Abstract
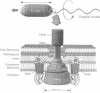
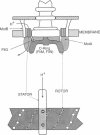
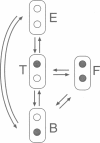
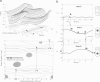
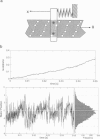
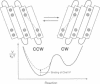
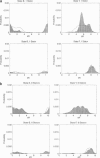
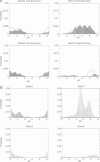
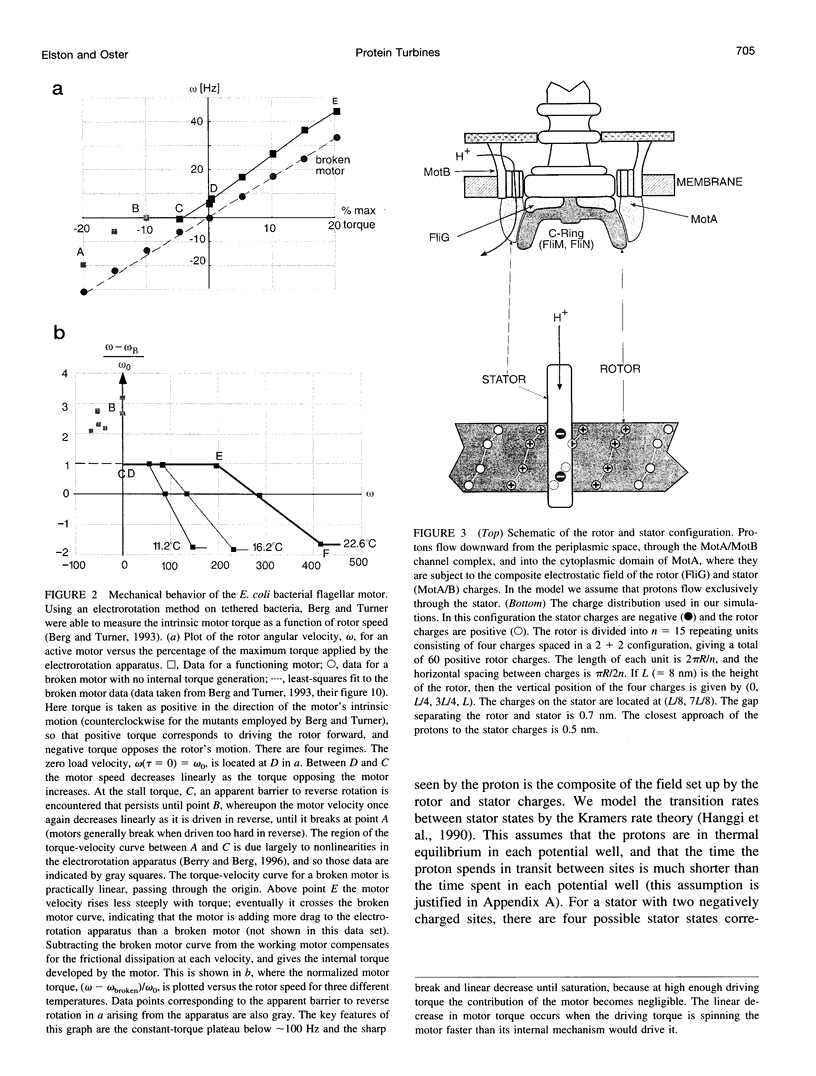
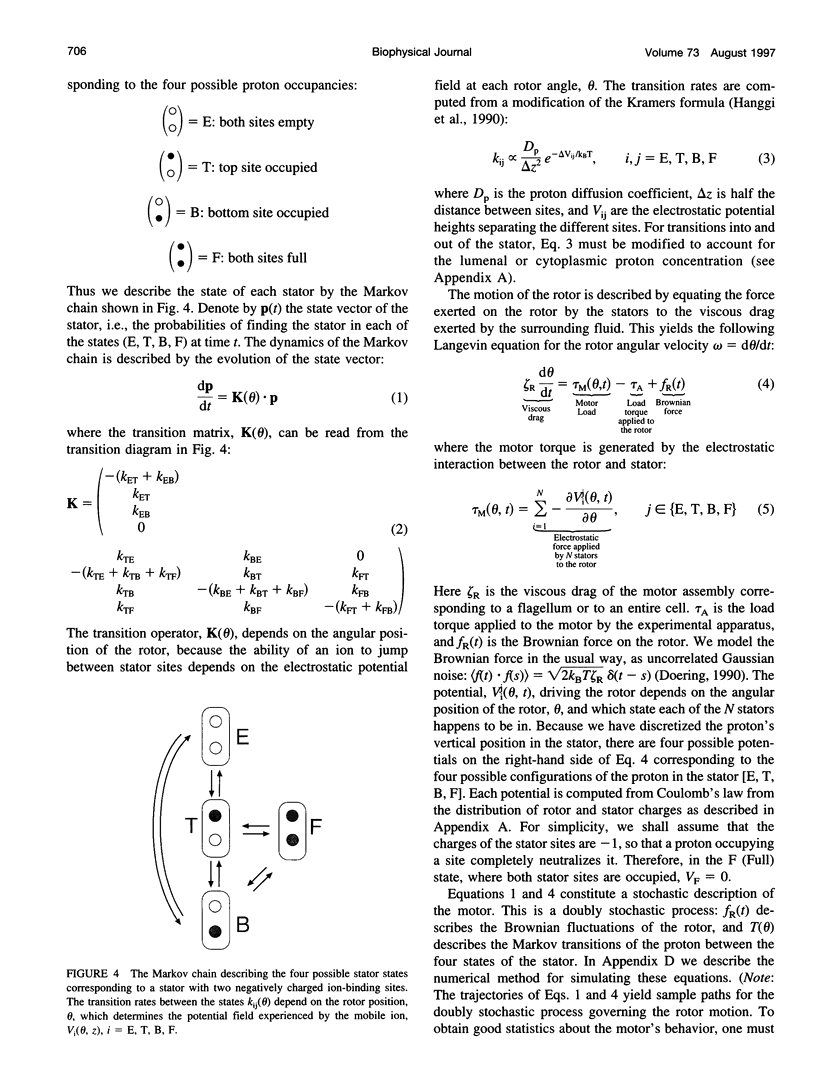
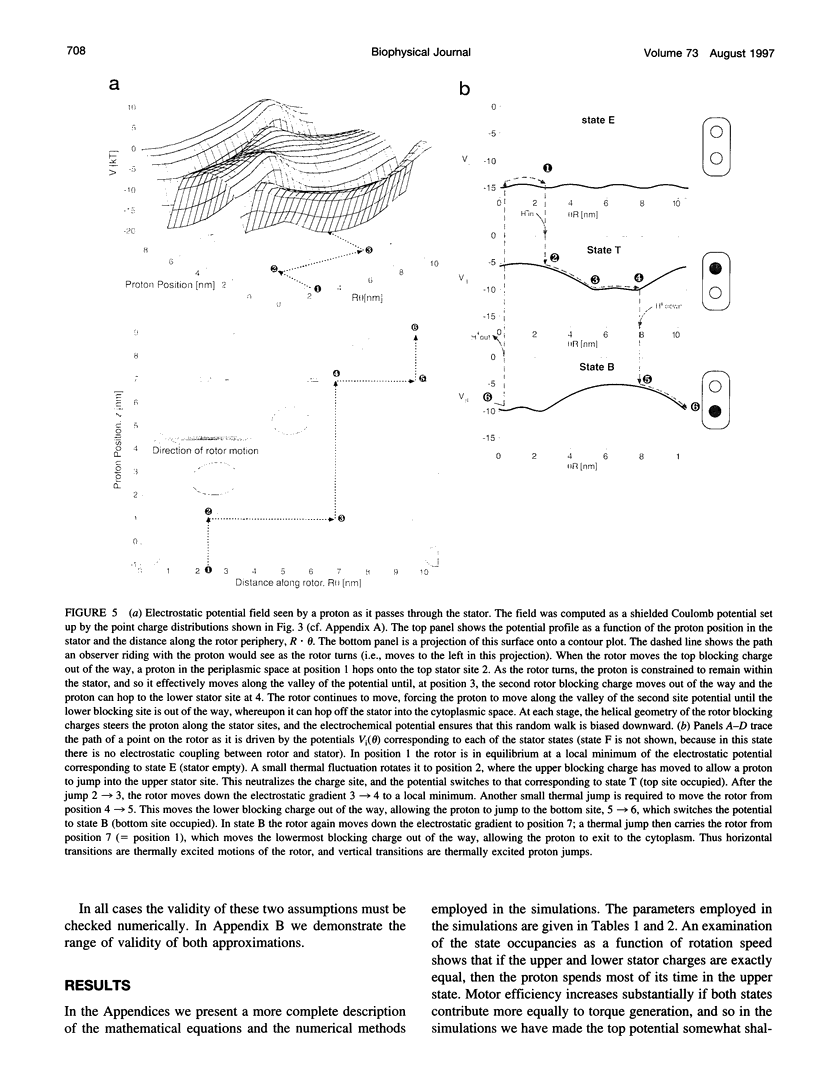
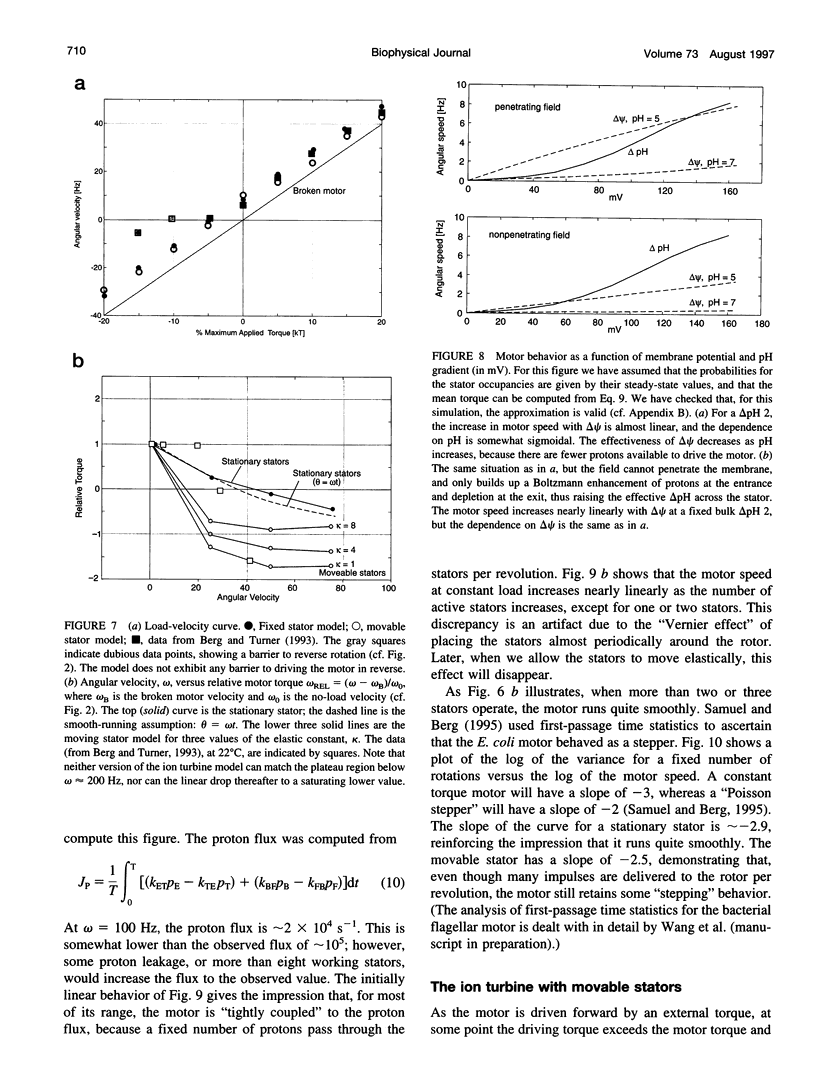
The bacterial flagellar motor is driven by a flux of ions between the cytoplasm and the periplasmic lumen. Here we show how an electrostatic mechanism can convert this ion flux into a rotary torque. We demonstrate that, with reasonable parameters, the model can reproduce many of the experimental measurements.
