Abstract
Wetting and capillary condensation are thermodynamic phenomena in which the special affinity of interfaces to a thermodynamic phase, relative to the stable bulk phase, leads to the stabilization of a wetting phase at the interfaces. Wetting and capillary condensation are here proposed as mechanisms that in membranes may serve to induce special lipid phases in between integral membrane proteins leading to long-range lipid-mediated joining forces acting between the proteins and hence providing a means of protein organization. The consequences of wetting in terms of protein aggregation and protein clustering are derived both within a simple phenomenological theory as well as within a concrete calculation on a microscopic model of lipid-protein interactions that accounts for the lipid bilayer phase equilibria and direct lipid-protein interactions governed by hydrophobic matching between the lipid bilayer hydrophobic thickness and the length of the hydrophobic membrane domain. The theoretical results are expected to be relevant for optimizing the experimental conditions required for forming protein aggregates and regular protein arrays in membranes.
Full text
PDF



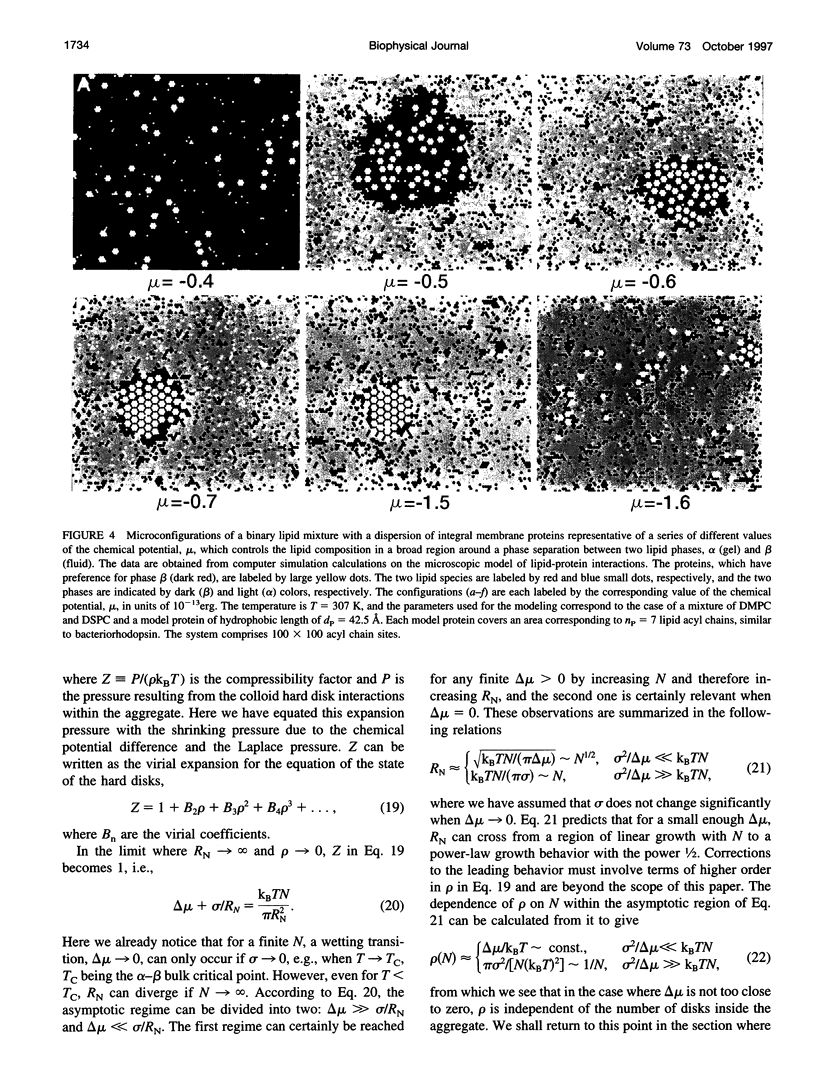

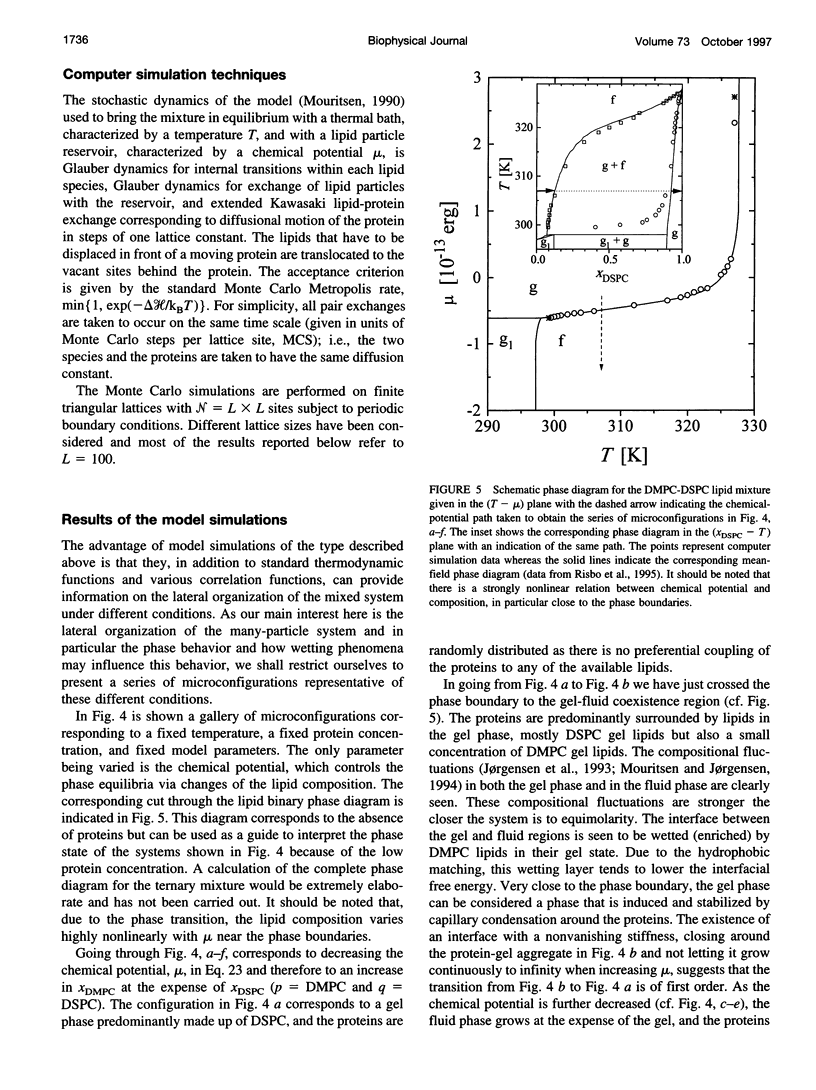


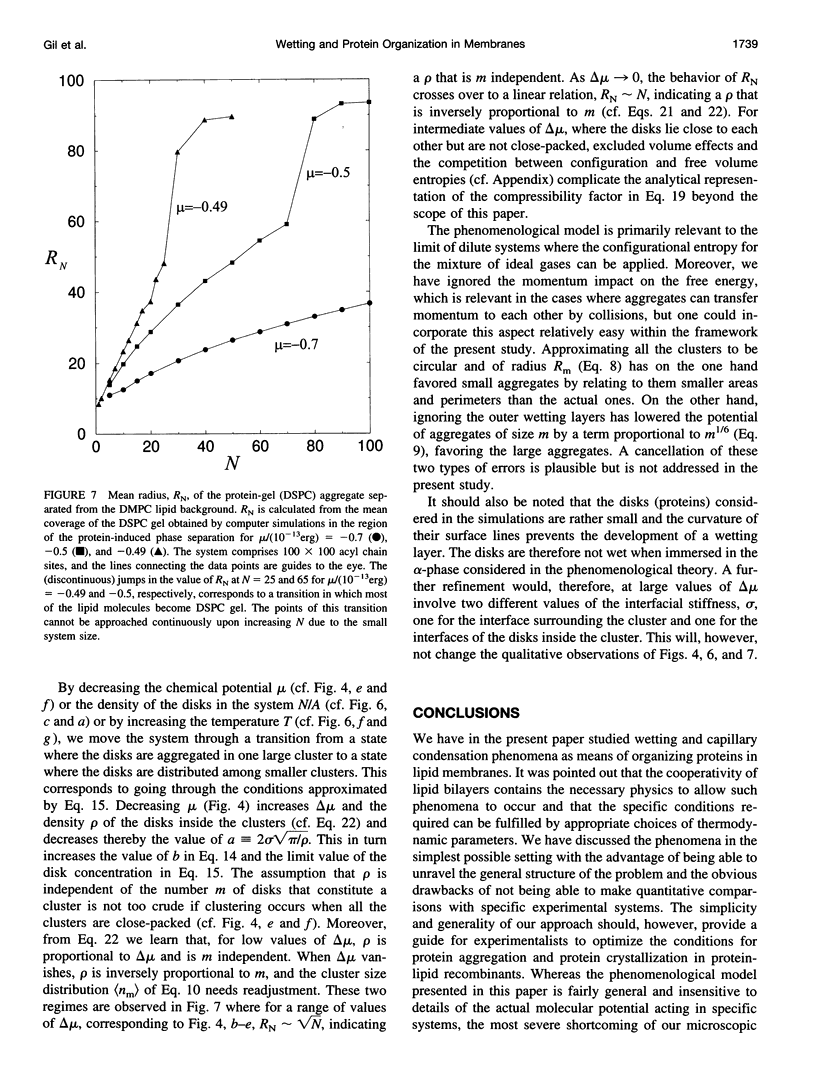


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aranda-Espinoza H., Berman A., Dan N., Pincus P., Safran S. Interaction between inclusions embedded in membranes. Biophys J. 1996 Aug;71(2):648–656. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79265-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beysens D, Estève D. Adsorption phenomena at the surface of silica spheres in a binary liquid mixture. Phys Rev Lett. 1985 May 13;54(19):2123–2126. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.54.2123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bladon P, Frenkel D. Dislocation unbinding in dense two-dimensional crystals. Phys Rev Lett. 1995 Mar 27;74(13):2519–2522. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.74.2519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruinsma R., Goulian M., Pincus P. Self-assembly of membrane junctions. Biophys J. 1994 Aug;67(2):746–750. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80535-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fattal D. R., Ben-Shaul A. A molecular model for lipid-protein interaction in membranes: the role of hydrophobic mismatch. Biophys J. 1993 Nov;65(5):1795–1809. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81249-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil T, Mikheev LV. Curvature controlled wetting in two dimensions. Phys Rev E Stat Phys Plasmas Fluids Relat Interdiscip Topics. 1995 Jul;52(1):772–780. doi: 10.1103/physreve.52.772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen K., Mouritsen O. G. Phase separation dynamics and lateral organization of two-component lipid membranes. Biophys J. 1995 Sep;69(3):942–954. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)79968-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen K., Sperotto M. M., Mouritsen O. G., Ipsen J. H., Zuckermann M. J. Phase equilibria and local structure in binary lipid bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Oct 10;1152(1):135–145. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(93)90240-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühlbrandt W. Two-dimensional crystallization of membrane proteins. Q Rev Biophys. 1992 Feb;25(1):1–49. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500004716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipowsky R, Fisher ME. Scaling regimes and functional renormalization for wetting transitions. Phys Rev B Condens Matter. 