Abstract
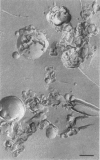
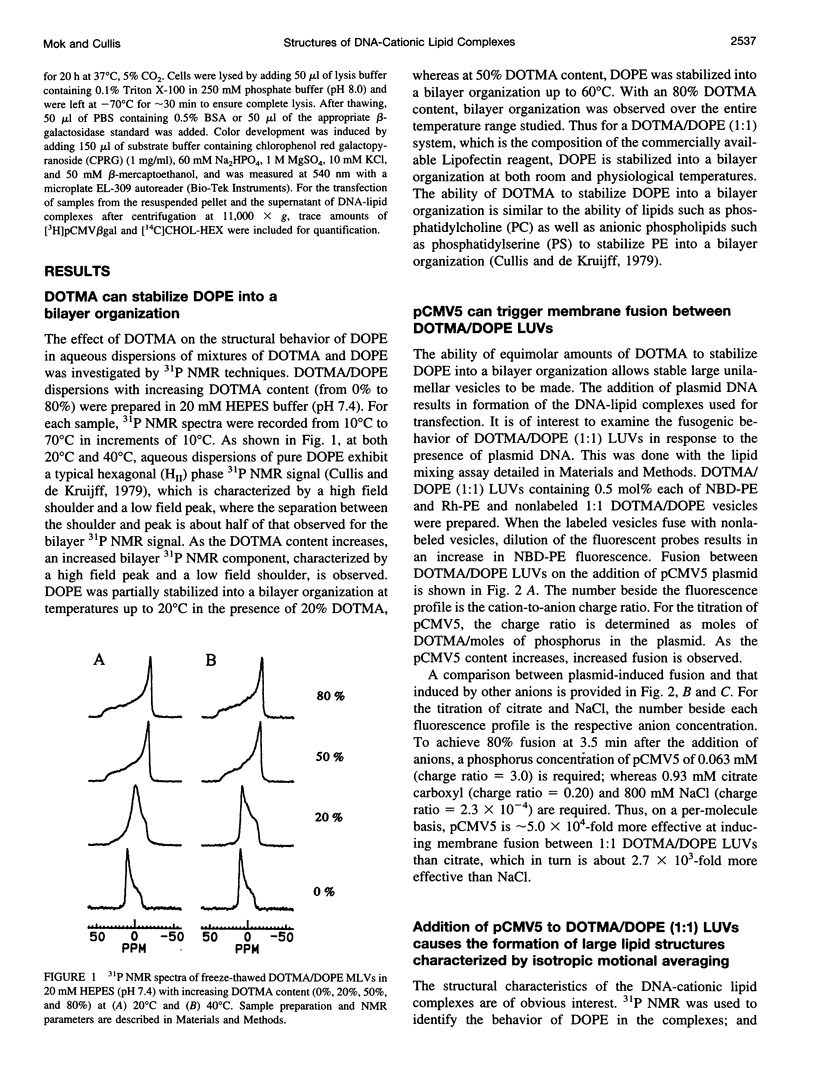
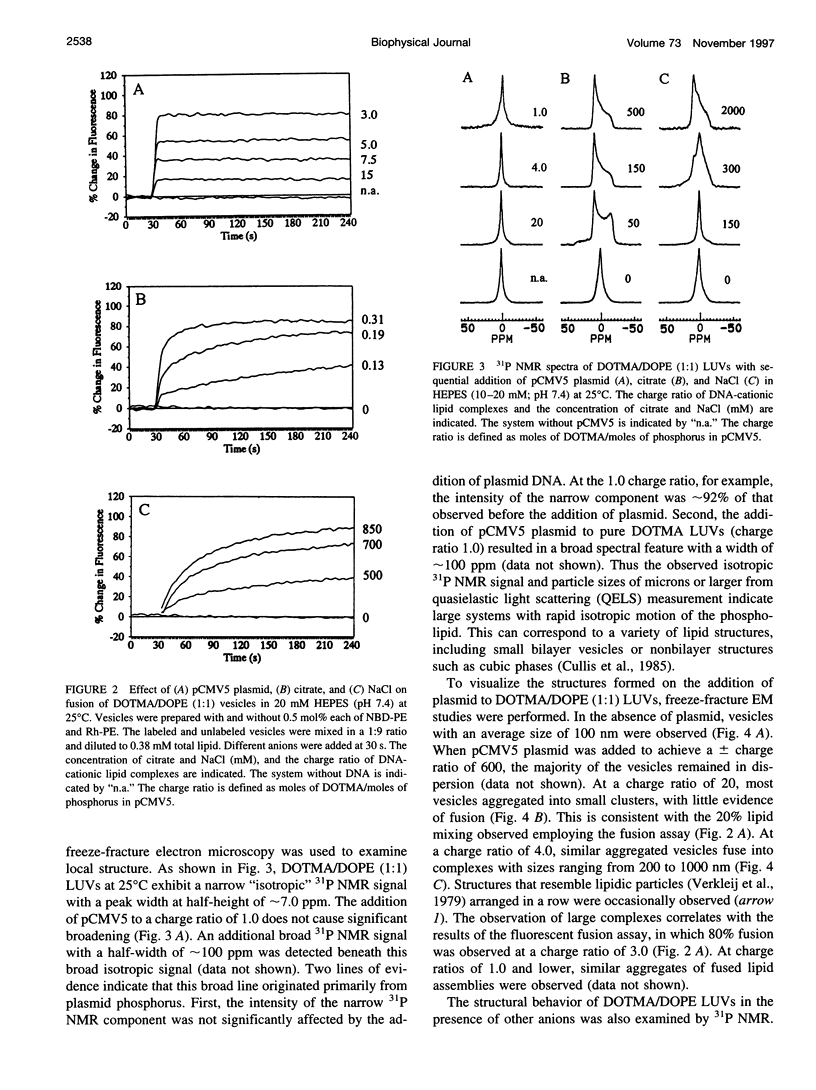
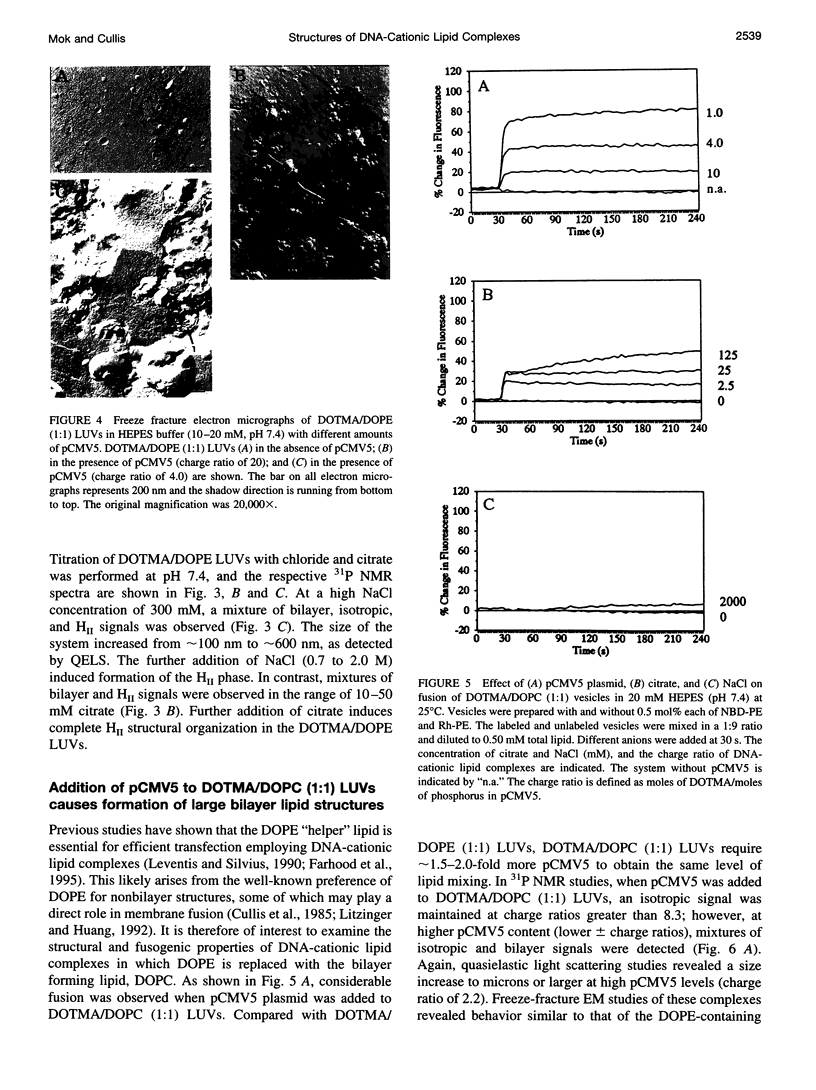
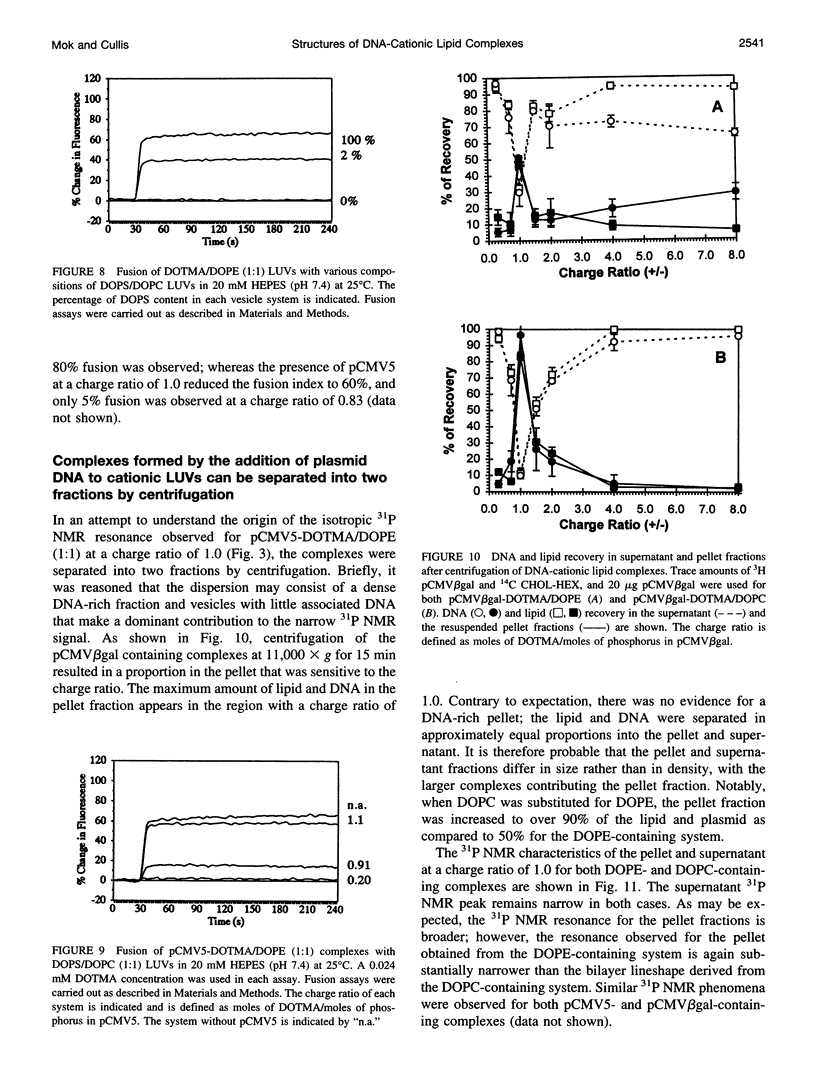
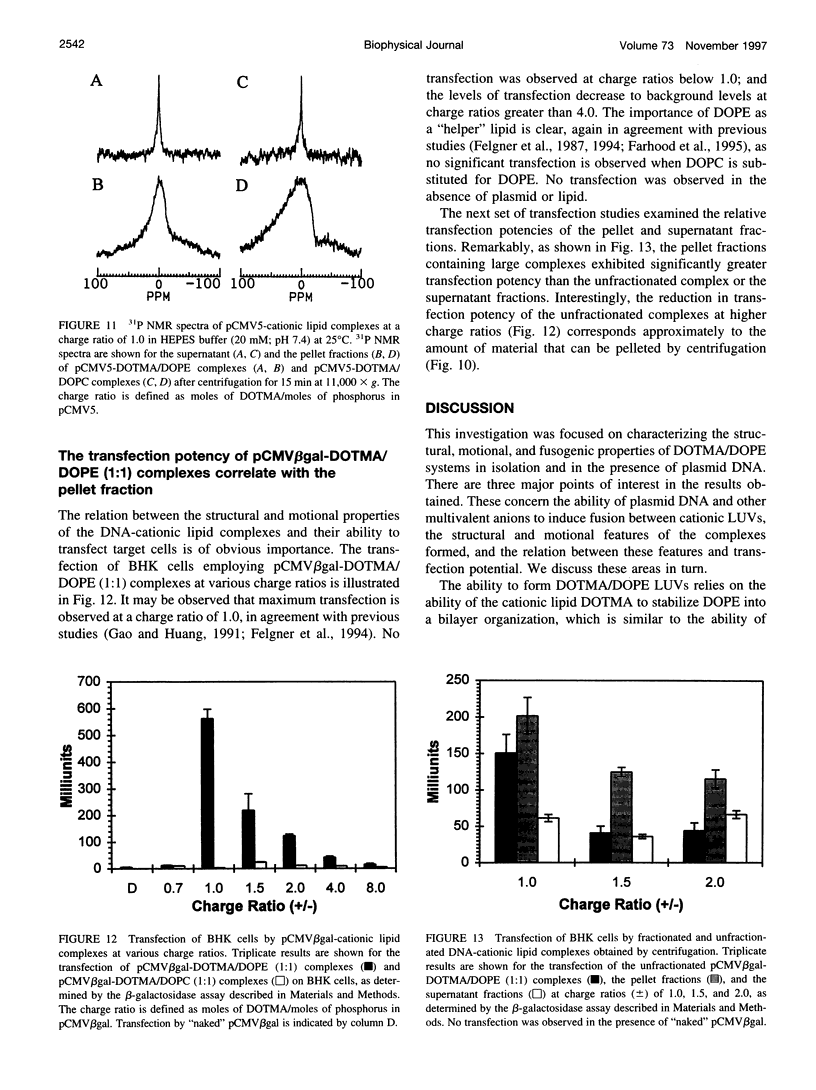
The structural and fusogenic properties of large unilamellar vesicles (LUVs) composed of the cationic lipid N-[2,3-(dioleyloxy)propyl]-N,N,N-trimethylammonium chloride (DOTMA) and 1,2-dioleoyl-3-phosphatidylethanotamine (DOPE) have been examined in the presence of pCMV5 plasmid and correlated with transfection potency. It is shown, employing lipid mixing fusion assays, that pCMV5 plasmid strongly promotes fusion between DOTMA/DOPE (1:1) LUVs and DOTMA/1,2-dioleoyl-3-phosphatidylcholine (DOTMA/DOPC) (1:1) LUVs such that at a cationic lipid-to-DNA charge ratio of 3.0, approximately 80% fusion is observed. The anions citrate and chloride can also trigger fusion, but at much higher concentrations. Freeze-fracture electron microscopy studies demonstrate the tendency of cationic vesicles to form clusters at low pCMV5 content, whereas macroscopic fused aggregates can be observed at higher plasmid levels. 31P NMR studies of the fused DNA-DOTMA/DOPE (1:1) complexes obtained at high plasmid levels (charge ratio 1.0) reveal narrow "isotropic" 31P NMR resonances, whereas the corresponding DOPC containing systems exhibit much broader "bilayer" 31P NMR spectra. In agreement with previous studies, the transfection potency of the DOPE-containing systems is dramatically higher than for the DOPC-containing complexes, indicating a correlation between transfection potential and the motional properties of endogenous lipids. Interestingly, it was found that the complexes could be separated by centrifugation into a pellet fraction, which exhibits superior transfection potencies, and a supernatant fraction. Again, the pellet fraction in the DOPE-containing system exhibits a significantly narrower 31P NMR resonance than the corresponding DOPC-containing system. It is suggested that the 31P NMR characteristics of complexes exhibiting higher transfection potencies are consistent with the presence of nonbilayer lipid structures, which may play a direct role in the fusion or membrane destabilization events vital to transfection.