Abstract
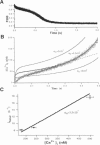
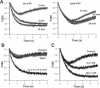
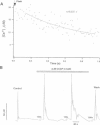
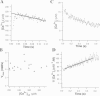
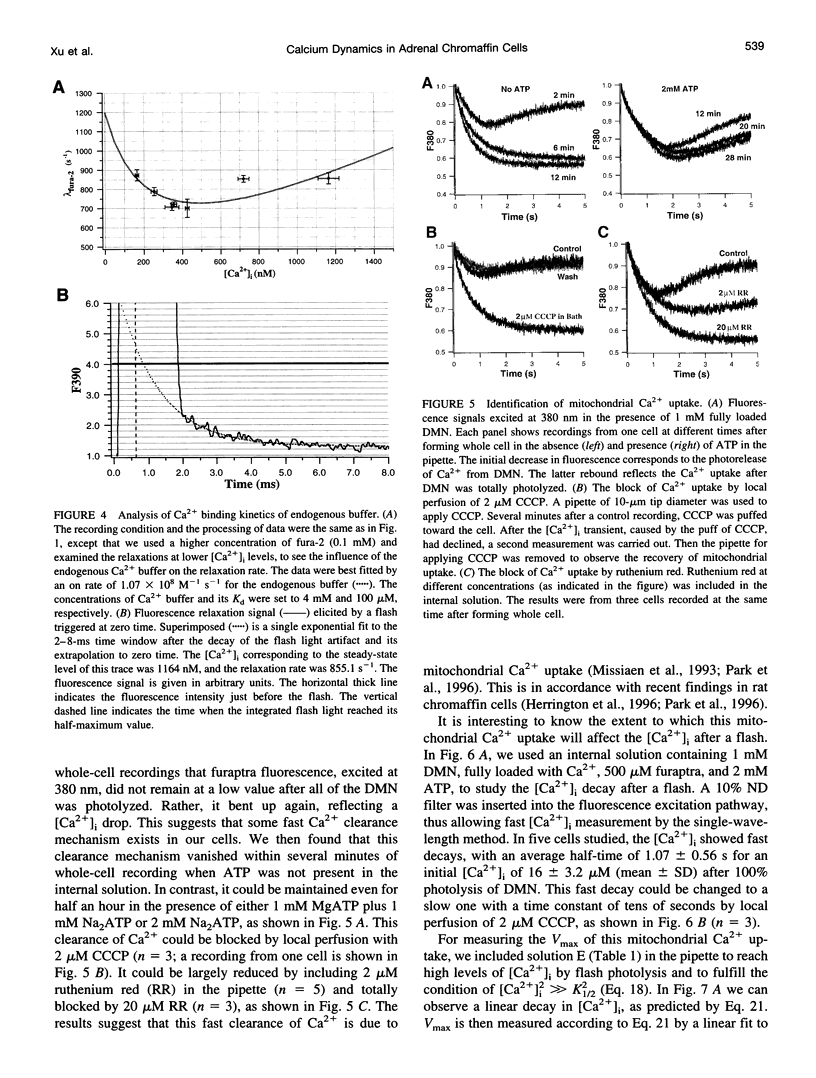
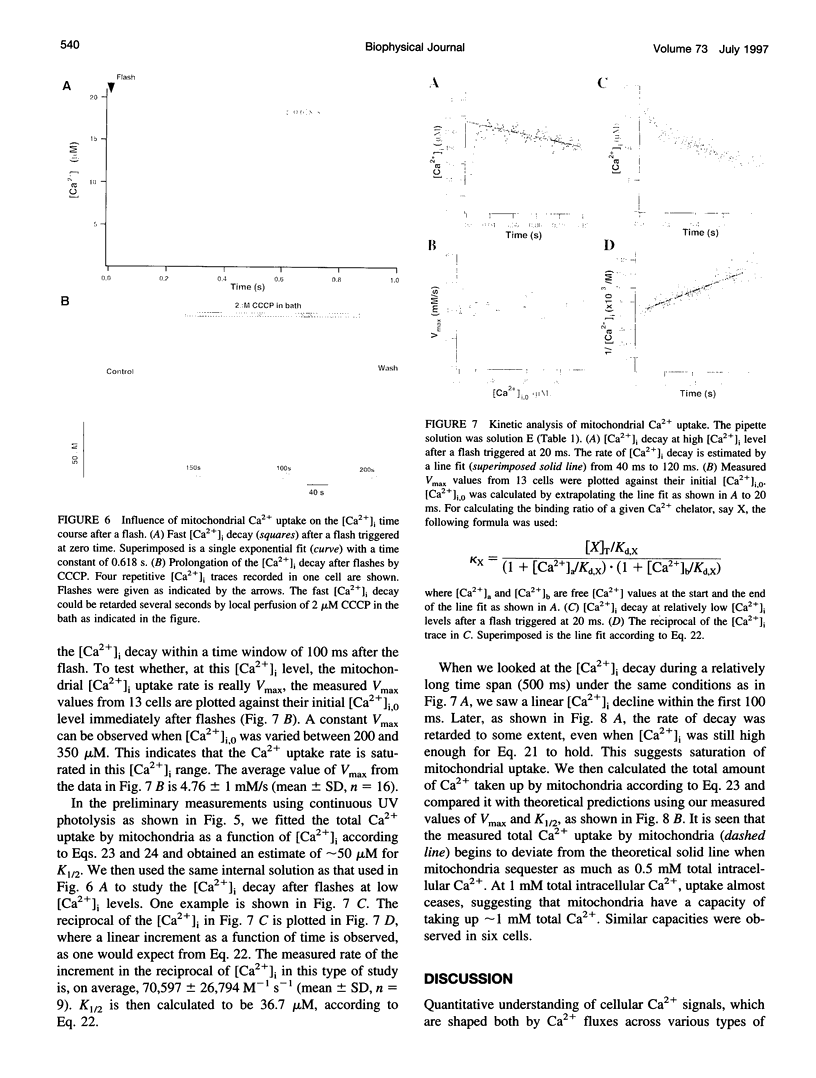
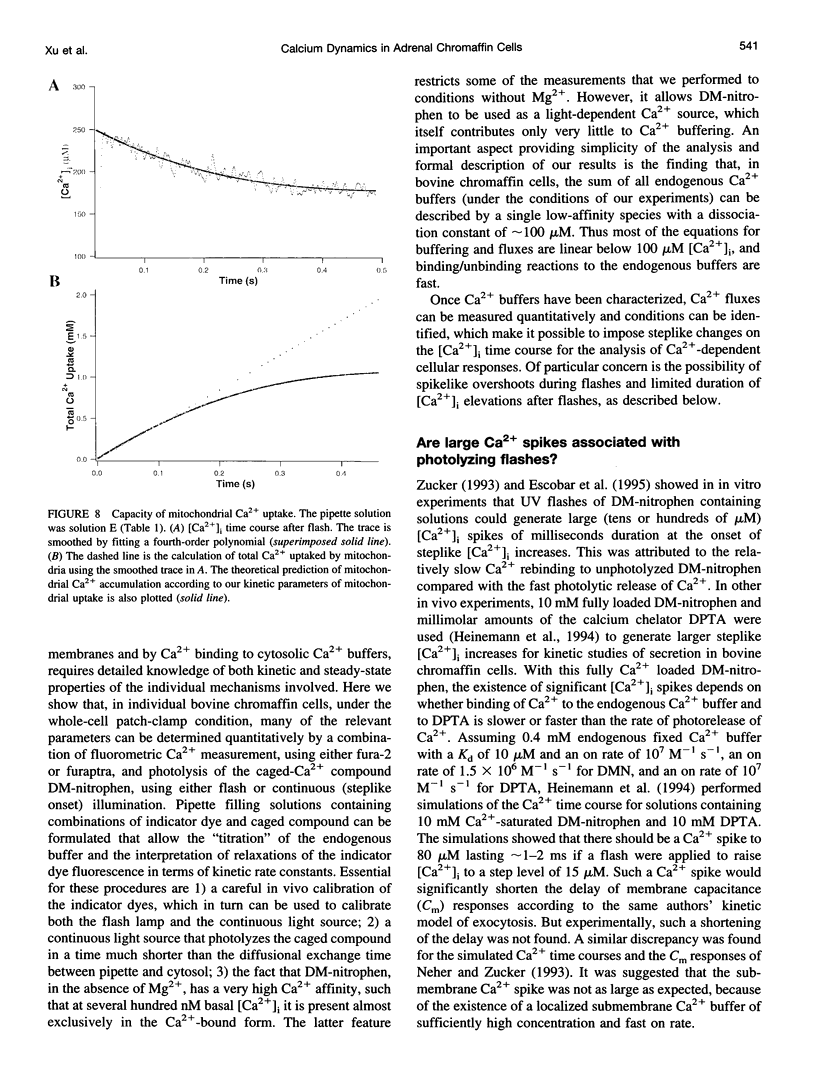
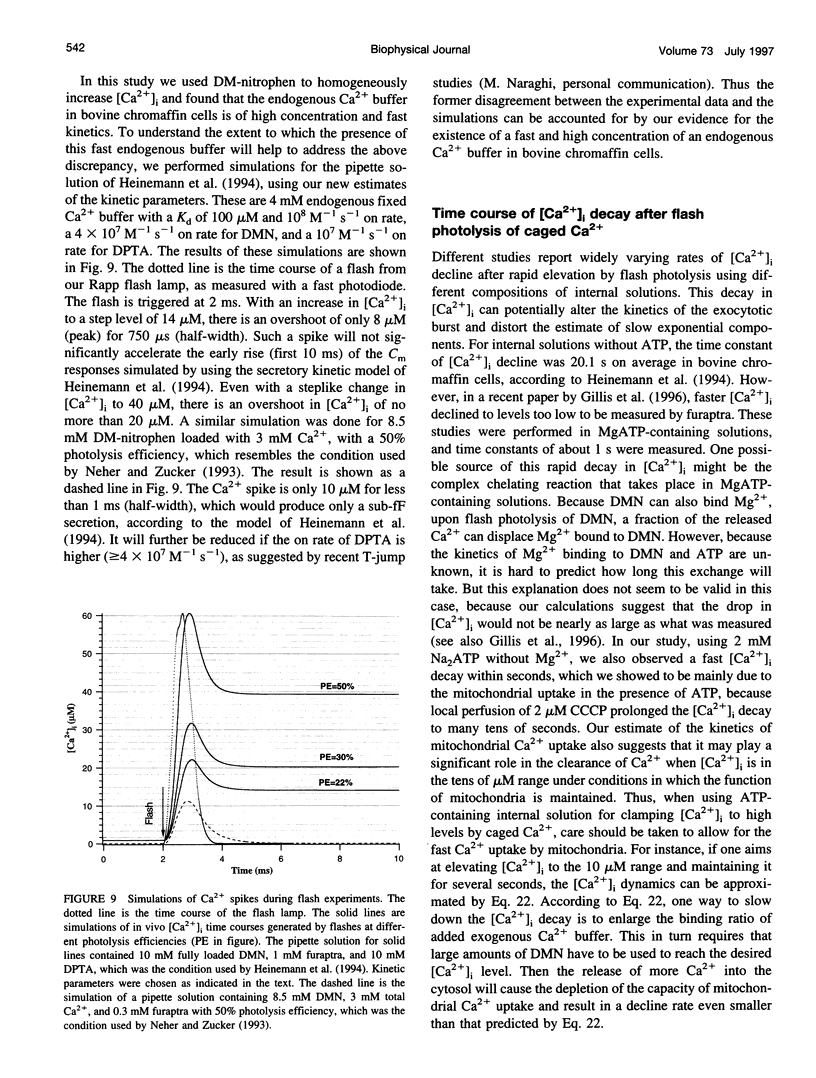
The Ca2+ binding kinetics of fura-2, DM-nitrophen, and the endogenous Ca2+ buffer, which determine the time course of Ca2+ changes after photolysis of DM-nitrophen, were studied in bovine chromaffin cells. The in vivo Ca2+ association rate constants of fura-2, DM-nitrophen, and the endogenous Ca2+ buffer were measured to be 5.17 x 10(8) M-1 s-1, 3.5 x 10(7) M-1 s-1, and 1.07 x 10(8) M-1 s-1, respectively. The endogenous Ca2+ buffer appeared to have a low affinity for Ca2+ with a dissociation constant around 100 microM. A fast Ca2+ uptake mechanism was also found to play a dominant role in the clearance of Ca2+ after flashes at high intracellular free Ca2+ concentrations ([Ca2+]), causing a fast [Ca2+]i decay within seconds. This Ca2+ clearance was identified as mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake. Its uptake kinetics were studied by analyzing the Ca2+ decay at high [Ca2+]i after flash photolysis of DM-nitrophen. The capacity of the mitochondrial uptake corresponds to a total cytosolic Ca2+ load of approximately 1 mM.
