Abstract
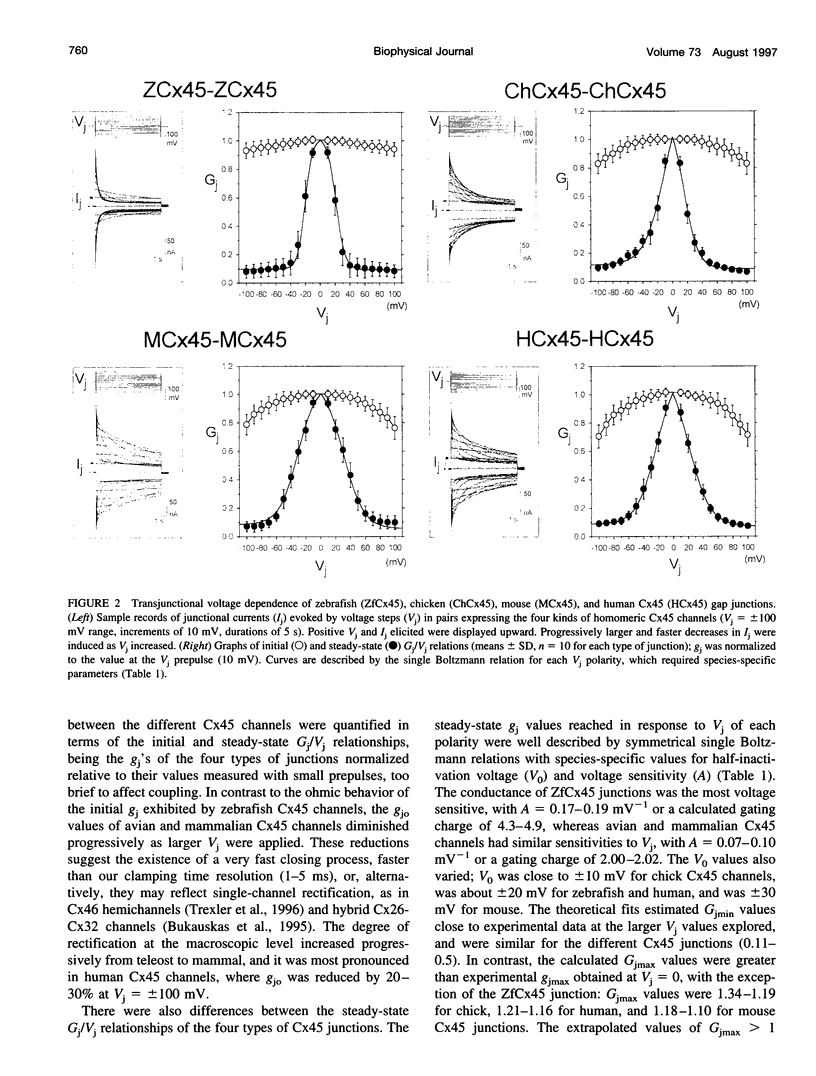
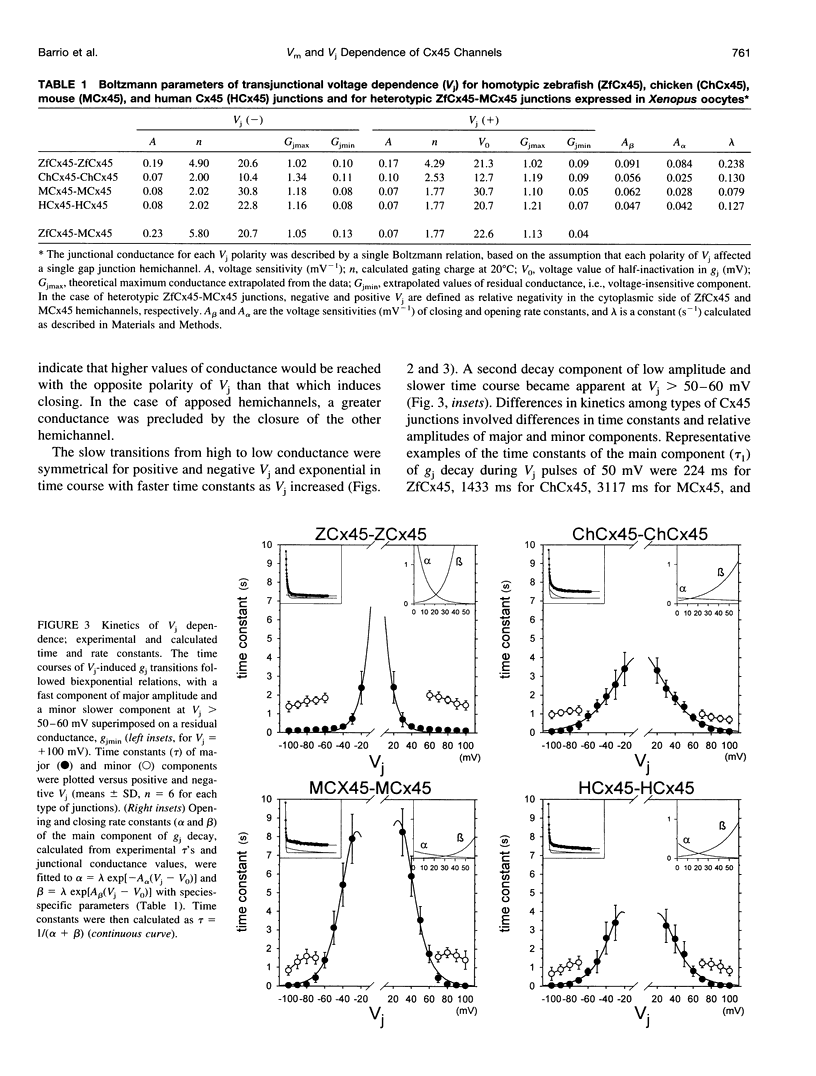
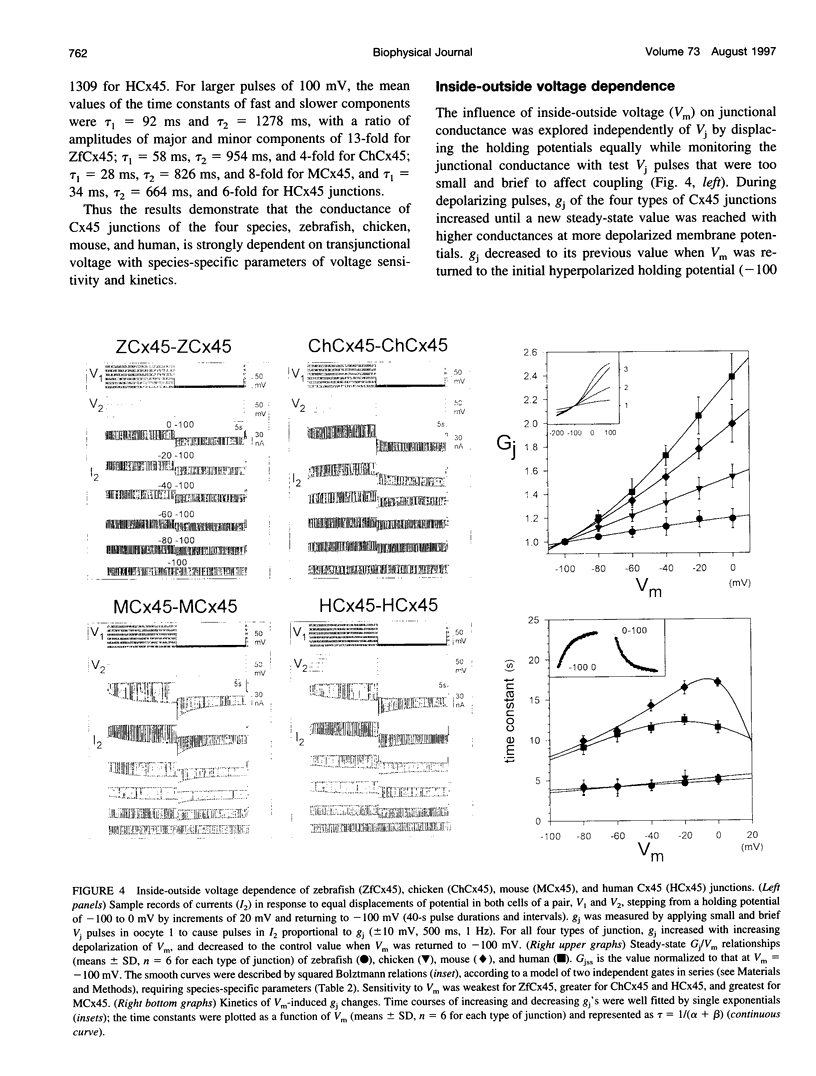
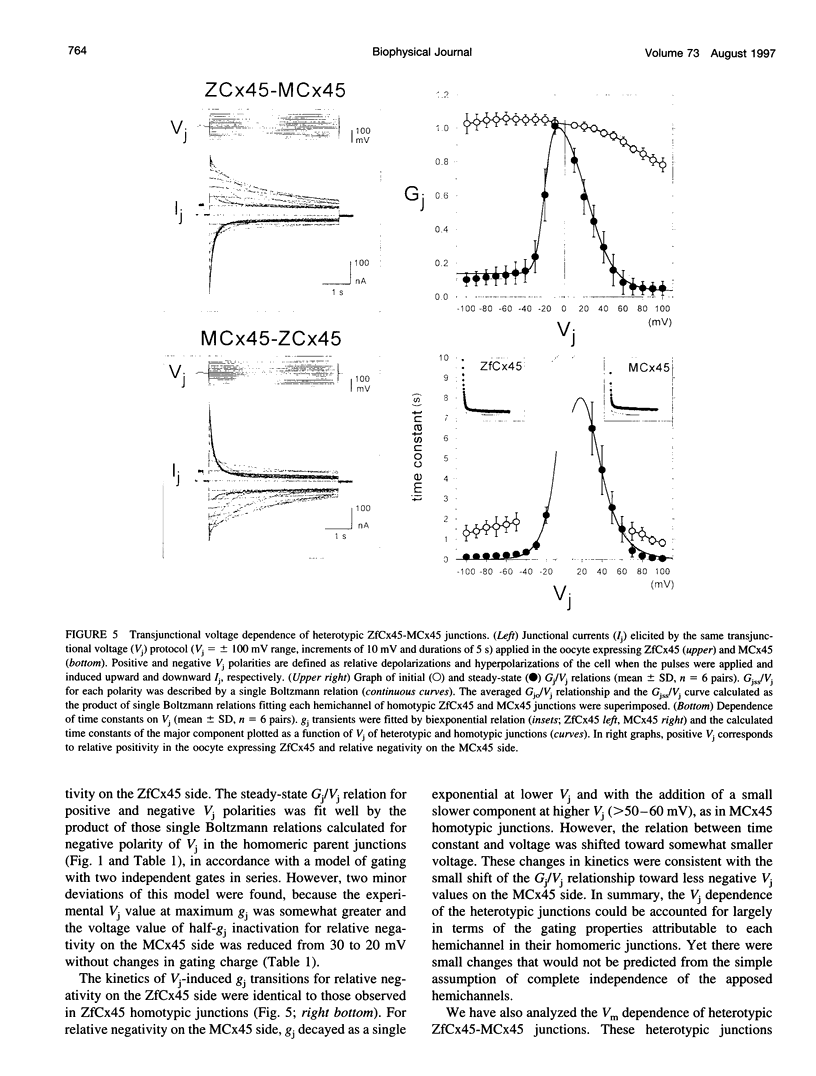
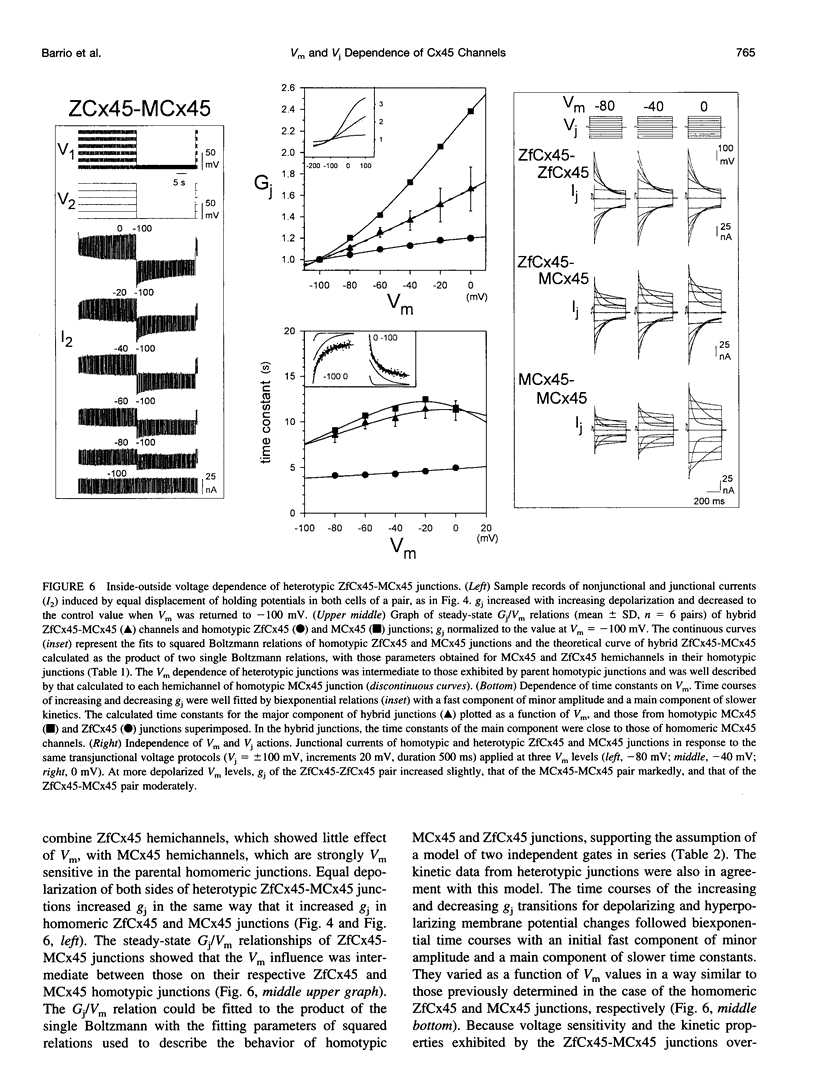
Gap junctions composed of connexin-45 (Cx45) homologs from four species, zebrafish, chicken, mouse, and human, were expressed in pairs of Xenopus oocytes. The macroscopic conductance (gj) of all Cx45 junctions was modulated by transjunctional voltage (Vj) and by the inside-outside voltage (Vm), and the modulation was species specific. Although their gating characteristics varied in voltage sensitivity and kinetics, the four Cx45 junctions shared 1) maximum conductance at Vj = 0 and symmetrical gj reduction in response to positive and negative Vj of low amplitude, with little residual conductance; and 2) gj increases in response to simultaneous depolarization of the paired cells. The formation of hybrid channels, comprising Cx45 hemichannels from different species, allowed us to infer that two separate gates exist, one in each hemichannel, and that each Cx45 hemichannel is closed by the negativity of Vj on its cytoplasmic side. Interestingly, the Vm dependence of hybrid channels also suggests the presence of two gates in series, one Vm gate in each hemichannel. Thus the Vj and Vm dependence provides evidence that two independent voltage gates in each Cx45 hemichannel exist, reacting through specific voltage sensors and operating by different mechanisms, properties that have evolved divergently among species.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrio L. C., Suchyna T., Bargiello T., Xu L. X., Roginski R. S., Bennett M. V., Nicholson B. J. Gap junctions formed by connexins 26 and 32 alone and in combination are differently affected by applied voltage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8410–8414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beblo D. A., Wang H. Z., Beyer E. C., Westphale E. M., Veenstra R. D. Unique conductance, gating, and selective permeability properties of gap junction channels formed by connexin40. Circ Res. 1995 Oct;77(4):813–822. doi: 10.1161/01.res.77.4.813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. V., Barrio L. C., Bargiello T. A., Spray D. C., Hertzberg E., Sáez J. C. Gap junctions: new tools, new answers, new questions. Neuron. 