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson S., Davis D. L., Dahlbäck H., Jörnvall H., Russell D. W. Cloning, structure, and expression of the mitochondrial cytochrome P-450 sterol 26-hydroxylase, a bile acid biosynthetic enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8222–8229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey A. L., Cullis P. R. Membrane fusion with cationic liposomes: effects of target membrane lipid composition. Biochemistry. 1997 Feb 18;36(7):1628–1634. doi: 10.1021/bi961173x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bally M. B., Tilcock C. P., Hope M. J., Cullis P. R. Polymorphism of phosphatidylethanolamine-phosphatidylserine model systems: influence of cholesterol and Mg2+ on Ca2+-triggered bilayer to hexagonal (HII) transitions. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;61(6):346–352. doi: 10.1139/o83-048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullis P. R., de Kruijff B. Lipid polymorphism and the functional roles of lipids in biological membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 20;559(4):399–420. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(79)90012-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Düzgüneş N., Allen T. M., Fedor J., Papahadjopoulos D. Lipid mixing during membrane aggregation and fusion: why fusion assays disagree. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 15;26(25):8435–8442. doi: 10.1021/bi00399a061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Düzgüneş N., Goldstein J. A., Friend D. S., Felgner P. L. Fusion of liposomes containing a novel cationic lipid, N-[2,3-(dioleyloxy)propyl]-N,N,N-trimethylammonium: induction by multivalent anions and asymmetric fusion with acidic phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry. 1989 Nov 14;28(23):9179–9184. doi: 10.1021/bi00449a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egilmez N. K., Iwanuma Y., Bankert R. B. Evaluation and optimization of different cationic liposome formulations for in vivo gene transfer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996 Apr 5;221(1):169–173. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1996.0564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellens H., Siegel D. P., Alford D., Yeagle P. L., Boni L., Lis L. J., Quinn P. J., Bentz J. Membrane fusion and inverted phases. Biochemistry. 