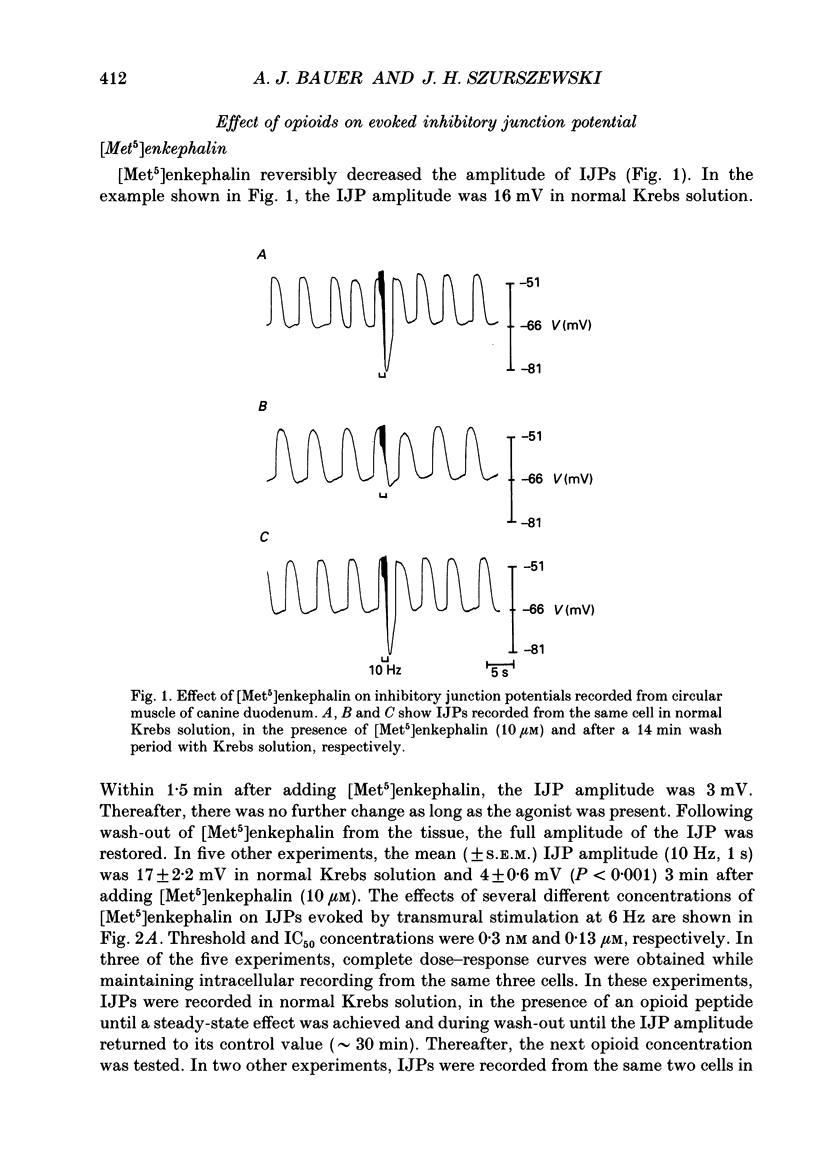
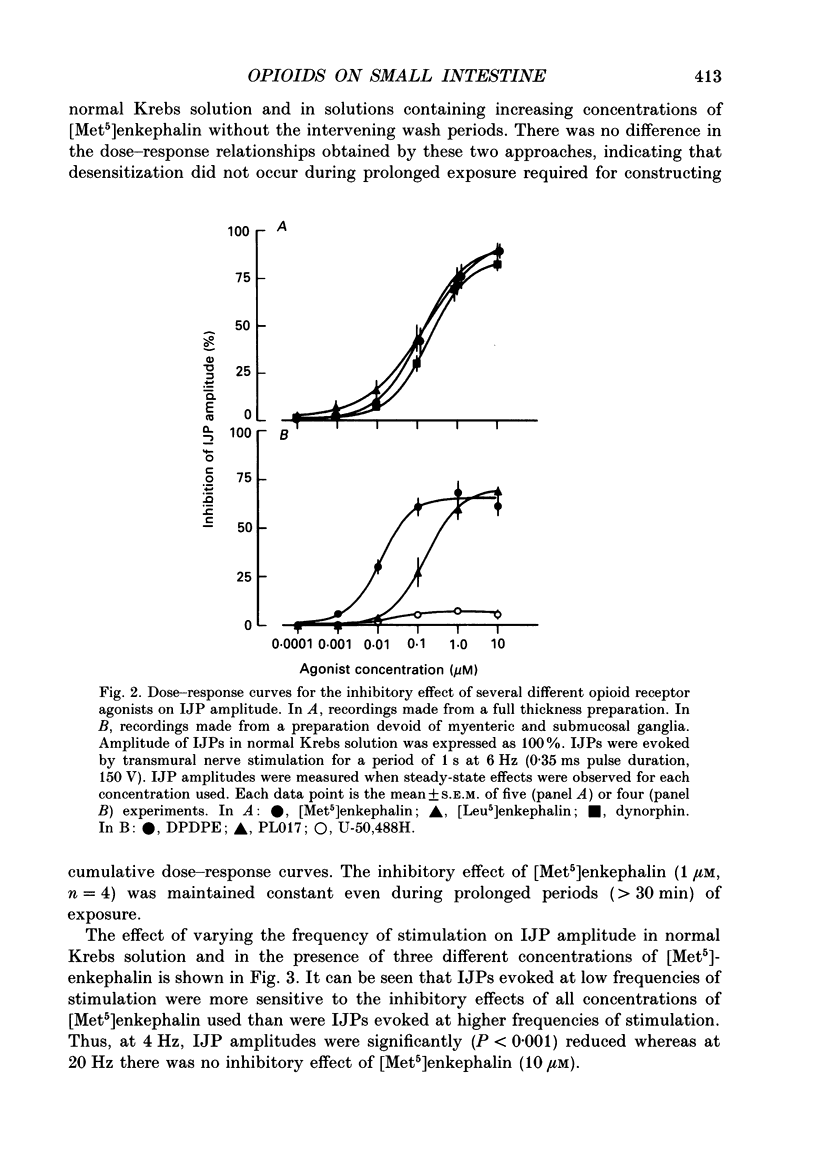
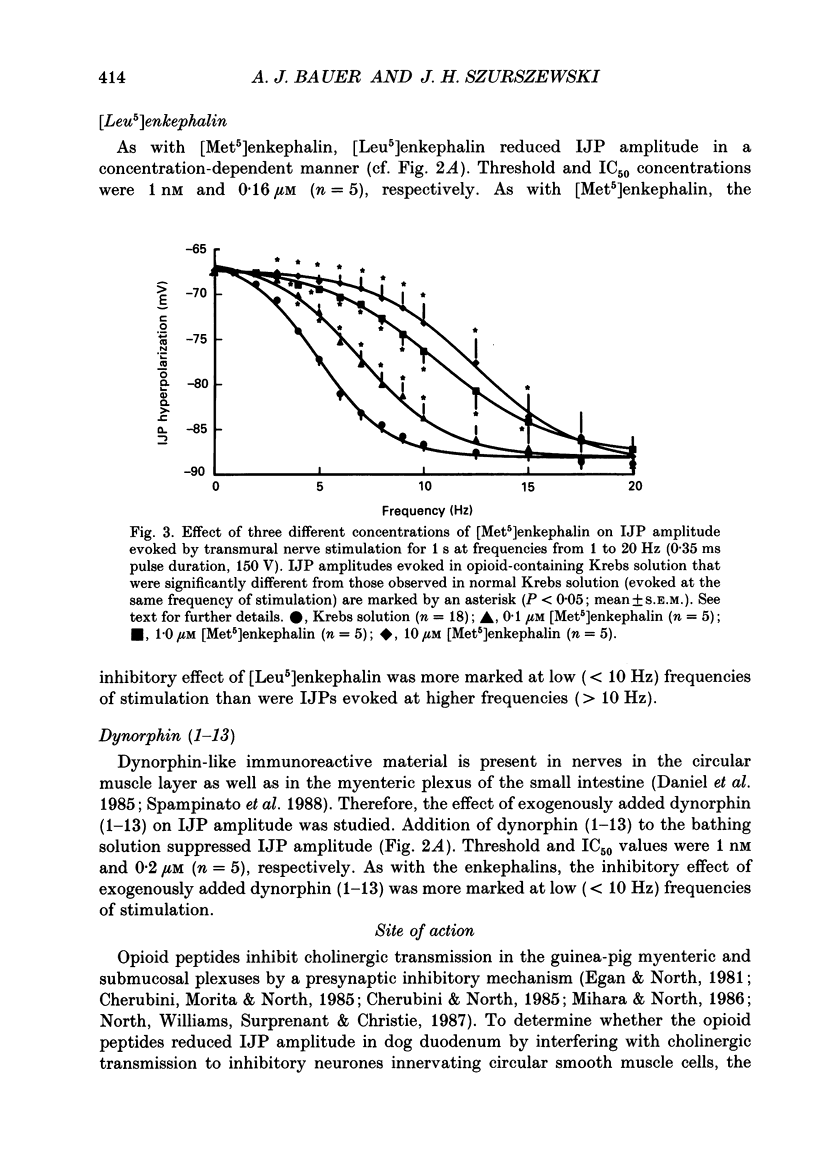
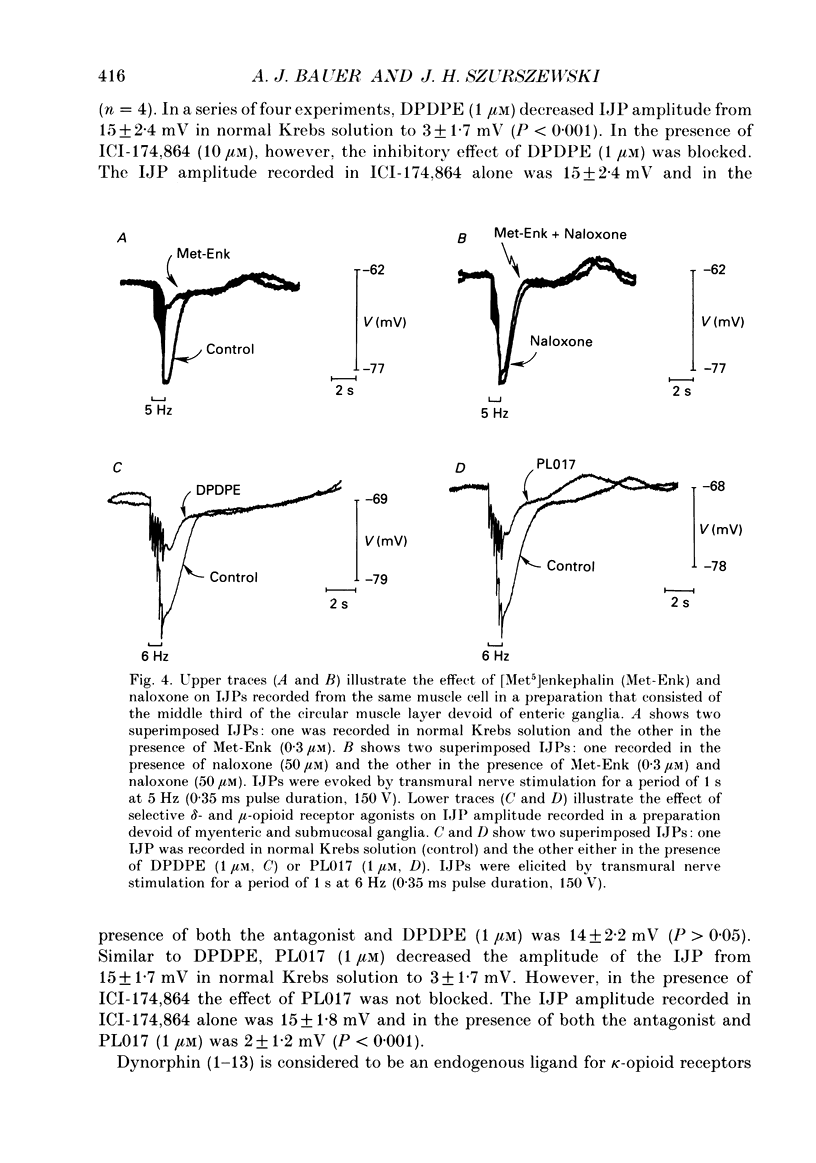
Abstract
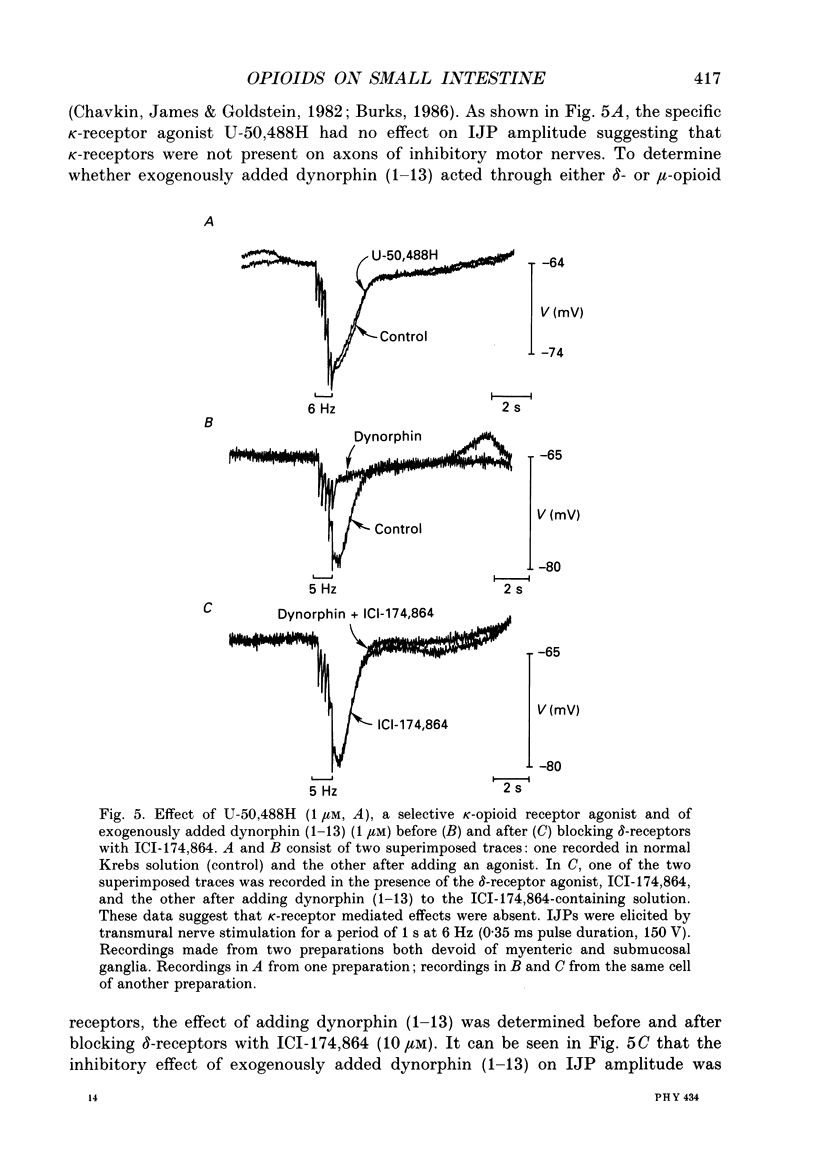
1. The effects of opioid peptides on inhibitory transmission in the circular muscle layer of canine duodenum were investigated in vitro using simultaneous mechanical and intracellular electrical recording techniques. 2. Exogenously added [Met5]enkephalin, [Leu5]enkephalin and dynorphin (1-13) decreased the amplitude of non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic inhibitory junction potentials (IJPs) evoked by transmural nerve stimulation. 3. A selective delta-receptor agonist, DPDPE ([D-Pen2, D-Pen5]enkephalin), and a selective mu-receptor agonist, PL017 (Try-Pro-NMePhe-D-Pro-NH2), decreased the amplitude of IJPs whereas a selective kappa-receptor agonist, U-50,488H ([trans-3,4-dichloro-N-methyl-N-(2-91-pyrolidinyl)-cyclohexyl]- benzeneacetamide methanesulphonate), in large doses (1 microM) produced only a small reduction. 4. A selective delta-receptor antagonist, ICI-174,864, blocked the effect of DPDPE but not that of PL017 suggesting the presence of distinct delta- and mu-opioid receptors on inhibitory motor nerves. 5. Exogenously added dynorphin (1-13) decreased the amplitude of IJPs. delta-Opioid receptors appeared to be involved because ICI-174,864, a selective delta-antagonist, blocked the inhibitory effect of exogenously added dynorphin (1-13). 6. The inhibitory effect of the opioid peptides was still observed in preparations of circular muscle devoid of myenteric and submucosal plexuses, indicating that the site of action was on inhibitory motor nerve fibres located within the circular muscle layer and not on neuronal cell bodies in the enteric plexuses. 7. It was concluded that in the canine small intestine, opioid peptides could modulate release of inhibitory transmitter(s) at or near nerve terminals of inhibitory motor nerves innervating circular muscle cells.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allescher H. D., Ahmad S., Kostka P., Kwan C. Y., Daniel E. E. Distribution of opioid receptors in canine small intestine: implications for function. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jun;256(6 Pt 1):G966–G974. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.256.6.G966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alumets J., Håkanson R., Sundler F., Chang K. J. Leu-enkephalin-like material in nerves and enterochromaffin cells in the gut. An immunohistochemical study. Histochemistry. 1978 Jul 12;56(3-4):187–196. doi: 10.1007/BF00495979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer A. J., Reed J. B., Sanders K. M. Slow wave heterogeneity within the circular muscle of the canine gastric antrum. J Physiol. 1985 Sep;366:221–232. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitar K. N., Makhlouf G. M. Selective presence of opiate receptors on intestinal circular muscle cells. Life Sci. 1985 Oct 21;37(16):1545–1550. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(85)90187-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burks T. F., Hirning L. D., Galligan J. J., Davis T. P. Motility effects of opioid peptides in dog intestine. Life Sci. 1982 Nov 15;31(20-21):2237–2240. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90127-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bywater R. A., Holman M. E., Taylor G. S. Atropine-resistant depolarization in the guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol. 1981 Jul;316:369–378. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. J., Wei E. T., Killian A., Chang J. K. Potent morphiceptin analogs: structure activity relationships and morphine-like activities. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Nov;227(2):403–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavkin C., James I. F., Goldstein A. Dynorphin is a specific endogenous ligand of the kappa opioid receptor. Science. 1982 Jan 22;215(4531):413–415. doi: 10.1126/science.6120570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherubini E., Morita K., North R. A. Opioid inhibition of synaptic transmission in the guinea-pig myenteric plexus. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Aug;85(4):805–817. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb11079.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherubini E., North R. A. Mu and kappa opioids inhibit transmitter release by different mechanisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1860–1863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. J., Smith T. W. Opiate-induced inhibition of the visceral distension reflex by peripheral and central mechanisms. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1985 Sep;330(3):179–183. doi: 10.1007/BF00572431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. J., Smith T. W. Peristalsis abolishes the release of methionine-enkephalin from guinea-pig ileum in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Mar 26;70(3):421–424. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90175-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa M., Furness J. B., Cuello A. C. Separate populations of opioid containing neurons in the guinea-pig intestine. Neuropeptides. 1985 Feb;5(4-6):445–448. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(85)90050-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel E. E., Costa M., Furness J. B., Keast J. R. Peptide neurons in the canine small intestine. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Jul 8;237(2):227–238. doi: 10.1002/cne.902370207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnerer J., Barthó L., Holzer P., Lembeck F. Intestinal peristalsis associated with release of immunoreactive substance P. Neuroscience. 1984 Apr;11(4):913–918. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan T. M., North R. A. Both mu and delta opiate receptors exist on the same neuron. Science. 1981 Nov 20;214(4523):923–924. doi: 10.1126/science.6272393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. E., Daniel E. E. Exogenous opiates: their local mechanisms of action in the canine small intestine and stomach. Am J Physiol. 1987 Aug;253(2 Pt 1):G179–G188. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1987.253.2.G179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furness J. B., Costa M., Miller R. J. Distribution and projections of nerves with enkephalin-like immunoreactivity in the guinea-pig small intestine. Neuroscience. 