Abstract
1. The interaction between MgADP and rigor cross-bridges in glycerol-extracted single fibres from rabbit psoas muscle has been investigated using laser pulse photolysis of caged ATP (P3-1(2-nitrophenyl)ethyladenosine 5'-triphosphate) in the presence of MgADP and following small length changes applied to the rigor fibre. 2. Addition of 465 microM-MgADP to a rigor fibre caused rigor tension to decrease by 15.3 +/- 0.7% (S.E.M., n = 24 trials in thirteen fibres). The half-saturation value for this tension reduction was 18 +/- 4 microM (n = 23, thirteen fibres). 3. Relaxation from rigor by photolysis of caged ATP in the absence of Ca2+ was markedly slowed by inclusion of 20 microM-2 mM-MgADP in the photolysis medium. 4. Four phases of tension relaxation occurred with MgADP in the medium: at, a quick partial relaxation (in pre-stretch fibres); bt, a slowing of relaxation or a rise in tension for 50-100 ms; ct, a sudden acceleration of relaxation; and dt, a final, nearly exponential relaxation. 5. Experiments at varied MgATP and MgADP concentrations suggested that phase at is due to MgATP binding to nucleotide-free cross-bridges. 6. Phase bt was abbreviated by including 1-20 mM-orthophosphate (Pi) in the photolysis medium, or by applying quick stretches before photolysis or during phase bt. These results suggest that phases bt and ct are complex processes involving ADP dissociation, cross-bridge reattachment and co-operative detachment involving filament sliding and the Ca(2+)-regulatory system. 7. Stretching relaxed muscle fibres to 3.2-3.4 microns striation spacing followed by ATP removal and release of the rigor fibre until tension fell below the relaxed level allowed investigation of the strain dependence of relaxation in the regions of negative cross-bridge strain. In the presence of 50 microM-2 mM-MgADP and either 10 mM-Pi or 20 mM-2,3-butanedione monoxime, relaxation following photolysis of caged ATP was 6- to 8-fold faster for negatively strained cross-bridges than for positively strained ones. This marked strain dependence of cross-bridge detachment is predicted from the model of A. F. Huxley (1957). 8. In the presence of Ca2+, activation of contraction following photolysis of caged ATP was slowed by inclusion of 20-500 microM-MgADP in the medium. An initial decrease in tension related to cross-bridge detachment by MgATP was markedly suppressed in the presence of MgADP. 9. Ten millimolar Pi partly suppressed active tension generation in the presence of MgADP.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF













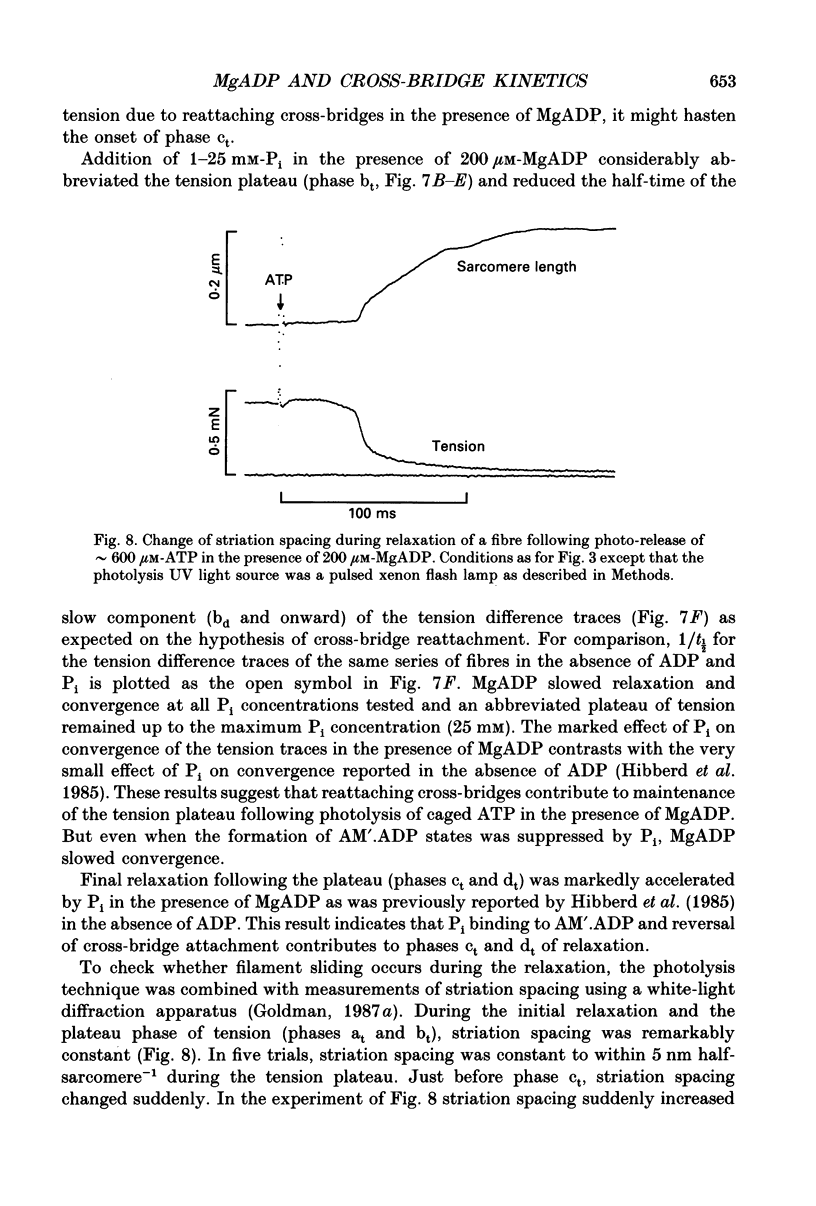

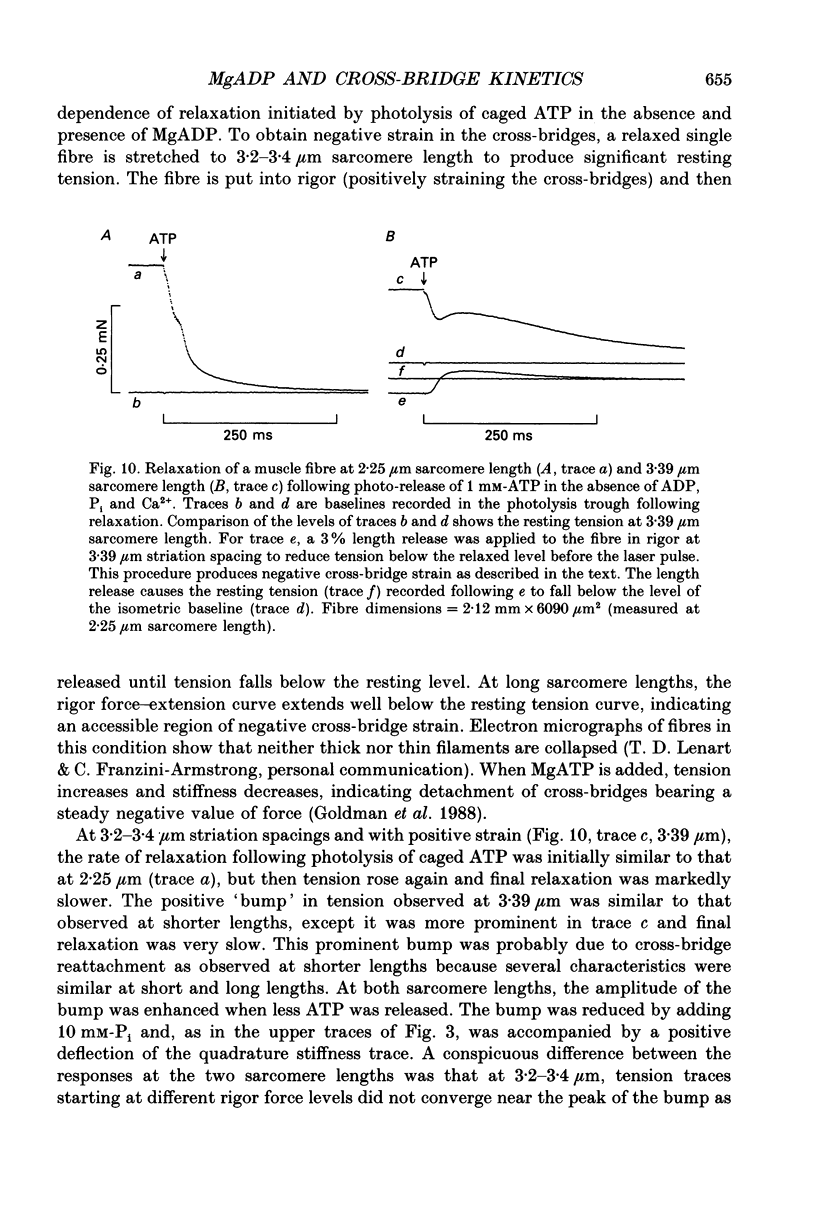

























Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABBOTT B. C. The heat production associated with the maintenance of a prolonged contraction and the extra heat produced during large shortening. J Physiol. 1951 Feb;112(3-4):438–445. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biosca J. A., Greene L. E., Eisenberg E. Binding of ADP and 5'-adenylyl imidodiphosphate to rabbit muscle myofibrils. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14231–14235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biosca J. A., Greene L. E., Eisenberg E. Binding of ADP and ATP analogs to cross-linked and non-cross-linked acto X S-1. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9793–9800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borejdo J., Ando T., Burghardt T. P. The rate of MgADP binding to and dissociation from acto-S1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Apr 5;828(2):172–176. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(85)90054-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannell M. B. Effect of tetanus duration on the free calcium during the relaxation of frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1986 Jul;376:203–218. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R., Pate E. The effects of ADP and phosphate on the contraction of muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1985 Nov;48(5):789–798. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83837-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R. The mechanism of muscle contraction. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1986;21(1):53–118. doi: 10.3109/10409238609113609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenn W. O. A quantitative comparison between the energy liberated and the work performed by the isolated sartorius muscle of the frog. J Physiol. 1923 Dec 28;58(2-3):175–203. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1923.sp002115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferenczi M. A. Phosphate burst in permeable muscle fibers of the rabbit. Biophys J. 1986 Sep;50(3):471–477. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83484-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford L. E., Huxley A. F., Simmons R. M. Tension responses to sudden length change in stimulated frog muscle fibres near slack length. J Physiol. 1977 Jul;269(2):441–515. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geeves M. A. Dynamic interaction between actin and myosin subfragment 1 in the presence of ADP. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 11;28(14):5864–5871. doi: 10.1021/bi00440a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis J. M. Relaxation of vertebrate skeletal muscle. A synthesis of the biochemical and physiological approaches. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jun 3;811(2):97–145. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(85)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman Y. E., Hibberd M. G., McCray J. A., Trentham D. R. Relaxation of muscle fibres by photolysis of caged ATP. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):701–705. doi: 10.1038/300701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman Y. E., Hibberd M. G., Trentham D. R. Initiation of active contraction by photogeneration of adenosine-5'-triphosphate in rabbit psoas muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:605–624. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman Y. E., Hibberd M. G., Trentham D. R. Relaxation of rabbit psoas muscle fibres from rigor by photochemical generation of adenosine-5'-triphosphate. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:577–604. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman Y. E. Kinetics of the actomyosin ATPase in muscle fibers. Annu Rev Physiol. 1987;49:637–654. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.49.030187.003225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman Y. E. Measurement of sarcomere shortening in skinned fibers from frog muscle by white light diffraction. Biophys J. 1987 Jul;52(1):57–68. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83188-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman Y. E., Simmons R. M. Active and rigor muscle stiffness [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1977 Jul;269(1):55P–57P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman Y. E., Simmons R. M. Control of sarcomere length in skinned muscle fibres of Rana temporaria during mechanical transients. J Physiol. 