Abstract
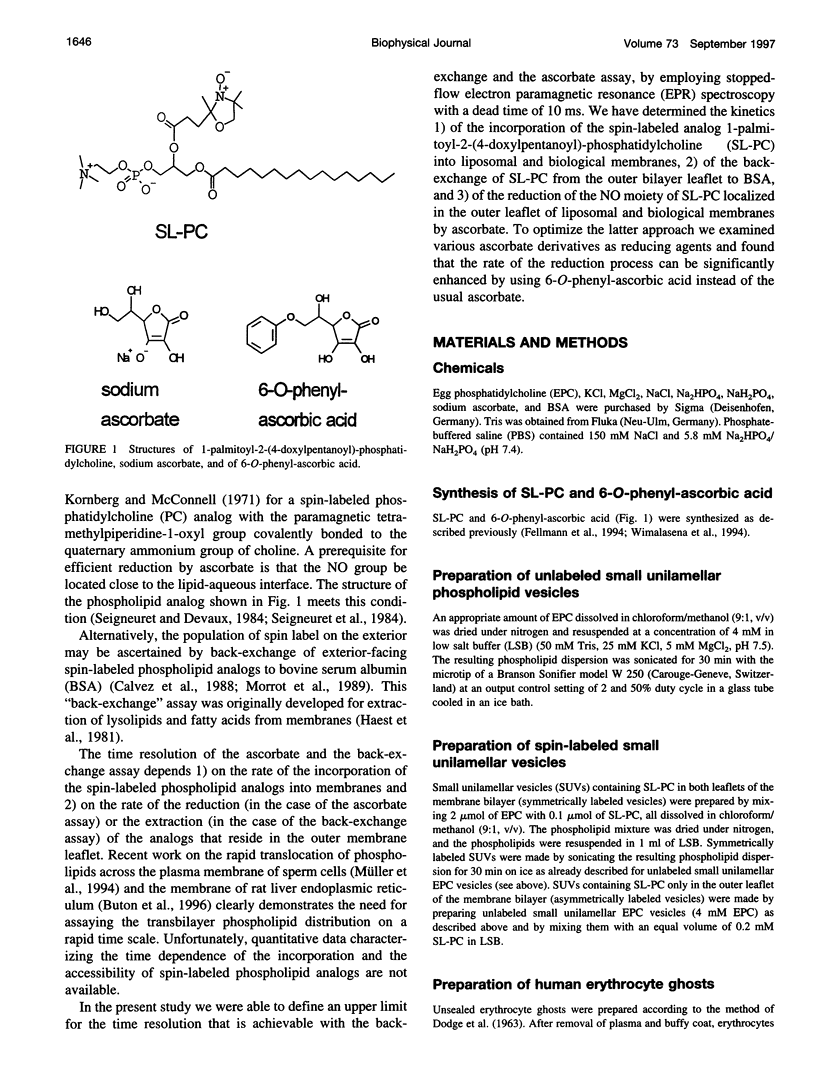
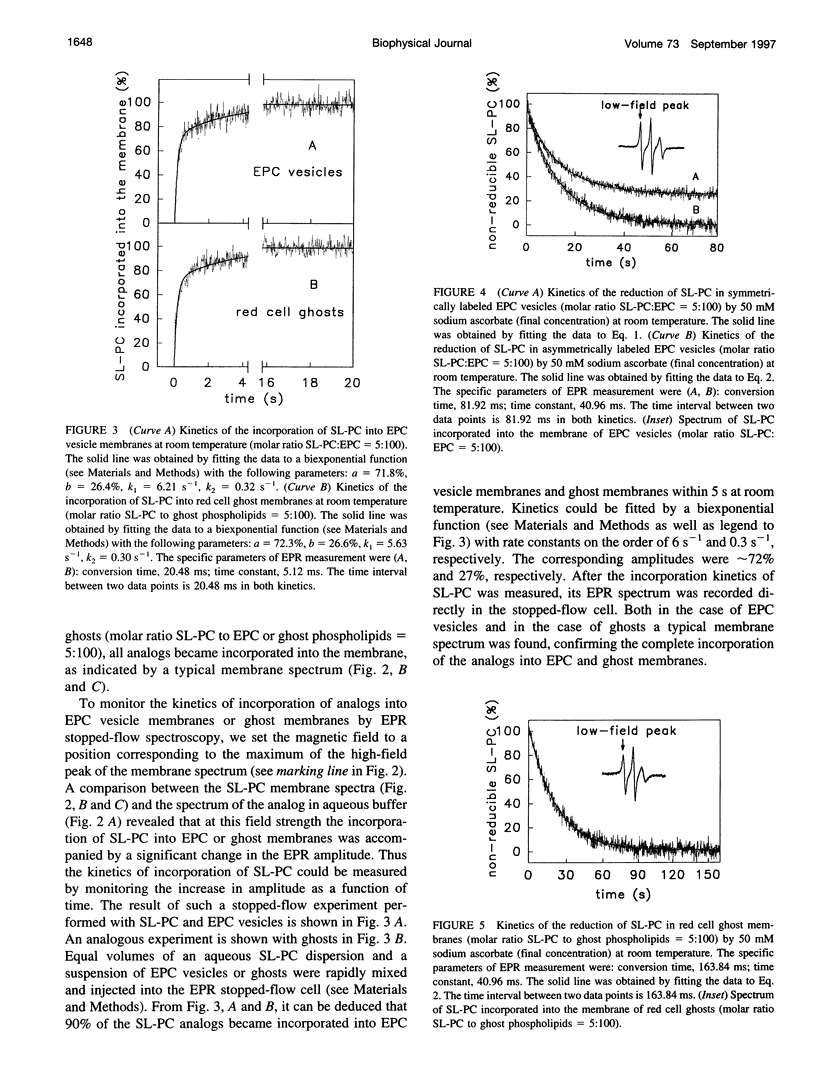
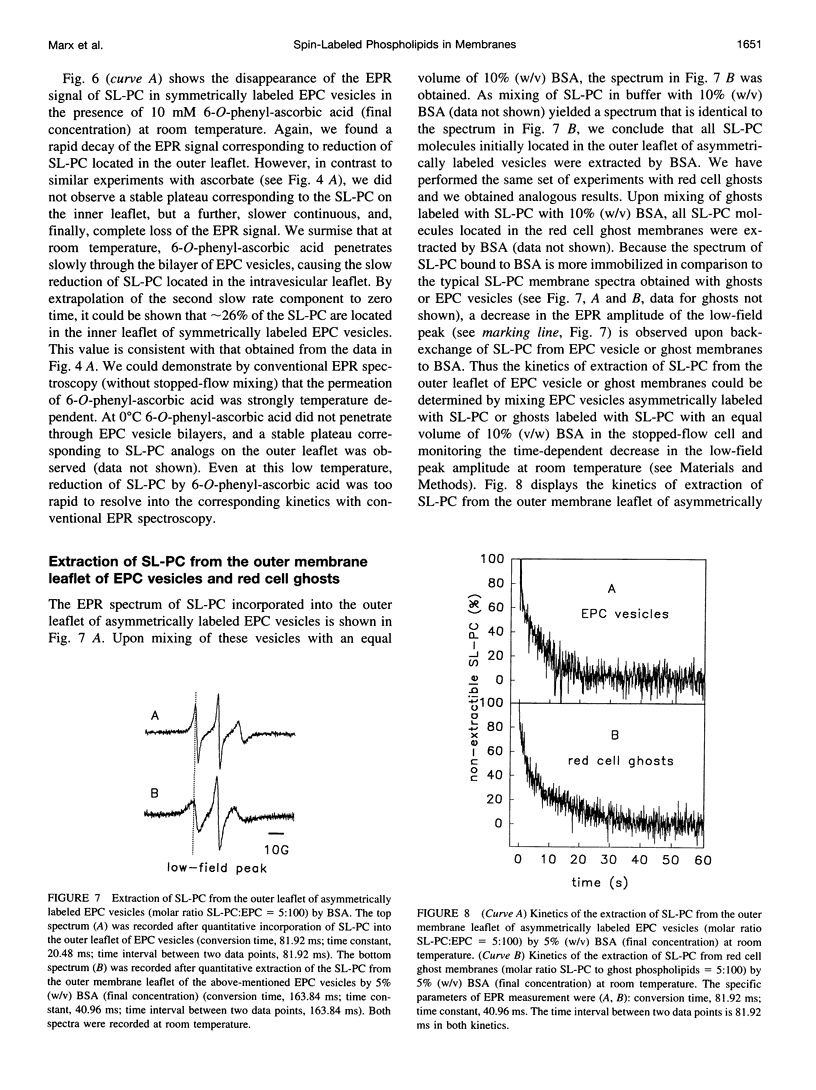
Spin-labeled phospholipid analogs have been employed to probe the transbilayer distribution of endogenous phospholipids in various membrane systems. To determine the transmembrane distribution of the spin-labeled analogs, the analogs are usually inserted into the membrane of interest and subsequently the amount of analog in the outer membrane leaflet is determined either by chemical reduction with ascorbate or by back-exchange to bovine serum albumin (BSA). For accurate determination of the transbilayer distribution of analogs, both the kinetics of incorporation and those of accessibility of analogs to ascorbate or BSA have to be fast in comparison to their transbilayer movement. By means of stopped-flow electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy, we have studied the kinetics of incorporation of the spin-labeled phosphatidylcholine (PC) analog 1-palmitoyl-2-(4-doxylpentanoyl)-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (SL-PC) and of its accessibility to chemical reduction and to back-exchange at room temperature. Incorporation of SL-PC into the outer leaflet of egg phosphatidylcholine (EPC) and red cell ghost membranes was essentially completed within 5 s. Ninety percent of the SL-PC molecules located in the outer membrane leaflet of those membranes were extracted by BSA within 15 s. All exterior-facing SL-PC molecules were reduced by ascorbate in a pseudo-first-order reaction within 60 s in EPC membranes and within 90 s in red cell ghost membranes. The rate of the reduction process could be enhanced by approximately 30-fold when 6-O-phenyl-ascorbic acid was used instead of ascorbate as the reducing agent. The results are discussed in light of assaying rapid transbilayer movement of spin-labeled analogs in biological membranes.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auland M. E., Roufogalis B. D., Devaux P. F., Zachowski A. Reconstitution of ATP-dependent aminophospholipid translocation in proteoliposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 8;91(23):10938–10942. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.10938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitbol M., Devaux P. F. Measurement of outward translocation of phospholipids across human erythrocyte membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6783–6787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buton X., Morrot G., Fellmann P., Seigneuret M. Ultrafast glycerophospholipid-selective transbilayer motion mediated by a protein in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. J Biol Chem. 1996 Mar 22;271(12):6651–6657. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.12.6651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvez J. Y., Zachowski A., Herrmann A., Morrot G., Devaux P. F. Asymmetric distribution of phospholipids in spectrin-poor erythrocyte vesicles. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 26;27(15):5666–5670. doi: 10.1021/bi00415a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J., Gillum K., Schroit A. J. Maintenance of lipid asymmetry in red blood cells and ghosts: effect of divalent cations and serum albumin on the transbilayer distribution of phosphatidylserine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jun 11;1025(1):82–86. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90193-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGE J. T., MITCHELL C., HANAHAN D. J. The preparation and chemical characteristics of hemoglobin-free ghosts of human erythrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Jan;100:119–130. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devaux P. F. Static and dynamic lipid asymmetry in cell membranes. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 5;30(5):1163–1173. doi: 10.1021/bi00219a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolis D., de Kroon A. I., de Kruijff B. Transmembrane movement of phosphatidylcholine in mitochondrial outer membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1996 May 17;271(20):11879–11883. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.20.11879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellmann P., Zachowski A., Devaux P. F. Synthesis and use of spin-labeled lipids for studies of the transmembrane movement of phospholipids. Methods Mol Biol. 1994;27:161–175. doi: 10.1385/0-89603-250-7:161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haest C. W., Plasa G., Deuticke B. Selective removal of lipids from the outer membrane layer of human erythrocytes without hemolysis. Consequences for bilayer stability and cell shape. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec 21;649(3):701–708. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90174-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King M. D., Marsh D. Head group and chain length dependence of phospholipid self-assembly studied by spin-label electron spin resonance. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 10;26(5):1224–1231. doi: 10.1021/bi00379a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D., McConnell H. M. Inside-outside transitions of phospholipids in vesicle membranes. Biochemistry. 1971 Mar 30;10(7):1111–1120. doi: 10.1021/bi00783a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassmann G., Thelander L., Gräslund A. EPR stopped-flow studies of the reaction of the tyrosyl radical of protein R2 from ribonucleotide reductase with hydroxyurea. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Oct 30;188(2):879–887. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91138-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin O. C., Pagano R. E. Transbilayer movement of fluorescent analogs of phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylethanolamine at the plasma membrane of cultured cells. Evidence for a protein-mediated and ATP-dependent process(es). J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5890–5898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon A. K. Flippases. Trends Cell Biol. 1995 Sep;5(9):355–360. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(00)89069-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrot G., Hervé P., Zachowski A., Fellmann P., Devaux P. F. Aminophospholipid translocase of human erythrocytes: phospholipid substrate specificity and effect of cholesterol. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 18;28(8):3456–3462. doi: 10.1021/bi00434a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller K., Pomorski T., Müller P., Zachowski A., Herrmann A. Protein-dependent translocation of aminophospholipids and asymmetric transbilayer distribution of phospholipids in the plasma membrane of ram sperm cells. Biochemistry. 1994 Aug 23;33(33):9968–9974. doi: 10.1021/bi00199a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Op den Kamp J. A. Lipid asymmetry in membranes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:47–71. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.000403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomorski T., Muller P., Zimmermann B., Burger K., Devaux P. F., Herrmann A. Transbilayer movement of fluorescent and spin-labeled phospholipids in the plasma membrane of human fibroblasts: a quantitative approach. J Cell Sci. 1996 Mar;109(Pt 3):687–698. doi: 10.1242/jcs.109.3.687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousselet A., Guthmann C., Matricon J., Bienvenue A., Devaux P. F. Study of the transverse diffusion of spin labeled phospholipids in biological membranes. I. Human red bloods cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Mar 19;426(3):357–371. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90382-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier-Muccillo S., Marsh D., Smith I. C. Monitoring the permeability profile of lipid membranes with spin probes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Jan;172(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90041-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seigneuret M., Devaux P. F. ATP-dependent asymmetric distribution of spin-labeled phospholipids in the erythrocyte membrane: relation to shape changes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3751–3755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seigneuret M., Zachowski A., Hermann A., Devaux P. F. Asymmetric lipid fluidity in human erythrocyte membrane: new spin-label evidence. Biochemistry. 1984 Sep 11;23(19):4271–4275. doi: 10.1021/bi00314a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. D., Poznansky M. J. Curvature and composition-dependent lipid asymmetry in phosphatidylcholine vesicles containing phosphatidylethanolamine and gangliosides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 16;978(1):85–90. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90502-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimalasena K., Dharmasena S., Wimalasena D. S. Ascorbate based novel high affinity alternate reductants and competitive inhibitors of dopamine beta-monooxygenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Apr 15;200(1):113–119. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu G., Hubbell W. L. Phospholipid asymmetry and transmembrane diffusion in photoreceptor disc membranes. Biochemistry. 1993 Jan 26;32(3):879–888. doi: 10.1021/bi00054a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachowski A., Favre E., Cribier S., Hervé P., Devaux P. F. Outside-inside translocation of aminophospholipids in the human erythrocyte membrane is mediated by a specific enzyme. Biochemistry. 1986 May 6;25(9):2585–2590. doi: 10.1021/bi00357a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachowski A., Herrmann A., Paraf A., Devaux P. F. Phospholipid outside-inside translocation in lymphocyte plasma membranes is a protein-mediated phenomenon. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Feb 12;897(1):197–200. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90328-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachowski A. Phospholipids in animal eukaryotic membranes: transverse asymmetry and movement. Biochem J. 1993 Aug 15;294(Pt 1):1–14. doi: 10.1042/bj2940001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