1983 Apr;8(4):653–664. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90001-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grider J. R., Makhlouf G. M. Role of opioid neurons in the regulation of intestinal peristalsis. Am J Physiol. 1987 Aug;253(2 Pt 1):G226–G231. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1987.253.2.G226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grider J. R., Makhlouf G. M. Suppression of inhibitory neural input to colonic circular muscle by opioid peptides. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Oct;243(1):205–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara Y., Kubota M., Szurszewski J. H. Electrophysiology of smooth muscle of the small intestine of some mammals. J Physiol. 1986 Mar;372:501–520. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara Y., Szurszewski J. H. Effect of potassium and acetylcholine on canine intestinal smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1986 Mar;372:521–537. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirning L. D., Porreca F., Burks T. F. Mu, but not kappa, opioid agonists induce contractions of the canine small intestine ex vivo. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb 12;109(1):49–54. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90538-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Tajima K. Action of morphine on the neuro-effector transmission in the guinea-pig ileum and in the mouse vas deferens. J Physiol. 1980 Oct;307:367–383. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOSTERLITZ H. W., LEES G. M. PHARMACOLOGICAL ANALYSIS OF INTRINSIC INTESTINAL REFLEXES. Pharmacol Rev. 1964 Sep;16:301–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W. The Wellcome Foundation lecture, 1982. Opioid peptides and their receptors. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985 Jul 22;225(1238):27–40. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1985.0048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson L. I., Childers S., Snyder S. H. Met- and Leu-enkephalin immunoreactivity in separate neurones. Nature. 