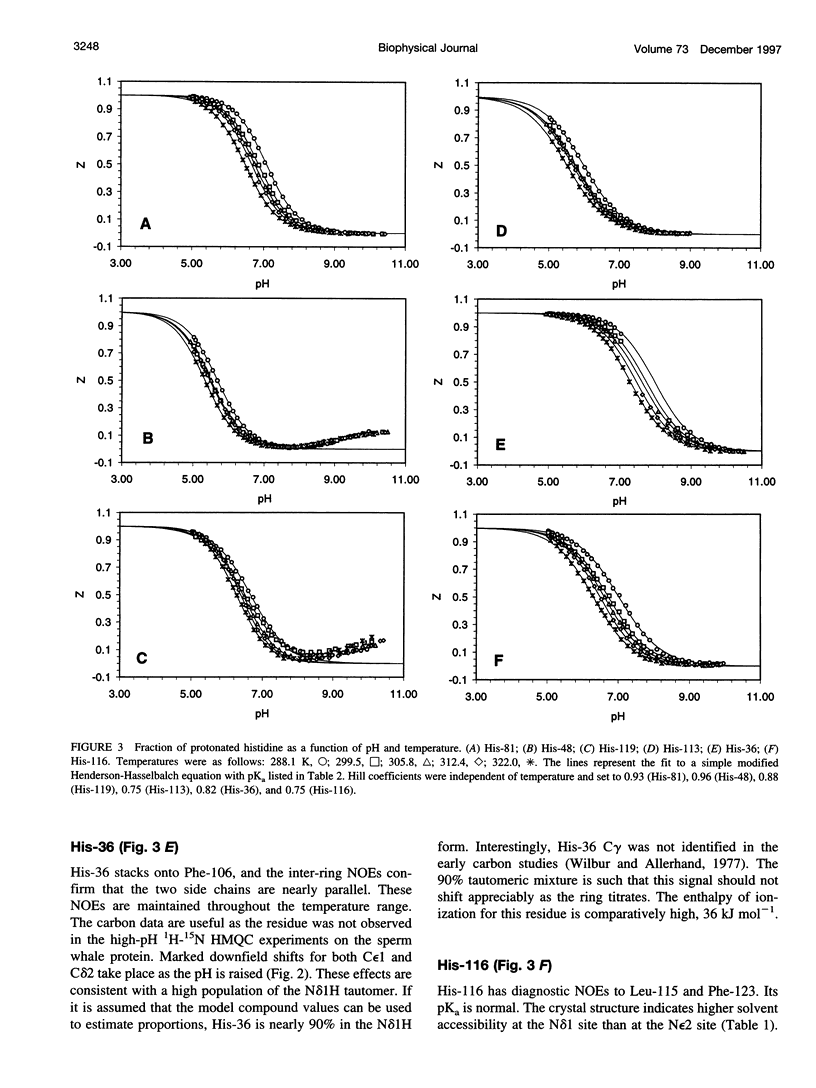
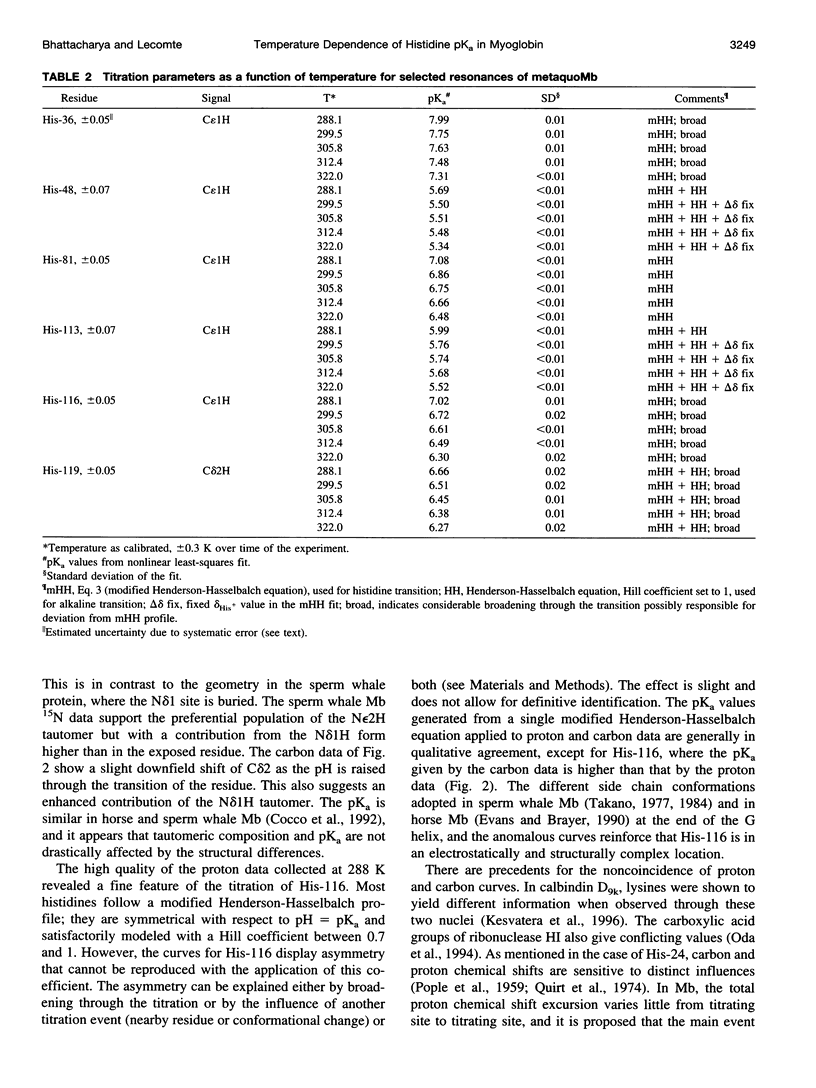
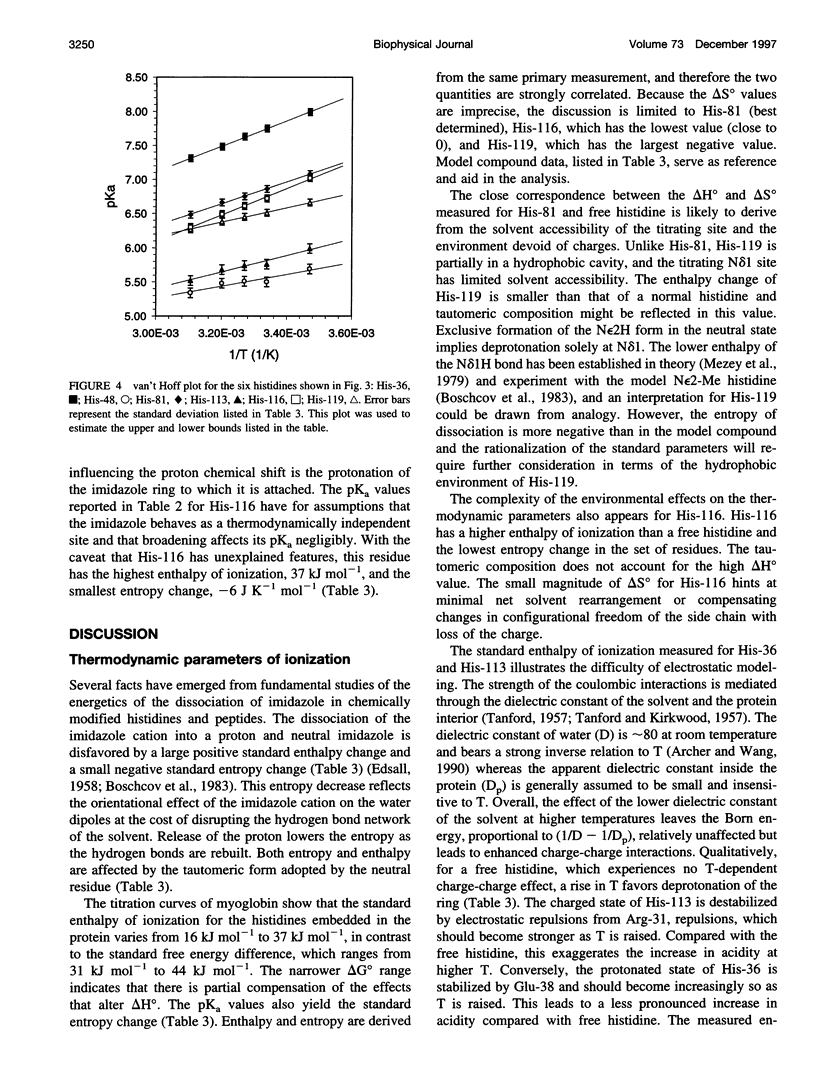
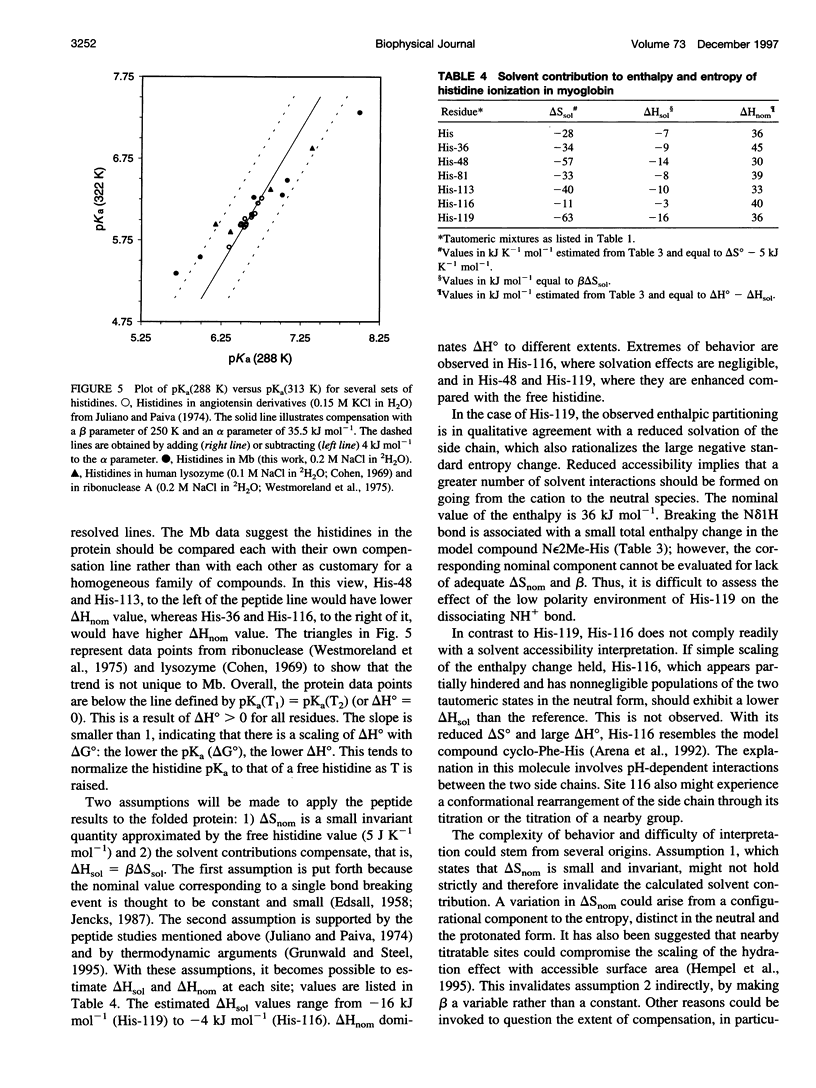
Abstract
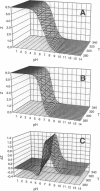
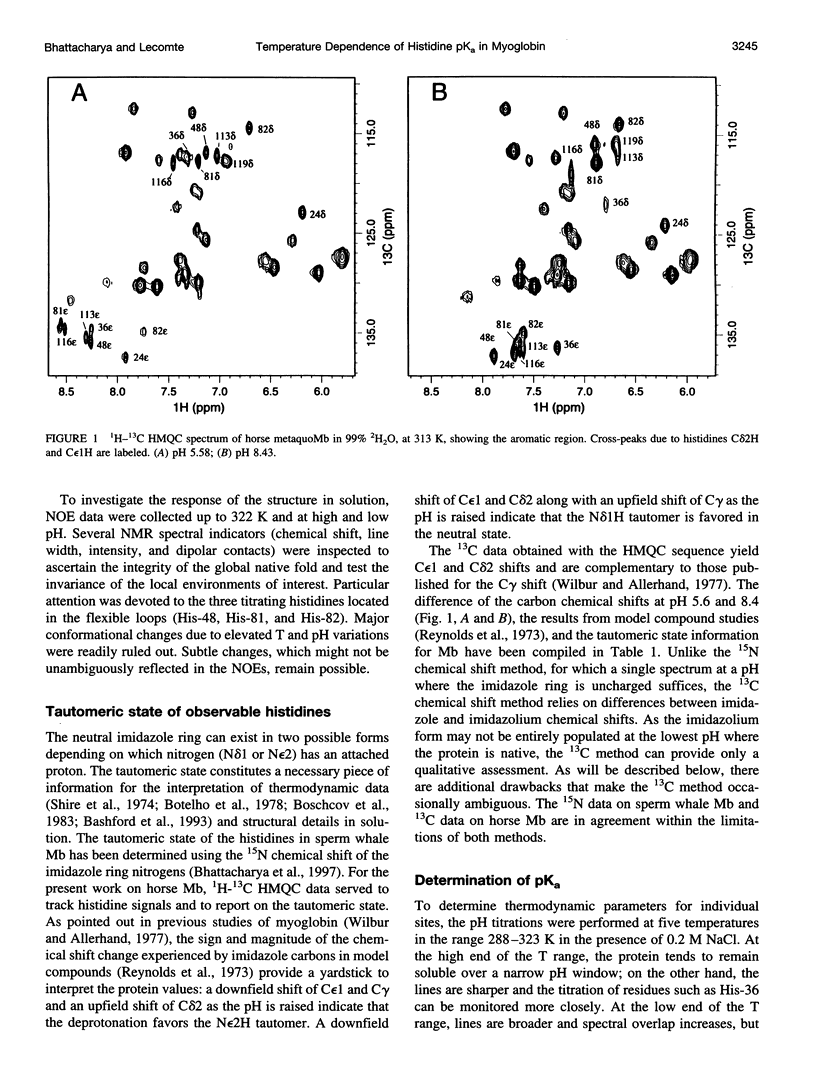
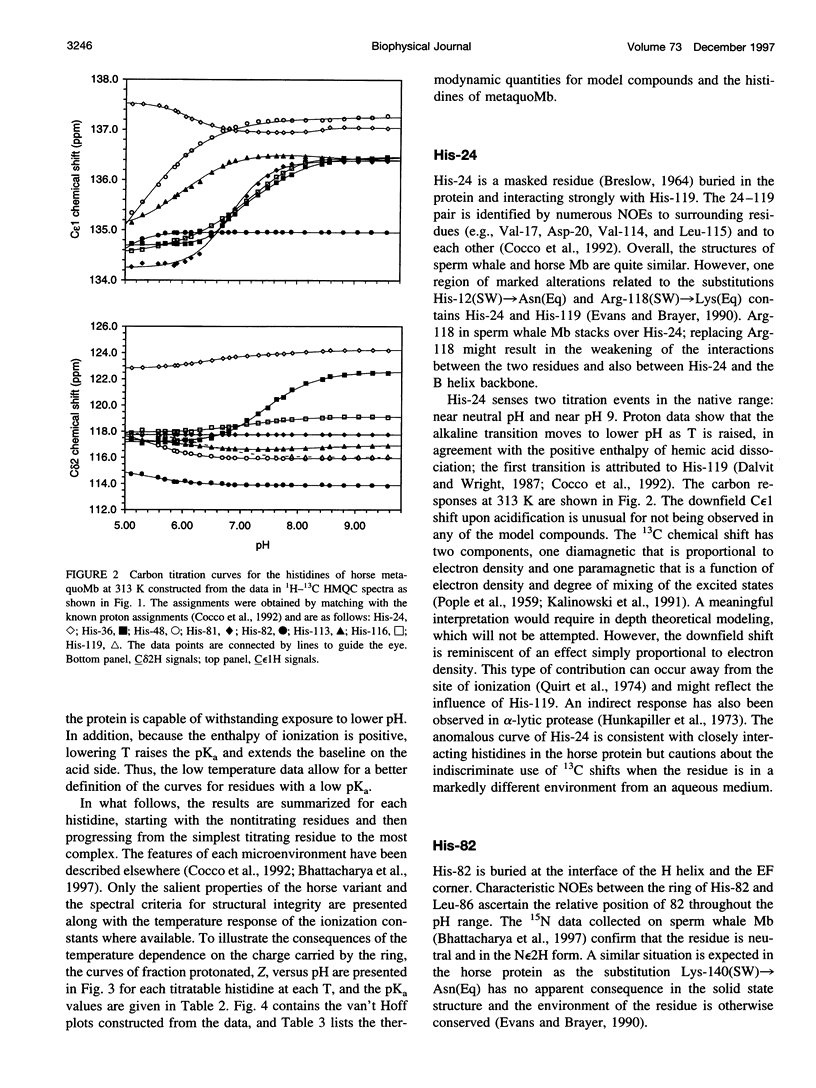
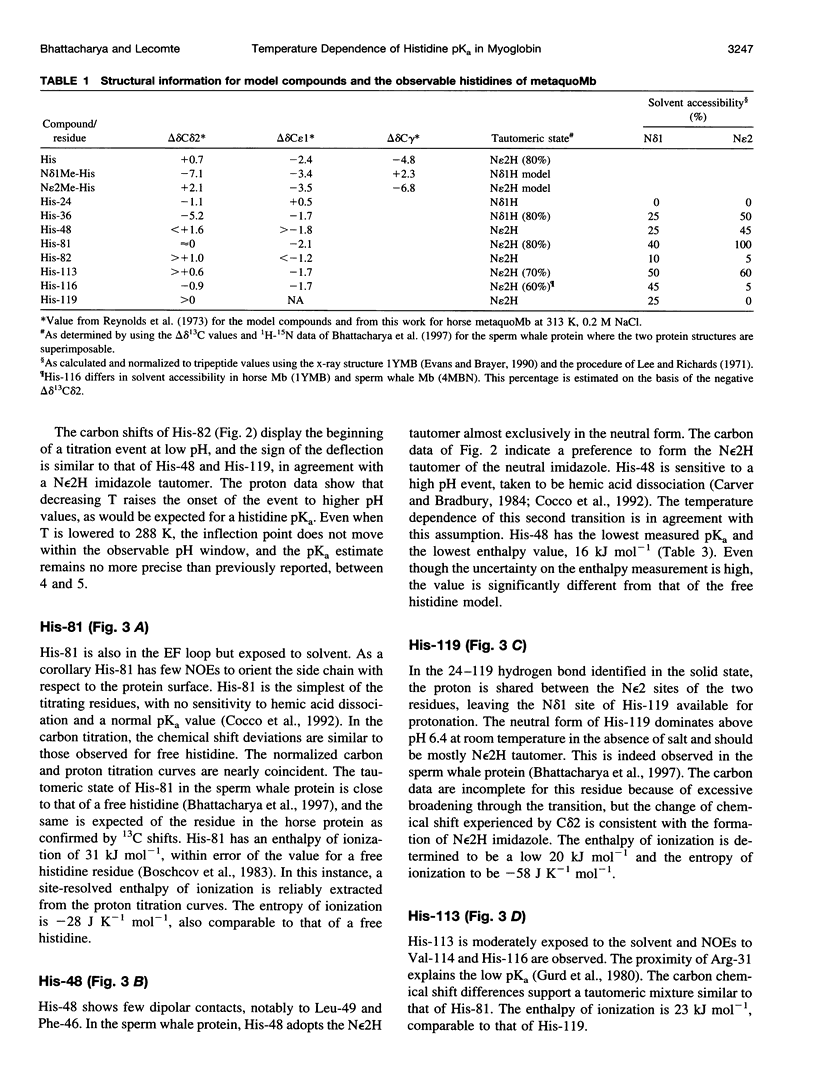
The standard enthalpy of ionization of six titratable histidines in horse metaquomyoglobin was determined by repeating proton NMR titrations as a function of temperature and using the van't Hoff relationship. It was found that deltaH degrees varies between 16 and 37 kJ mol(-1) in the protein, compared with a value of 29 kJ mol(-1) in free histidine. The standard entropy change was evaluated by combining the enthalpy and free energy changes derived from the pKa values. Although the entropy change could not be precisely and accurately obtained by this method, it could be established that it spans a wide range, from -60 to 0 J K(-1) mol(-1), about the value of -23 J K(-1) mol(-1) for the free histidine. The entropy change was used within the framework of enthalpy-entropy compensation to partition the solvation component from the standard thermodynamic quantities for each of the titrating residues. It was shown that the partitioning of the values in the protein is not readily understood in terms of solvent accessibility or electrostatic interactions. The contribution of solvation effects to the temperature response appeared to be significant only in the case of His-119 and His-48. The standard quantities were also used to explore the energetics of proton binding in the native state at temperatures below the onset of thermal denaturation.
Full text
PDF




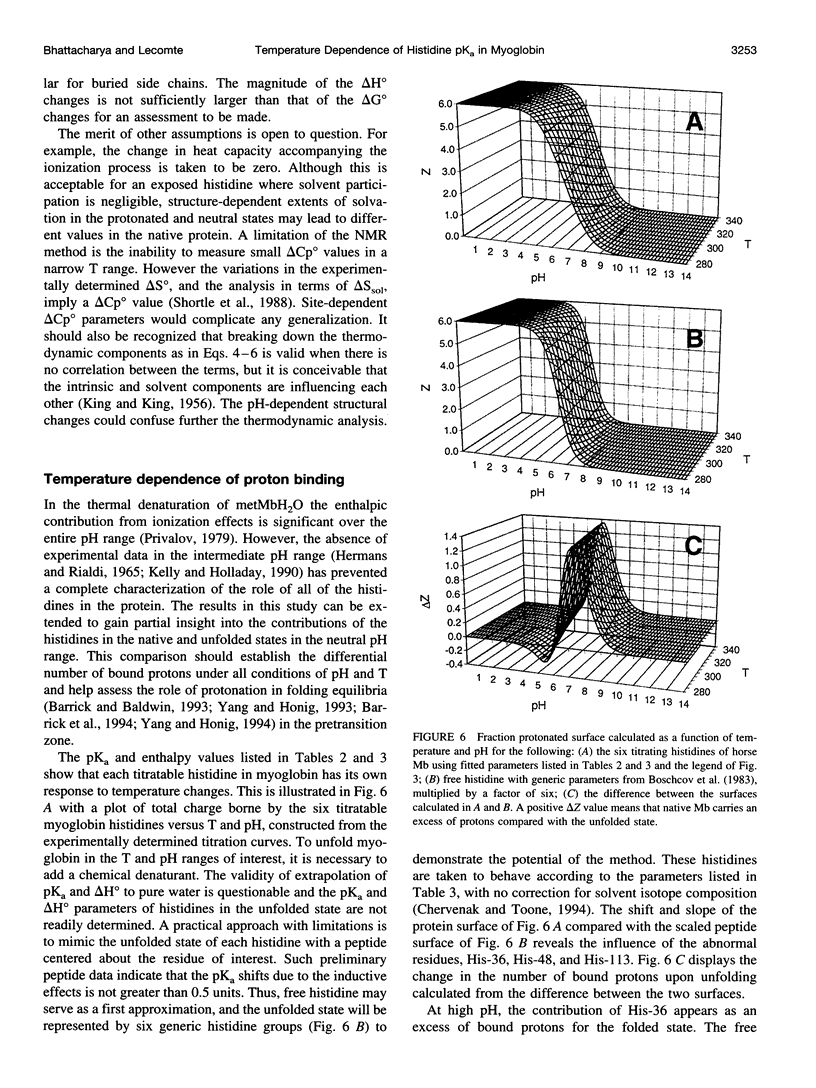
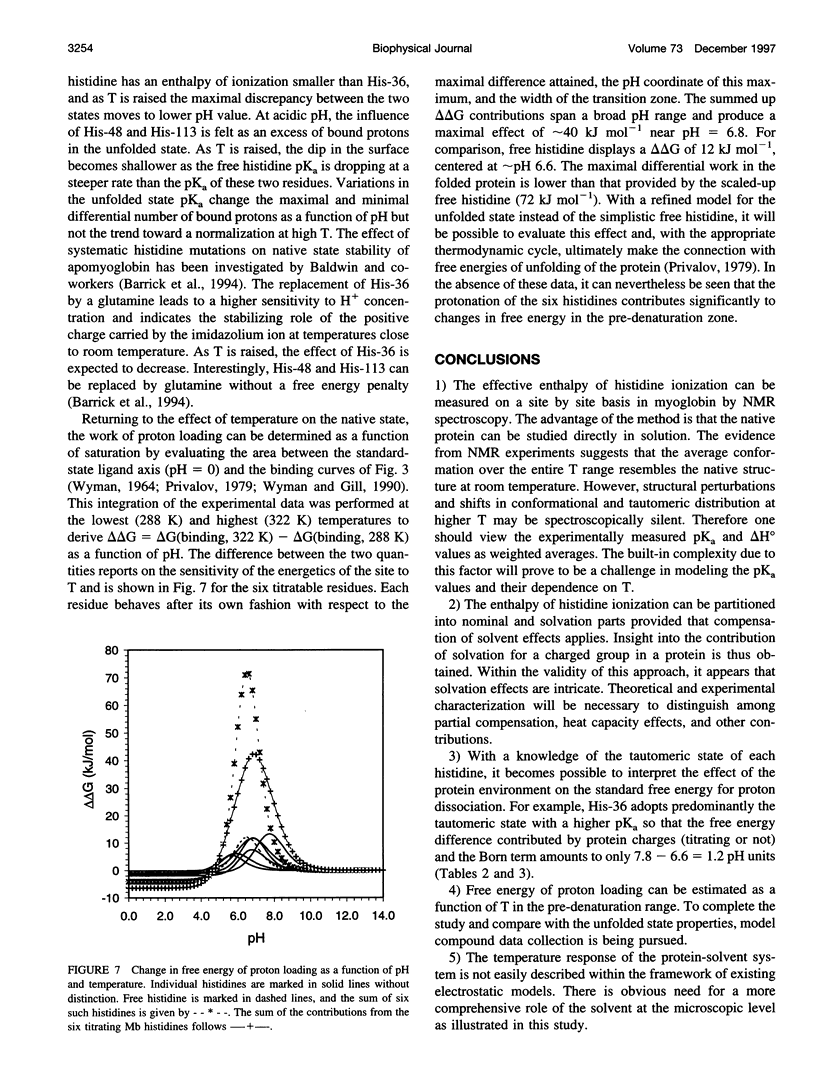


