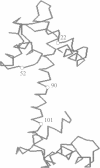
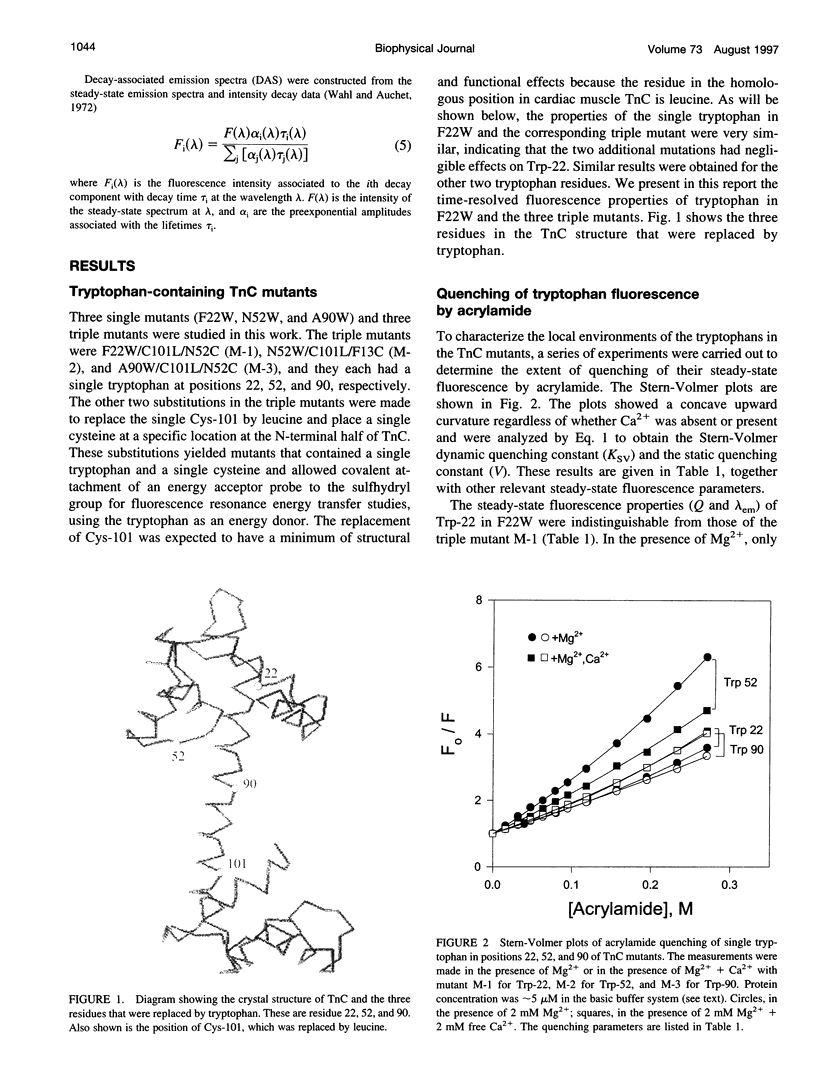
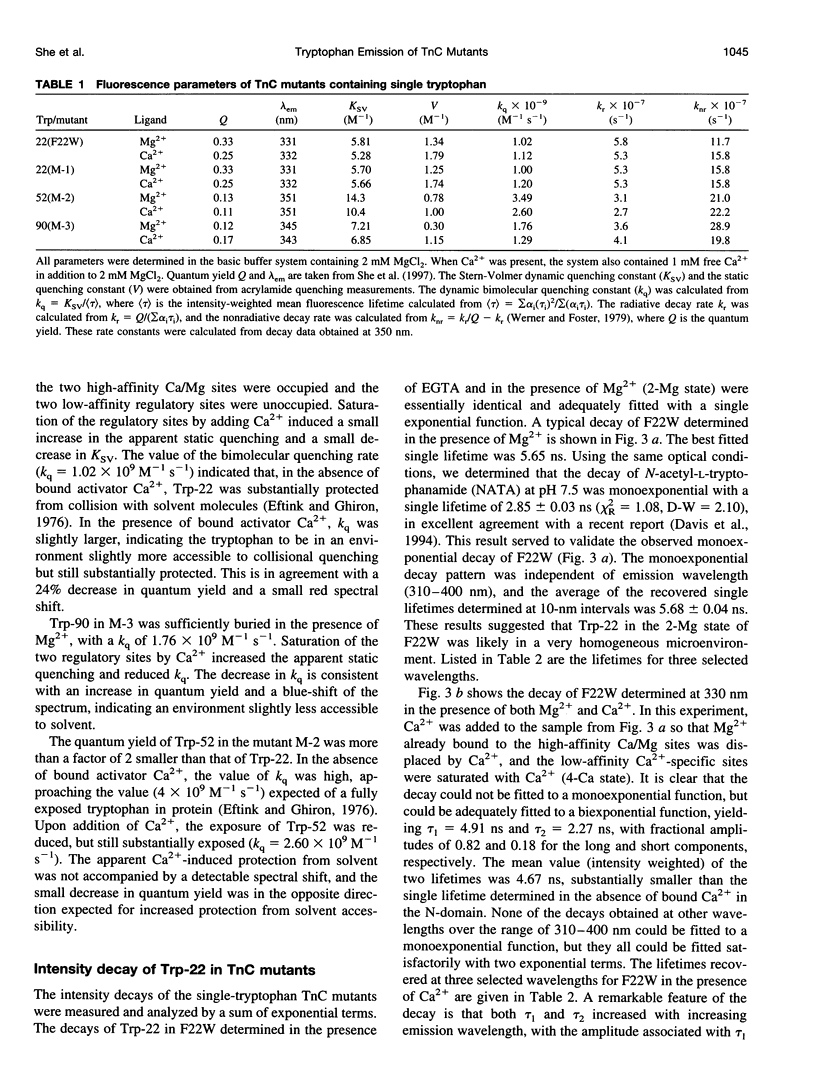
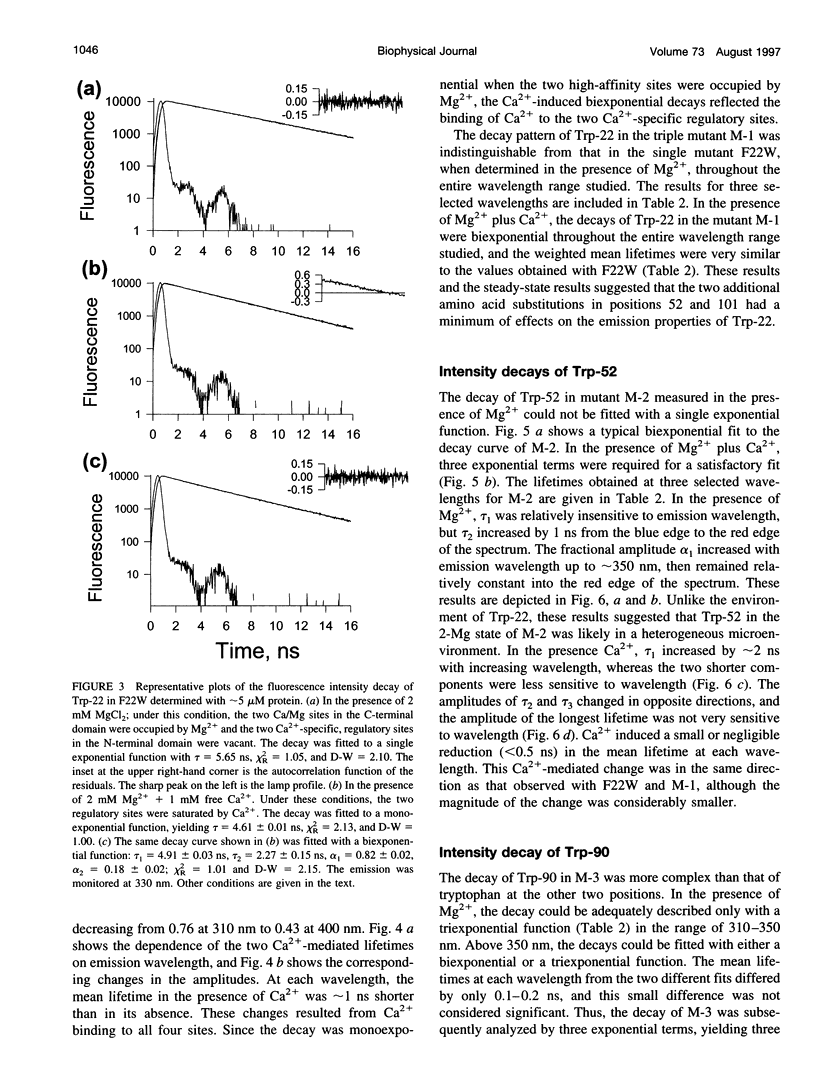
Abstract
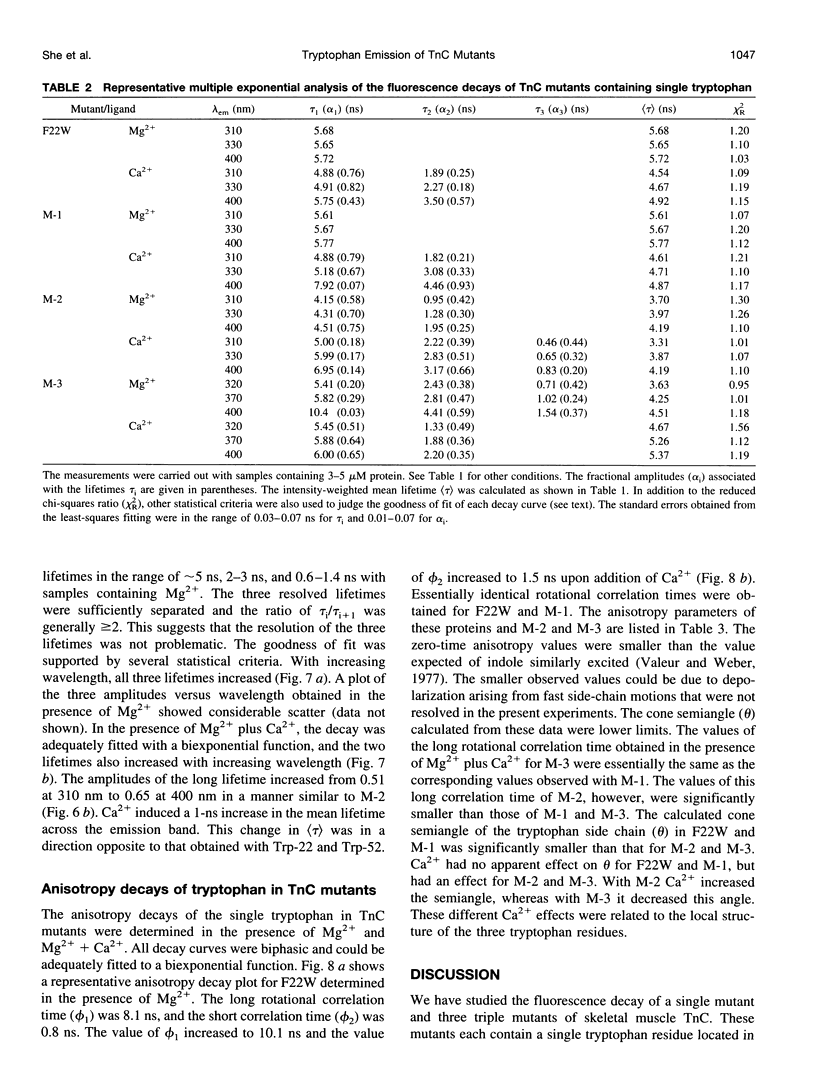
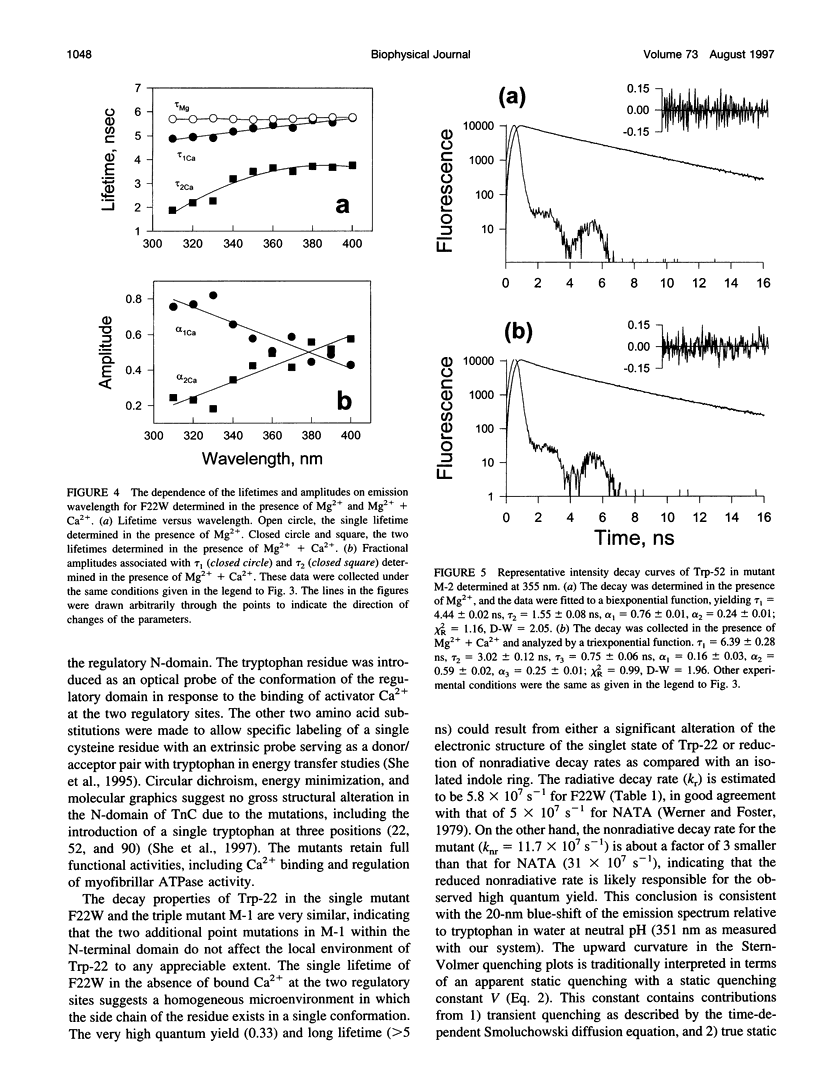
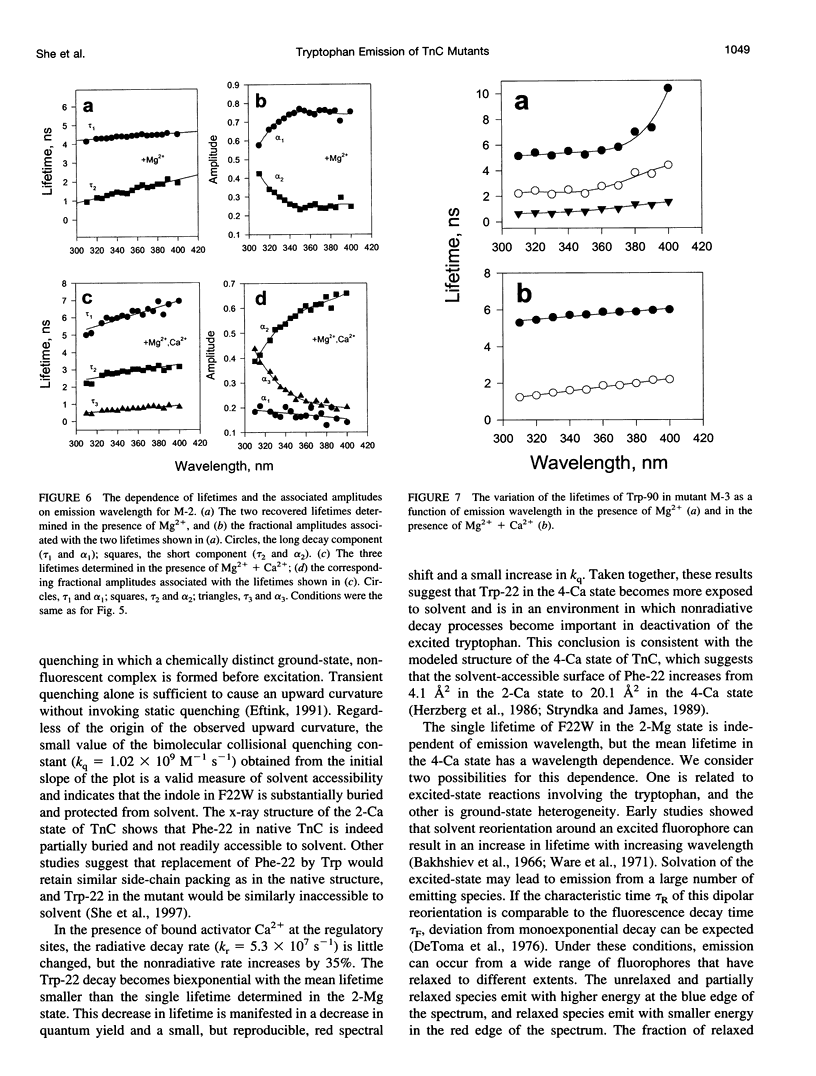
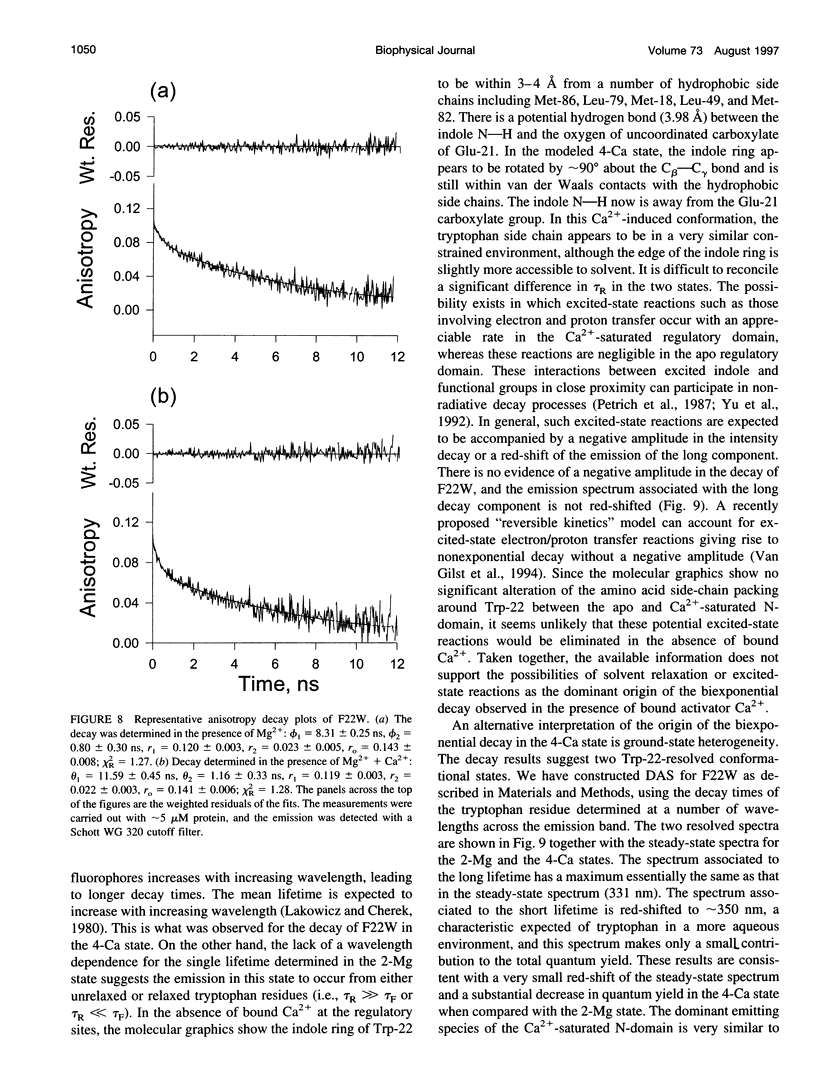
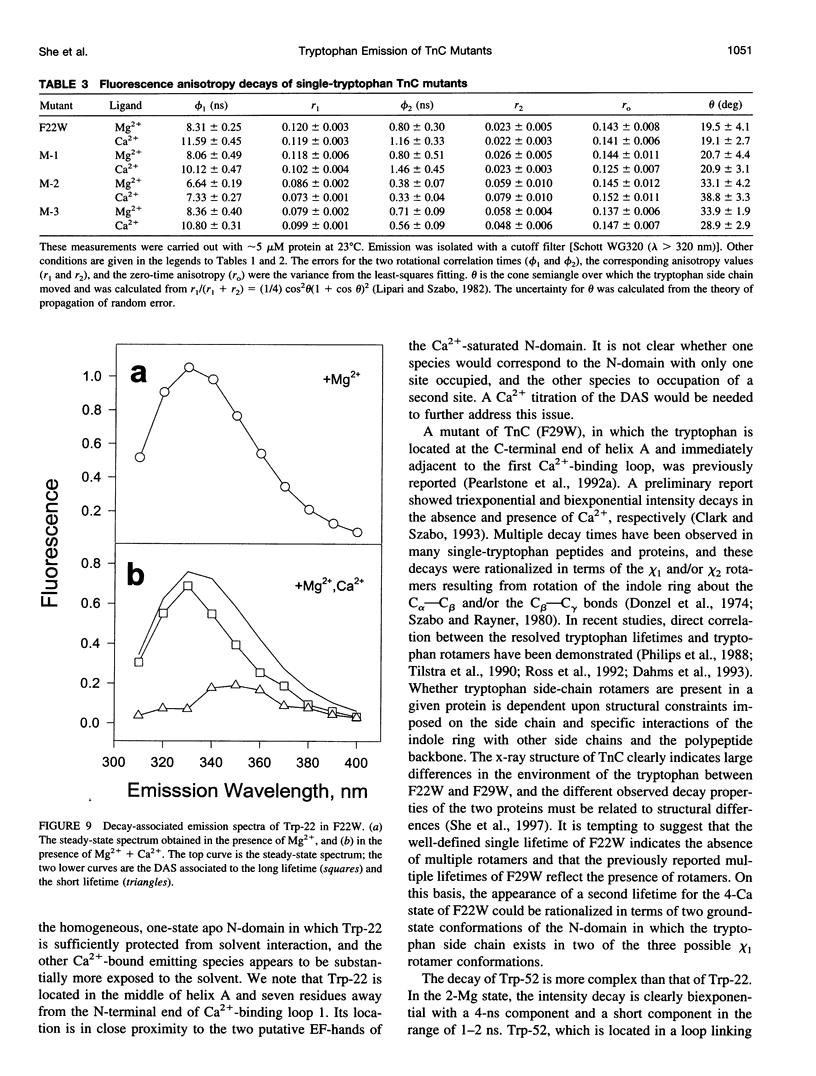
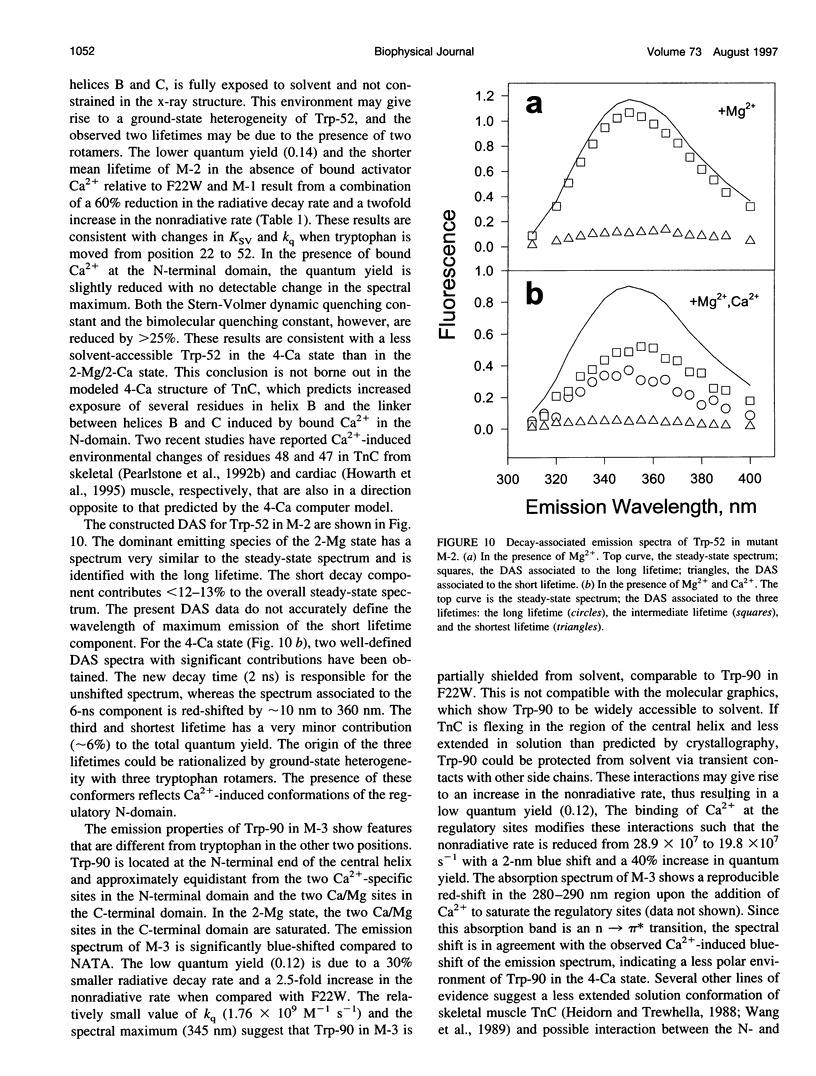
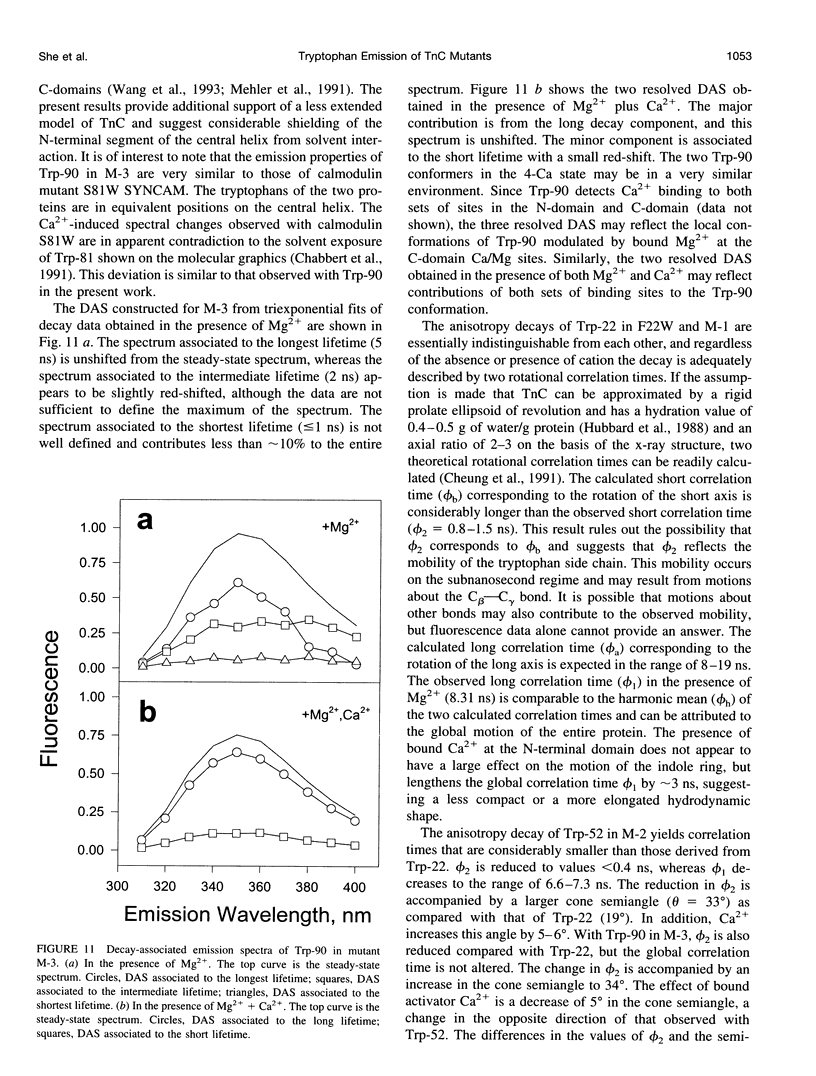
The regulatory domain of troponin C (TnC) from chicken skeletal muscle was studied using genetically generated mutants which contained a single tryptophan at positions 22, 52, and 90. The quantum yields of Trp-22 are 0.33 and 0.25 in the presence of Mg2+ (2-Mg state) and Ca2+ (4-Ca state), respectively. The large quantum yield of the 2-Mg state is due to a relatively small nonradiative decay rate and consistent with the emission peak at 331 nm. The intensity decay of this state is monoexponential with a single lifetime of 5.65 ns, independent of wavelength. In the 4-Ca state, the decay is biexponential with the mean of the two lifetimes increasing from 4.54 to 4.92 ns across the emission band. The decay-associated spectrum of the short lifetime is red-shifted by 