Abstract
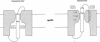
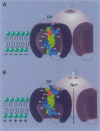
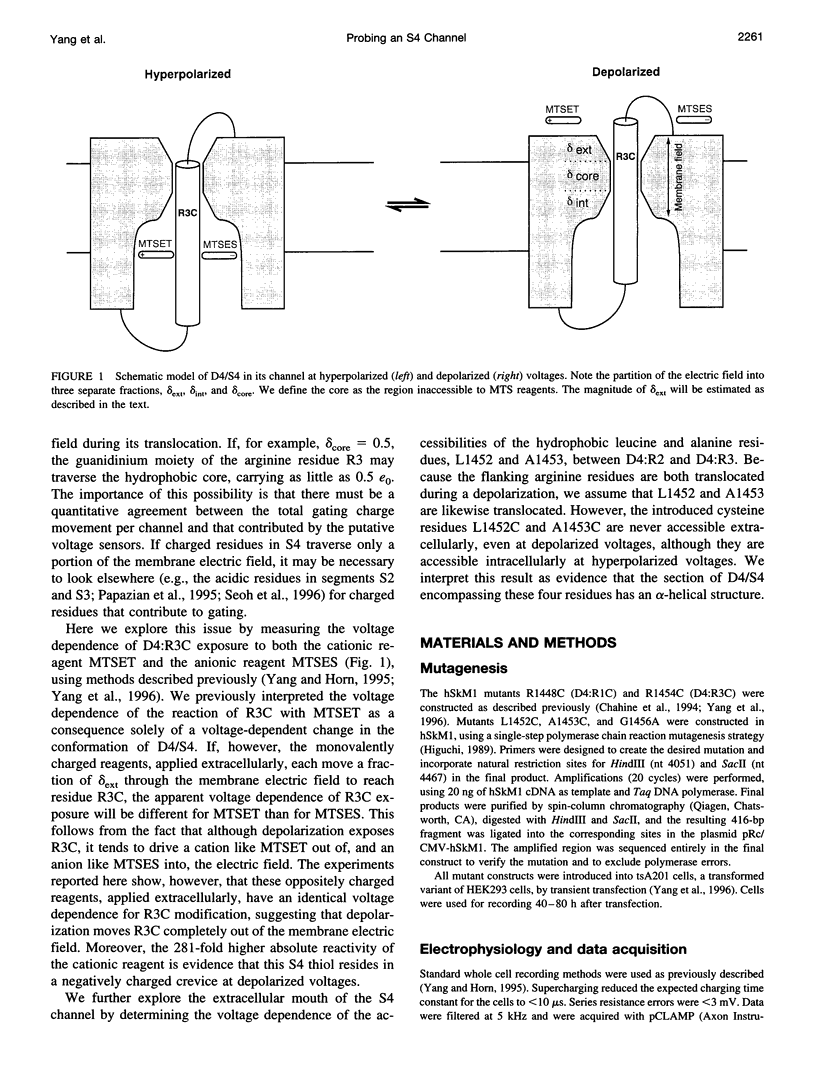
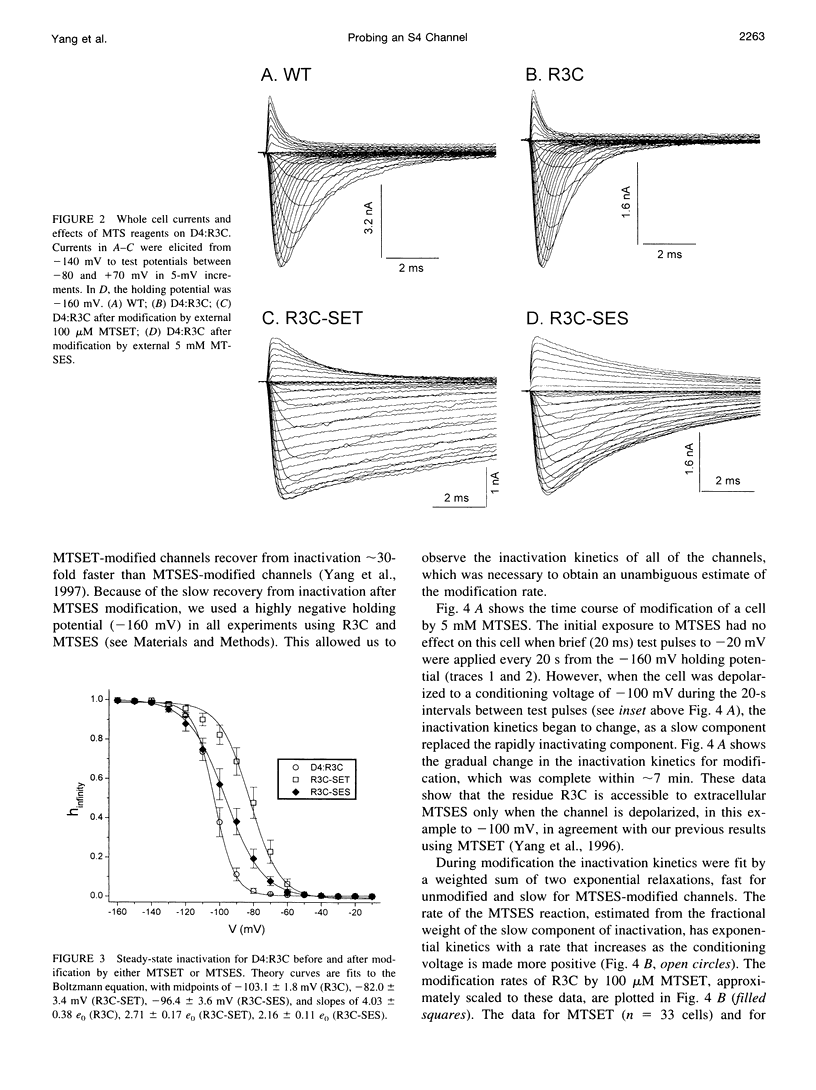
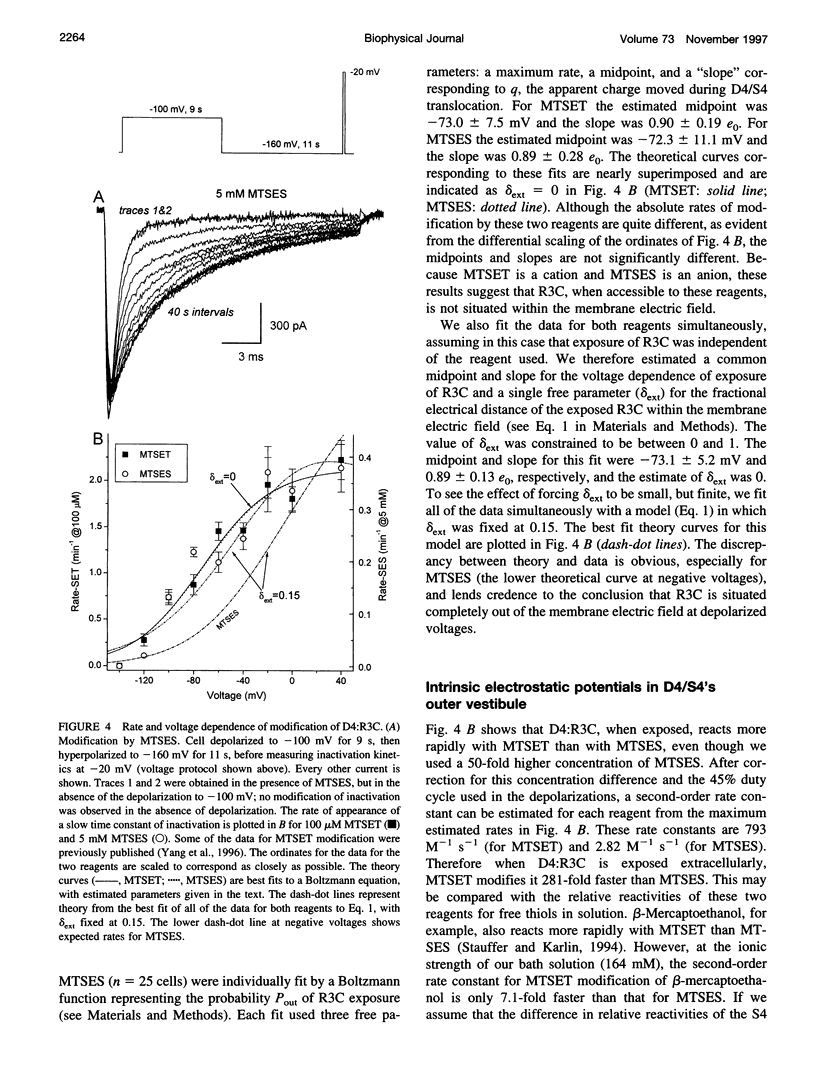
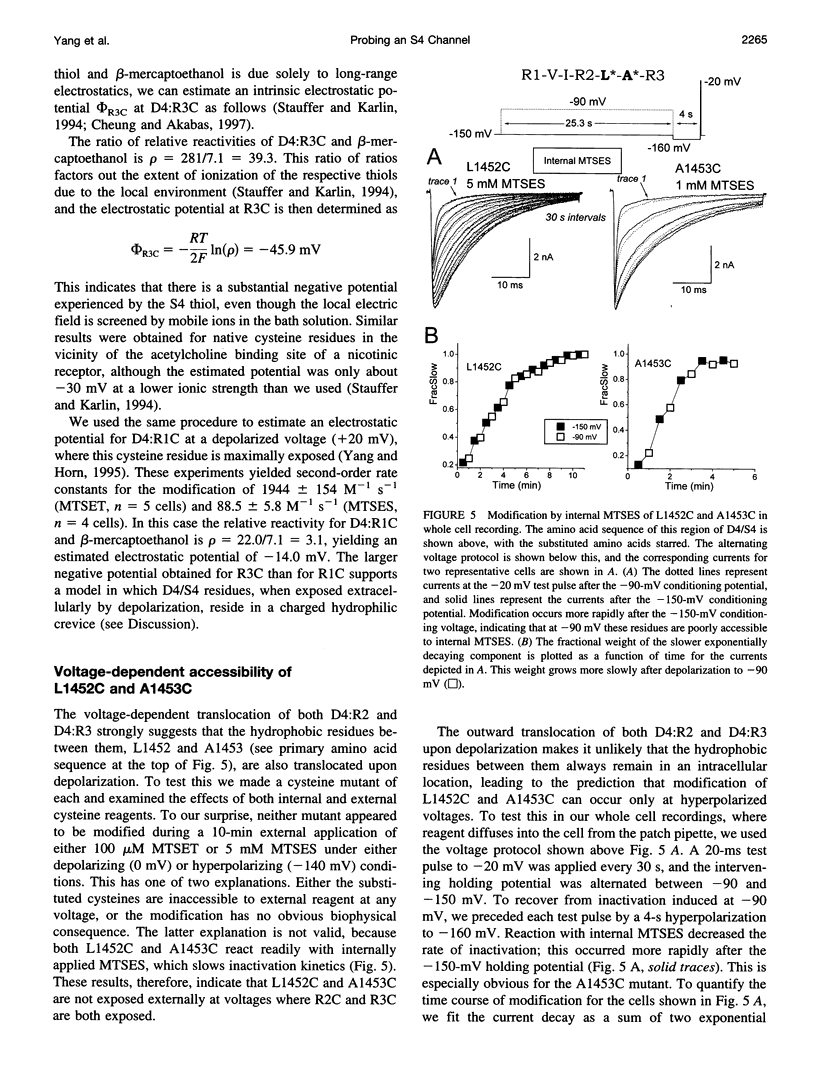
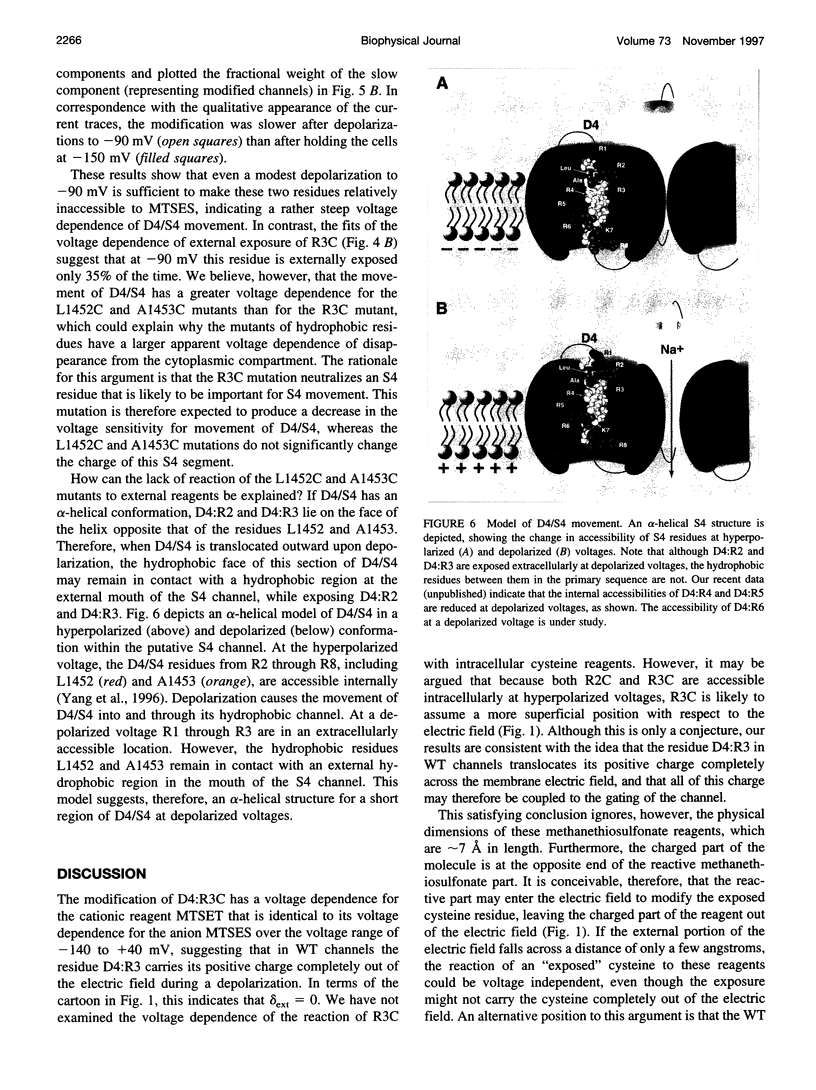
The second and third basic residues of the S4 segment of domain 4 (D4:R2 and D4:R3) of the human skeletal muscle Na+ channel are known to be translocated from a cytoplasmic to an extracellular position during depolarization. Accessibilities of individual S4 residues were assayed by alteration of inactivation kinetics during modification of cysteine mutants by hydrophilic methanethiosulfonate reagents. The voltage dependences of the reaction rates are identical for extracellular application of cationic methanethiosulfonate-ethyltrimethylammonium (MTSET) and anionic methanethiosulfonate-ethylsulfonate (MTSES), suggesting that D4:R3C is situated outside the membrane electric field at depolarized voltages. The absolute rate of R3C modification is 281-fold greater for MTSET than for MTSES, however, suggesting that at depolarized voltages this S4 thiol resides in a negatively charged hydrophilic crevice. The two hydrophobic residues between D4:R2C and D4:R3C in the primary sequence (L1452 and A1453) are not externally exposed at any