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acampora G., Hermans J., Jr Reversible denaturation of sperm whale myoglobin. I. Dependence on temperature, pH, and composition. J Am Chem Soc. 1967 Mar 29;89(7):1543–1547. doi: 10.1021/ja00983a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allewell N. M., Oberoi H. Electrostatic effects in protein folding, stability, and function. Methods Enzymol. 1991;202:3–19. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)02003-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRESLOW E. CHANGES IN SIDE CHAIN REACTIVITY ACCOMPANYING THE BINDING OF HEME TO SPERM WHALE APOMYOGLOBIN. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:486–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrick D., Baldwin R. L. Three-state analysis of sperm whale apomyoglobin folding. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 13;32(14):3790–3796. doi: 10.1021/bi00065a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrick D., Hughson F. M., Baldwin R. L. Molecular mechanisms of acid denaturation. The role of histidine residues in the partial unfolding of apomyoglobin. J Mol Biol. 1994 Apr 15;237(5):588–601. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bashford D., Case D. A., Dalvit C., Tennant L., Wright P. E. Electrostatic calculations of side-chain pK(a) values in myoglobin and comparison with NMR data for histidines. Biochemistry. 1993 Aug 10;32(31):8045–8056. doi: 10.1021/bi00082a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya S., Sukits S. F., MacLaughlin K. L., Lecomte J. T. The tautomeric state of histidines in myoglobin. Biophys J. 1997 Dec;73(6):3230–3240. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(97)78348-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botelho L. H., Friend S. H., Matthew J. B., Lehman L. D., Hanania G. I., Gurd F. R. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance study of histidine ionizations in myoglobins of various species. Comparison of observed and computed pK values. Biochemistry. 1978 Nov 28;17(24):5197–5205. doi: 10.1021/bi00617a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunori M., Amiconi G., Antonin E., Wyman J., Zito R., Fanelli A. R. The transition between 'acid' and 'alkaline' ferric heme proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Feb 19;154(2):315–322. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90045-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carver J. A., Bradbury J. H. Assignment of 1H NMR resonances of histidine and other aromatic residues in met-, cyano-, oxy-, and (carbon monoxy)myoglobins. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):4890–4905. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho K. C., Poon H. T., Choy C. L. The thermodynamics of myoglobin stability. Effects of axial ligand. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Feb 18;701(2):206–215. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90115-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocco M. J., Kao Y. H., Phillips A. T., Lecomte J. T. Structural comparison of apomyoglobin and metaquomyoglobin: pH titration of histidines by NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1992 Jul 21;31(28):6481–6491. doi: 10.1021/bi00143a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. S. Proton magnetic resonance studies of human lysozyme. Nature. 1969 Jul 5;223(5201):43–46. doi: 10.1038/223043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalvit C., Wright P. E. Assignment of resonances in the 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum of the carbon monoxide complex of sperm whale myoglobin by phase-sensitive two-dimensional techniques. J Mol Biol. 1987 Mar 20;194(2):313–327. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90378-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dill K. A. Dominant forces in protein folding. Biochemistry. 1990 Aug 7;29(31):7133–7155. doi: 10.1021/bi00483a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans S. V., Brayer G. D. High-resolution study of the three-dimensional structure of horse heart metmyoglobin. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):885–897. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80270-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEORGE P., HANANIA G. The ionization of acidic metmyoglobin. Biochem J. 1952 Nov;52(3):517–523. doi: 10.1042/bj0520517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurd F. R., Friend S. H., Rothgeb T. M., Gurd R. S., Scouloudi H. Electrostatic stabilization in sperm whale and harbor seal myoglobins. Identification of groups primarily responsible for changes in anchoring of the A helix. Biophys J. 1980 Oct;32(1):65–75. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)84916-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann H., Parak F., Steigemann W., Petsko G. A., Ponzi D. R., Frauenfelder H. Conformational substates in a protein: structure and dynamics of metmyoglobin at 80 K. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4967–4971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempel J. C., Fine R. M., Hassan M., Ghoul W., Guaragna A., Koerber S. C., Li Z., Hagler A. T. Conformational analysis of endothelin-1: effects of solvation free energy. Biopolymers. 1995 Sep;36(3):283–301. doi: 10.1002/bip.360360304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermans J., Jr, Rialdi G. Heat of ionization and denaturation of sperm-whale myoglobin determined with a microcalorimeter. Biochemistry. 1965 Jul;4(7):1277–1281. doi: 10.1021/bi00883a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Smallcombe S. H., Whitaker D. R., Richards J. H. Carbon nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the histidine residue in alpha-lytic protease. Implications for the catalytic mechanism of serine proteases. Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 6;12(23):4732–4743. doi: 10.1021/bi00747a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juliano L., Paiva A. C. Conformation of angiotensin II in aqueous solution. Titration of several peptide analogs and homologs. Biochemistry. 1974 May 21;13(11):2445–2450. doi: 10.1021/bi00708a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly L., Holladay L. A. A comparative study of the unfolding thermodynamics of vertebrate metmyoglobins. Biochemistry. 