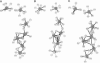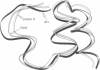Abstract
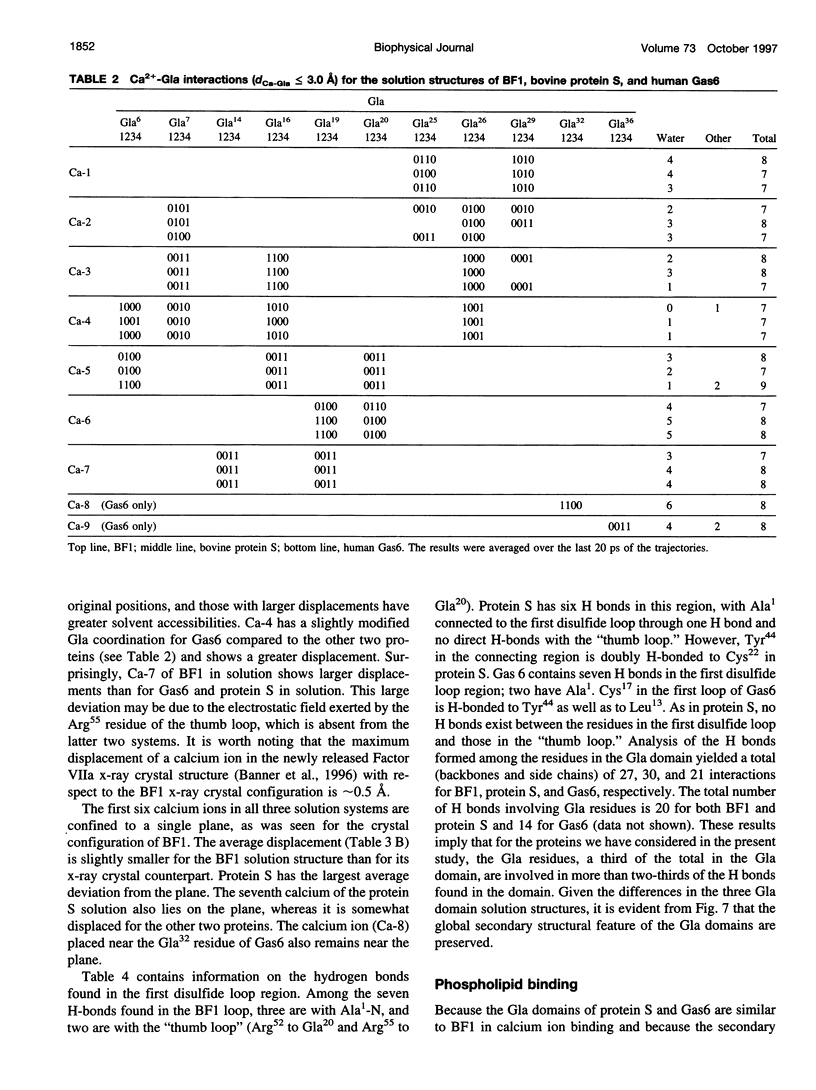
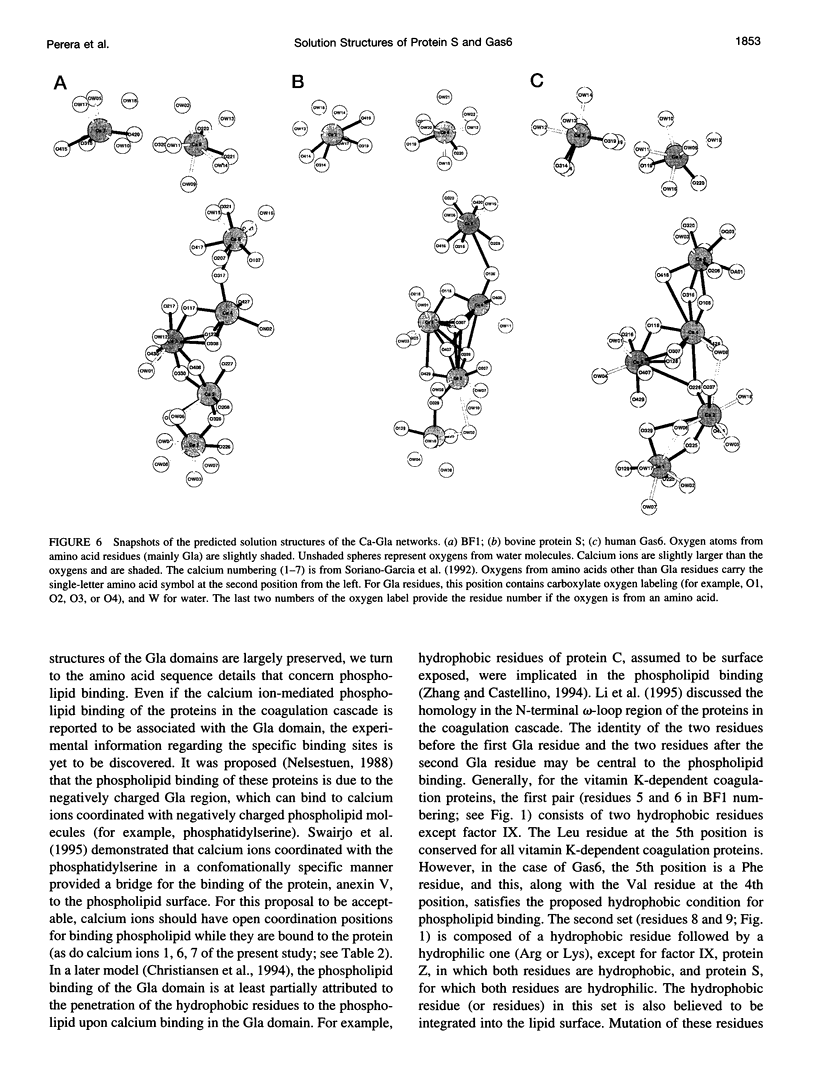
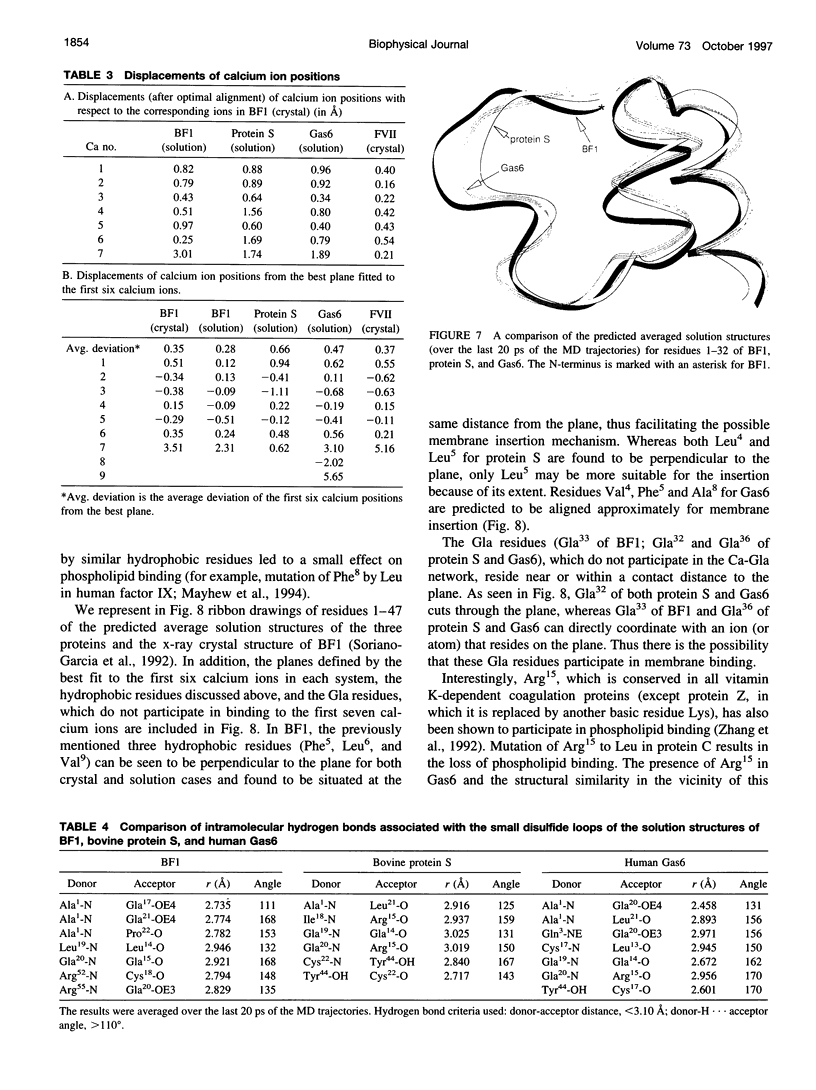
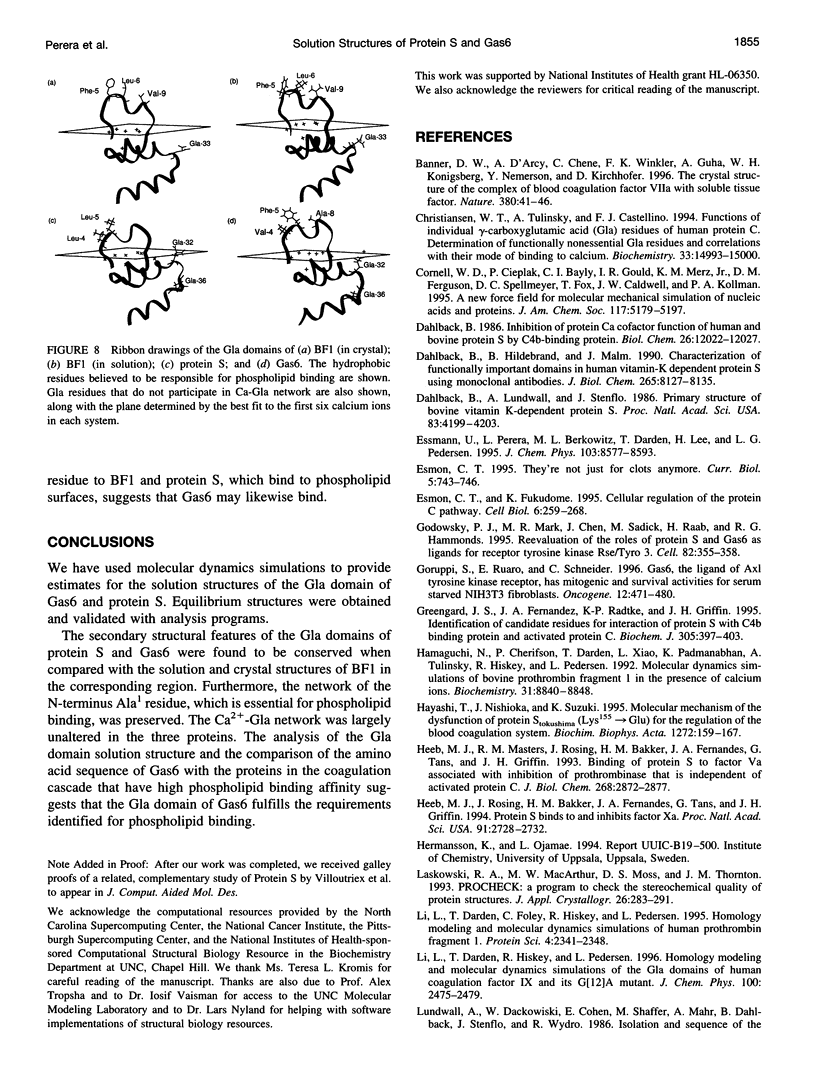
The solution structures of the N-terminal domains of protein S, a plasma vitamin K-dependent glycoprotein, and its homolog growth arrest specific protein 6 (Gas6) were predicted by molecular dynamics computer simulations. The initial structures were based on the x-ray crystallographic structure of the corresponding region of bovine prothrombin fragment 1. The subsequent molecular dynamics trajectories were calculated using the second-generation AMBER force field. The long-range electrostatic forces were evaluated by the particle mesh Ewald method. The structures that stabilized over a 400-ps time interval were compared with the corresponding region of the simulated solution structure of bovine prothrombin fragment 1. Structural properties of the gamma-carboxyglutamic acid (Gla) domains obtained from simulations and calcium binding were found to be conserved for all three proteins. Analysis of the predicted solution structure of the Gla domain of Gas6 suggests that this domain should bind with negatively charged phospholipid surfaces analogous to bovine prothrombin fragment 1 and protein S.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banner D. W., D'Arcy A., Chène C., Winkler F. K., Guha A., Konigsberg W. H., Nemerson Y., Kirchhofer D. The crystal structure of the complex of blood coagulation factor VIIa with soluble tissue factor. Nature. 1996 Mar 7;380(6569):41–46. doi: 10.1038/380041a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen W. T., Tulinsky A., Castellino F. J. Functions of individual gamma-carboxyglutamic acid (Gla) residues of human protein c. Determination of functionally nonessential Gla residues and correlations with their mode of binding to calcium. Biochemistry. 