Abstract
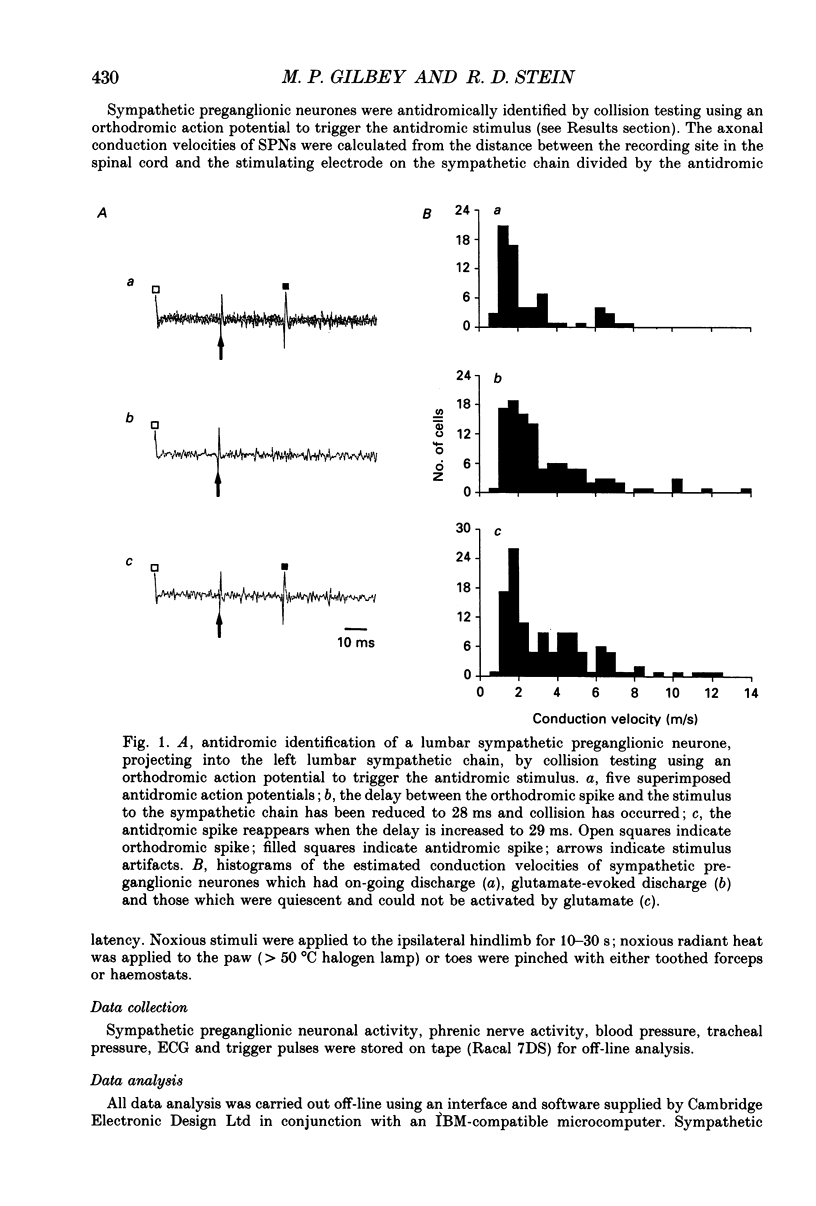
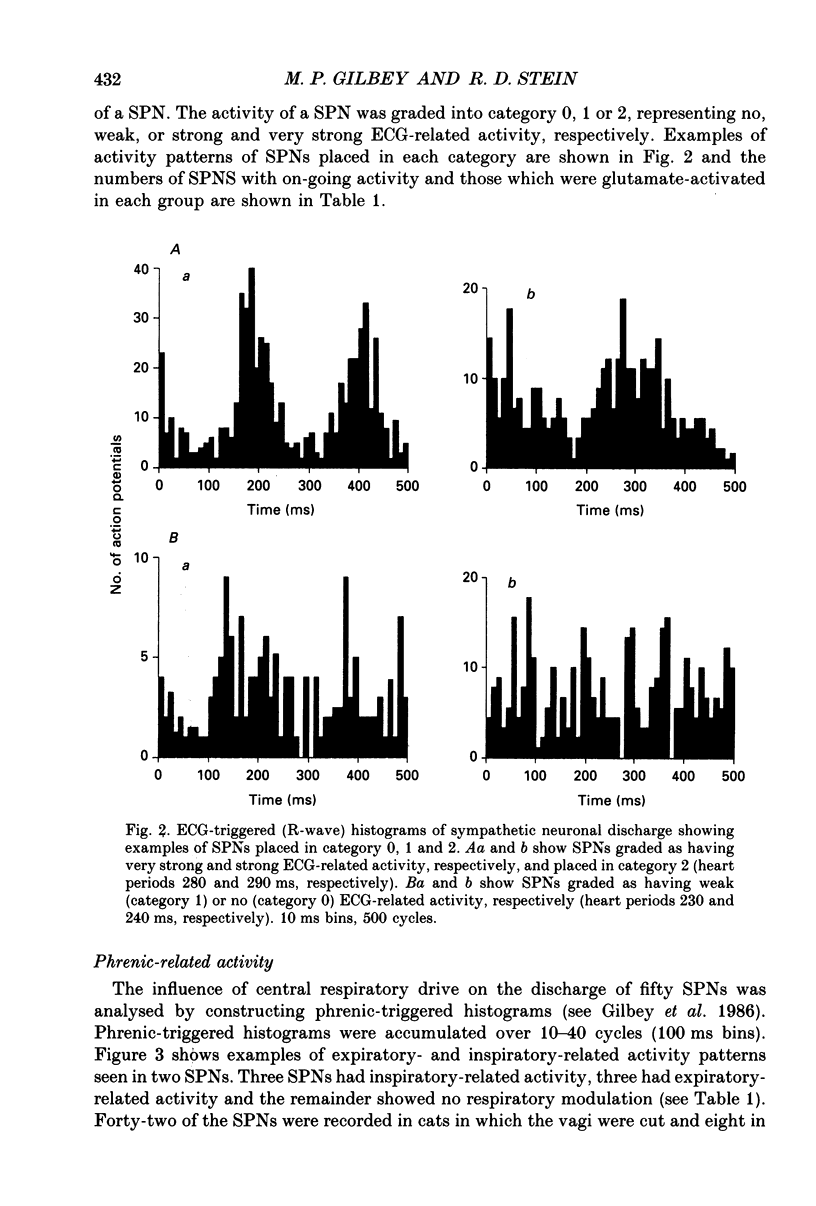
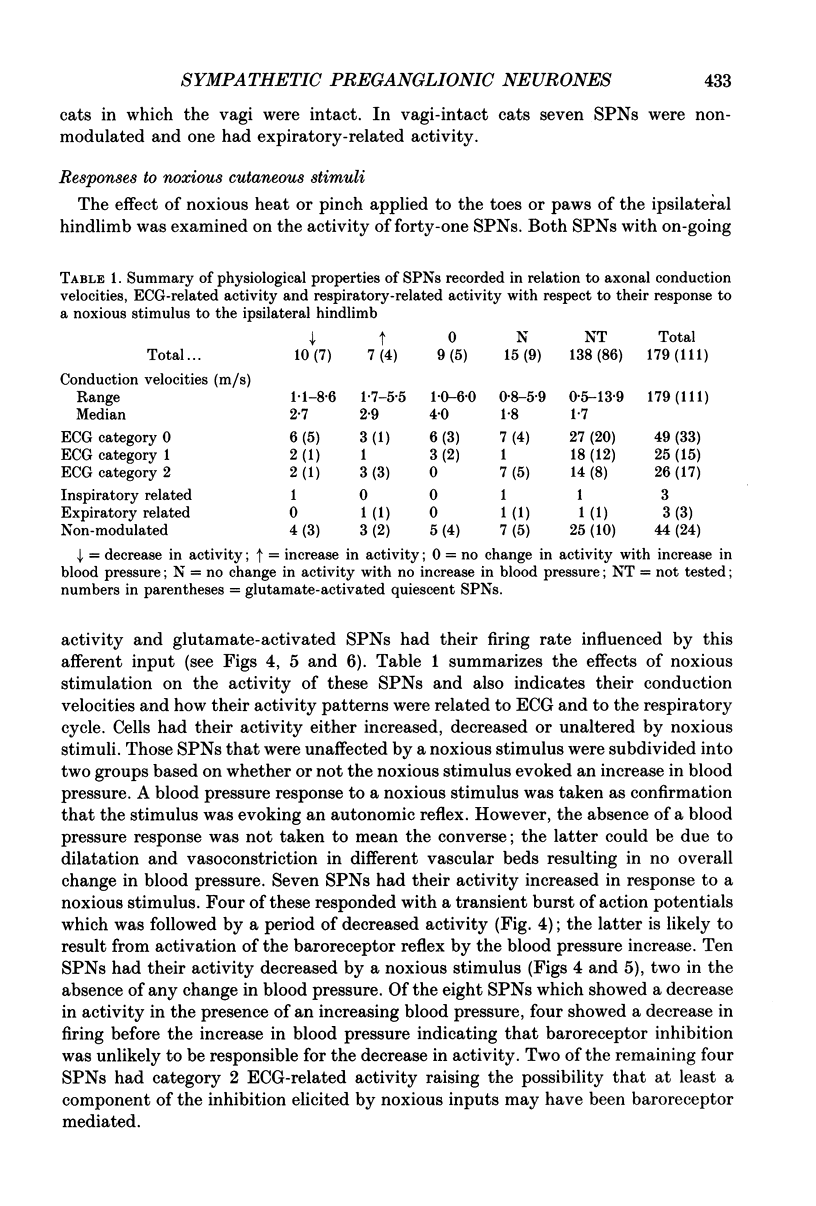
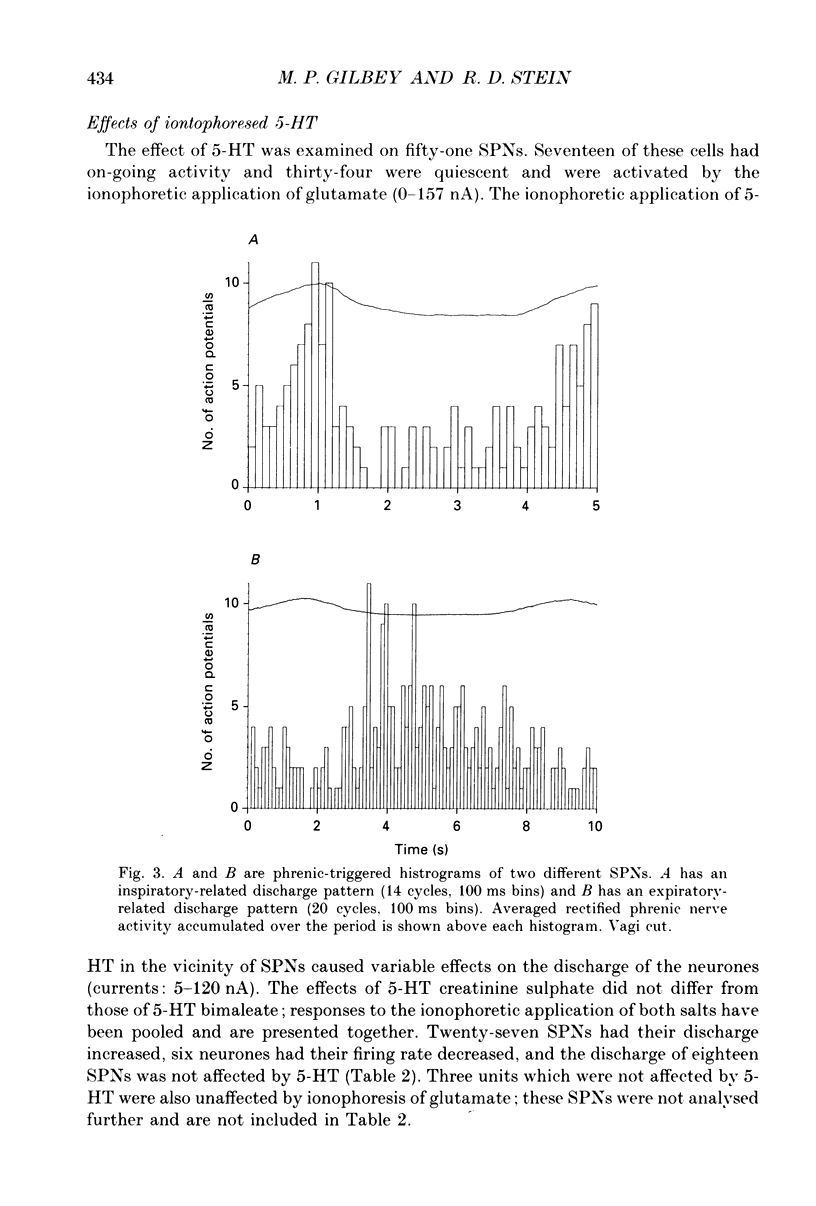
1. In anaesthetized cats extracellular recordings have been made from antidromically identified sympathetic preganglionic neurones, located in the 2nd and 3rd lumbar segments, with axons projecting into the left lumbar sympathetic chain beyond the L4 ganglion. Sympathetic preganglionic neurones have been characterized with respect to: axonal conduction velocities, firing patterns in relation to ECG and phrenic nerve activity, responses to noxious stimuli applied to the ipsilateral hindlimb and ionophoretically applied 5-HT. 2. Two hundred and ninety-seven sympathetic preganglionic neurones were studied. Their axonal conduction velocities (0.5-13.9 m/s) were in the B and C fibre range. Sixty-eight had on-going activity and the remainder were quiescent. Of the 229 quiescent sympathetic preganglionic neurons, 111 were activated by the ionophoretic application of glutamate. 3. Of the 100 sympathetic preganglionic neurones analysed for an ECG-related pattern of discharge, forty-nine had no, and fifty-one had an ECG-related pattern of discharge. Both sympathetic preganglionic neurones with on-going activity and glutamate activated cells exhibited ECG-related patterns of discharge. 