Full text
PDF







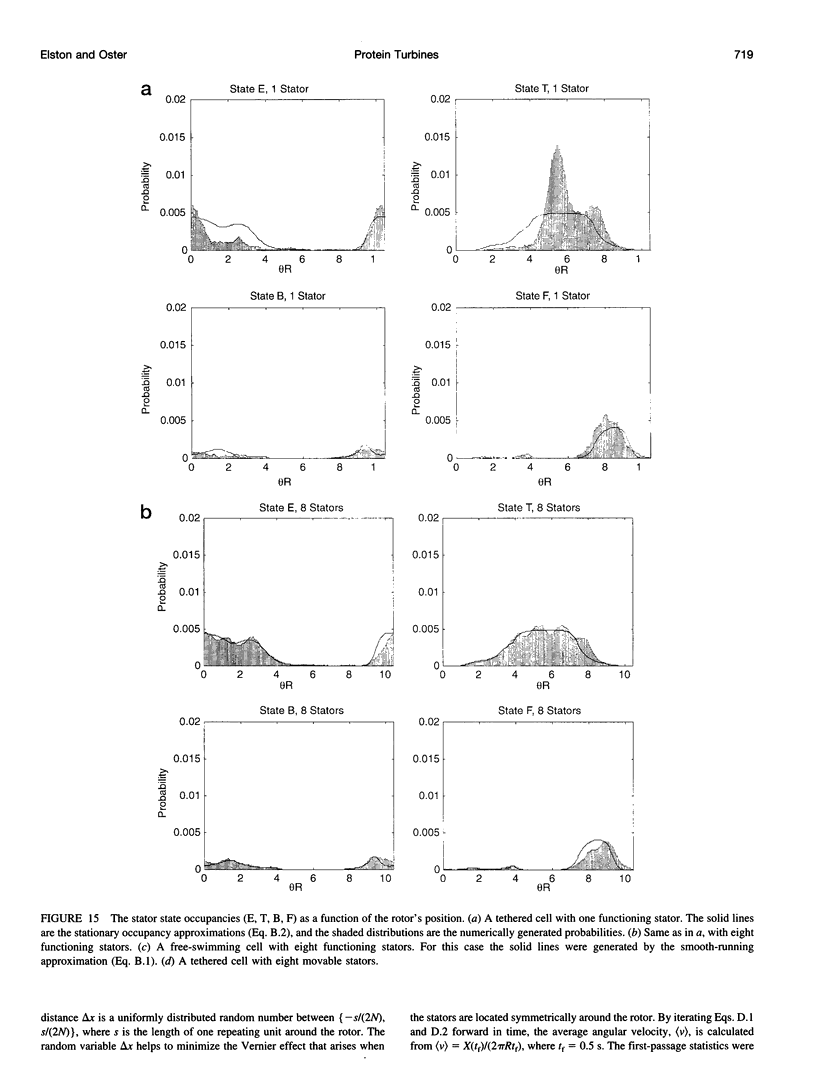
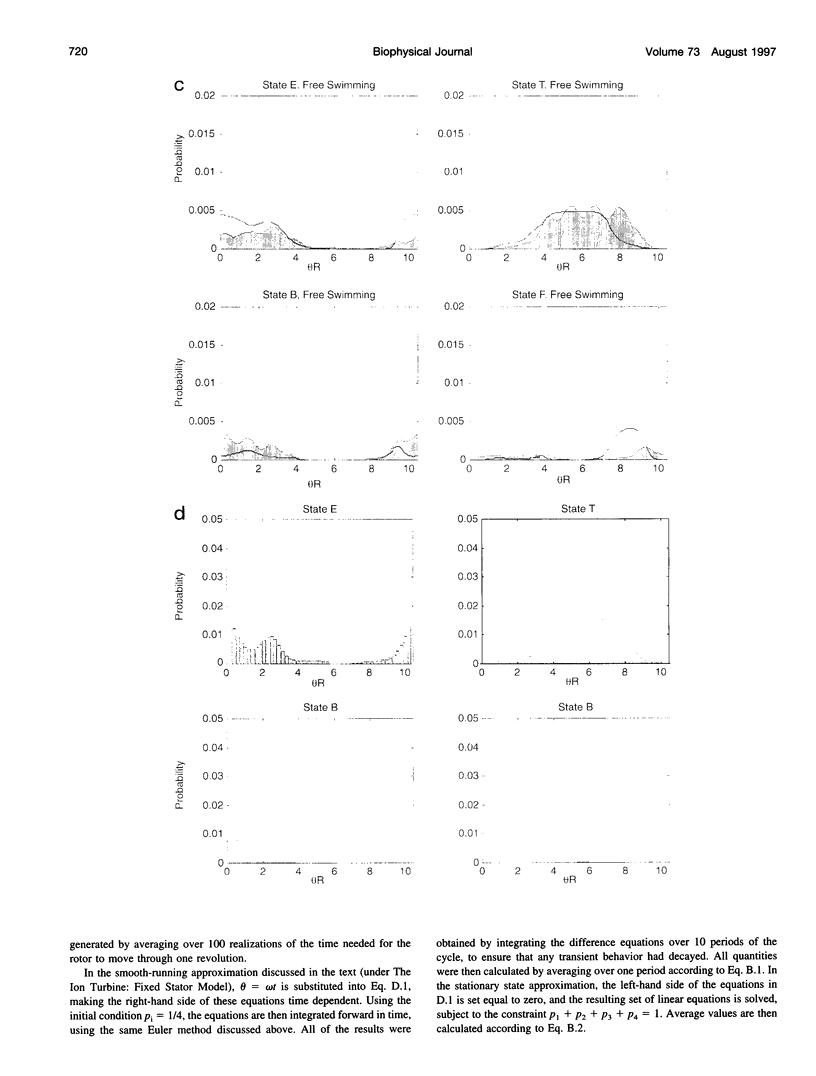

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg H. C. Torque generation by the flagellar rotary motor. Biophys J. 1995 Apr;68(4 Suppl):163S–167S. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Turner L. Torque generated by the flagellar motor of Escherichia coli. Biophys J. 1993 Nov;65(5):2201–2216. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81278-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry R. M., Berg H. C. Torque generated by the bacterial flagellar motor close to stall. Biophys J. 1996 Dec;71(6):3501–3510. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79545-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry R. M. Torque and switching in the bacterial flagellar motor. An electrostatic model. Biophys J. 1993 Apr;64(4):961–973. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81462-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean G. E., Macnab R. M., Stader J., Matsumura P., Burks C. Gene sequence and predicted amino acid sequence of the motA protein, a membrane-associated protein required for flagellar rotation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):991–999. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.991-999.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douady S, Couder Y. Phyllotaxis as a physical self-organized growth process. Phys Rev Lett. 1992 Mar 30;68(13):2098–2101. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.68.2098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis N. R., Sosinsky G. E., Thomas D., DeRosier D. J. Isolation, characterization and structure of bacterial flagellar motors containing the switch complex. J Mol Biol. 1994 Jan 28;235(4):1261–1270. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY A. F. Muscle structure and theories of contraction. Prog Biophys Biophys Chem. 1957;7:255–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama E., Shiraishi T., Oosawa K., Baba N., Aizawa S. Geometry of the flagellar motor in the cytoplasmic membrane of Salmonella typhimurium as determined by stereo-photogrammetry of quick-freeze deep-etch replica images. J Mol Biol. 1996 Jan 26;255(3):458–475. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd S. A., Blair D. F. Charged residues of the rotor protein FliG essential for torque generation in the flagellar motor of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1997 Mar 7;266(4):733–744. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Läuger P. Ion transport and rotation of bacterial flagella. Nature. 1977 Jul 28;268(5618):360–362. doi: 10.1038/268360a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M. Bacterial flagella rotating in bundles: a study in helical geometry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):221–225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister M., Berg H. C. The stall torque of the bacterial flagellar motor. Biophys J. 1987 Sep;52(3):413–419. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83230-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister M., Caplan S. R., Berg H. C. Dynamics of a tightly coupled mechanism for flagellar rotation. Bacterial motility, chemiosmotic coupling, protonmotive force. Biophys J. 1989 May;55(5):905–914. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82889-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naber H. Two alternative models for spontaneous flagellar motor switching in Halobacterium salinarium. J Theor Biol. 1996 Aug 21;181(4):343–358. doi: 10.1006/jtbi.1996.0136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peskin C. S., Oster G. Coordinated hydrolysis explains the mechanical behavior of kinesin. Biophys J. 1995 Apr;68(4 Suppl):202S–211S. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel A. D., Berg H. C. Fluctuation analysis of rotational speeds of the bacterial flagellar motor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 11;92(8):3502–3506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.8.3502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel A. D., Berg H. C. Torque-generating units of the bacterial flagellar motor step independently. Biophys J. 1996 Aug;71(2):918–923. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79295-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster S. C., Khan S. The bacterial flagellar motor. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1994;23:509–539. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.23.060194.002453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp L. L., Zhou J., Blair D. F. Features of MotA proton channel structure revealed by tryptophan-scanning mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 15;92(17):7946–7950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.17.7946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp L. L., Zhou J., Blair D. F. Tryptophan-scanning mutagenesis of MotB, an integral membrane protein essential for flagellar rotation in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1995 Jul 18;34(28):9166–9171. doi: 10.1021/bi00028a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svoboda K., Mitra P. P., Block S. M. Fluctuation analysis of motor protein movement and single enzyme kinetics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 6;91(25):11782–11786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.25.11782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang H., Braun T. F., Blair D. F. Motility protein complexes in the bacterial flagellar motor. J Mol Biol. 1996 Aug 16;261(2):209–221. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao R., Pathak N., Jaffe H., Reese T. S., Khan S. FliN is a major structural protein of the C-ring in the Salmonella typhimurium flagellar basal body. J Mol Biol. 1996 Aug 16;261(2):195–208. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]