1989 May 2;28(9):3692–3703. doi: 10.1021/bi00435a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farhood H., Serbina N., Huang L. The role of dioleoyl phosphatidylethanolamine in cationic liposome mediated gene transfer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995 May 4;1235(2):289–295. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(95)80016-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner J. H., Kumar R., Sridhar C. N., Wheeler C. J., Tsai Y. J., Border R., Ramsey P., Martin M., Felgner P. L. Enhanced gene delivery and mechanism studies with a novel series of cationic lipid formulations. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 28;269(4):2550–2561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Gadek T. R., Holm M., Roman R., Chan H. W., Wenz M., Northrop J. P., Ringold G. M., Danielsen M. Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7413–7417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Holm M., Chan H. Cationic liposome mediated transfection. Proc West Pharmacol Soc. 1989;32:115–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend D. S., Papahadjopoulos D., Debs R. J. Endocytosis and intracellular processing accompanying transfection mediated by cationic liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1996 Jan 12;1278(1):41–50. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(95)00219-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao X., Huang L. A novel cationic liposome reagent for efficient transfection of mammalian cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 30;179(1):280–285. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91366-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon H., Ghirlando R., Guttman S. B., Minsky A. Mode of formation and structural features of DNA-cationic liposome complexes used for transfection. Biochemistry. 1993 Jul 20;32(28):7143–7151. doi: 10.1021/bi00079a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson J., Arvidson G., Karlsson G., Almgren M. Complexes between cationic liposomes and DNA visualized by cryo-TEM. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995 May 4;1235(2):305–312. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(95)80018-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra D. Role of lipid phase separations and membrane hydration in phospholipid vesicle fusion. Biochemistry. 