voltage. An alpha-helical representation of D4/S4 shows that the basic residues D4:R2 and D4:R3 are on the face opposite that of L1452 and A1453. We propose that in the depolarized conformation, the hydrophobic face of this portion of D4/S4 remains in contact with a hydrophobic region of the extracellular vestibule of the S4 channel.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggarwal S. K., MacKinnon R. Contribution of the S4 segment to gating charge in the Shaker K+ channel. Neuron. 1996 Jun;16(6):1169–1177. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80143-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Molecular properties of voltage-sensitive sodium channels. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:953–985. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chahine M., George A. L., Jr, Zhou M., Ji S., Sun W., Barchi R. L., Horn R. Sodium channel mutations in paramyotonia congenita uncouple inactivation from activation. Neuron. 1994 Feb;12(2):281–294. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90271-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung M., Akabas M. H. Locating the anion-selectivity filter of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) chloride channel. J Gen Physiol. 1997 Mar;109(3):289–299. doi: 10.1085/jgp.109.3.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desideri A., Falconi M., Polticelli F., Bolognesi M., Djinovic K., Rotilio G. Evolutionary conservativeness of electric field in the Cu,Zn superoxide dismutase active site. Evidence for co-ordinated mutation of charged amino acid residues. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jan 5;223(1):337–342. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90734-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durell S. R., Guy H. R. Atomic scale structure and functional models of voltage-gated potassium channels. Biophys J. 1992 Apr;62(1):238–250. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81809-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Getzoff E. D., Tainer J. A., Weiner P. K., Kollman P. A., Richardson J. S., Richardson D. C. Electrostatic recognition between superoxide and copper, zinc superoxide dismutase. Nature. 1983 Nov 17;306(5940):287–290. doi: 10.1038/306287a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy H. R., Conti F. Pursuing the structure and function of voltage-gated channels. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Jun;13(6):201–206. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90160-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschberg B., Rovner A., Lieberman M., Patlak J. Transfer of twelve charges is needed to open skeletal muscle Na+ channels. J Gen Physiol. 