1991 Mar;6(3):305–320. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90241-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. V., Verselis V. K. Biophysics of gap junctions. Semin Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;3(1):29–47. doi: 10.1016/s1043-4682(10)80006-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer E. C. Molecular cloning and developmental expression of two chick embryo gap junction proteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14439–14443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruzzone R., Haefliger J. A., Gimlich R. L., Paul D. L. Connexin40, a component of gap junctions in vascular endothelium, is restricted in its ability to interact with other connexins. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Jan;4(1):7–20. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruzzone R., White T. W., Paul D. L. Connections with connexins: the molecular basis of direct intercellular signaling. Eur J Biochem. 1996 May 15;238(1):1–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1996.0001q.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruzzone R., White T. W., Yoshizaki G., Patiño R., Paul D. L. Intercellular channels in teleosts: functional characterization of two connexins from Atlantic croaker. FEBS Lett. 1995 Jan 30;358(3):301–304. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)01457-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukauskas F. F., Elfgang C., Willecke K., Weingart R. Heterotypic gap junction channels (connexin26-connexin32) violate the paradigm of unitary conductance. Pflugers Arch. 1995 Apr;429(6):870–872. doi: 10.1007/BF00374812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukauskas F. F., Weingart R. Voltage-dependent gating of single gap junction channels in an insect cell line. Biophys J. 1994 Aug;67(2):613–625. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80521-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukauskas F., Kempf C., Weingart R. Electrical coupling between cells of the insect Aedes albopictus. J Physiol. 1992 Mar;448:321–337. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. C., Davis L. M., Westphale E. M., Beyer E. C., Saffitz J. E. Expression of multiple gap junction proteins in human fetal and infant hearts. Pediatr Res. 1994 Nov;36(5):561–566. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199411000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill D., Caveney S. Double whole-cell patch-clamp characterization of gap junctional channels in isolated insect epidermal cell pairs. J Membr Biol. 1993 Aug;135(2):165–180. doi: 10.1007/BF00231442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebihara L., Berthoud V. M., Beyer E. C. Distinct behavior of connexin56 and connexin46 gap junctional channels can be predicted from the behavior of their hemi-gap-junctional channels. Biophys J. 1995 May;68(5):1796–1803. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80356-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebihara L., Beyer E. C., Swenson K. I., Paul D. L., Goodenough D. A. Cloning and expression of a Xenopus embryonic gap junction protein. Science. 1989 Mar 3;243(4895):1194–1195. doi: 10.1126/science.2466337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elfgang C., Eckert R., Lichtenberg-Fraté H., Butterweck A., Traub O., Klein R. A., Hülser D. F., Willecke K. Specific permeability and selective formation of gap junction channels in connexin-transfected HeLa cells. J Cell Biol. 1995 May;129(3):805–817. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.3.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Essner J. J., Laing J. G., Beyer E. C., Johnson R. G., Hackett P. B., Jr Expression of zebrafish connexin43.4 in the notochord and tail bud of wild-type and mutant no tail embryos. Dev Biol. 1996 Aug 1;177(2):449–462. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1996.0177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman G. I., Moreno A. P., Spray D. C., Leinwand L. A. Functional analysis of human cardiac gap junction channel mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3525–3529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta V. K., Berthoud V. M., Atal N., Jarillo J. A., Barrio L. C., Beyer E. C. Bovine connexin44, a lens gap junction protein: molecular cloning, immunologic characterization, and functional expression. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1994 Sep;35(10):3747–3758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. L., Spray D. C., Bennett M. V. Control of intercellular communication by voltage dependence of gap junctional conductance. J Neurosci. 1983 Jan;3(1):79–100. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-01-00079.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. L., Spray D. C., Bennett M. V. Kinetic properties of a voltage-dependent junctional conductance. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Jan;77(1):95–117. doi: 10.1085/jgp.77.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennemann H., Schwarz H. J., Willecke K. Characterization of gap junction genes expressed in F9 embryonic carcinoma cells: molecular cloning of mouse connexin31 and -45 cDNAs. Eur J Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;57(1):51–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermans M. M., Kortekaas P., Jongsma H. J., Rook M. B. pH sensitivity of the cardiac gap junction proteins, connexin 45 and 43. Pflugers Arch. 1995 Nov;431(1):138–140. doi: 10.1007/BF00374389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
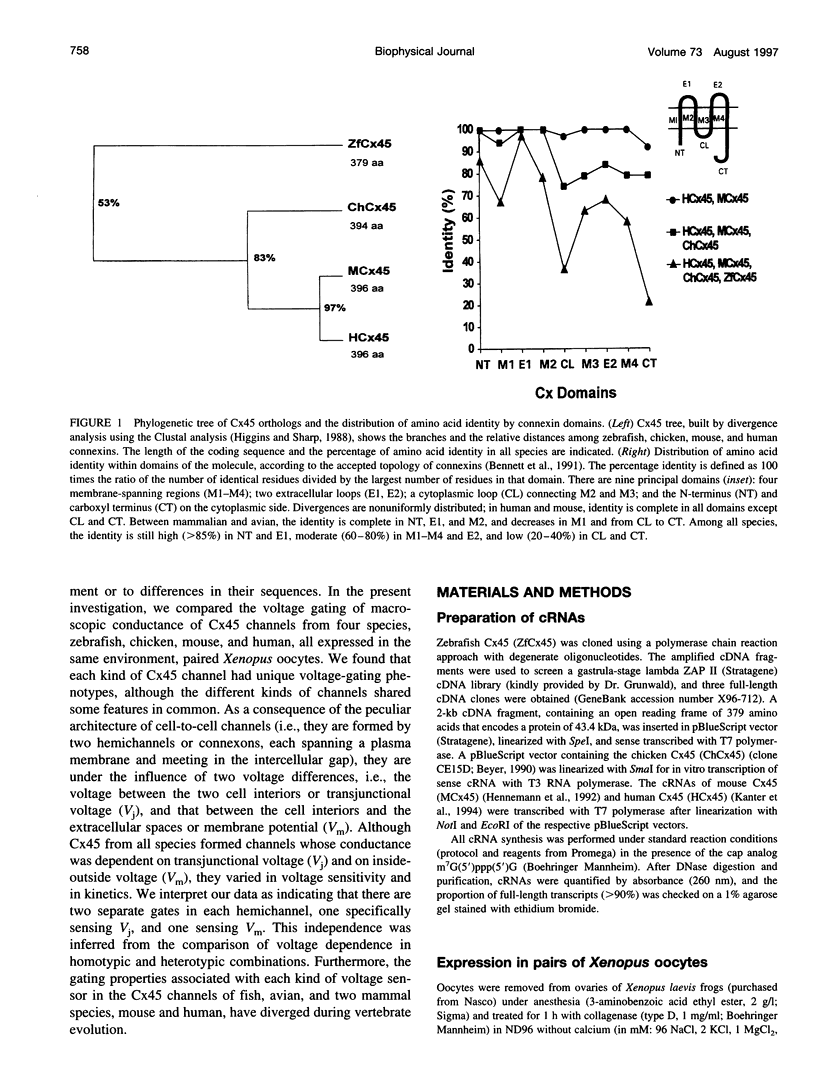