1982 Jun 8;21(12):2833–2840. doi: 10.1021/bi00541a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope M. J., Walker D. C., Cullis P. R. Ca2+ and pH induced fusion of small unilamellar vesicles consisting of phosphatidylethanolamine and negatively charged phospholipids: a freeze fracture study. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jan 14;110(1):15–22. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91253-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarnagin W. R., Debs R. J., Wang S. S., Bissell D. M. Cationic lipid-mediated transfection of liver cells in primary culture. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 25;20(16):4205–4211. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.16.4205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jäskeläinen I., Mönkkönen J., Urtti A. Oligonucleotide-cationic liposome interactions. A physicochemical study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Oct 12;1195(1):115–123. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(94)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leventis R., Silvius J. R. Interactions of mammalian cells with lipid dispersions containing novel metabolizable cationic amphiphiles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Mar 30;1023(1):124–132. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90017-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litzinger D. C., Huang L. Phosphatidylethanolamine liposomes: drug delivery, gene transfer and immunodiagnostic applications. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Aug 14;1113(2):201–227. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(92)90039-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu L., Zeitlin P. L., Guggino W. B., Craig R. W. Gene transfer by lipofection in rabbit and human secretory epithelial cells. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Nov;415(2):198–203. doi: 10.1007/BF00370592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer L. D., Hope M. J., Cullis P. R. Vesicles of variable sizes produced by a rapid extrusion procedure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 13;858(1):161–168. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90302-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitrakos P., Macdonald P. M. DNA-induced lateral segregation of cationic amphiphiles in lipid bilayer membranes as detected via 2H NMR. Biochemistry. 1996 Dec 24;35(51):16714–16722. doi: 10.1021/bi961911h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel E. G., Gordon D., Yang Z. Y., Xu L., San H., Plautz G. E., Wu B. Y., Gao X., Huang L., Nabel G. J. Gene transfer in vivo with DNA-liposome complexes: lack of autoimmunity and gonadal localization. Hum Gene Ther. 1992 Dec;3(6):649–656. doi: 10.1089/hum.1992.3.6-649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinnaduwage P., Schmitt L., Huang L. Use of a quaternary ammonium detergent in liposome mediated DNA transfection of mouse L-cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Oct 2;985(1):33–37. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90099-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel D. P., Burns J. L., Chestnut M. H., Talmon Y. Intermediates in membrane fusion and bilayer/nonbilayer phase transitions imaged by time-resolved cryo-transmission electron microscopy. Biophys J. 1989 Jul;56(1):161–169. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82661-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamatatos L., Leventis R., Zuckermann M. J., Silvius J. R. Interactions of cationic lipid vesicles with negatively charged phospholipid vesicles and biological membranes. Biochemistry. 1988 May 31;27(11):3917–3925. doi: 10.1021/bi00411a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg B., Sorgi F. L., Huang L. New structures in complex formation between DNA and cationic liposomes visualized by freeze-fracture electron microscopy. FEBS Lett. 1994 Dec 19;356(2-3):361–366. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)01315-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struck D. K., Hoekstra D., Pagano R. E. Use of resonance energy transfer to monitor membrane fusion. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 7;20(14):4093–4099. doi: 10.1021/bi00517a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilcock C. P., Bally M. B., Farren S. B., Cullis P. R., Gruner S. M. Cation-dependent segregation phenomena and phase behavior in model membrane systems containing phosphatidylserine: influence of cholesterol and acyl chain composition. Biochemistry. 