4. Only six of fifty sympathetic preganglionic neurones had a respiratory-related activity pattern. Three had maximal discharge during expiration and three during inspiration. 5. Forty-one sympathetic preganglionic neurones were examined for their response to noxious stimulation of the ipsilateral hindlimb. Ten had their activity decreased (seven glutamate-activated, three with on-going activity), seven had their activity increased (four glutamate-activated and three with on-going activity) and twenty-four were unaffected. These results demonstrate that both sympathetic preganglionic neurones with on-going activity and glutamate-activated neurones can be influenced by noxious input. Ten sympathetic preganglionic neurones had properties consistent with them having a skin vasoconstrictor function and three with muscle vasoconstrictor function. 6. Ionophoretic application of 5-HT in the vicinity of fifty-one sympathetic preganglionic neurones caused increases in the discharge of 53%, decreases in the firing of 12% and did not affect the discharge of 35%. 7. Sympathetic preganglionic neurones which had excitatory responses to 5-HT showed only decreased discharge or no response to noxious stimulation of the ipsilateral hindlimb. Conversely, sympathetic preganglionic neurones which had discharge decreased by 5-HT had primarily excitatory responses to noxious inputs. 8. It is concluded that lumbar sympathetic preganglionic neurones consist of a heterogeneous population with respect to their physiological properties and their responses to ionophoretically applied 5-HT: both may be related to function.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
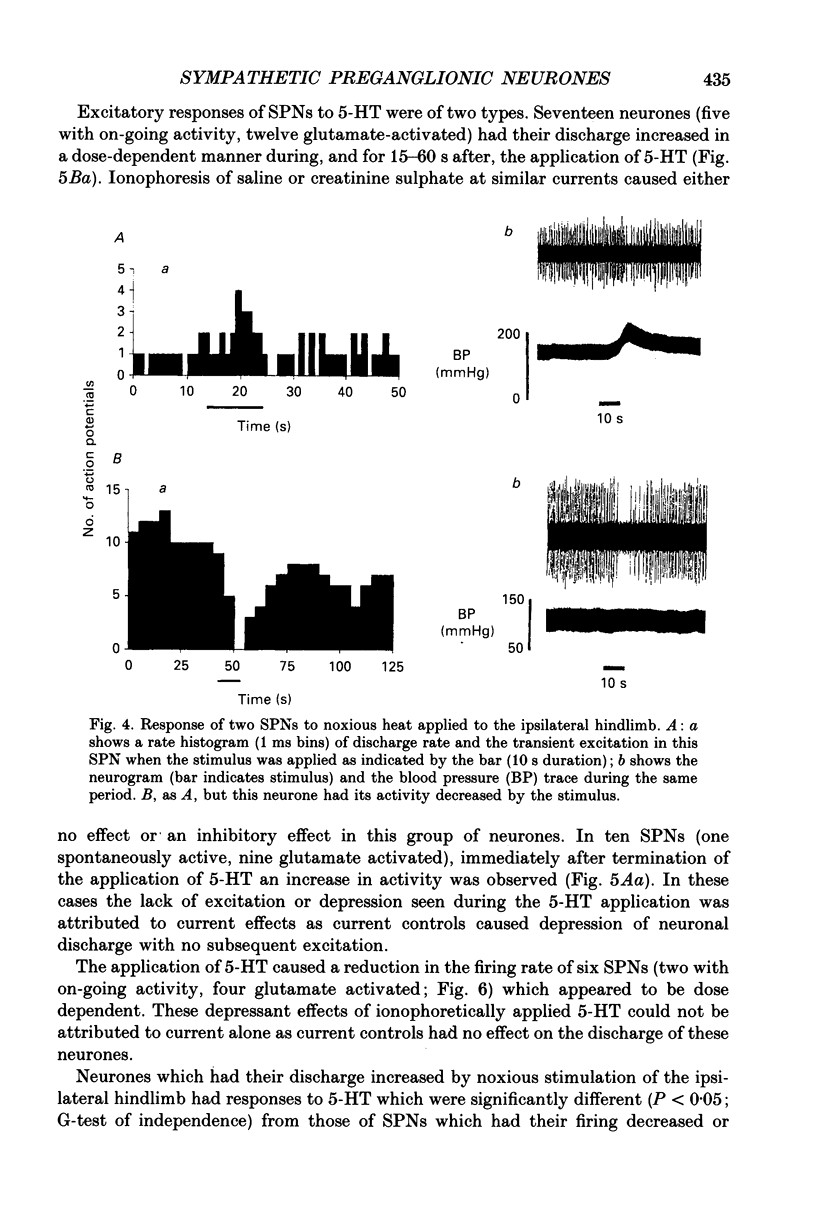
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
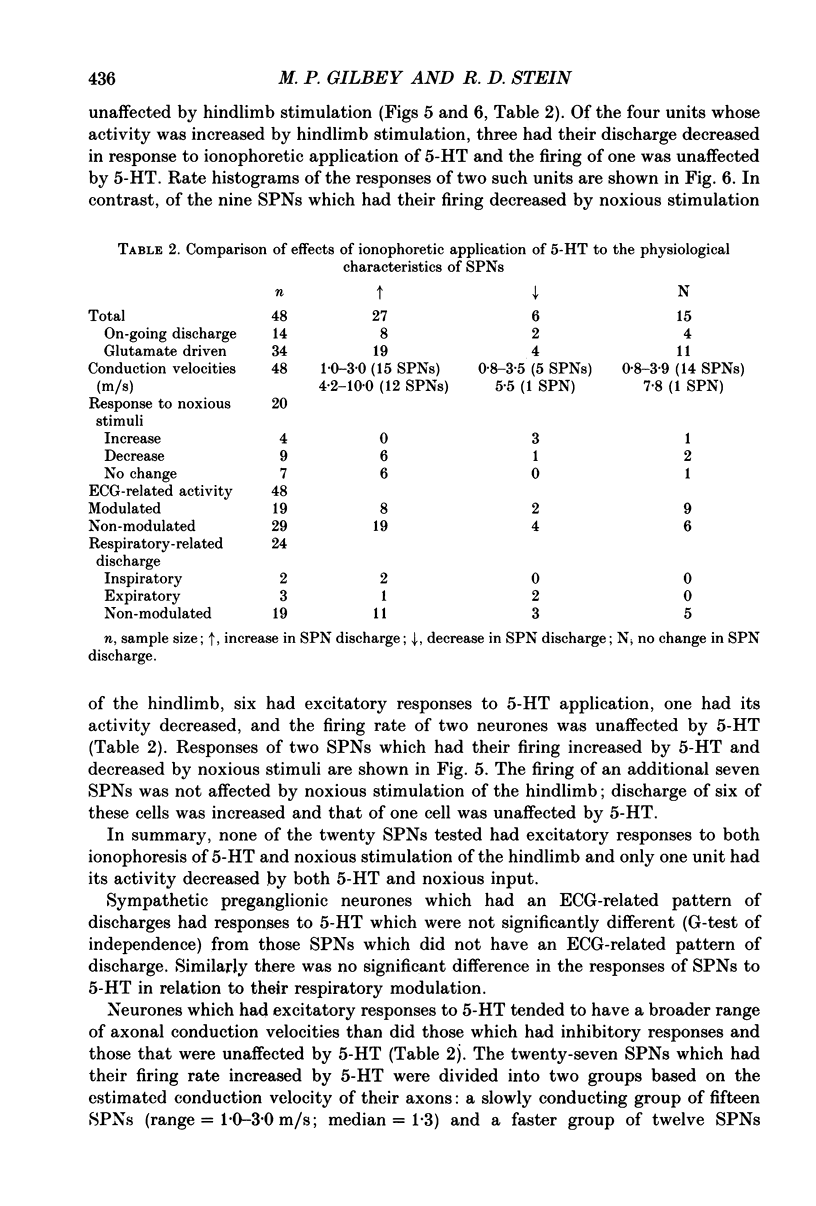
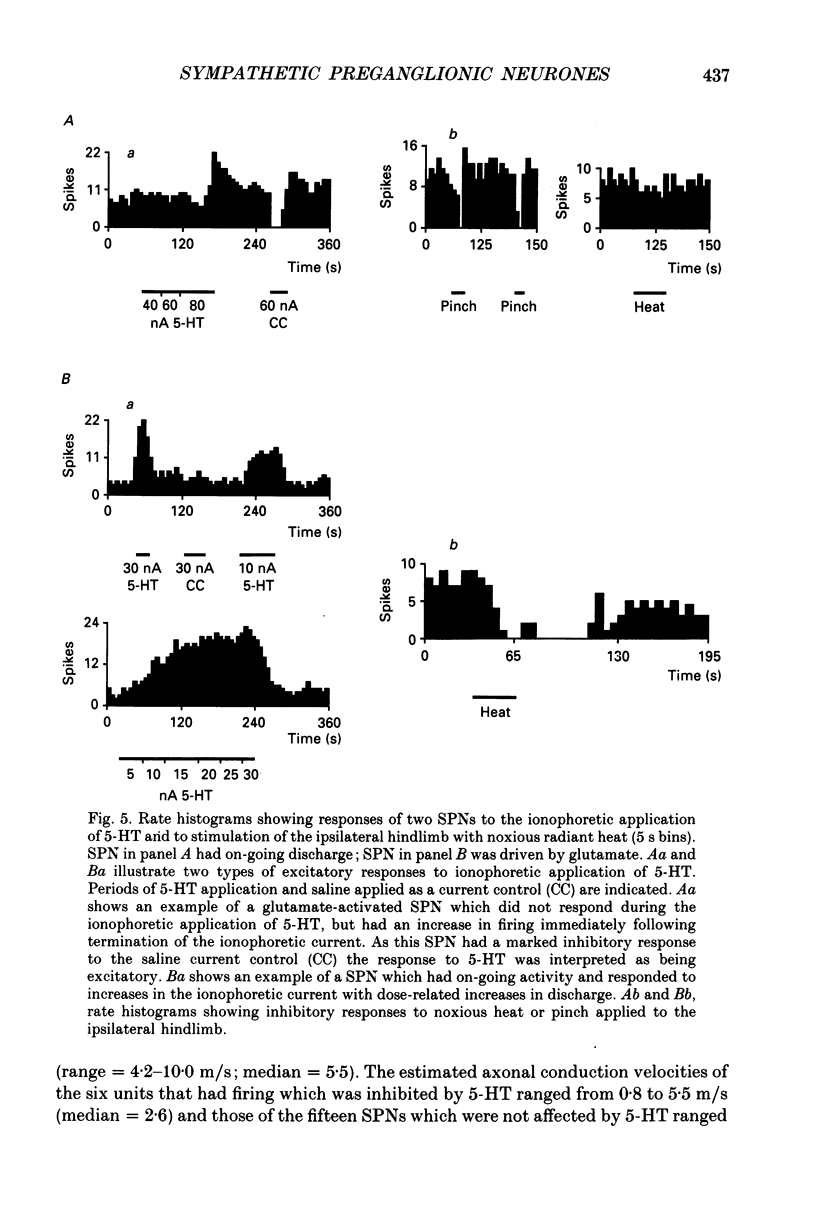
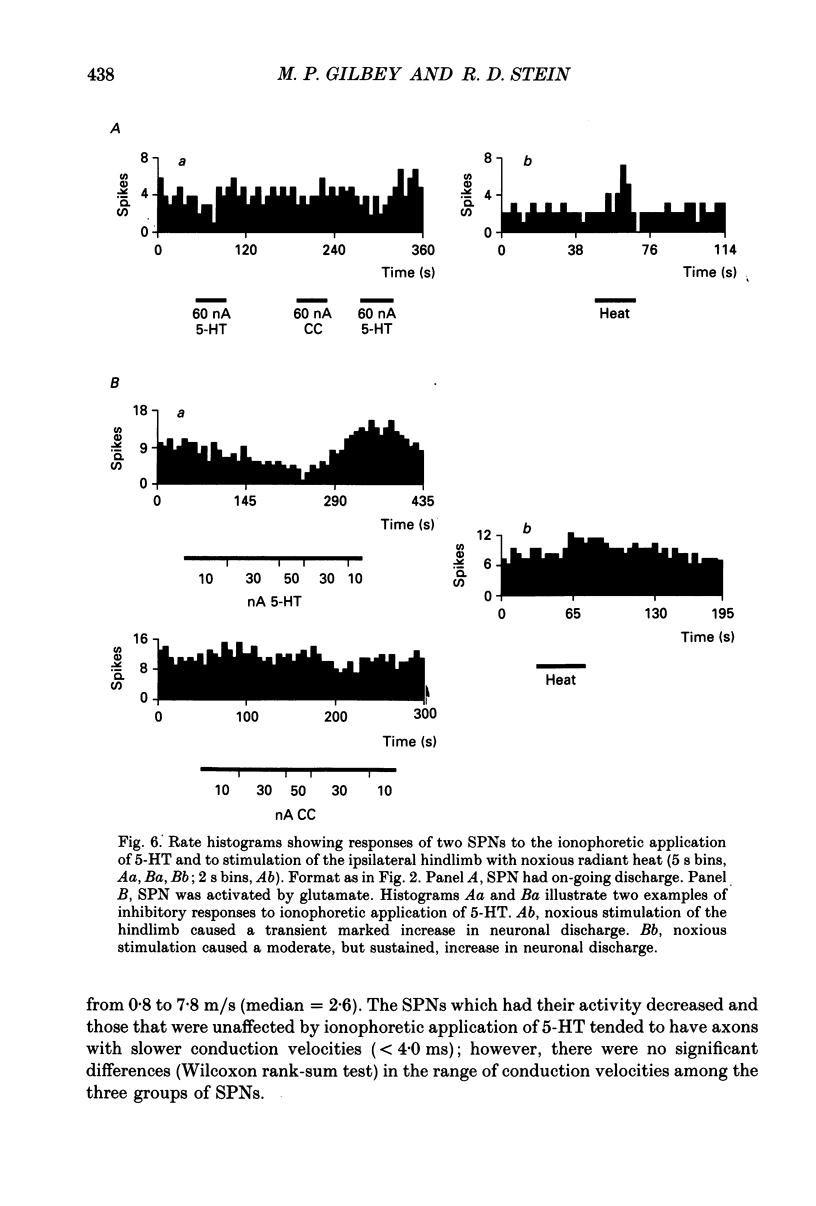
- Baron R., Janig W., McLachlan E. M. The afferent and sympathetic components of the lumbar spinal outflow to the colon and pelvic organs in the cat. III. The colonic nerves, incorporating an analysis of all components of the lumbar prevertebral outflow. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Aug 8;238(2):158–168. doi: 10.1002/cne.902380204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron R., Jänig W., McLachlan E. M. The afferent and sympathetic components of the lumbar spinal outflow to the colon and pelvic organs in the cat. I. The hypogastric nerve. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Aug 8;238(2):135–146. doi: 10.1002/cne.902380202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron R., Jänig W., McLachlan E. M. The afferent and sympathetic components of the lumbar spinal outflow to the colon and pelvic organs in the cat. II. The lumbar splanchnic nerves. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Aug 8;238(2):147–157. doi: 10.1002/cne.902380203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg H., Jänig W., Rieckmann C., Szulczyk P. Baroreceptor and chemoreceptor reflexes in postganglionic neurones supplying skeletal muscle and hairy skin. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1980 Oct;2(3):223–240. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(80)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coote J. H., Macleod V. H., Fleetwood-Walker S., Gilbey M. P. The response of individual sympathetic preganglionic neurones to microelectrophoretically applied endogenous monoamines. Brain Res. 1981 Jun 29;215(1-2):135–145. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90497-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crone C., Hultborn H., Kiehn O., Mazieres L., Wigström H. Maintained changes in motoneuronal excitability by short-lasting synaptic inputs in the decerebrate cat. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:321–343. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Groat W. C., Ryall R. W. An excitatory action 0f 5-hydroxytryptamine on sympathetic preganglionic neurones. Exp Brain Res. 1967;3(4):299–305. doi: 10.1007/BF00237556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbey M. P., Jordan D., Richter D. W., Spyer K. M. Synaptic mechanisms involved in the inspiratory modulation of vagal cardio-inhibitory neurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1984 Nov;356:65–78. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbey M. P., Numao Y., Spyer K. M. Discharge patterns of cervical sympathetic preganglionic neurones related to central respiratory drive in the rat. J Physiol. 1986 Sep;378:253–265. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbey M. P., Peterson D. F., Coote J. H. Some characteristics of sympathetic preganglionic neurones in the rat. Brain Res. 1982 Jun 3;241(1):43–48. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)91226-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregor M., Jänig W., Wiprich L. Cardiac and respiratory rhythmicities in cutaneous and muscle vasoconstrictor neurones to the cat's hindlimb. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Sep 16;370(3):299–302. doi: 10.1007/BF00585543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselton J. R., Guyenet P. G. Central respiratory modulation of medullary sympathoexcitatory neurons in rat. Am J Physiol. 1989 Mar;256(3 Pt 2):R739–R750. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1989.256.3.R739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jänig W., McLachlan E. M. Identification of distinct topographical distributions of lumbar sympathetic and sensory neurons projecting to end organs with different functions in the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1986 Apr 1;246(1):104–112. doi: 10.1002/cne.902460107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jänig W., McLachlan E. M. Organization of lumbar spinal outflow to distal colon and pelvic organs. Physiol Rev. 1987 Oct;67(4):1332–1404. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1987.67.4.1332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jänig W. Organization of the lumbar sympathetic outflow to skeletal muscle and skin of the cat hindlimb and tail. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1985;102:119–213. doi: 10.1007/BFb0034086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jänig W., Szulczyk P. Functional properties of lumbar preganglionic neurones. Brain Res. 1980 Mar 17;186(1):115–131. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90259-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jänig W., Szulczyk P. The organization of lumbar preganglionic neurons. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1981 Apr;3(2-4):177–191. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(81)90062-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadzielawa K. Antagonism of the excitatory effects of 5-hydroxytryptamine on sympathetic preganglionic neurones and neurones activated by visceral afferents. Neuropharmacology. 1983 Jan;22(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(83)90256-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo D. C., Hisamitsu T., de Groat W. C. A sympathetic projection from sacral paravertebral ganglia to the pelvic nerve and to postganglionic nerves on the surface of the urinary bladder and large intestine of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1984 Jun 10;226(1):76–86. doi: 10.1002/cne.902260106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. I., Coote J. H. The influence of 5-hydroxytryptamine agonists and antagonists on identified sympathetic preganglionic neurones in the rat, in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Apr;99(4):667–672. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12987.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCall R. B. Serotonergic excitation of sympathetic preganglionic neurons: a microiontophoretic study. Brain Res. 1983 Dec 19;289(1-2):121–127. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiss G., Kirchner F., Polosa C. Patterning of sympathetic preganglionic neuron firing by the central respiratory drive. Brain Res. 1975 Apr 11;87(2-3):363–374. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90434-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seller H. The discharge pattern of single units in thoracic and lumbar white rami in relation to cardiovascular events. Pflugers Arch. 1973 Nov 8;343(4):317–330. doi: 10.1007/BF00595819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