- Higgins D. G., Sharp P. M. CLUSTAL: a package for performing multiple sequence alignment on a microcomputer. Gene. 1988 Dec 15;73(1):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90330-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang J. X., White T. W., Goodenough D. A., Paul D. L. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of chick lens fiber connexin 45.6. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Mar;5(3):363–373. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.3.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanter H. L., Laing J. G., Beyer E. C., Green K. G., Saffitz J. E. Multiple connexins colocalize in canine ventricular myocyte gap junctions. Circ Res. 1993 Aug;73(2):344–350. doi: 10.1161/01.res.73.2.344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanter H. L., Saffitz J. E., Beyer E. C. Cardiac myocytes express multiple gap junction proteins. Circ Res. 1992 Feb;70(2):438–444. doi: 10.1161/01.res.70.2.438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanter H. L., Saffitz J. E., Beyer E. C. Molecular cloning of two human cardiac gap junction proteins, connexin40 and connexin45. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1994 Jul;26(7):861–868. doi: 10.1006/jmcc.1994.1103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S., Taffet S., Stoner L., Delmar M., Vallano M. L., Jalife J. A structural basis for the unequal sensitivity of the major cardiac and liver gap junctions to intracellular acidification: the carboxyl tail length. Biophys J. 1993 May;64(5):1422–1433. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81508-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno A. P., Laing J. G., Beyer E. C., Spray D. C. Properties of gap junction channels formed of connexin 45 endogenously expressed in human hepatoma (SKHep1) cells. Am J Physiol. 1995 Feb;268(2 Pt 1):C356–C365. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1995.268.2.C356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno A. P., Rook M. B., Fishman G. I., Spray D. C. Gap junction channels: distinct voltage-sensitive and -insensitive conductance states. Biophys J. 1994 Jul;67(1):113–119. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80460-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. E., Westphale E. M., Larson D. M., Wang H. Z., Veenstra R. D., Beyer E. C. Molecular cloning and functional expression of human connexin37, an endothelial cell gap junction protein. J Clin Invest. 