1990 May 29;29(21):5062–5069. doi: 10.1021/bi00473a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kesvatera T., Jönsson B., Thulin E., Linse S. Measurement and modelling of sequence-specific pKa values of lysine residues in calbindin D9k. J Mol Biol. 1996 Jun 21;259(4):828–839. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khare D., Alexander P., Antosiewicz J., Bryan P., Gilson M., Orban J. pKa measurements from nuclear magnetic resonance for the B1 and B2 immunoglobulin G-binding domains of protein G: comparison with calculated values for nuclear magnetic resonance and X-ray structures. Biochemistry. 1997 Mar 25;36(12):3580–3589. doi: 10.1021/bi9630927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuriyan J., Wilz S., Karplus M., Petsko G. A. X-ray structure and refinement of carbon-monoxy (Fe II)-myoglobin at 1.5 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1986 Nov 5;192(1):133–154. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90470-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecomte J. T., Kao Y. H., Cocco M. J. The native state of apomyoglobin described by proton NMR spectroscopy: the A-B-G-H interface of wild-type sperm whale apomyoglobin. Proteins. 1996 Jul;25(3):267–285. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0134(199607)25:3<267::AID-PROT1>3.0.CO;2-D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B., Richards F. M. The interpretation of protein structures: estimation of static accessibility. J Mol Biol. 1971 Feb 14;55(3):379–400. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90324-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumry R., Rajender S. Enthalpy-entropy compensation phenomena in water solutions of proteins and small molecules: a ubiquitous property of water. Biopolymers. 1970;9(10):1125–1227. doi: 10.1002/bip.1970.360091002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makhatadze G. I., Privalov P. L. Contribution of hydration to protein folding thermodynamics. I. The enthalpy of hydration. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jul 20;232(2):639–659. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makhatadze G. I., Privalov P. L. Hydration effects in protein unfolding. Biophys Chem. 1994 Aug;51(2-3):291–309. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(94)00050-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meeker A. K., Garcia-Moreno B., Shortle D. Contributions of the ionizable amino acids to the stability of staphylococcal nuclease. Biochemistry. 1996 May 21;35(20):6443–6449. doi: 10.1021/bi960171+. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda Y., Yamazaki T., Nagayama K., Kanaya S., Kuroda Y., Nakamura H. Individual ionization constants of all the carboxyl groups in ribonuclease HI from Escherichia coli determined by NMR. Biochemistry. 1994 May 3;33(17):5275–5284. doi: 10.1021/bi00183a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piotto M., Saudek V., Sklenár V. Gradient-tailored excitation for single-quantum NMR spectroscopy of aqueous solutions. J Biomol NMR. 1992 Nov;2(6):661–665. doi: 10.1007/BF02192855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privalov P. L., Griko YuV, Venyaminov SYu, Kutyshenko V. P. Cold denaturation of myoglobin. J Mol Biol. 1986 Aug 5;190(3):487–498. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90017-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privalov P. L., Makhatadze G. I. Contribution of hydration to protein folding thermodynamics. II. The entropy and Gibbs energy of hydration. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jul 20;232(2):660–679. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privalov P. L. Stability of proteins: small globular proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1979;33:167–241. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60460-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quirt A. R., Lyerla J. R., Jr, Peat I. R., Cohen J. S., Reynolds W. F., Freedman M. H. Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance titration shifts in amino acids. J Am Chem Soc. 1974 Jan 23;96(2):570–574. doi: 10.1021/ja00809a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds W. F., Peat I. R., Freedman M. H., Lyerla J. R., Jr Determination of the tautomeric form of the imidazole ring of L-histidine in basic solution by carbon-13 magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc. 1973 Jan 24;95(2):328–331. doi: 10.1021/ja00783a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. C., Meadows D. H., Jardetzky O. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the sx.ucture and binding sites of enzymes. VII. Solvent and temperature effects on the ionization of histidine residues of ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1969 May;8(5):2053–2056. doi: 10.1021/bi00833a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller W., Robertson A. D. pH, ionic strength, and temperature dependences of ionization equilibria for the carboxyl groups in turkey ovomucoid third domain. Biochemistry. 1995 Apr 11;34(14):4714–4723. doi: 10.1021/bi00014a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shire S. J., Hanania G. I., Gurd F. R. Electrostatic effects in myoglobin. Hydrogen ion equilibria in sperm whale ferrimyoglobin. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 2;13(14):2967–2974. doi: 10.1021/bi00711a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortle D., Meeker A. K., Freire E. Stability mutants of staphylococcal nuclease: large compensating enthalpy-entropy changes for the reversible denaturation reaction. Biochemistry. 1988 Jun 28;27(13):4761–4768. doi: 10.1021/bi00413a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrager R. I., Cohen J. S., Heller S. R., Sachs D. H., Schechter A. N. Mathematical models for interacting groups in nuclear magnetic resonance titration curves. Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 15;11(4):541–547. doi: 10.1021/bi00754a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stigter D., Dill K. A. Charge effects on folded and unfolded proteins. Biochemistry. 