1987 Aug 1;36(4):2126–2141. doi: 10.1103/physrevb.36.2126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouritsen O. G., Bloom M. Mattress model of lipid-protein interactions in membranes. Biophys J. 1984 Aug;46(2):141–153. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84007-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouritsen O. G., Bloom M. Models of lipid-protein interactions in membranes. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1993;22:145–171. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.22.060193.001045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouritsen O. G., Jørgensen K. Dynamical order and disorder in lipid bilayers. Chem Phys Lipids. 1994 Sep 6;73(1-2):3–25. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(94)90171-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen M, Miao L, Ipsen JH, Mouritsen OG, Zuckermann MJ. Random-lattice models and simulation algorithms for the phase equilibria in two-dimensional condensed systems of particles with coupled internal and translational degrees of freedom. Phys Rev E Stat Phys Plasmas Fluids Relat Interdiscip Topics. 1996 Dec;54(6):6889–6905. doi: 10.1103/physreve.54.6889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pink D. A., Green T. J., Chapman D. Raman scattering in bilayers of saturated phosphatidylcholines. Experiment and theory. Biochemistry. 1980 Jan 22;19(2):349–356. doi: 10.1021/bi00543a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sackmann E. The seventh Datta Lecture. Membrane bending energy concept of vesicle- and cell-shapes and shape-transitions. FEBS Lett. 1994 Jun 6;346(1):3–16. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00484-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]