1993 Mar;91(3):997–1004. doi: 10.1172/JCI116321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spray D. C., Harris A. L., Bennett M. V. Equilibrium properties of a voltage-dependent junctional conductance. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Jan;77(1):77–93. doi: 10.1085/jgp.77.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner E., Ebihara L. Functional characterization of canine connexin45. J Membr Biol. 1996 Mar;150(2):153–161. doi: 10.1007/s002329900040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trexler E. B., Bennett M. V., Bargiello T. A., Verselis V. K. Voltage gating and permeation in a gap junction hemichannel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Jun 11;93(12):5836–5841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.12.5836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veenstra R. D., Wang H. Z., Beyer E. C., Brink P. R. Selective dye and ionic permeability of gap junction channels formed by connexin45. Circ Res. 1994 Sep;75(3):483–490. doi: 10.1161/01.res.75.3.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veenstra R. D., Wang H. Z., Beyer E. C., Ramanan S. V., Brink P. R. Connexin37 forms high conductance gap junction channels with subconductance state activity and selective dye and ionic permeabilities. Biophys J. 1994 Jun;66(6):1915–1928. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80985-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veenstra R. D., Wang H. Z., Westphale E. M., Beyer E. C. Multiple connexins confer distinct regulatory and conductance properties of gap junctions in developing heart. Circ Res. 1992 Nov;71(5):1277–1283. doi: 10.1161/01.res.71.5.1277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verselis V. K., Bennett M. V., Bargiello T. A. A voltage-dependent gap junction in Drosophila melanogaster. Biophys J. 1991 Jan;59(1):114–126. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82204-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verselis V. K., Ginter C. S., Bargiello T. A. Opposite voltage gating polarities of two closely related connexins. Nature. 1994 Mar 24;368(6469):348–351. doi: 10.1038/368348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner R., Levine E., Rabadan-Diehl C., Dahl G. Formation of hybrid cell-cell channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5380–5384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White T. W., Bruzzone R., Goodenough D. A., Paul D. L. Mouse Cx50, a functional member of the connexin family of gap junction proteins, is the lens fiber protein MP70. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jul;3(7):711–720. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.7.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White T. W., Bruzzone R., Paul D. L. The connexin family of intercellular channel forming proteins. Kidney Int. 1995 Oct;48(4):1148–1157. doi: 10.1038/ki.1995.398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White T. W., Bruzzone R., Wolfram S., Paul D. L., Goodenough D. A. Selective interactions among the multiple connexin proteins expressed in the vertebrate lens: the second extracellular domain is a determinant of compatibility between connexins. J Cell Biol. 1994 May;125(4):879–892. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.4.879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilders R., Jongsma H. J. Limitations of the dual voltage clamp method in assaying conductance and kinetics of gap junction channels. Biophys J. 1992 Oct;63(4):942–953. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81664-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willecke K., Heynkes R., Dahl E., Stutenkemper R., Hennemann H., Jungbluth S., Suchyna T., Nicholson B. J. Mouse connexin37: cloning and functional expression of a gap junction gene highly expressed in lung. J Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;114(5):1049–1057. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.5.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]