Abstract
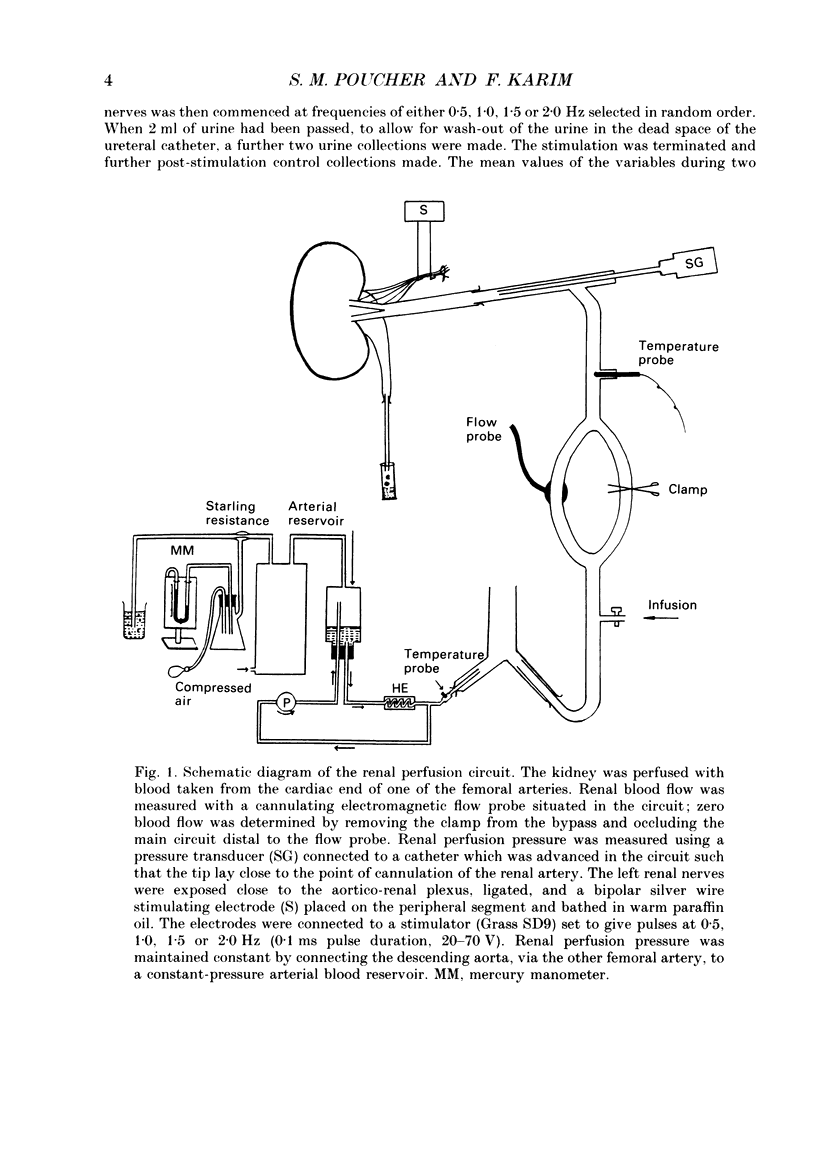
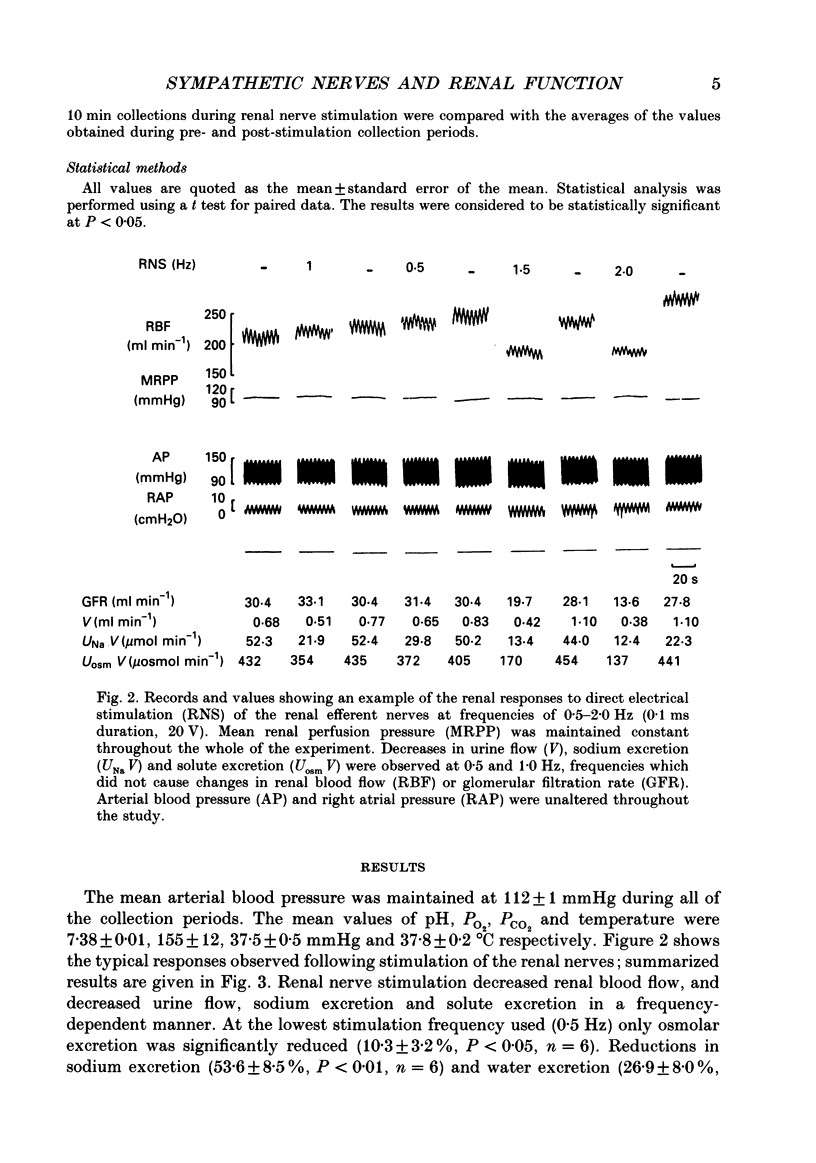
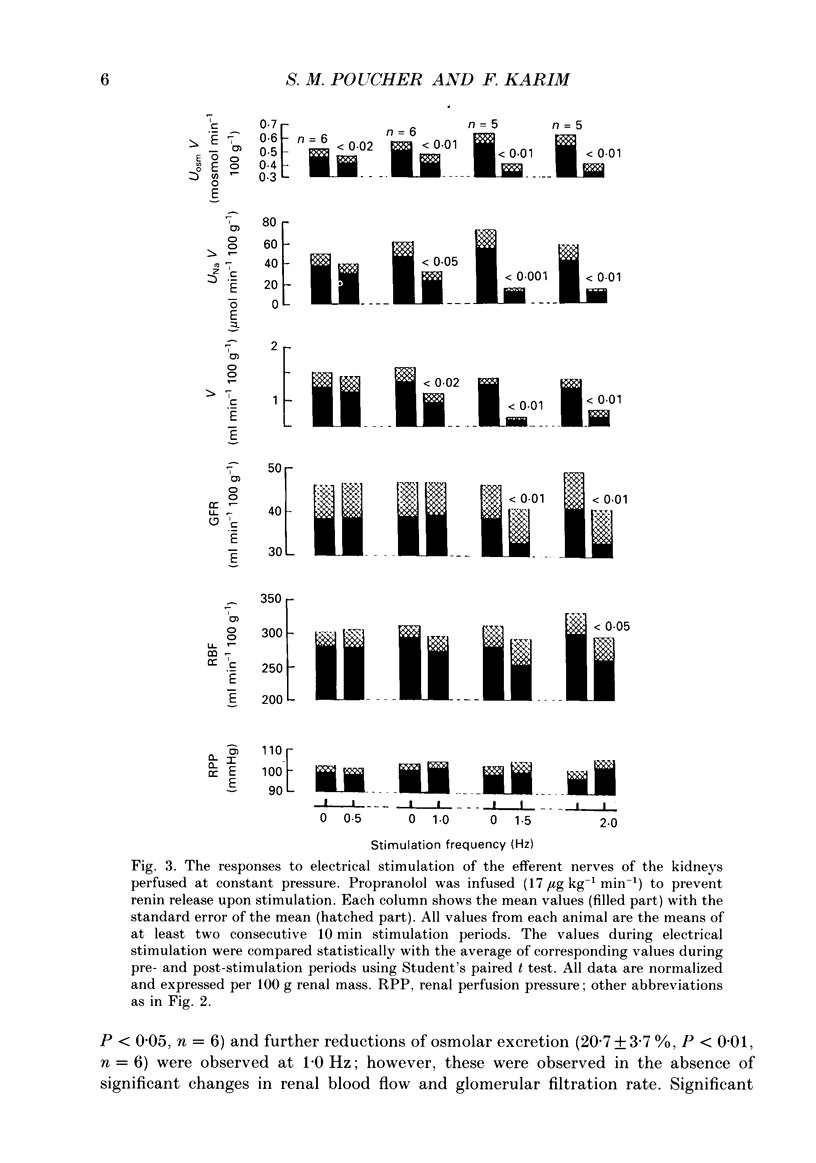
1. The effect of direct electrical stimulation of the renal efferent nerves upon renal haemodynamics and function was studied in greyhounds anaesthetized with chloralose and artificially ventilated. The left kidney was neurally and vascularly isolated, and perfused with blood from one of the femoral arteries at a constant pressure of 99 +/- 1 mmHg. Renal blood flow was measured with a cannulating electromagnetic flow probe placed in the perfusion circuit, glomerular filtration rate by creatinine clearance, urinary sodium excretion by flame photometry and solute excretion by osmometry. Beta-Adrenergic receptor activation was blocked by the infusion of dl-propranolol (17 micrograms kg-1 min-1). The peripheral ends of the ligated renal nerves were stimulated at 0.5, 1.0, 1.5 and 2.0 Hz. 2. At 0.5 Hz frequency only osmolar excretion was significantly reduced (10.3 +/- 3.2%, P less than 0.05, n = 6). Reductions in sodium excretion (53.6 +/- 8.5%, P less than 0.01, n = 6) and water excretion (26.9 +/- 8.0%, P less than 0.05, n = 6) and further reductions of osmolar excretion (20.7 +/- 3.7%, P less than 0.01, n = 6) were observed at 1.0 Hz; however, these were observed in the absence of significant changes in renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate. Significant reductions were observed in glomerular filtration rate at 1.5 Hz (16.3 +/- 4.1%, P less than 0.02, n = 5) and in renal blood flow at 2.0 Hz (13.1 +/- 4.0%, P less than 0.05, n = 5). Further reductions in urine flow and sodium excretion were also observed at these higher frequencies. 3. These results clearly show that significant changes in renal tubular function can occur in the absence of changes in renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate when the renal nerves are stimulated electrically from a zero baseline activity up to a frequency of 1.5 Hz. Higher frequencies caused significant changes in both renal haemodynamics and function.