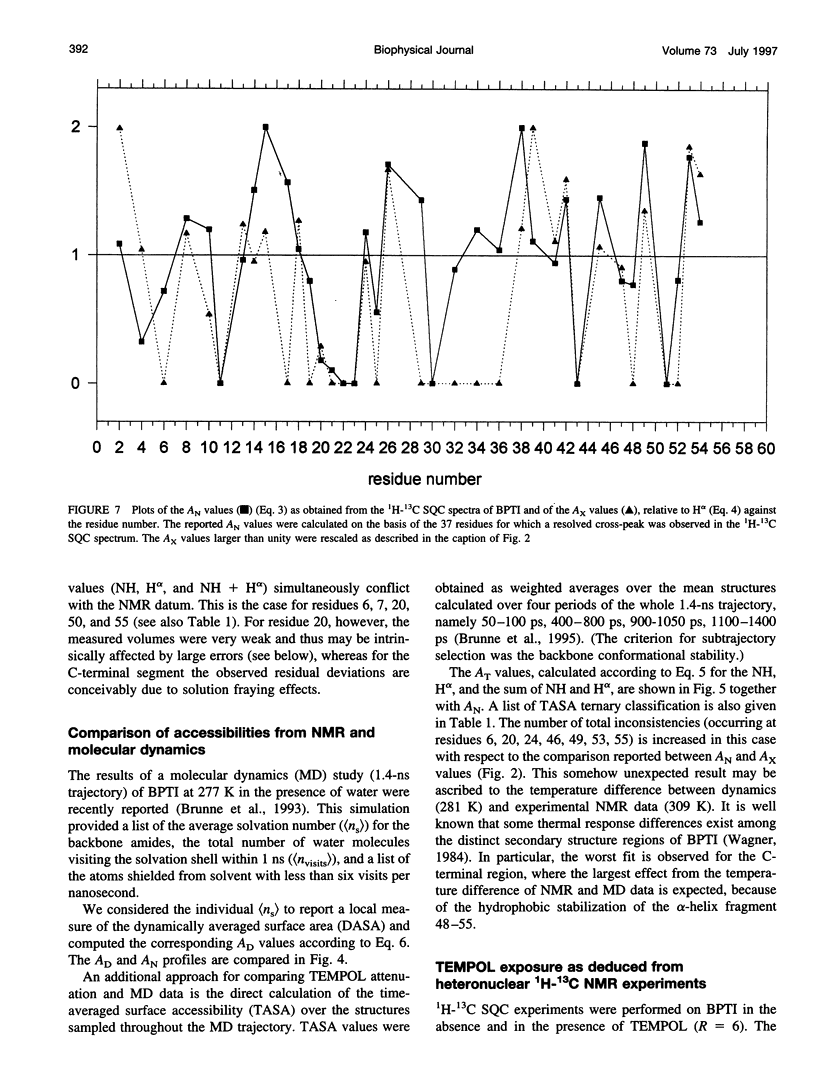
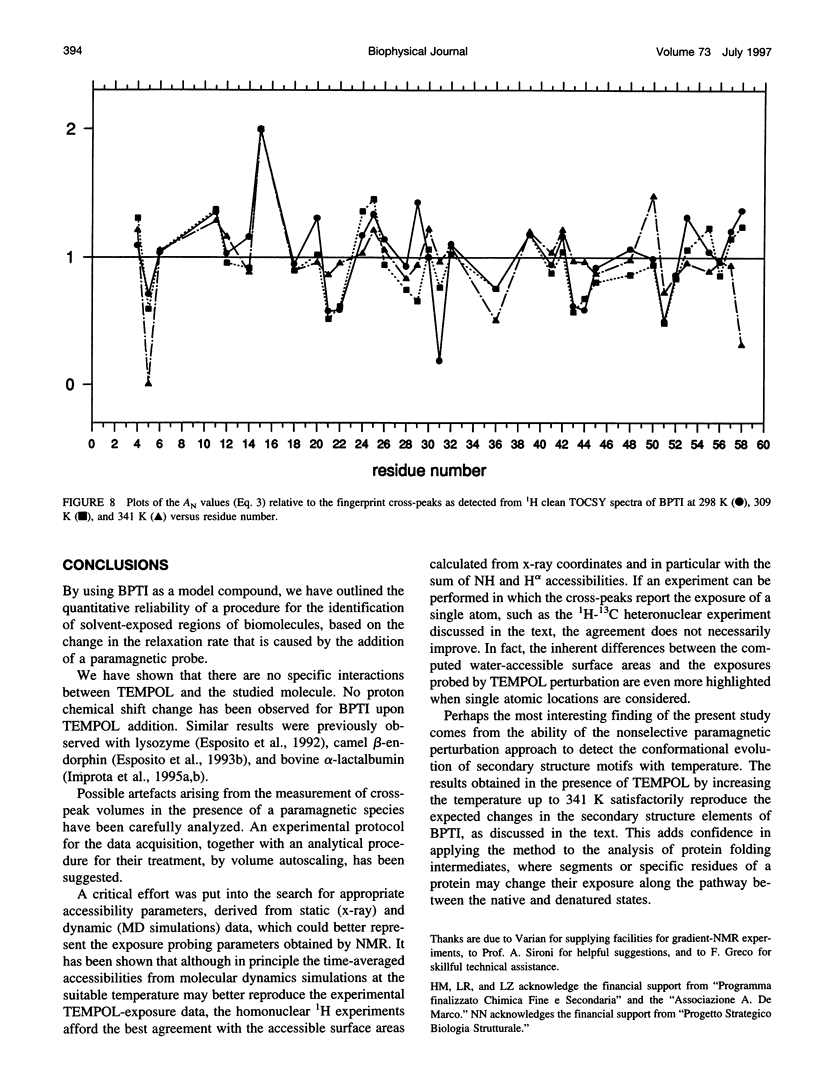
Abstract
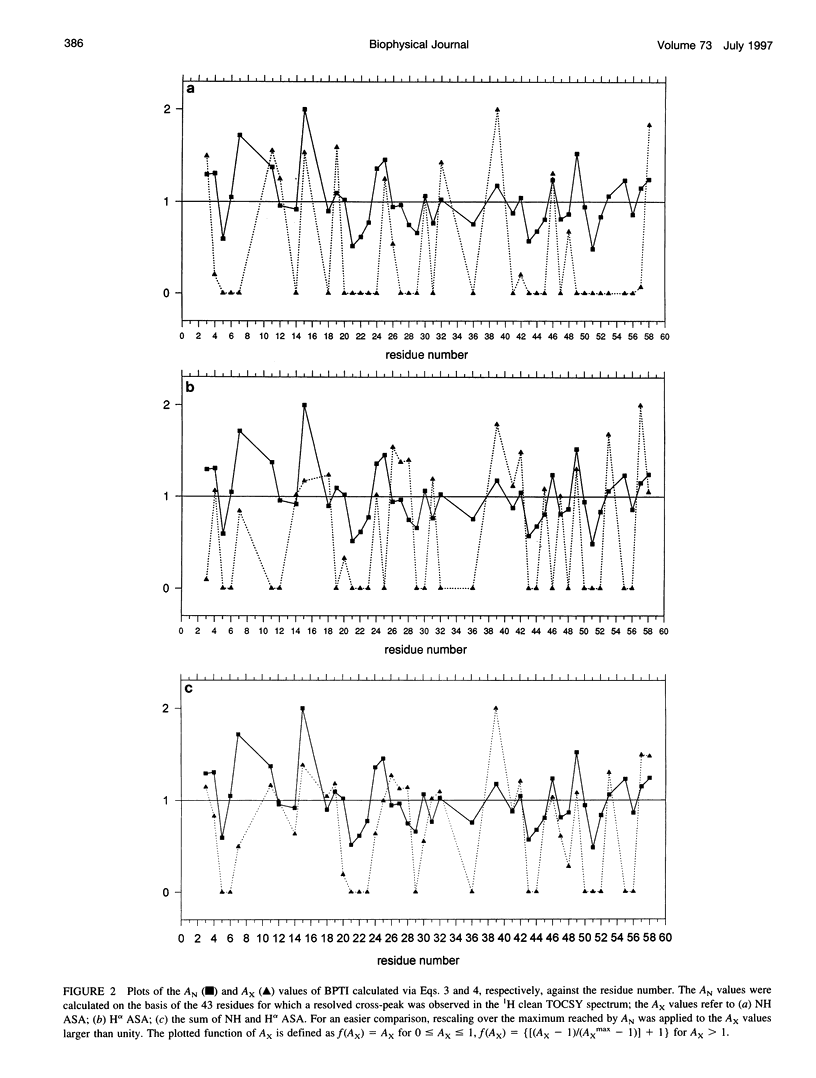
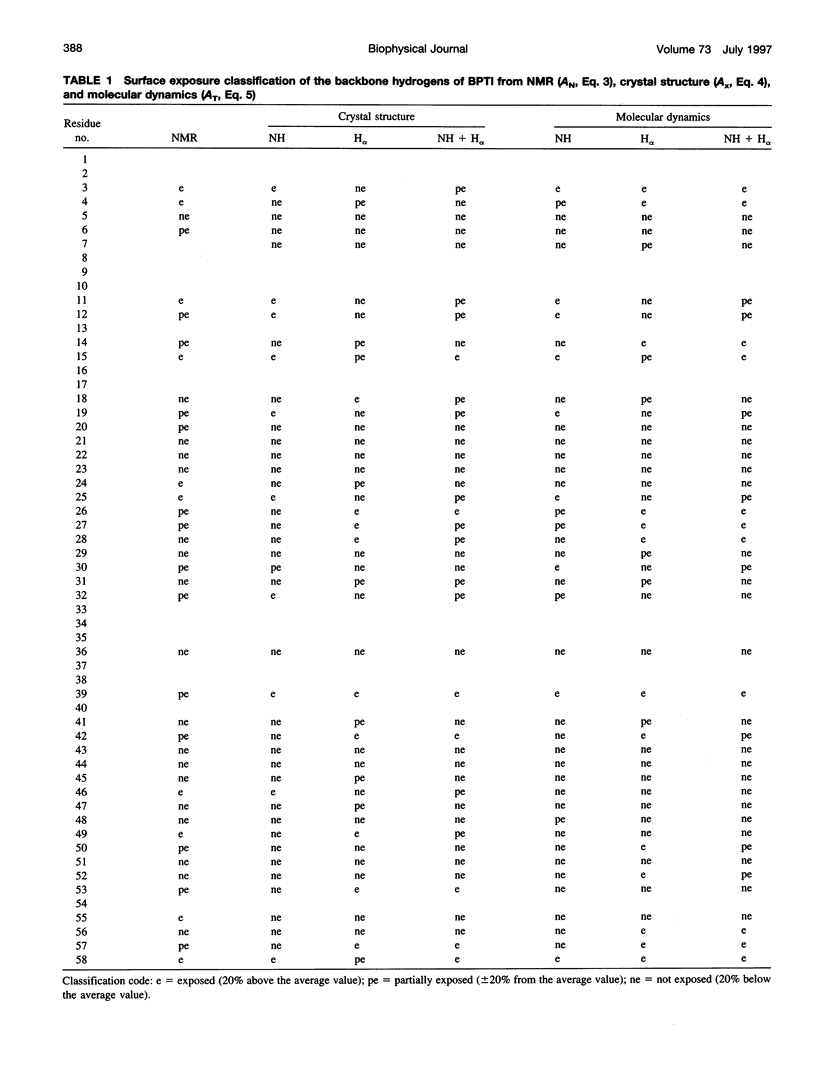
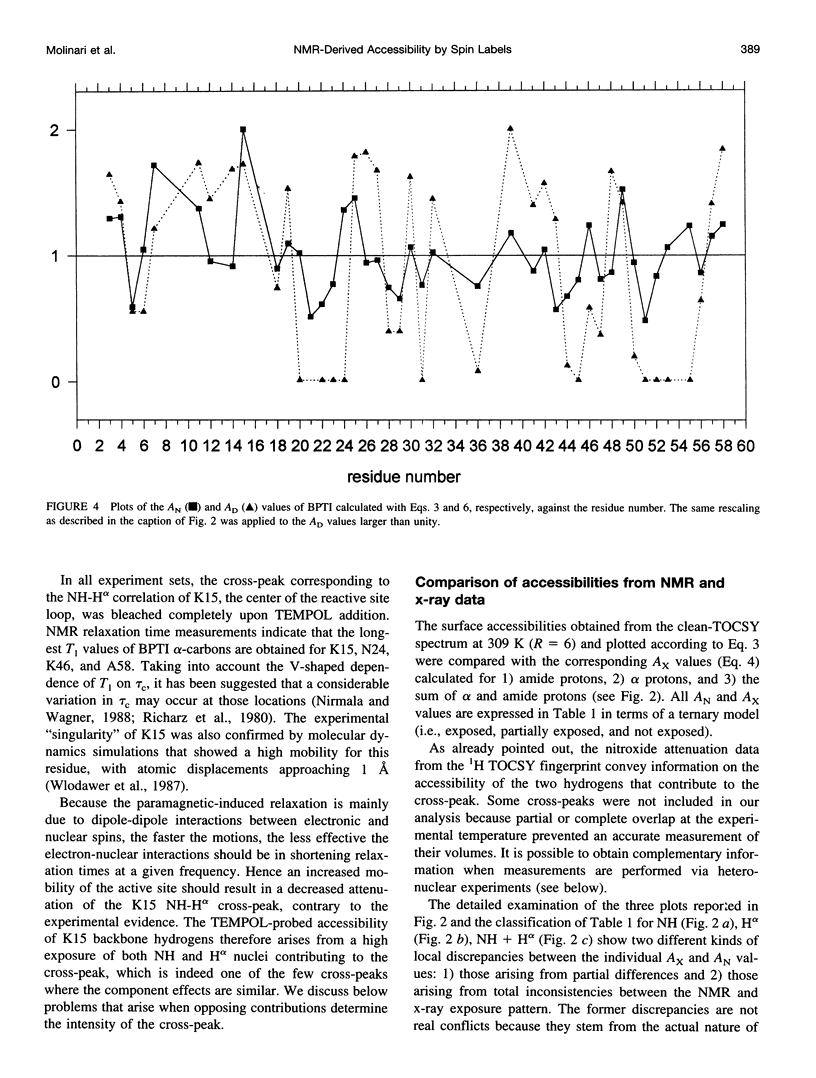
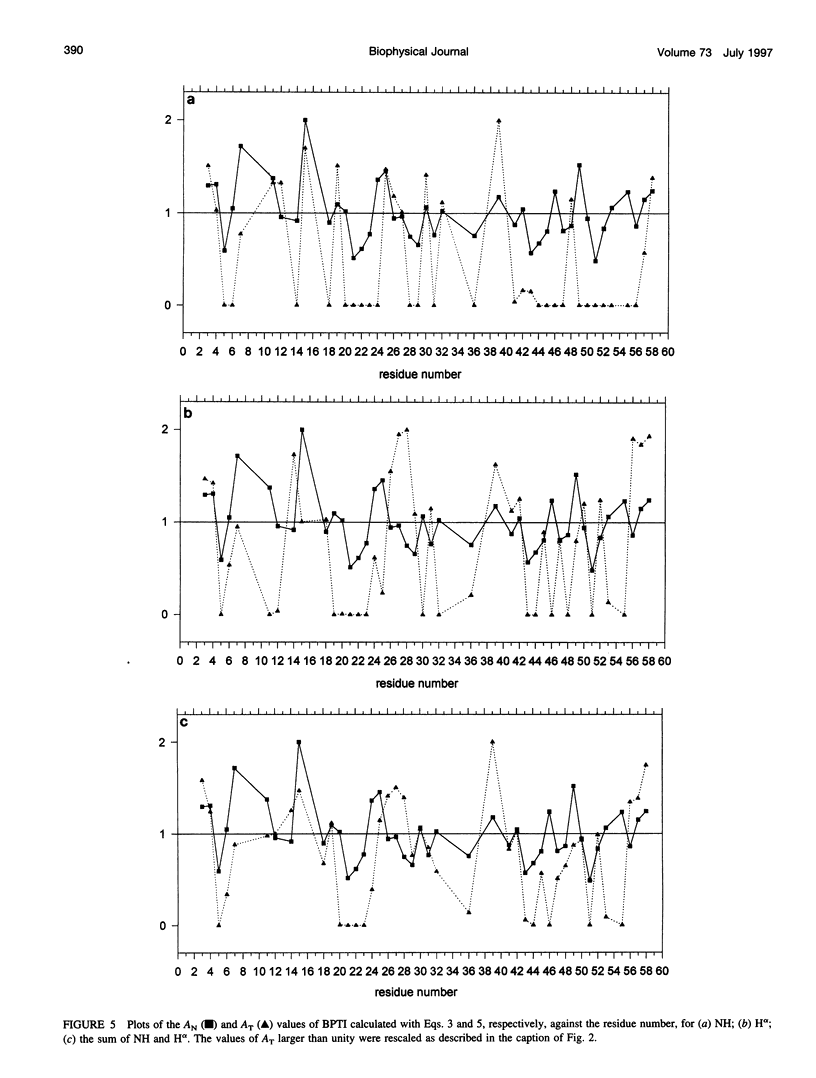
In the absence of specific interactions, the relative attenuation of protein NMR signals due to added stable free radicals such as TEMPOL should reflect the solvent accessibility of the molecular surface. The quantitative correlation between observed attenuation and surface accessibility was investigated with a model system, i.e., the small protein bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. A detailed discussion is presented on the reliability and limits of the approach, and guidelines are provided for data acquisition, treatment, and interpretation. The NMR-derived accessibilities are compared with those obtained from x-ray diffraction and molecular dynamics data. Although the time-averaged accessibilities from molecular dynamics are ideally suited to fit the NMR data, better agreement was observed between the paramagnetic attenuations of the fingerprint cross-peaks of homonuclear proton spectra and the total NH and H alpha accessibilities calculated from x-ray coordinates, than from time-averaged molecular dynamics simulations. In addition, the solvent perturbation response appears to be a promising approach for detecting the thermal conformational evolution of secondary structure elements in proteins.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aime S., Botta M., Terreno E., Anelli P. L., Uggeri F. Gd(DOTP)5-outer-sphere relaxation enhancement promoted by nitrogen bases. Magn Reson Med. 1993 Nov;30(5):583–591. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910300509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anglister J., Frey T., McConnell H. M. Distances of tyrosine residues from a spin-label hapten in the combining site of a specific monoclonal antibody. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 23;23(22):5372–5375. doi: 10.1021/bi00317a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arean C. O., Moore G. R., Williams G., Williams R. J. Ion binding to cytochrome c. Eur J Biochem. 1988 May 2;173(3):607–615. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14042.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berndt K. D., Güntert P., Orbons L. P., Wüthrich K. Determination of a high-quality nuclear magnetic resonance solution structure of the bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor and comparison with three crystal structures. J Mol Biol. 1992 Oct 5;227(3):757–775. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90222-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunne R. M., Berndt K. D., Güntert P., Wüthrich K., van Gunsteren W. F. Structure and internal dynamics of the bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor in aqueous solution from long-time molecular dynamics simulations. Proteins. 1995 Sep;23(1):49–62. doi: 10.1002/prot.340230107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunne R. M., Liepinsh E., Otting G., Wüthrich K., van Gunsteren W. F. Hydration of proteins. A comparison of experimental residence times of water molecules solvating the bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor with theoretical model calculations. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jun 20;231(4):1040–1048. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito G., Lesk A. M., Molinari H., Motta A., Niccolai N., Pastore A. Probing protein structure by solvent perturbation of NMR spectra. II. Determination of surface and buried residues in homologous proteins. Biopolymers. 1993 May;33(5):839–846. doi: 10.1002/bip.360330512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito G., Lesk A. M., Molinari H., Motta A., Niccolai N., Pastore A. Probing protein structure by solvent perturbation of nuclear magnetic resonance spectra. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectral editing and topological mapping in proteins by paramagnetic relaxation filtering. J Mol Biol. 1992 Apr 5;224(3):659–670. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90551-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Improta S., Molinari H., Pastore A., Consonni R., Zetta L. Probing protein structure by solvent perturbation of NMR spectra. A comparison with photochemically induced dynamic nuclear polarization techniques applied to native alpha-lactalbumin. Eur J Biochem. 1995 Jan 15;227(1-2):78–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1995.tb20361.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Improta S., Molinari H., Pastore A., Consonni R., Zetta L. Probing protein structure by solvent perturbation of NMR spectra. Photochemically induced dynamic nuclear polarization and paramagnetic perturbation techniques applied to the study of the molten globule state of alpha-lactalbumin. Eur J Biochem. 