Abstract
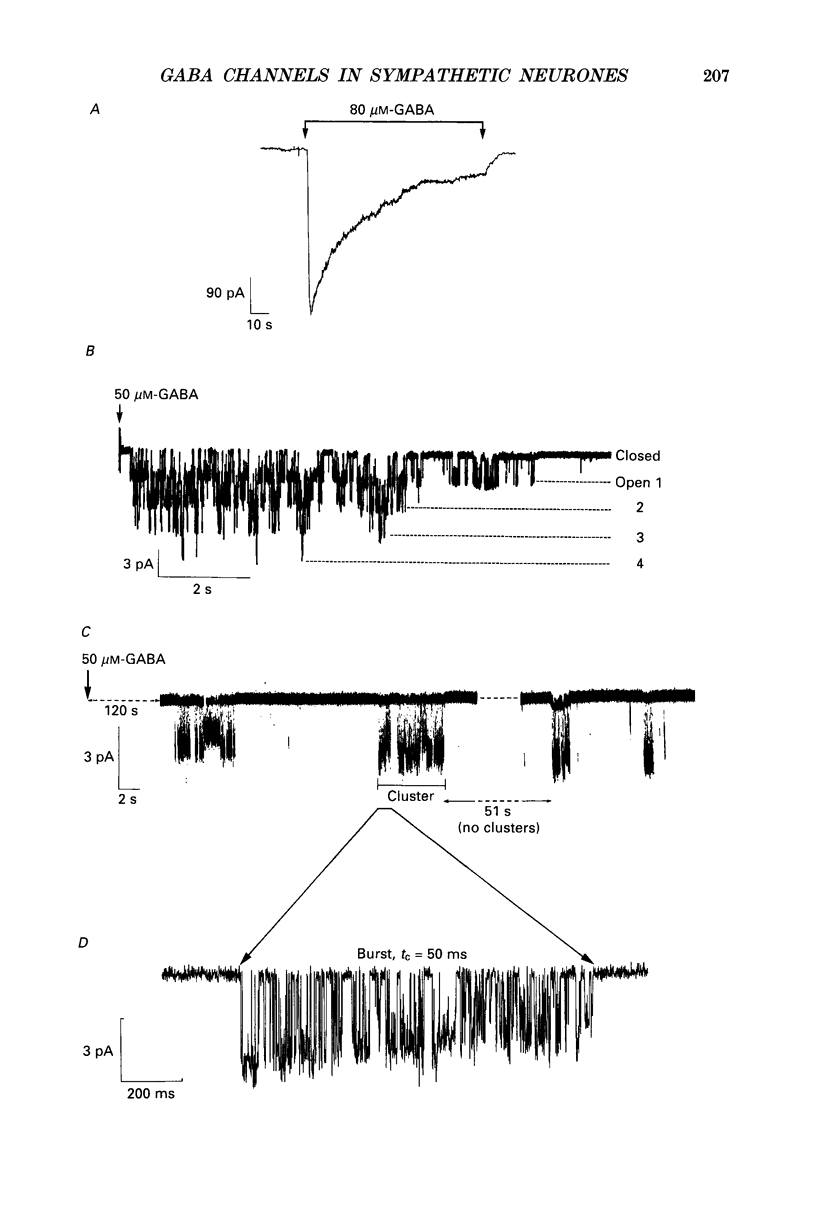
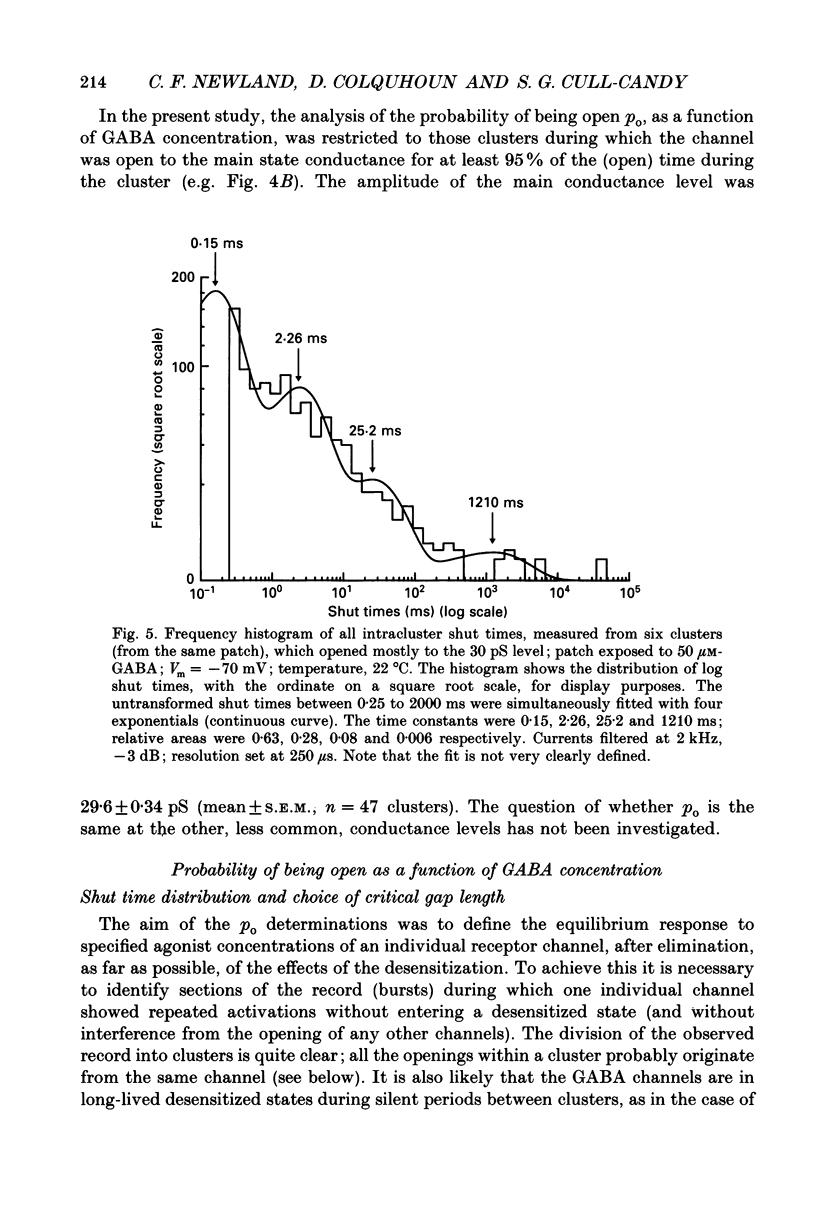
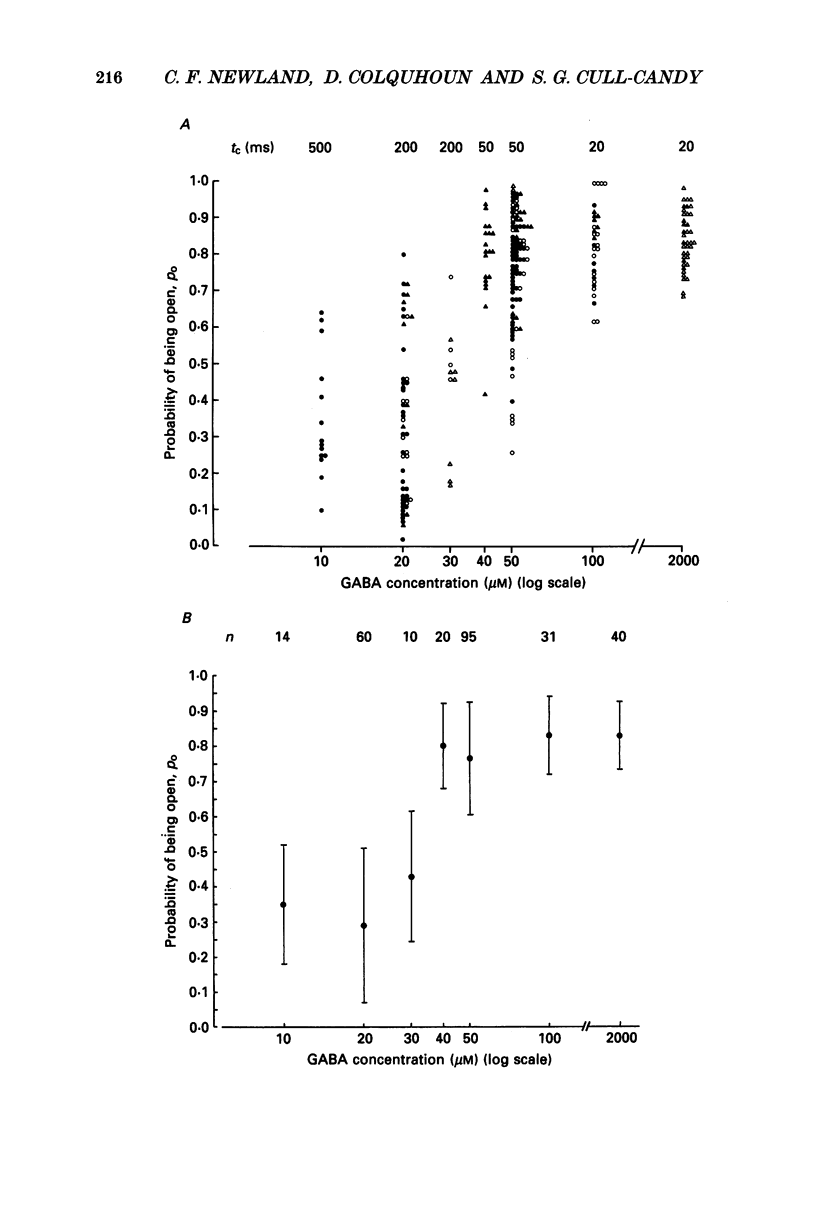
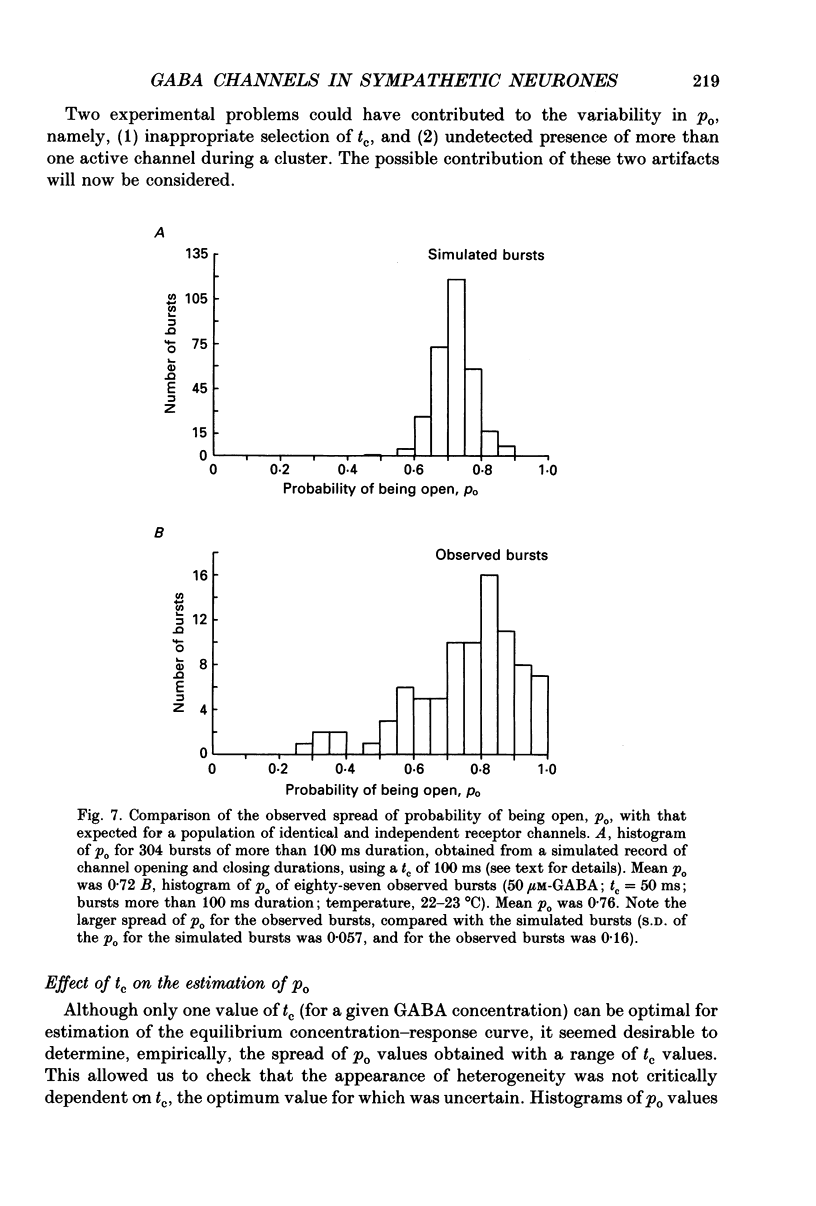
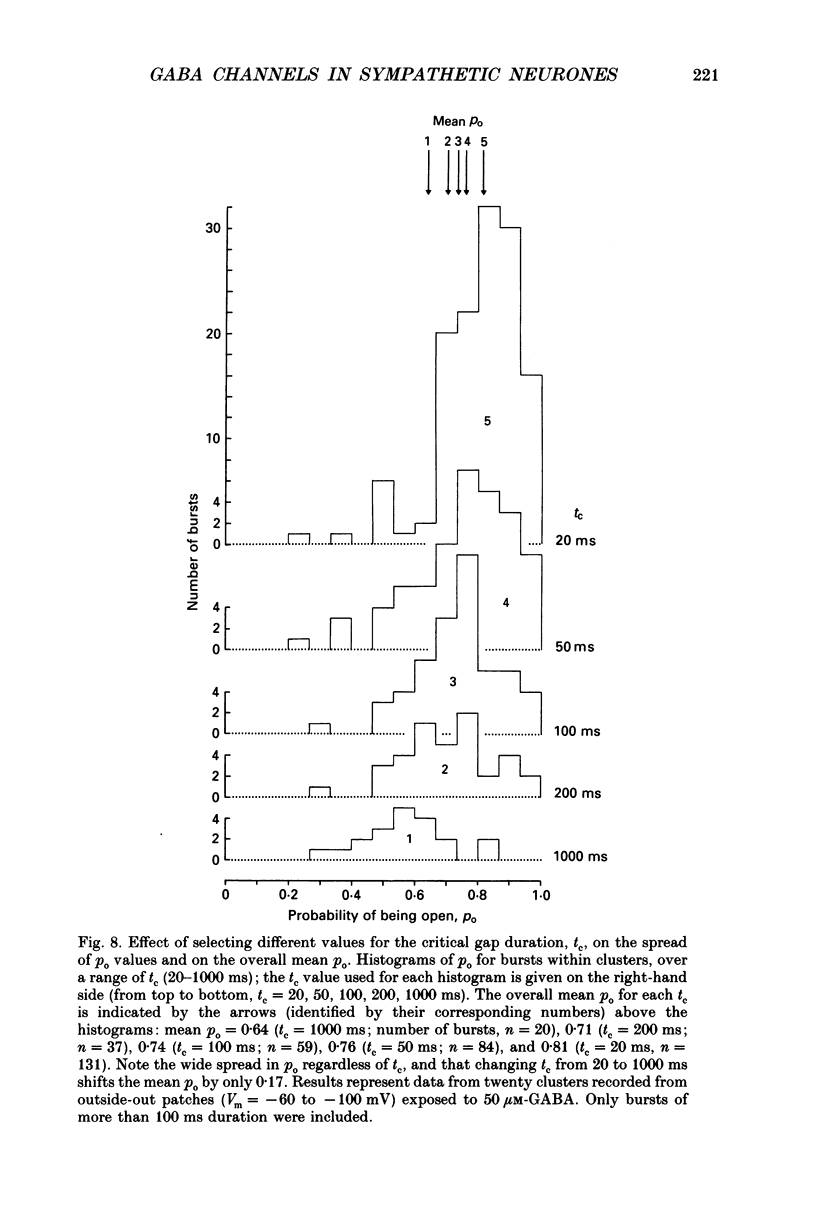
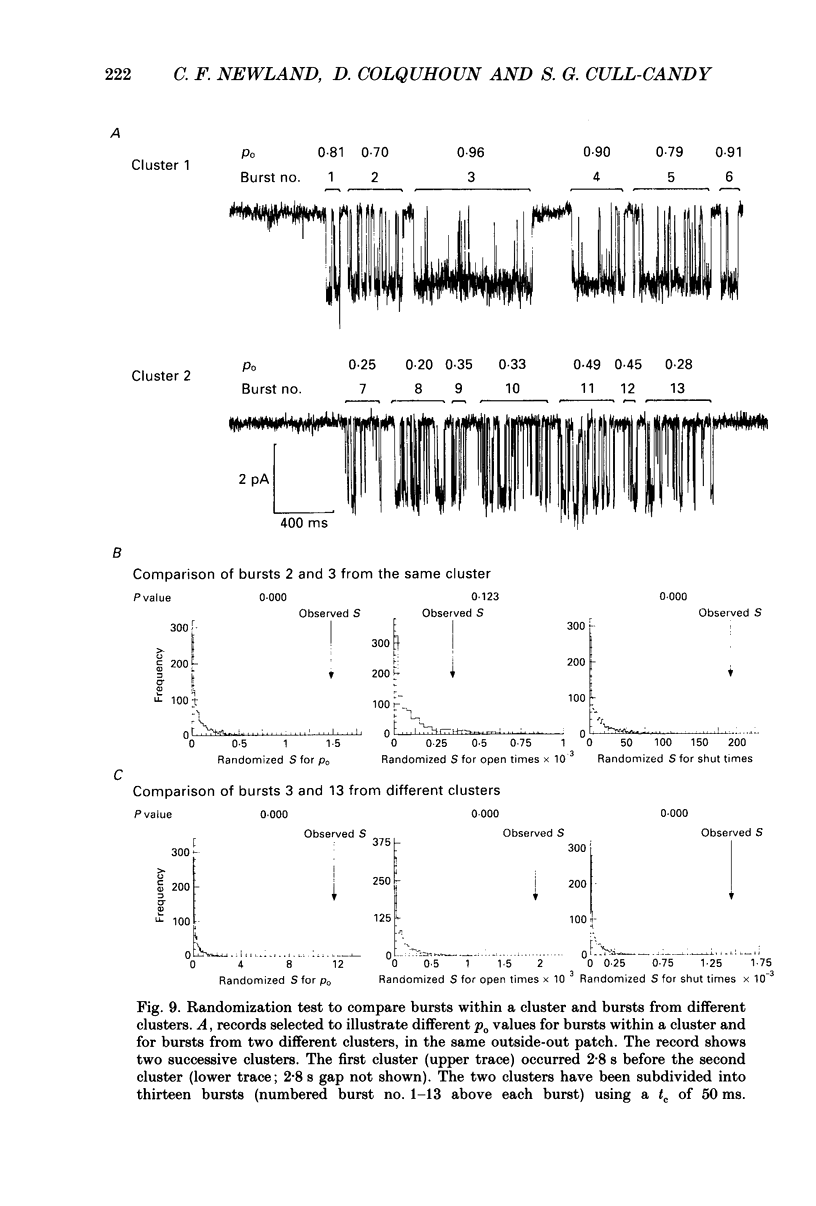
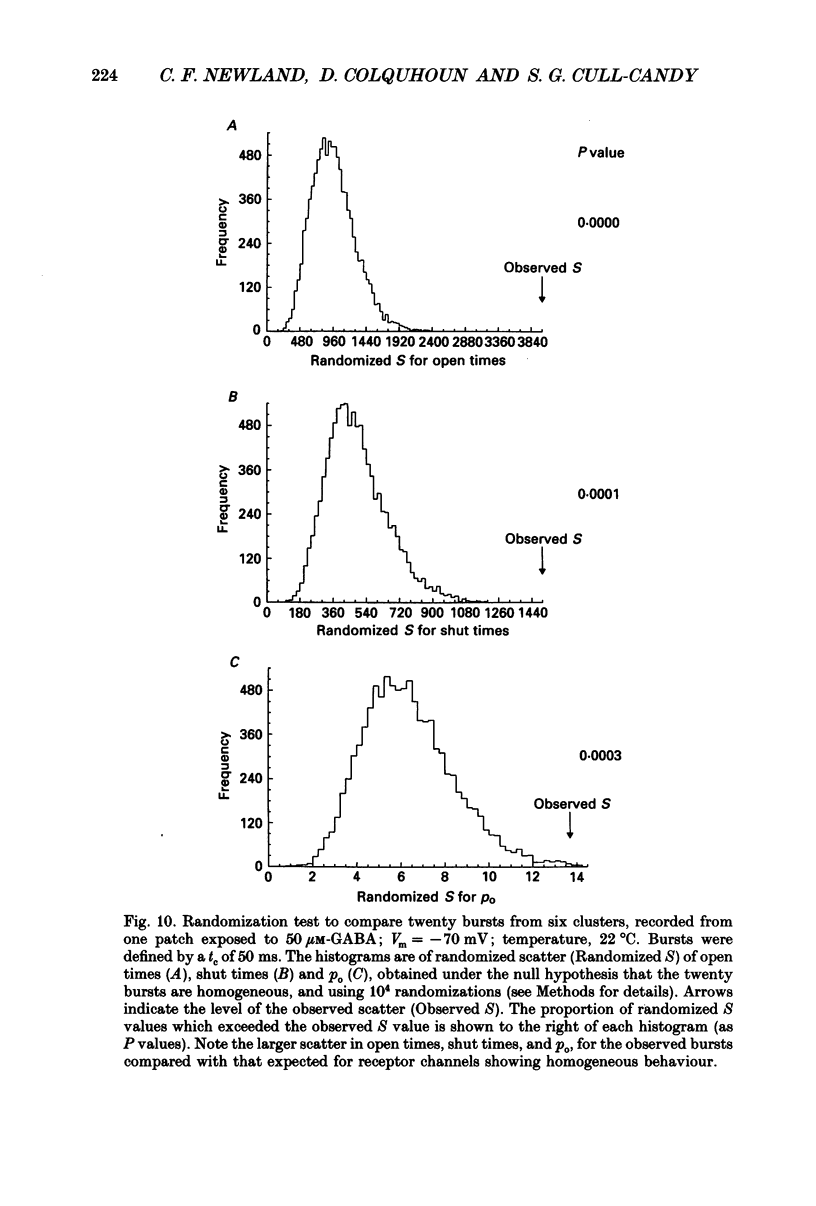
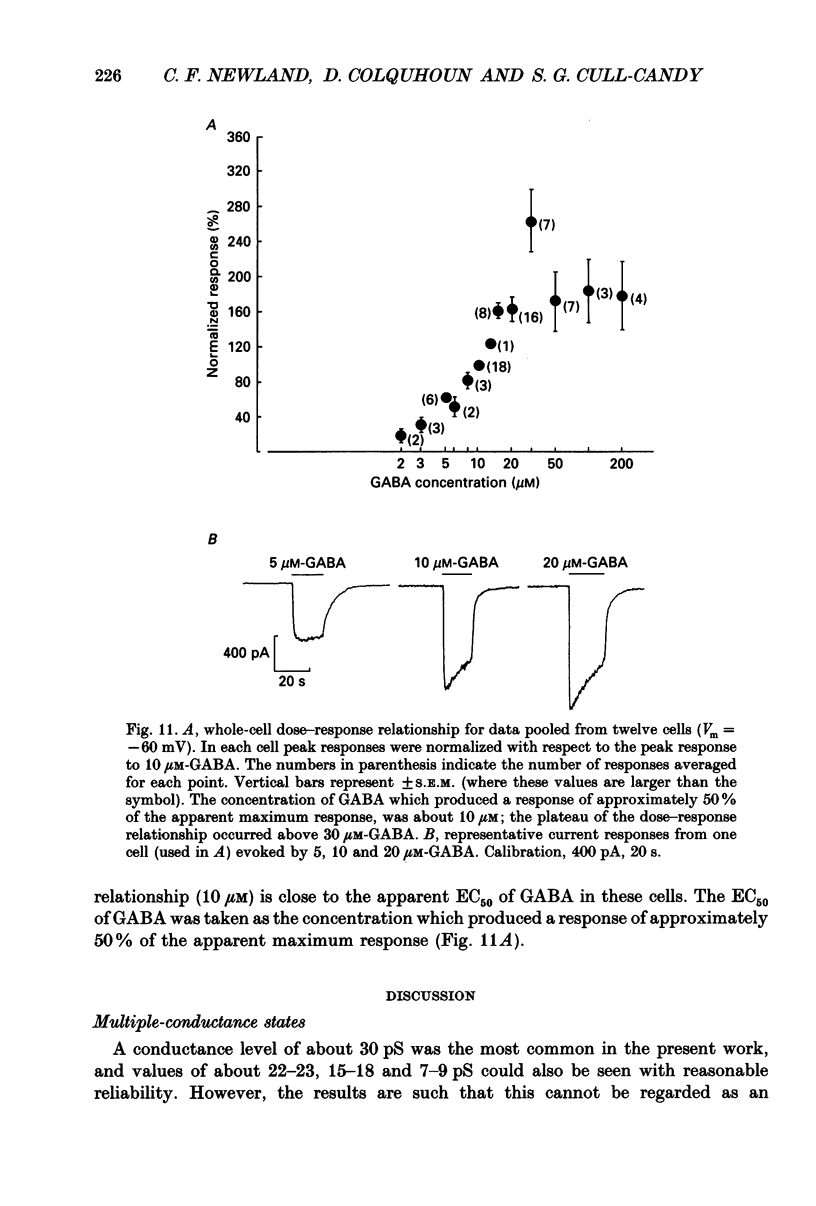
1. Single-channel currents evoked by high concentrations of GABA (10-2000 microM) have been analysed to investigate the characteristics of GABAA receptor channels in outside-out patches from rat sympathetic neurones. When high concentrations of GABA were applied to a patch, channel openings occurred in prolonged clusters (3.8 +/- 3.7 s (mean +/- S.D.) at 50 microM-GABA) consisting, on average, of 350 apparent openings per cluster. Individual clusters were separated by long silent intervals. 2. Channel openings were to many (often ill-defined) conductance states (range 7-36 pS), but the most frequently observed conductance level was approximately 30 pS, (29.6 +/- 0.34 pS). Only these clusters during which the channel was open to this main state conductance for at least 95% of the cluster open time were used in the analysis of probability of being open. Other less frequently observed conductance levels were 15-18 and 22-23 pS, while levels of 33-36 and 7-9 pS were occasionally, but reliably, observed. 3. Bursts within clusters were defined as a series of openings separated by closed intervals shorter than some critical value, tc. At 50 microM-GABA the mean burst length was 439 +/- 434 ms (+/- S.D., tc = 50 ms). 4. The probability of being open, po, during bursts within clusters has been analysed as a function of GABA concentration. As expected, increasing the concentration of GABA resulted in an overall increase in po. However, for a given agonist concentration there was a wide spread in po, far greater than that predicted for a population of identical and independent receptor channels (demonstrated by comparison with stimulated channel activity). 5. The wide range of po values at a particular concentration of GABA was not due to inappropriate selection of tc. At 50 microM-GABA the range of po values was similar for tc of 20-1000 ms, although the overall mean po became lower (0.64 rather than 0.81). 