19 nm relative to the steady-state spectrum. The decay of Trp-52 is biexponential in the 2-Mg state and triexponential in the 4-Ca state. The decay of Trp-90 requires three exponential terms for a satisfactory fit, but can be fitted with two exponential terms in the 4-Ca state. The lower quantum yields (< 0.15) of these two tryptophans are due to a combination of smaller radiative and larger nonradiative decay rates. The results from Trp-22 suggest a homogeneous ground-state indole ring in the absence of bound Ca2+ at the regulatory sites and a ground-state heterogeneity induced by activator Ca2+. The Ca(2+)-induced environmental changes of Trp-52 and Trp-90 deviate from those predicted by a modeled structure of the 4-Ca state. The anisotropy decays of all three tryptophans show two rotational correlation times. The long correlation times (phi 1 = 8.1-8.3 ns) derived from Trp-22 and Trp-90 suggest an asymmetric hydrodynamic shape. TnC becomes more asymmetric upon binding activator Ca2+ (phi 1 = 10.1-11.6 ns). The values of phi 1 obtained from Trp-52 are 3-4 ns shorter than those from Trp-22 and Trp-90, and these reduced correlation times may be related to the mobility of the residue and/or local segmental flexibility.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chabbert M., Lukas T. J., Watterson D. M., Axelsen P. H., Prendergast F. G. Fluorescence analysis of calmodulin mutants containing tryptophan: conformational changes induced by calmodulin-binding peptides from myosin light chain kinase and protein kinase II. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 30;30(30):7615–7630. doi: 10.1021/bi00244a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung H. C., Wang C. K., Malik N. A. Interactions of troponin subunits: free energy of binary and ternary complexes. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 8;26(18):5904–5907. doi: 10.1021/bi00392a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Toma R. P., Easter J. H., Brand L. Dynamic interactions of fluorescence probes with the solvent environment. J Am Chem Soc. 1976 Aug 4;98(16):5001–5007. doi: 10.1021/ja00432a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eftink M. R., Ghiron C. A. Exposure of tryptophanyl residues in proteins. Quantitative determination by fluorescence quenching studies. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):672–680. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Computer programs for calculating total from specified free or free from specified total ionic concentrations in aqueous solutions containing multiple metals and ligands. Methods Enzymol. 1988;157:378–417. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)57093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinvald A., Steinberg I. Z. On the analysis of fluorescence decay kinetics by the method of least-squares. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jun;59(2):583–598. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90312-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidorn D. B., Trewhella J. Comparison of the crystal and solution structures of calmodulin and troponin C. Biochemistry. 1988 Feb 9;27(3):909–915. doi: 10.1021/bi00403a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzberg O., James M. N. Structure of the calcium regulatory muscle protein troponin-C at 2.8 A resolution. Nature. 1985 Feb 21;313(6004):653–659. doi: 10.1038/313653a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzberg O., Moult J., James M. N. A model for the Ca2+-induced conformational transition of troponin C. A trigger for muscle contraction. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2638–2644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howarth J. W., Krudy G. A., Lin X., Putkey J. A., Rosevear P. R. An NMR and spin label study of the effects of binding calcium and troponin I inhibitory peptide to cardiac troponin C. Protein Sci. 1995 Apr;4(4):671–680. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560040407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard S. R., Hodgson K. O., Doniach S. Small-angle x-ray scattering investigation of the solution structure of troponin C. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 25;263(9):4151–4158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretsinger R. H., Nockolds C. E. Carp muscle calcium-binding protein. II. Structure determination and general description. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 10;248(9):3313–3326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakowicz J. R., Cherek H. Dipolar relaxation in proteins on the nanosecond timescale observed by wavelength-resolved phase fluorometry of tryptophan fluorescence. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):831–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leavis P. C., Rosenfeld S. S., Gergely J., Grabarek Z., Drabikowski W. Proteolytic fragments of troponin C. Localization of high and low affinity Ca2+ binding sites and interactions with troponin I and troponin T. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 10;253(15):5452–5459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao R., Wang C. K., Cheung H. C. Time-resolved tryptophan emission study of cardiac troponin I. Biophys J. 1992 Oct;63(4):986–995. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81685-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehler E. L., Pascual-Ahuir J. L., Weinstein H. Structural dynamics of calmodulin and troponin C. Protein Eng. 1991 Aug;4(6):625–637. doi: 10.1093/protein/4.6.625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlstone J. R., Borgford T., Chandra M., Oikawa K., Kay C. M., Herzberg O., Moult J., Herklotz A., Reinach F. C., Smillie L. B. Construction and characterization of a spectral probe mutant of troponin C: application to analyses of mutants with increased Ca2+ affinity. Biochemistry. 1992 Jul 21;31(28):6545–6553. doi: 10.1021/bi00143a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlstone J. R., McCubbin W. D., Kay C. M., Sykes B. D., Smillie L. B. Spectroscopic analysis of a methionine-48 to tyrosine mutant of chicken troponin C. Biochemistry. 1992 Oct 13;31(40):9703–9708. doi: 10.1021/bi00155a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrich J. W., Longworth J. W., Fleming G. R. Internal motion and electron transfer in proteins: a picosecond fluorescence study of three homologous azurins. Biochemistry. 1987 May 19;26(10):2711–2722. doi: 10.1021/bi00384a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter J. D., Gergely J. The calcium and magnesium binding sites on troponin and their role in the regulation of myofibrillar adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4628–4633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J. B., Wyssbrod H. R., Porter R. A., Schwartz G. P., Michaels C. A., Laws W. R. Correlation of tryptophan fluorescence intensity decay parameters with 1H NMR-determined rotamer conformations: [tryptophan2]oxytocin. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 18;31(6):1585–1594. doi: 10.1021/bi00121a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strynadka N. C., James M. N. Crystal structures of the helix-loop-helix calcium-binding proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:951–998. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundaralingam M., Bergstrom R., Strasburg G., Rao S. T., Roychowdhury P., Greaser M., Wang B. C. Molecular structure of troponin C from chicken skeletal muscle at 3-angstrom resolution. Science. 1985 Feb 22;227(4689):945–948. doi: 10.1126/science.3969570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao T., Gong B. J., Leavis P. C. Calcium-induced movement of troponin-I relative to actin in skeletal muscle thin filaments. Science. 1990 Mar 16;247(4948):1339–1341. doi: 10.1126/science.2138356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valeur B., Weber G. Resolution of the fluorescence excitation spectrum of indole into the 1La and 1Lb excitation bands. Photochem Photobiol. 1977 May;25(5):441–444. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1977.tb09168.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl P., Auchet J. C. Résolution des spectres de fluorescence au moyen des déclins. Application à l'étude de la sérum albumin humaine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 28;285(1):99–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. K., Lebowitz J., Cheung H. C. Acid-induced dimerization of skeletal troponin C. Proteins. 1989;6(4):424–430. doi: 10.1002/prot.340060409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]