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ammons W. S., Koyama S., Manning J. W. Neural and vascular interaction in renin response to graded renal nerve stimulation. Am J Physiol. 1982 May;242(5):R552–R562. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1982.242.5.R552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barajas L., Müller J. The innervation of the juxtaglomerular apparatus and surrounding tubules: a quantitative analysis by serial section electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1973 Apr;43(1):107–132. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(73)90073-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell-Reuss E., Trevino D. L., Gottschalk C. W. Effect of renal sympathetic nerve stimulation on proximal water and sodium reabsorption. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):1104–1107. doi: 10.1172/JCI108355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBona G. F. Neurogenic regulation of renal tubular sodium reabsorption. Am J Physiol. 1977 Aug;233(2):F73–F81. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.233.2.F73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBona G. F., Sawin L. L. Effect of renal nerve stimulation on NaCl and H2O transport in Henle's loop of the rat. Am J Physiol. 1982 Dec;243(6):F576–F580. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.243.6.F576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiSalvo J., Fell C. Changes in renal blood flow during renal nerve stimulation. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Jan;136(1):150–153. doi: 10.3181/00379727-136-35215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermansson K., Larson M., Källskog O., Wolgast M. Influence of renal nerve activity on arteriolar resistance, ultrafiltration dynamics and fluid reabsorption. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Jan;389(2):85–90. doi: 10.1007/BF00582096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim F., Kidd C., Malpus C. M., Penna P. E. The effects of stimulation of the left atrial receptors on sympathetic efferent nerve activity. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(1):243–260. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim F., Majid D. S. Inhibition of atrial receptor-induced renal responses by stimulation of carotid baroreceptors in anaesthetized dogs. J Physiol. 1991 Jan;432:509–520. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim F., Majid D. S., Summerill R. A. Sympathetic nerves in the mediation of renal response to localized stimulation of atrial receptors in anaesthetized dogs. J Physiol. 1989 Oct;417:63–78. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim F., Poucher S. M., Summerill R. A. Effects of small changes in carotid sinus pressure on renal haemodynamics and function in dogs. J Physiol. 1989 Oct;417:295–305. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim F., Poucher S. M., Summerill R. A. The effects of stimulating carotid chemoreceptors on renal haemodynamics and function in dogs. J Physiol. 1987 Nov;392:451–462. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim F., Poucher S. M., Summerill R. A. The reflex effects of changes in carotid sinus pressure upon renal function in dogs. J Physiol. 1984 Oct;355:557–566. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendrick E., Oberg B., Wennergren G. Vasoconstrictor fibre discharge to skeletal muscle, kidney, intestine and skin at varying levels of arterial baroreceptor activity in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1972 Aug;85(4):464–476. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb05284.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kezdi P., Geller E. Baroreceptor control of postganglionic sympathetic nerve discharge. Am J Physiol. 1968 Mar;214(3):427–435. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.3.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopp U., Aurell M., Nilsson I. M., Ablad B. The role of beta-1-adrenoceptors in the renin release response to graded renal sympathetic nerve stimulation. Pflugers Arch. 1980 Sep;387(2):107–113. doi: 10.1007/BF00584260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopp U., DiBona G. F. Interaction of renal beta 1-adrenoceptors and prostaglandins in reflex renin release. Am J Physiol. 