6. On the basis of simulated channel activity, it appears that most clusters which do not contain multiple openings, arise from the activity of one individual channel. Furthermore, there was no detectable tendency for gaps between bursts to be shorter in the middle of a cluster than at its ends. Therefore it is unlikely that variability in po arose from overlapping activity of two or more channels. 7. The values for po, mean open time, and mean shut time for bursts within the same cluster, and between different clusters, were compared by a randomization test.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
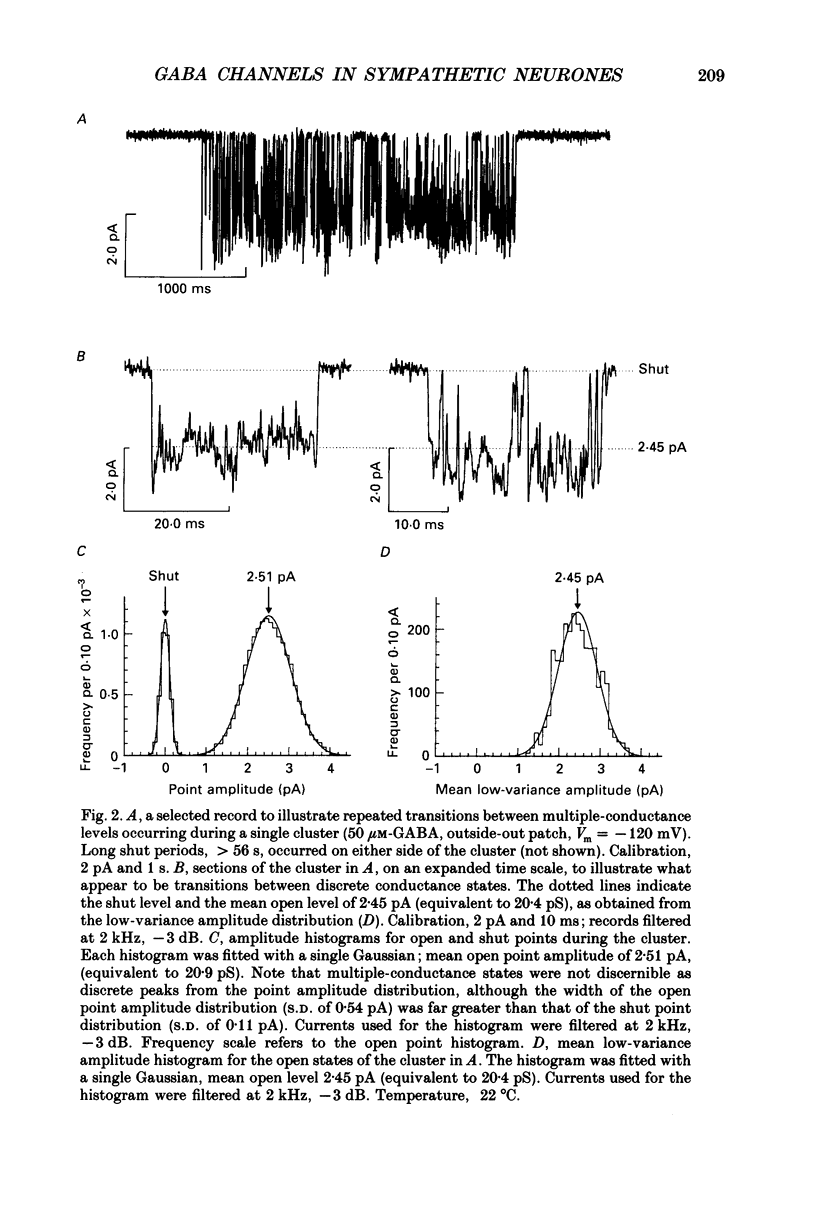
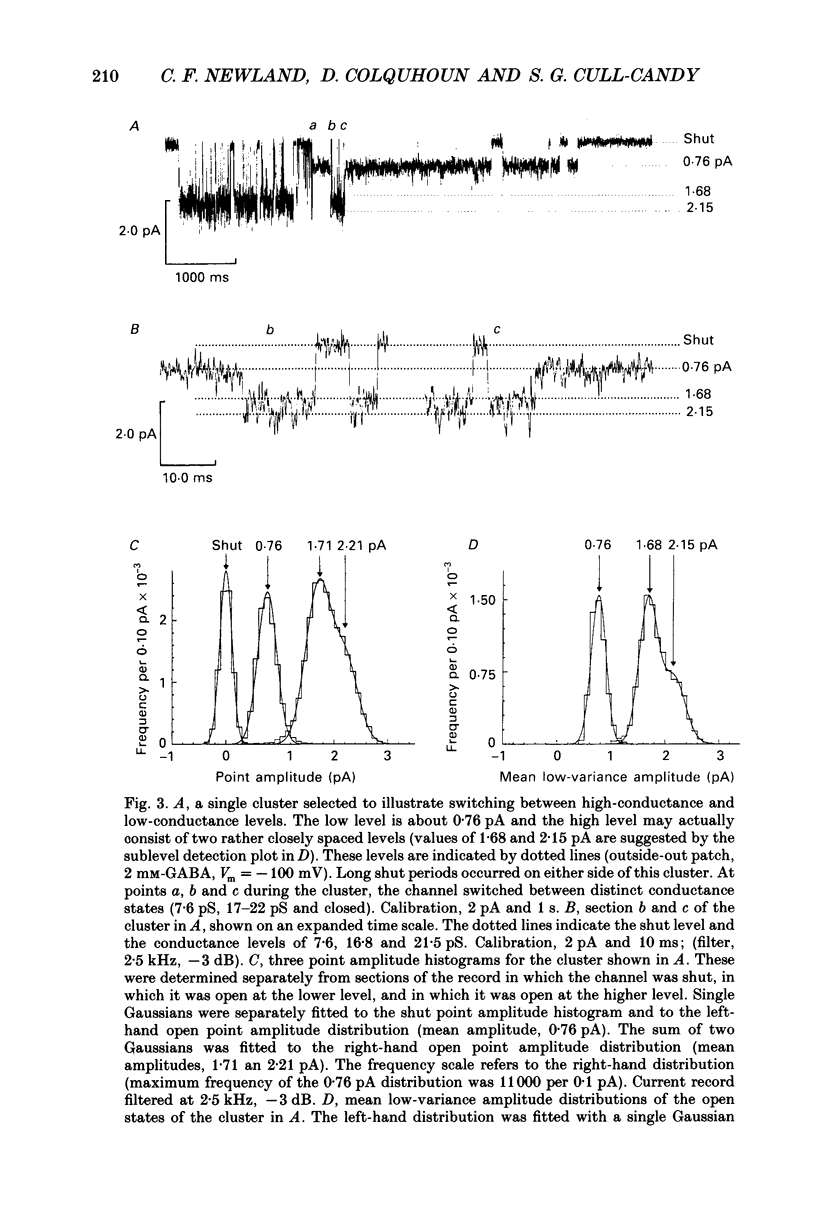
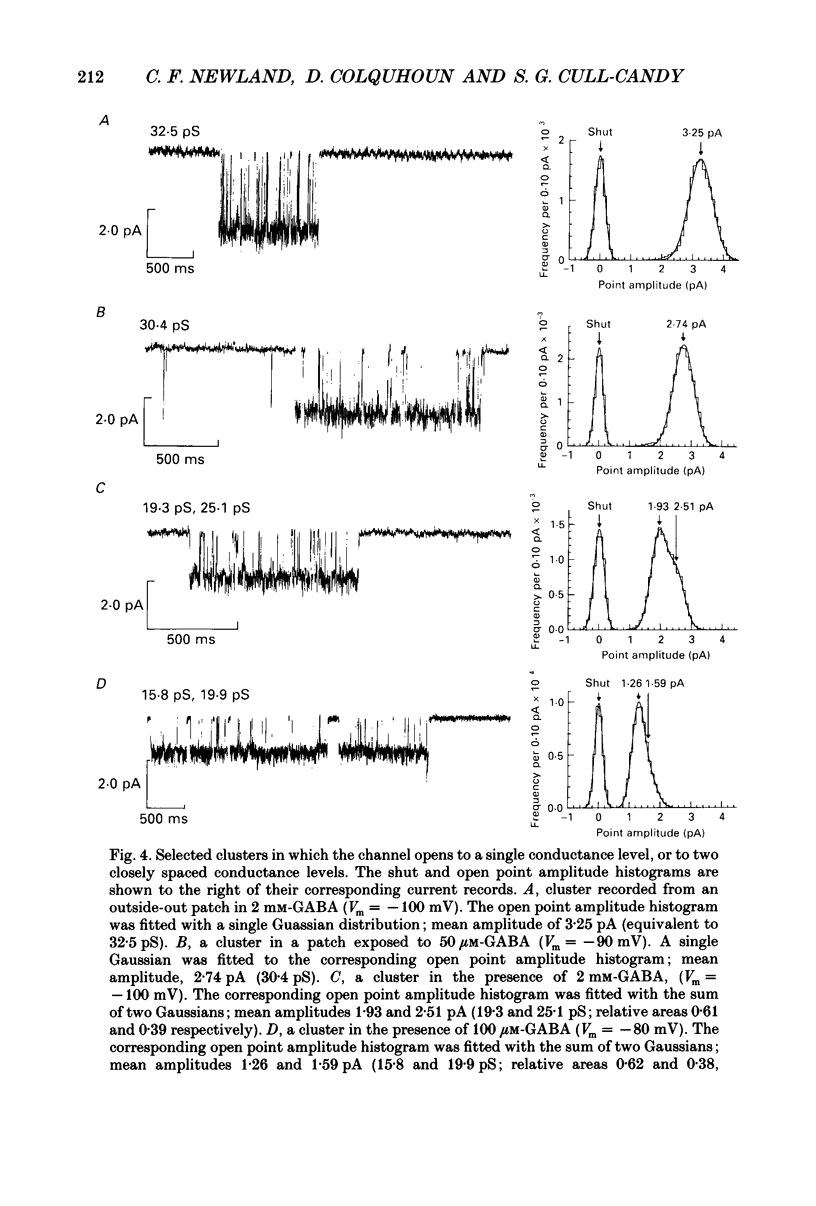
Full text
PDF



















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akaike N., Hattori K., Oomura Y., Carpenter D. O. Bicuculline and picrotoxin block gamma-aminobutyric acid-gated Cl- conductance by different mechanisms. Experientia. 1985 Jan 15;41(1):70–71. doi: 10.1007/BF02005880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akaike N., Inoue M., Krishtal O. A. 'Concentration-clamp' study of gamma-aminobutyric-acid-induced chloride current kinetics in frog sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1986 Oct;379:171–185. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen C. N., Albuquerque E. X. Conductance properties of GABA-activated chloride currents recorded from cultured hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1987 Apr 28;410(1):159–163. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(87)80039-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auerbach A., Lingle C. J. Activation of the primary kinetic modes of large- and small-conductance cholinergic ion channels in Xenopus myocytes. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;393:437–466. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auerbach A., Lingle C. J. Heterogeneous kinetic properties of acetylcholine receptor channels in Xenopus myocytes. J Physiol. 1986 Sep;378:119–140. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatz A. L., Magleby K. L. Quantitative description of three modes of activity of fast chloride channels from rat skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1986 Sep;378:141–174. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bormann J., Clapham D. E. gamma-Aminobutyric acid receptor channels in adrenal chromaffin cells: a patch-clamp study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):2168–2172. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.2168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bormann J., Hamill O. P., Sakmann B. Mechanism of anion permeation through channels gated by glycine and gamma-aminobutyric acid in mouse cultured spinal neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Apr;385:243–286. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brett R. S., Dilger J. P., Adams P. R., Lancaster B. A method for the rapid exchange of solutions bathing excised membrane patches. Biophys J. 1986 Nov;50(5):987–992. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83539-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cachelin A. B., Colquhoun D. Desensitization of the acetylcholine receptor of frog end-plates measured in a Vaseline-gap voltage clamp. J Physiol. 1989 Aug;415:159–188. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cash D. J., Subbarao K. Channel opening of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor from rat brain: molecular mechanisms of the receptor responses. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 1;26(24):7562–7570. doi: 10.1021/bi00398a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi D. W., Fischbach G. D. GABA conductance of chick spinal cord and dorsal root ganglion neurons in cell culture. J Neurophysiol. 1981 Apr;45(4):605–620. doi: 10.1152/jn.1981.45.4.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Hawkes A. G. On the stochastic properties of bursts of single ion channel openings and of clusters of bursts. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Dec 24;300(1098):1–59. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1982.0156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Hawkes A. G. Relaxation and fluctuations of membrane currents that flow through drug-operated channels. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Nov 14;199(1135):231–262. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Hawkes A. G. Stochastic properties of ion channel openings and bursts in a membrane patch that contains two channels: evidence concerning the number of channels present when a record containing only single openings is observed. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1990 Jun 22;240(1299):453–477. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1990.0048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Ogden D. C. Activation of ion channels in the frog end-plate by high concentrations of acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1988 Jan;395:131–159. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Sakmann B. Fast events in single-channel currents activated by acetylcholine and its analogues at the frog muscle end-plate. J Physiol. 1985 Dec;369:501–557. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Sakmann B. Fluctuations in the microsecond time range of the current through single acetylcholine receptor ion channels. Nature. 1981 Dec 3;294(5840):464–466. doi: 10.1038/294464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Howe J. R., Ogden D. C. Noise and single channels activated by excitatory amino acids in rat cerebellar granule neurones. J Physiol. 1988 Jun;400:189–222. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Mathie A. Ion channels activated by acetylcholine and gamma-aminobutyric acid in freshly dissociated sympathetic neurones of the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1986 May 23;66(3):275–280. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90031-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Miledi R., Parker I. Single glutamate-activated channels recorded from locust muscle fibres with perfused patch-clamp electrodes. J Physiol. 1981 Dec;321:195–210. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Parker I. Rapid kinetics of single glutamate-receptor channels. Nature. 1982 Feb 4;295(5848):410–412. doi: 10.1038/295410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Usowicz M. M. Multiple-conductance channels activated by excitatory amino acids in cerebellar neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):525–528. doi: 10.1038/325525a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Usowicz M. M. On the multiple-conductance single channels activated by excitatory amino acids in large cerebellar neurones of the rat. J Physiol. 1989 Aug;415:555–582. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feltz A., Trautmann A. Desensitization at the frog neuromuscular junction: a biphasic process. J Physiol. 1982 Jan;322:257–272. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs K., Möhler H., Sieghart W. Various proteins from rat brain, specifically and irreversibly labeled by [3H]flunitrazepam, are distinct alpha-subunits of the GABA-benzodiazepine receptor complex. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Aug 1;90(3):314–319. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90208-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs K., Sieghart W. Evidence for the existence of several different alpha- and beta-subunits of the GABA/benzodiazepine receptor complex from rat brain. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Feb 27;97(3):329–333. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90619-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Bormann J., Sakmann B. Activation of multiple-conductance state chloride channels in spinal neurones by glycine and GABA. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):805–808. doi: 10.1038/305805a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P., Lansman J. B., Tsien R. W. Different modes of Ca channel gating behaviour favoured by dihydropyridine Ca agonists and antagonists. Nature. 1984 Oct 11;311(5986):538–544. doi: 10.1038/311538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. R., Colquhoun D., Cull-Candy S. G. On the kinetics of large-conductance glutamate-receptor ion channels in rat cerebellar granule neurons. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 May 23;233(1273):407–422. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1988.0030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. R., Cull-Candy S. G., Colquhoun D. Currents through single glutamate receptor channels in outside-out patches from rat cerebellar granule cells. J Physiol. 1991 Jan;432:143–202. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemoto Y., Akaike N., Kijima H. Kinetic and pharmacological properties of the GABA-induced chloride current in Aplysia neurones: a 'concentration clamp' study. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Nov;95(3):883–895. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11718.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahr C. E., Stevens C. F. Glutamate activates multiple single channel conductances in hippocampal neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):522–525. doi: 10.1038/325522a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., THESLEFF S. A study of the desensitization produced by acetylcholine at the motor end-plate. J Physiol. 1957 Aug 29;138(1):63–80. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitan E. S., Schofield P. R., Burt D. R., Rhee L. M., Wisden W., Köhler M., Fujita N., Rodriguez H. F., Stephenson A., Darlison M. G. Structural and functional basis for GABAA receptor heterogeneity. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):76–79. doi: 10.1038/335076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald R. L., Rogers C. J., Twyman R. E. Kinetic properties of the GABAA receptor main conductance state of mouse spinal cord neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1989 Mar;410:479–499. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathers D. A. Spontaneous and GABA-induced single channel currents in cultured murine spinal cord neurons. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1985 Oct;63(10):1228–1233. doi: 10.1139/y85-203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathers D. A., Wang Y. H. Effect of agonist concentration on the lifetime of GABA-activated membrane channels in spinal cord neurons. Synapse. 1988;2(6):627–632. doi: 10.1002/syn.890020608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathie A., Cull-Candy S. G., Colquhoun D. Single-channel and whole-cell currents evoked by acetylcholine in dissociated sympathetic neurons of the rat. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1987 Nov 23;232(1267):239–248. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1987.0072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McManus O. B., Blatz A. L., Magleby K. L. Sampling, log binning, fitting, and plotting durations of open and shut intervals from single channels and the effects of noise. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Nov;410(4-5):530–553. doi: 10.1007/BF00586537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McManus O. B., Magleby K. L. Kinetic states and modes of single large-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels in cultured rat skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1988 Aug;402:79–120. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogden D. C., Colquhoun D. Ion channel block by acetylcholine, carbachol and suberyldicholine at the frog neuromuscular junction. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985 Sep 23;225(1240):329–355. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1985.0065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patlak J. B., Gration K. A., Usherwood P. N. Single glutamate-activated channels in locust muscle. Nature. 1979 Apr 12;278(5705):643–645. doi: 10.1038/278643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patlak J. B., Ortiz M., Horn R. Opentime heterogeneity during bursting of sodium channels in frog skeletal muscle. Biophys J. 1986 Mar;49(3):773–777. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83704-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patlak J. B. Sodium channel subconductance levels measured with a new variance-mean analysis. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Oct;92(4):413–430. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.4.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchett D. B., Sontheimer H., Shivers B. D., Ymer S., Kettenmann H., Schofield P. R., Seeburg P. H. Importance of a novel GABAA receptor subunit for benzodiazepine pharmacology. Nature. 1989 Apr 13;338(6216):582–585. doi: 10.1038/338582a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakmann B., Bormann J., Hamill O. P. Ion transport by single receptor channels. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;48(Pt 1):247–257. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.048.01.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakmann B., Hamill O. P., Bormann J. Patch-clamp measurements of elementary chloride currents activated by the putative inhibitory transmitter GABA and glycine in mammalian spinal neurons. J Neural Transm Suppl. 1983;18:83–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakmann B., Patlak J., Neher E. Single acetylcholine-activated channels show burst-kinetics in presence of desensitizing concentrations of agonist. Nature. 1980 Jul 3;286(5768):71–73. doi: 10.1038/286071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivers B. D., Killisch I., Sprengel R., Sontheimer H., Köhler M., Schofield P. R., Seeburg P. H. Two novel GABAA receptor subunits exist in distinct neuronal subpopulations. Neuron. 1989 Sep;3(3):327–337. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90257-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieghart W. Benzodiazepine receptors: multiple receptors or multiple conformations? J Neural Transm. 1985;63(3-4):191–208. doi: 10.1007/BF01252025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieghart W. Multiplicity of GABAA--benzodiazepine receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Oct;10(10):407–411. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90189-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigworth F. J., Sine S. M. Data transformations for improved display and fitting of single-channel dwell time histograms. Biophys J. 1987 Dec;52(6):1047–1054. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83298-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sine S. M., Steinbach J. H. Activation of a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):175–185. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84146-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sine S. M., Steinbach J. H. Activation of acetylcholine receptors on clonal mammalian BC3H-1 cells by high concentrations of agonist. J Physiol. 1987 Apr;385:325–359. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sine S. M., Steinbach J. H. Activation of acetylcholine receptors on clonal mammalian BC3H-1 cells by low concentrations of agonist. J Physiol. 1986 Apr;373:129–162. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sine S. M., Steinbach J. H. Agonists block currents through acetylcholine receptor channels. Biophys J. 1984 Aug;46(2):277–283. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84022-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires R. F. Benzodiazepine receptor multiplicity. Neuropharmacology. 1983 Dec;22(12B):1443–1450. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(83)90112-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss D. S., Magleby K. L. Gating scheme for single GABA-activated Cl- channels determined from stability plots, dwell-time distributions, and adjacent-interval durations. J Neurosci. 1989 Apr;9(4):1314–1324. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-04-01314.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisden W., Morris B. J., Darlison M. G., Hunt S. P., Barnard E. A. Distinct GABAA receptor alpha subunit mRNAs show differential patterns of expression in bovine brain. Neuron. 1988 Dec;1(10):937–947. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90151-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasui S., Ishizuka S., Akaike N. GABA activates different types of chloride-conducting receptor-ionophore complexes in a dose-dependent manner. Brain Res. 1985 Sep 30;344(1):176–180. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91206-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ymer S., Schofield P. R., Draguhn A., Werner P., Köhler M., Seeburg P. H. GABAA receptor beta subunit heterogeneity: functional expression of cloned cDNAs. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1665–1670. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03557.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