1990 Feb 6;29(5):1262–1271. doi: 10.1021/bi00457a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano T. Structure of myoglobin refined at 2-0 A resolution. I. Crystallographic refinement of metmyoglobin from sperm whale. J Mol Biol. 1977 Mar 5;110(3):537–568. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80111-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WYMAN J., Jr LINKED FUNCTIONS AND RECIPROCAL EFFECTS IN HEMOGLOBIN: A SECOND LOOK. Adv Protein Chem. 1964;19:223–286. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westmoreland D. G., Matthews C. R., Hayes M. B., Cohen J. S. Nuclear magnetic resonance titration curves of histidine ring protons. The effect of temperature on ribonuclease A. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 25;250(18):7456–7460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilbur D. J., Allerhand A. Titration behavior and tautomeric states of individual histidine residues of myoglobins. Application of natural abundance carbon 13 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4968–4975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wishart D. S., Bigam C. G., Yao J., Abildgaard F., Dyson H. J., Oldfield E., Markley J. L., Sykes B. D. 1H, 13C and 15N chemical shift referencing in biomolecular NMR. J Biomol NMR. 1995 Sep;6(2):135–140. doi: 10.1007/BF00211777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang A. S., Honig B. On the pH dependence of protein stability. J Mol Biol. 1993 May 20;231(2):459–474. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang A. S., Honig B. Structural origins of pH and ionic strength effects on protein stability. Acid denaturation of sperm whale apomyoglobin. J Mol Biol. 1994 Apr 15;237(5):602–614. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang F., Phillips G. N., Jr Crystal structures of CO-, deoxy- and met-myoglobins at various pH values. J Mol Biol. 1996 Mar 8;256(4):762–774. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]