1984 May;350:497–518. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. E., Eisenberg E. Dissociation of the actin.subfragment 1 complex by adenyl-5'-yl imidodiphosphate, ADP, and PPi. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):543–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL A. V. THE EFFECT OF LOAD ON THE HEAT OF SHORTENING OF MUSCLE. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1964 Jan 14;159:297–318. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1964.0004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY A. F. Muscle structure and theories of contraction. Prog Biophys Biophys Chem. 1957;7:255–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselgrove J. C., Huxley H. E. X-ray evidence for radial cross-bridge movement and for the sliding filament model in actively contracting skeletal muscle. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jul 15;77(4):549–568. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90222-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibberd M. G., Dantzig J. A., Trentham D. R., Goldman Y. E. Phosphate release and force generation in skeletal muscle fibers. Science. 1985 Jun 14;228(4705):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.3159090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibberd M. G., Trentham D. R. Relationships between chemical and mechanical events during muscular contraction. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1986;15:119–161. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.15.060186.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi H., Takemori S. Butanedione monoxime suppresses contraction and ATPase activity of rabbit skeletal muscle. J Biochem. 1989 Apr;105(4):638–643. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuti K., Higuchi H., Umazume Y., Konishi M., Okazaki O., Kurihara S. Mechanism of action of 2, 3-butanedione 2-monoxime on contraction of frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1988 Apr;9(2):156–164. doi: 10.1007/BF01773737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley A. F. Muscular contraction. J Physiol. 1974 Nov;243(1):1–43. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley A. F., Simmons R. M. Proposed mechanism of force generation in striated muscle. Nature. 1971 Oct 22;233(5321):533–538. doi: 10.1038/233533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley H. E., Kress M. Crossbridge behaviour during muscle contraction. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1985 Apr;6(2):153–161. doi: 10.1007/BF00713057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley H. E. The mechanism of muscular contraction. Science. 1969 Jun 20;164(3886):1356–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3886.1356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. H., Forbush B., 3rd, Hoffman J. F. Rapid photolytic release of adenosine 5'-triphosphate from a protected analogue: utilization by the Na:K pump of human red blood cell ghosts. Biochemistry. 1978 May 16;17(10):1929–1935. doi: 10.1021/bi00603a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai M., Brandt P. W. Sinusoidal analysis: a high resolution method for correlating biochemical reactions with physiological processes in activated skeletal muscles of rabbit, frog and crayfish. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1980 Sep;1(3):279–303. doi: 10.1007/BF00711932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai M., Halvorson H. R. Role of MgATP and MgADP in the cross-bridge kinetics in chemically skinned rabbit psoas fibers. Study of a fast exponential process (C) Biophys J. 1989 Apr;55(4):595–603. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82857-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai M. The role of orthophosphate in crossbridge kinetics in chemically skinned rabbit psoas fibres as detected with sinusoidal and step length alterations. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1986 Oct;7(5):421–434. doi: 10.1007/BF01753585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marston S. B., Tregear R. T., Rodger C. D., Clarke M. L. Coupling between the enzymatic site of myosin and the mechanical output of muscle. J Mol Biol. 1979 Feb 25;128(2):111–126. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90121-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marston S. The nucleotide complexes of myosin in glycerol-extracted muscle fibres. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 30;305(2):397–412. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90186-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara I., Yagi N., Hashizume H. Use of an X-ray television for diffraction of the frog striated muscle. Nature. 1975 Jun 26;255(5511):728–729. doi: 10.1038/255728a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peckham M., Woledge R. C. Labile heat and changes in rate of relaxation of frog muscles. J Physiol. 1986 May;374:123–135. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall J. A. Relationship of isometric unexplained energy production to parvalbumin content in frog skeletal muscle. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1989;315:117–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld S. S., Taylor E. W. The dissociation of 1-N6-ethenoadenosine diphosphate from regulated actomyosin subfragment 1. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):9994–9999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld S. S., Taylor E. W. The mechanism of regulation of actomyosin subfragment 1 ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):9984–9993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenberg M., Eisenberg E. ADP binding to myosin cross-bridges and its effect on the cross-bridge detachment rate constants. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Jun;89(6):905–920. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.6.905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siemankowski R. F., Wiseman M. O., White H. D. ADP dissociation from actomyosin subfragment 1 is sufficiently slow to limit the unloaded shortening velocity in vertebrate muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):658–662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor E. W. Mechanism of actomyosin ATPase and the problem of muscle contraction. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1979;6(2):103–164. doi: 10.3109/10409237909102562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb M. R., Hibberd M. G., Goldman Y. E., Trentham D. R. Oxygen exchange between Pi in the medium and water during ATP hydrolysis mediated by skinned fibers from rabbit skeletal muscle. Evidence for Pi binding to a force-generating state. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15557–15564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