1983 Apr;244(4):F418–F424. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.244.4.F418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linden R. J., Mary D. A., Weatherill D. The responses in renal nerves to stimulation of atrial receptors, carotid sinus baroreceptors and carotid chemoreceptors. Q J Exp Physiol. 1981 Apr;66(2):179–191. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1981.sp002544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor W. J., Summerill R. A. Sodium excretion in normal conscious dogs. Cardiovasc Res. 1979 Jan;13(1):22–30. doi: 10.1093/cvr/13.1.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn J. L., Francisco L. L., DiBona G. F. Effect of renal nerve stimulation on renal blood flow autoregulation and antinatriuresis during reductions in renal perfusion pressure. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1981 Oct;168(1):77–81. doi: 10.3181/00379727-168-41238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn J. L., Holdaas H., Thames M. D., DiBona G. F. Renal adrenoceptor mediation of antinatriuretic and renin secretion responses to low frequency renal nerve stimulation in the dog. Circ Res. 1983 Sep;53(3):298–305. doi: 10.1161/01.res.53.3.298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slick G. L., Aguilera A. J., Zambraski E. J., DiBona G. F., Kaloyanides G. J. Renal neuroadrenergic transmission. Am J Physiol. 1975 Jul;229(1):60–65. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.1.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambraski E. J., DiBona G. F., Kaloyanides G. J. Specificity of neural effect on renal tubular sodium reabsorption. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1976 Mar;151(3):543–546. doi: 10.3181/00379727-151-39254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambraski E. J., Dibona G. F., Kaloyanides G. J. Effect of sympathetic blocking agents on the antinatriuresis of reflex renal nerve stimulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Aug;198(2):464–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