Full text
PDF



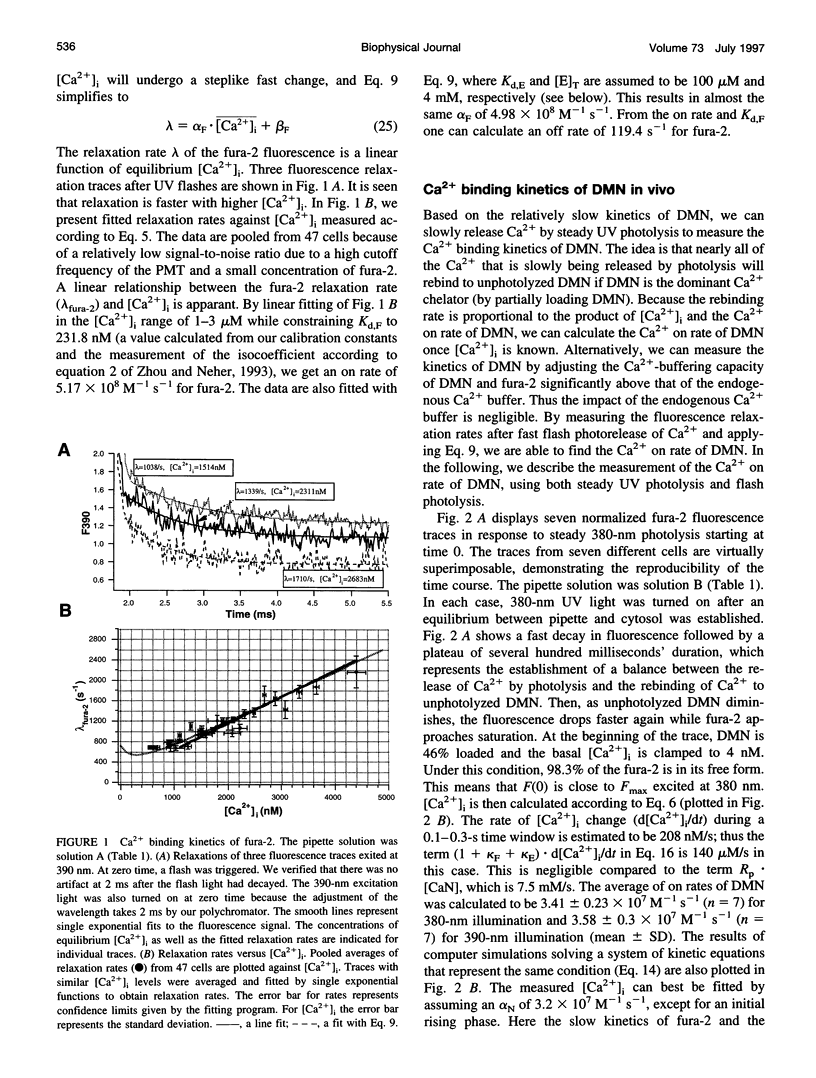



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed Z., Connor J. A. Calcium regulation by and buffer capacity of molluscan neurons during calcium transients. Cell Calcium. 1988 Apr;9(2):57–69. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(88)90025-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Hollingworth S. Fura-2 calcium transients in frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1988 Sep;403:151–192. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlin J. R., Bassani J. W., Bers D. M. Intrinsic cytosolic calcium buffering properties of single rat cardiac myocytes. Biophys J. 1994 Oct;67(4):1775–1787. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80652-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatter L. A., Wier W. G. Intracellular diffusion, binding, and compartmentalization of the fluorescent calcium indicators indo-1 and fura-2. Biophys J. 1990 Dec;58(6):1491–1499. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82494-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinley F. J., Jr, Tiffert T., Scarpa A., Mullins L. J. Intracellular calcium buffering capacity in isolated squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Sep;70(3):355–384. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.3.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durussel I., Rhyner J. A., Strehler E. E., Cox J. A. Cation binding and conformation of human calmodulin-like protein. Biochemistry. 1993 Jun 15;32(23):6089–6094. doi: 10.1021/bi00074a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis-Davies G. C., Kaplan J. H., Barsotti R. J. Laser photolysis of caged calcium: rates of calcium release by nitrophenyl-EGTA and DM-nitrophen. Biophys J. 1996 Feb;70(2):1006–1016. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79644-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobar A. L., Cifuentes F., Vergara J. L. Detection of Ca(2+)-transients elicited by flash photolysis of DM-nitrophen with a fast calcium indicator. FEBS Lett. 1995 May 15;364(3):335–338. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00425-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falke J. J., Drake S. K., Hazard A. L., Peersen O. B. Molecular tuning of ion binding to calcium signaling proteins. Q Rev Biophys. 1994 Aug;27(3):219–290. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500003012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fierro L., Llano I. High endogenous calcium buffering in Purkinje cells from rat cerebellar slices. J Physiol. 1996 Nov 1;496(Pt 3):617–625. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis K. D., Mossner R., Neher E. Protein kinase C enhances exocytosis from chromaffin cells by increasing the size of the readily releasable pool of secretory granules. Neuron. 1996 Jun;16(6):1209–1220. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80147-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grell E., Lewitzki E., Ruf H., Bamberg E., Ellis-Davies G. C., Kaplan J. H., de Weer P. Caged-Ca2+: a new agent allowing liberation of free Ca2+ in biological systems by photolysis. Cell Mol Biol. 1989;35(5):515–522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunter T. E., Gunter K. K., Sheu S. S., Gavin C. E. Mitochondrial calcium transport: physiological and pathological relevance. Am J Physiol. 1994 Aug;267(2 Pt 1):C313–C339. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1994.267.2.C313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidelberger R., Heinemann C., Neher E., Matthews G. Calcium dependence of the rate of exocytosis in a synaptic terminal. Nature. 1994 Oct 6;371(6497):513–515. doi: 10.1038/371513a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann C., Chow R. H., Neher E., Zucker R. S. Kinetics of the secretory response in bovine chromaffin cells following flash photolysis of caged Ca2+. Biophys J. 1994 Dec;67(6):2546–2557. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80744-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrington J., Park Y. B., Babcock D. F., Hille B. Dominant role of mitochondria in clearance of large Ca2+ loads from rat adrenal chromaffin cells. Neuron. 1996 Jan;16(1):219–228. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80038-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hove-Madsen L., Bers D. M. Indo-1 binding to protein in permeabilized ventricular myocytes alters its spectral and Ca binding properties. Biophys J. 1992 Jul;63(1):89–97. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81597-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson A. P., Timmerman M. P., Bagshaw C. R., Ashley C. C. The kinetics of calcium binding to fura-2 and indo-1. FEBS Lett. 1987 May 25;216(1):35–39. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80752-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao J. P., Tsien R. Y. Ca2+ binding kinetics of fura-2 and azo-1 from temperature-jump relaxation measurements. Biophys J. 1988 Apr;53(4):635–639. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83142-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. H., Ellis-Davies G. C. Photolabile chelators for the rapid photorelease of divalent cations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6571–6575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi M., Hollingworth S., Harkins A. B., Baylor S. M. Myoplasmic calcium transients in intact frog skeletal muscle fibers monitored with the fluorescent indicator furaptra. J Gen Physiol. 1991 Feb;97(2):271–301. doi: 10.1085/jgp.97.2.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller T. H., Partridge L. D., Swandulla D. Calcium buffering in bursting Helix pacemaker neurons. Pflugers Arch. 1993 Dec;425(5-6):499–505. doi: 10.1007/BF00374877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Augustine G. J. Calcium gradients and buffers in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:273–301. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Zucker R. S. Multiple calcium-dependent processes related to secretion in bovine chromaffin cells. Neuron. 1993 Jan;10(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90238-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D., Akerman K. Mitochondrial calcium transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Sep 1;683(1):57–88. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(82)90013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park Y. B., Herrington J., Babcock D. F., Hille B. Ca2+ clearance mechanisms in isolated rat adrenal chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1996 Apr 15;492(Pt 2):329–346. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzuto R., Simpson A. W., Brini M., Pozzan T. Rapid changes of mitochondrial Ca2+ revealed by specifically targeted recombinant aequorin. Nature. 1992 Jul 23;358(6384):325–327. doi: 10.1038/358325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter G. A., Theler J. M., Murgia M., Wollheim C. B., Pozzan T., Rizzuto R. Stimulated Ca2+ influx raises mitochondrial free Ca2+ to supramicromolar levels in a pancreatic beta-cell line. Possible role in glucose and agonist-induced insulin secretion. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 25;268(30):22385–22390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatsumi H., Katayama Y. Regulation of the intracellular free calcium concentration in acutely dissociated neurones from rat nucleus basalis. J Physiol. 1993 May;464:165–181. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P., Wong J. G., Lee A. K., Almers W. A low affinity Ca2+ receptor controls the final steps in peptide secretion from pituitary melanotrophs. Neuron. 1993 Jul;11(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90274-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein H., Mehler E. L. Ca(2+)-binding and structural dynamics in the functions of calmodulin. Annu Rev Physiol. 1994;56:213–236. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.56.030194.001241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Z., Neher E. Mobile and immobile calcium buffers in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1993 Sep;469:245–273. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker R. S. Effects of photolabile calcium chelators on fluorescent calcium indicators. Cell Calcium. 1992 Jan;13(1):29–40. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(92)90027-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker R. S. The calcium concentration clamp: spikes and reversible pulses using the photolabile chelator DM-nitrophen. Cell Calcium. 1993 Feb;14(2):87–100. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(93)90079-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Baldawi N. F., Abercrombie R. F. Cytoplasmic calcium buffer capacity determined with Nitr-5 and DM-nitrophen. Cell Calcium. 1995 Jun;17(6):409–421. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(95)90087-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]