1995 Dec;106(6):1053–1068. doi: 10.1085/jgp.106.6.1053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson H. P., Baker O. S., Dhillon D. S., Isacoff E. Y. Transmembrane movement of the shaker K+ channel S4. Neuron. 1996 Feb;16(2):387–397. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannuzzu L. M., Moronne M. M., Isacoff E. Y. Direct physical measure of conformational rearrangement underlying potassium channel gating. Science. 1996 Jan 12;271(5246):213–216. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5246.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neil K. T., DeGrado W. F. A thermodynamic scale for the helix-forming tendencies of the commonly occurring amino acids. Science. 1990 Nov 2;250(4981):646–651. doi: 10.1126/science.2237415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papazian D. M., Shao X. M., Seoh S. A., Mock A. F., Huang Y., Wainstock D. H. Electrostatic interactions of S4 voltage sensor in Shaker K+ channel. Neuron. 1995 Jun;14(6):1293–1301. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90276-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoppa N. E., McCormack K., Tanouye M. A., Sigworth F. J. The size of gating charge in wild-type and mutant Shaker potassium channels. Science. 1992 Mar 27;255(5052):1712–1715. doi: 10.1126/science.1553560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seoh S. A., Sigg D., Papazian D. M., Bezanilla F. Voltage-sensing residues in the S2 and S4 segments of the Shaker K+ channel. Neuron. 1996 Jun;16(6):1159–1167. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80142-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauffer D. A., Karlin A. Electrostatic potential of the acetylcholine binding sites in the nicotinic receptor probed by reactions of binding-site cysteines with charged methanethiosulfonates. Biochemistry. 1994 Jun 7;33(22):6840–6849. doi: 10.1021/bi00188a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang N., George A. L., Jr, Horn R. Molecular basis of charge movement in voltage-gated sodium channels. Neuron. 1996 Jan;16(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80028-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang N., Horn R. Evidence for voltage-dependent S4 movement in sodium channels. Neuron. 1995 Jul;15(1):213–218. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90078-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagotta W. N., Hoshi T., Dittman J., Aldrich R. W. Shaker potassium channel gating. II: Transitions in the activation pathway. J Gen Physiol. 1994 Feb;103(2):279–319. doi: 10.1085/jgp.103.2.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]