1984 Jun 5;23(12):2696–2703. doi: 10.1021/bi00307a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilcock C. P., Cullis P. R. The polymorphic phase behaviour of mixed phosphatidylserine-phosphatidylethanolamine model systems as detected by 31P-NMR. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 20;641(1):189–201. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90583-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkleij A. J., Mombers C., Gerritsen W. J., Leunissen-Bijvelt L., Cullis P. R. Fusion of phospholipid vesicles in association with the appearance of lipidic particles as visualized by freeze fracturing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 7;555(2):358–361. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90175-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler C. J., Sukhu L., Yang G., Tsai Y., Bustamente C., Felgner P., Norman J., Manthorpe M. Converting an alcohol to an amine in a cationic lipid dramatically alters the co-lipid requirement, cellular transfection activity and the ultrastructure of DNA-cytofectin complexes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1996 Apr 3;1280(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(95)00256-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrobel I., Collins D. Fusion of cationic liposomes with mammalian cells occurs after endocytosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995 May 4;1235(2):296–304. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(95)80017-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Y., Szoka F. C., Jr Mechanism of DNA release from cationic liposome/DNA complexes used in cell transfection. Biochemistry. 1996 May 7;35(18):5616–5623. doi: 10.1021/bi9602019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabner J., Fasbender A. J., Moninger T., Poellinger K. A., Welsh M. J. Cellular and molecular barriers to gene transfer by a cationic lipid. J Biol Chem. 1995 Aug 11;270(32):18997–19007. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.32.18997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu N., Liggitt D., Liu Y., Debs R. Systemic gene expression after intravenous DNA delivery into adult mice. Science. 1993 Jul 9;261(5118):209–211. doi: 10.1126/science.7687073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]