Abstract
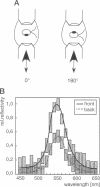
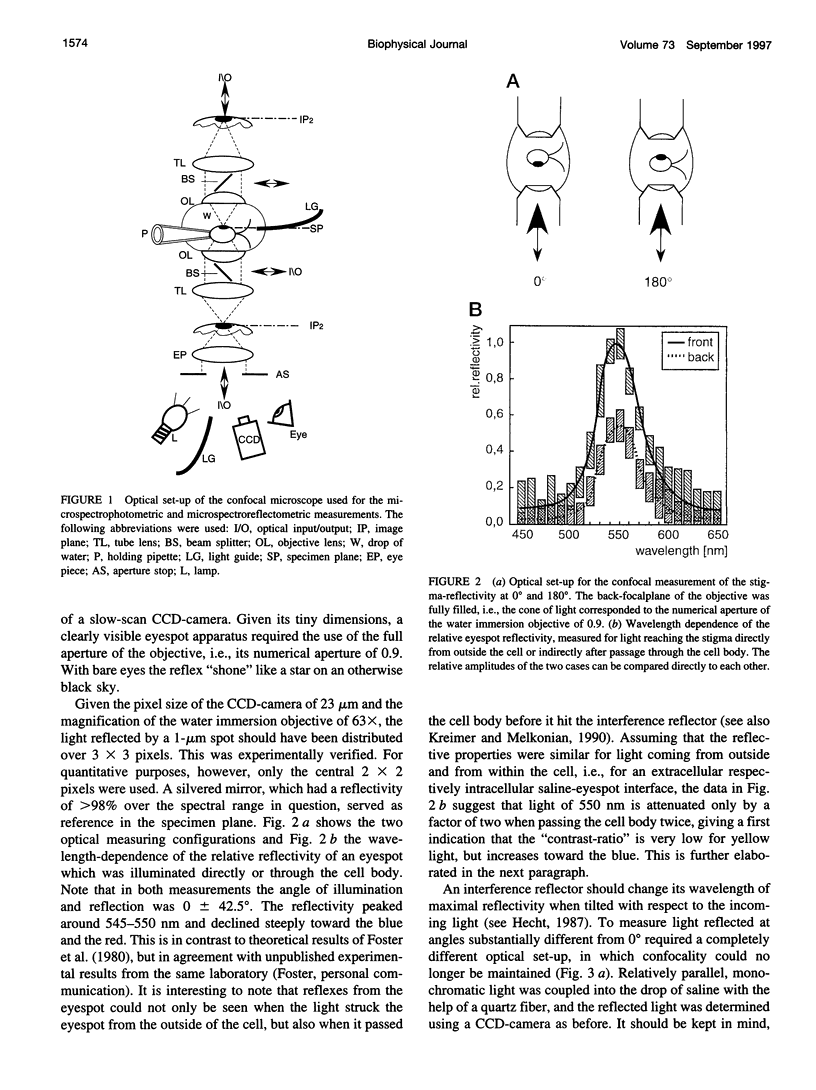
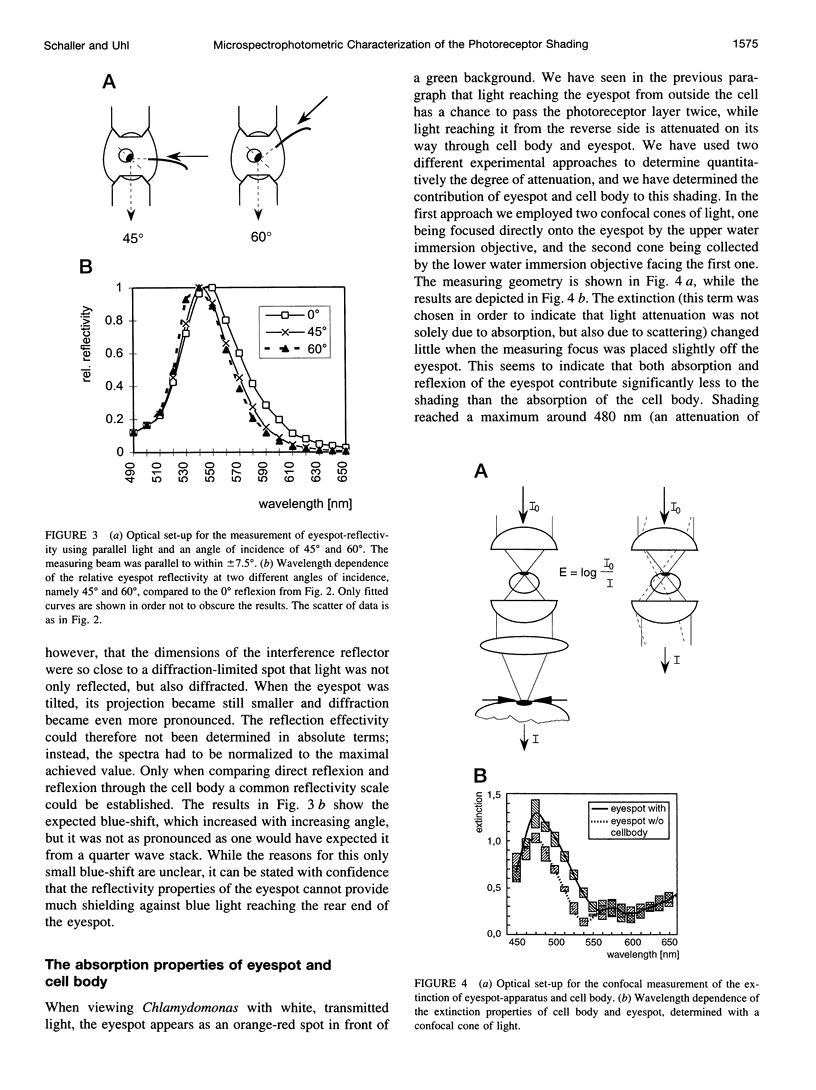
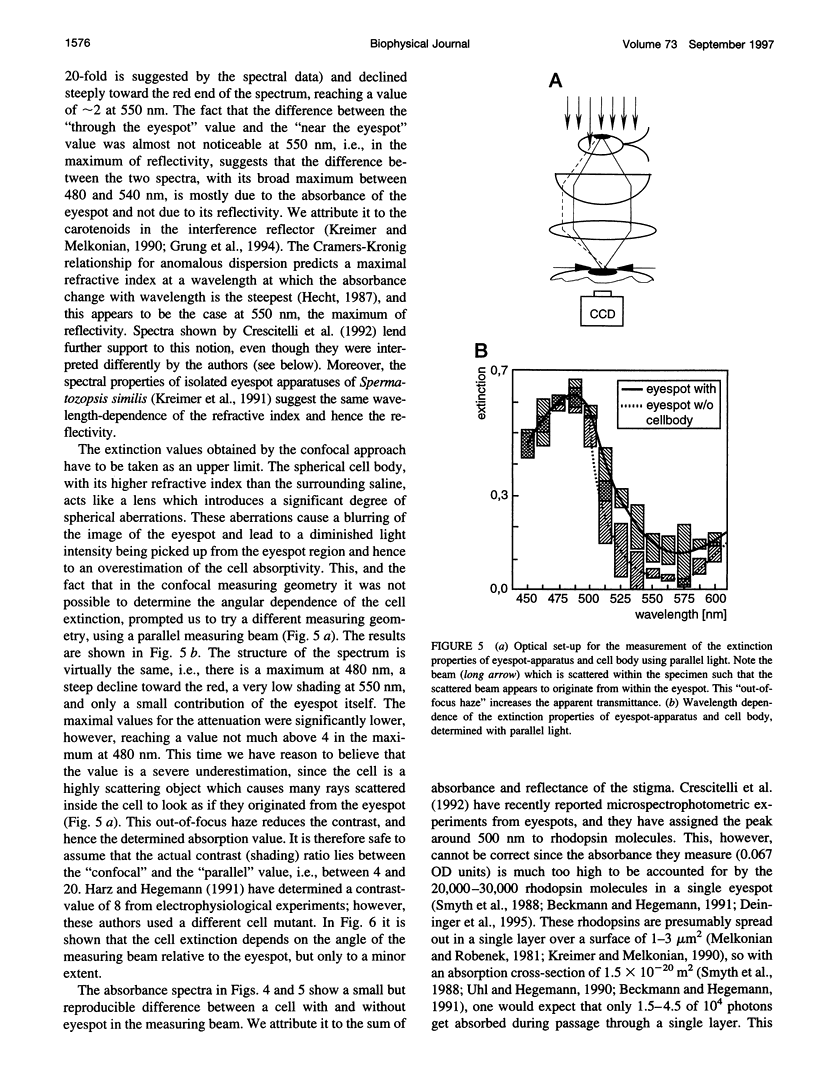
The eyespot apparatus of the unicellular alga Chlamydomonas exhibits a clear directivity, i.e., it perceives light from different directions with different sensitivity. Using a newly constructed confocal microscope we have studied how absorption and reflection of eyespot and cell body shape this directivity. In agreement with previous results the eyespot was found to be highly reflectant, owing to its interference reflector design, but only for yellow light. Light of 490 nm, the maximum of absorption of the photoreceptor, was hardly reflected at all, even when the reflector was "tuned" to lower wavelengths by tilting it relative to the incoming light. The absorption of the carotenoids in the interference reflector also contributed little to the shielding properties of the cell, leaving the major contribution to the cell body. Thus most of the attenuation of light reaching the eyespot from the rear is due to chlorophyll and other pigments within the cell. In its peak around 490 nm the "contrast-ratio" reached a value of 8-10.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beckmann M., Hegemann P. In vitro identification of rhodopsin in the green alga Chlamydomonas. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 16;30(15):3692–3697. doi: 10.1021/bi00229a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crescitelli F., James T. W., Erickson J. M., Loew E. R., McFarland W. N. The eyespot of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: a comparative microspectrophotometric study. Vision Res. 1992 Sep;32(9):1593–1600. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(92)90152-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger W., Kröger P., Hegemann U., Lottspeich F., Hegemann P. Chlamyrhodopsin represents a new type of sensory photoreceptor. EMBO J. 1995 Dec 1;14(23):5849–5858. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00273.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster K. W., Saranak J., Patel N., Zarilli G., Okabe M., Kline T., Nakanishi K. A rhodopsin is the functional photoreceptor for phototaxis in the unicellular eukaryote Chlamydomonas. Nature. 1984 Oct 25;311(5988):756–759. doi: 10.1038/311756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster K. W., Smyth R. D. Light Antennas in phototactic algae. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Dec;44(4):572–630. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.4.572-630.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreimer G., Brohsonn U., Melkonian M. Isolation and partial characterization of the photoreceptive organelle for phototaxis of a flagellate green alga. Eur J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;55(2):318–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreimer G., Melkonian M. Reflection confocal laser scanning microscopy of eyespots in flagellated green algae. Eur J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;53(1):101–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kröger P., Hegemann P. Photophobic responses and phototaxis in Chlamydomonas are triggered by a single rhodopsin photoreceptor. FEBS Lett. 1994 Mar 14;341(1):5–9. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80229-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson M. A., Satir P. Characterization of the eyespot regions of "blind" Chlamydomonas mutants after restoration of photophobic responses. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 1994 Nov-Dec;41(6):593–601. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1994.tb01521.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messler P., Harz H., Uhl R. Instrumentation for multiwavelengths excitation imaging. J Neurosci Methods. 1996 Nov;69(2):137–147. doi: 10.1016/S0165-0270(96)00032-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller K., David R., Uhl R. How Chlamydomonas keeps track of the light once it has reached the right phototactic orientation. Biophys J. 1997 Sep;73(3):1562–1572. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(97)78188-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhl R., Hegemann P. Probing visual transduction in a plant cell: Optical recording of rhodopsin-induced structural changes from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Biophys J. 1990 Nov;58(5):1295–1302. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82469-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]