1994 Dec 20;33(50):14993–15000. doi: 10.1021/bi00254a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B., Hildebrand B., Malm J. Characterization of functionally important domains in human vitamin K-dependent protein S using monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8127–8135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B. Inhibition of protein Ca cofactor function of human and bovine protein S by C4b-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12022–12027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B., Lundwall A., Stenflo J. Primary structure of bovine vitamin K-dependent protein S. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4199–4203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Fukudome K. Cellular regulation of the protein C pathway. Semin Cell Biol. 1995 Oct;6(5):259–268. doi: 10.1006/scel.1995.0035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T. Inflammation. They're not just for clots anymore. Curr Biol. 1995 Jul 1;5(7):743–746. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00150-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godowski P. J., Mark M. R., Chen J., Sadick M. D., Raab H., Hammonds R. G. Reevaluation of the roles of protein S and Gas6 as ligands for the receptor tyrosine kinase Rse/Tyro 3. Cell. 1995 Aug 11;82(3):355–358. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90424-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goruppi S., Ruaro E., Schneider C. Gas6, the ligand of Axl tyrosine kinase receptor, has mitogenic and survival activities for serum starved NIH3T3 fibroblasts. Oncogene. 1996 Feb 1;12(3):471–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard J. S., Fernandez J. A., Radtke K. P., Griffin J. H. Identification of candidate residues for interaction of protein S with C4b binding protein and activated protein C. Biochem J. 1995 Jan 15;305(Pt 2):397–403. doi: 10.1042/bj3050397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamaguchi N., Charifson P., Darden T., Xiao L., Padmanabhan K., Tulinsky A., Hiskey R., Pedersen L. Molecular dynamics simulation of bovine prothrombin fragment 1 in the presence of calcium ions. Biochemistry. 1992 Sep 22;31(37):8840–8848. doi: 10.1021/bi00152a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi T., Nishioka J., Suzuki K. Molecular mechanism of the dysfunction of protein S(Tokushima) (Lys155-->Glu) for the regulation of the blood coagulation system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995 Dec 12;1272(3):159–167. doi: 10.1016/0925-4439(95)00081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heeb M. J., Mesters R. M., Tans G., Rosing J., Griffin J. H. Binding of protein S to factor Va associated with inhibition of prothrombinase that is independent of activated protein C. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2872–2877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heeb M. J., Rosing J., Bakker H. M., Fernandez J. A., Tans G., Griffin J. H. Protein S binds to and inhibits factor Xa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 29;91(7):2728–2732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.7.2728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li L., Darden T., Foley C., Hiskey R., Pedersen L. Homology modeling and molecular dynamics simulation of human prothrombin fragment 1. Protein Sci. 1995 Nov;4(11):2341–2348. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560041112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundwall A., Dackowski W., Cohen E., Shaffer M., Mahr A., Dahlbäck B., Stenflo J., Wydro R. Isolation and sequence of the cDNA for human protein S, a regulator of blood coagulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6716–6720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manfioletti G., Brancolini C., Avanzi G., Schneider C. The protein encoded by a growth arrest-specific gene (gas6) is a new member of the vitamin K-dependent proteins related to protein S, a negative coregulator in the blood coagulation cascade. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;13(8):4976–4985. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.8.4976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mark M. R., Chen J., Hammonds R. G., Sadick M., Godowsk P. J. Characterization of Gas6, a member of the superfamily of G domain-containing proteins, as a ligand for Rse and Axl. J Biol Chem. 1996 Apr 19;271(16):9785–9789. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.16.9785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayhew M., Handford P., Brownlee G. G. The binding of natural variants of human factor IX to endothelial cells. FEBS Lett. 1994 Mar 14;341(1):74–78. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80243-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano T., Higashino K., Kikuchi N., Kishino J., Nomura K., Fujita H., Ohara O., Arita H. Vascular smooth muscle cell-derived, Gla-containing growth-potentiating factor for Ca(2+)-mobilizing growth factors. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 17;270(11):5702–5705. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.11.5702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano T., Kawamoto K., Kishino J., Nomura K., Higashino K., Arita H. Requirement of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid residues for the biological activity of Gas6: contribution of endogenous Gas6 to the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem J. 1997 Apr 15;323(Pt 2):387–392. doi: 10.1042/bj3230387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi K., Nagata K., Toshima J., Nakano T., Arita H., Tsuda H., Suzuki K., Mizuno K. Stimulation of sky receptor tyrosine kinase by the product of growth arrest-specific gene 6. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 29;270(39):22681–22684. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.39.22681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwalbe R. A., Ryan J., Stern D. M., Kisiel W., Dahlbäck B., Nelsestuen G. L. Protein structural requirements and properties of membrane binding by gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-containing plasma proteins and peptides. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20288–20296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwalbe R., Dahlbäck B., Hillarp A., Nelsestuen G. Assembly of protein S and C4b-binding protein on membranes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16074–16081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano-Garcia M., Padmanabhan K., de Vos A. M., Tulinsky A. The Ca2+ ion and membrane binding structure of the Gla domain of Ca-prothrombin fragment 1. Biochemistry. 1992 Mar 10;31(9):2554–2566. doi: 10.1021/bi00124a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt T. N., Conn G., Gore M., Lai C., Bruno J., Radziejewski C., Mattsson K., Fisher J., Gies D. R., Jones P. F. The anticoagulation factor protein S and its relative, Gas6, are ligands for the Tyro 3/Axl family of receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1995 Feb 24;80(4):661–670. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90520-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugo T., Dahlbäck B., Holmgren A., Stenflo J. Calcium binding of bovine protein S. Effect of thrombin cleavage and removal of the gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-containing region. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):5116–5120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swairjo M. A., Concha N. O., Kaetzel M. A., Dedman J. R., Seaton B. A. Ca(2+)-bridging mechanism and phospholipid head group recognition in the membrane-binding protein annexin V. Nat Struct Biol. 1995 Nov;2(11):968–974. doi: 10.1038/nsb1195-968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varnum B. C., Young C., Elliott G., Garcia A., Bartley T. D., Fridell Y. W., Hunt R. W., Trail G., Clogston C., Toso R. J. Axl receptor tyrosine kinase stimulated by the vitamin K-dependent protein encoded by growth-arrest-specific gene 6. Nature. 1995 Feb 16;373(6515):623–626. doi: 10.1038/373623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. J. Regulation of activated protein C by protein S. The role of phospholipid in factor Va inactivation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11128–11131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. J. Regulation of vitamin K-dependent protein S. Inactivation by thrombin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10335–10339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolberg A. S., Li L., Cheung W. F., Hamaguchi N., Pedersen L. G., Stafford D. W. Characterization of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid residue 21 of human factor IX. Biochemistry. 1996 Aug 13;35(32):10321–10327. doi: 10.1021/bi960502i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang L., Castellino F. J. The binding energy of human coagulation protein C to acidic phospholipid vesicles contains a major contribution from leucine 5 in the gamma-carboxyglutamic acid domain. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3590–3595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang L., Jhingan A., Castellino F. J. Role of individual gamma-carboxyglutamic acid residues of activated human protein C in defining its in vitro anticoagulant activity. Blood. 1992 Aug 15;80(4):942–952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]