1995 Jan 15;227(1-2):87–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1995.tb20362.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosen P. A., Scheek R. M., Naderi H., Basus V. J., Manogaran S., Schmidt P. G., Oppenheimer N. J., Kuntz I. D. Two-dimensional 1H NMR of three spin-labeled derivatives of bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. Biochemistry. 1986 May 6;25(9):2356–2364. doi: 10.1021/bi00357a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B., Richards F. M. The interpretation of protein structures: estimation of static accessibility. J Mol Biol. 1971 Feb 14;55(3):379–400. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90324-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtarge O., Jardetzky O., Li C. H. Secondary structure determination of human beta-endorphin by 1H NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 8;26(18):5916–5925. doi: 10.1021/bi00392a051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moonen C. T., Scheek R. M., Boelens R., Müller F. The use of two-dimensional nuclear-magnetic-resonance spectroscopy and two-dimensional difference spectra in the elucidation of the active center of Megasphaera elsdenii flavodoxin. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jun 1;141(2):323–330. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08195.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petros A. M., Mueller L., Kopple K. D. NMR identification of protein surfaces using paramagnetic probes. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 30;29(43):10041–10048. doi: 10.1021/bi00495a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petros A. M., Neri P., Fesik S. W. Identification of solvent-exposed regions of an FK-506 analog, ascomycin, bound to FKBP using a paramagnetic probe. J Biomol NMR. 1992 Jan;2(1):11–18. doi: 10.1007/BF02192797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piotto M., Saudek V., Sklenár V. Gradient-tailored excitation for single-quantum NMR spectroscopy of aqueous solutions. J Biomol NMR. 1992 Nov;2(6):661–665. doi: 10.1007/BF02192855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richarz R., Nagayama K., Wüthrich K. Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation studies of internal mobility of the polypeptide chain in basic pancreatic trypsin inhibitor and a selectively reduced analogue. Biochemistry. 1980 Nov 11;19(23):5189–5196. doi: 10.1021/bi00564a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt P. G., Kuntz I. D. Distance measurements in spin-labeled lysozyme. Biochemistry. 1984 Aug 28;23(18):4261–4266. doi: 10.1021/bi00313a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner G., Braun W., Havel T. F., Schaumann T., Go N., Wüthrich K. Protein structures in solution by nuclear magnetic resonance and distance geometry. The polypeptide fold of the basic pancreatic trypsin inhibitor determined using two different algorithms, DISGEO and DISMAN. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 5;196(3):611–639. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90037-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner G., Stassinopoulou C. I., Wüthrich K. Amide-proton exchange studies by two-dimensional correlated 1H NMR in two chemically modified analogs of the basic pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Dec 3;145(2):431–436. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08572.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wien R. W., Morrisett J. D., McConnell H. M. Spin-label-induced nuclear relaxation. Distances between bound saccharides, histidine-15, and tryptophan-123 on lysozyme in solution. Biochemistry. 1972 Sep 26;11(20):3707–3716. doi: 10.1021/bi00770a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. J. NMR studies of mobility within protein structure. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Aug 15;183(3):479–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb21076.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wlodawer A., Nachman J., Gilliland G. L., Gallagher W., Woodward C. Structure of form III crystals of bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. J Mol Biol. 1987 Dec 5;198(3):469–480. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90294-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zetta L., Consonni R., De Marco A., Longhi R., Manera E., Vecchio G. Opioid peptides in micellar systems: conformational analysis by CD and by one-dimensional and two-dimensional 1H-NMR spectroscopy. Biopolymers. 1990;30(9-10):899–909. doi: 10.1002/bip.360300905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zetta L., Kaptein R. Interaction of beta-endorphin with sodium dodecyl sulfate in aqueous solution. 1H-NMR investigation. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Nov 15;145(1):181–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08538.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