1979 Nov 22;282(5737):407–410. doi: 10.1038/282407a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadzean I. The ionic mechanisms underlying opioid actions. Neuropeptides. 1988 May-Jun;11(4):173–180. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(88)90072-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihara S., North R. A. Opioids increase potassium conductance in submucous neurones of guinea-pig caecum by activating delta-receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Jun;88(2):315–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10207.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosberg H. I., Hurst R., Hruby V. J., Gee K., Yamamura H. I., Galligan J. J., Burks T. F. Bis-penicillamine enkephalins possess highly improved specificity toward delta opioid receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5871–5874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Katayama Y., Williams J. T. On the mechanism and site of action of enkephalin on single myenteric neurons. Brain Res. 1979 Apr 6;165(1):67–77. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90045-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Williams J. T., Surprenant A., Christie M. J. Mu and delta receptors belong to a family of receptors that are coupled to potassium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5487–5491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polak J. M., Bloom S. R., Sullivan S. N., Facer P., Pearse A. G. Enkephalin-like immunoreactivity in the human gastrointestinal tract. Lancet. 1977 May 7;1(8019):972–974. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92277-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander H. W., Portoghese P. S., Gintzler A. R. Spinal kappa-opiate receptor involvement in the analgesia of pregnancy: effects of intrathecal nor-binaltorphimine, a kappa-selective antagonist. Brain Res. 1988 Dec 6;474(2):343–347. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90448-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultzberg M., Hökfelt T., Nilsson G., Terenius L., Rehfeld J. F., Brown M., Elde R., Goldstein M., Said S. Distribution of peptide- and catecholamine-containing neurons in the gastro-intestinal tract of rat and guinea-pig: immunohistochemical studies with antisera to substance P, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, enkephalins, somatostatin, gastrin/cholecystokinin, neurotensin and dopamine beta-hydroxylase. Neuroscience. 1980;5(4):689–744. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90166-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spampinato S., Ferri G. L., Candeletti S., Romualdi P., Cavicchini E., Soimero L., Labò G., Ferri S. Regional distribution of immunoreactive dynorphin A in the human gastrointestinal tract. Neuropeptides. 1988 Apr;11(3):101–105. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(88)90077-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telford G. L., Caudill A., Condon R. E., Szurszewski J. H. Ketocyclazocine, a kappa-opioid receptor agonist, and control of intestinal myoelectric activity in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1988 Nov;255(5 Pt 1):G566–G570. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1988.255.5.G566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traynor J. Subtypes of the kappa-opioid receptor: fact or fiction? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Feb;10(2):52–53. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90074-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAUGHAN WILLIAMS E. M. The mode of action of drugs upon intestinal motility. Pharmacol Rev. 1954 Jun;6(2):159–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaught J. L., Cowan A., Jacoby H. I. Mu and delta, but not kappa, opioid agonists induce contractions of the canine small intestine in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb 12;109(1):43–48. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90537-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vizi E. S., Ono K., Adam-Vizi V., Duncalf D., Földes F. F. Presynaptic inhibitory effect of Met-enkephalin on [14C] acetylcholine release from the myenteric plexus and its interaction with muscarinic negative feedback inhibition. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Aug;230(2):493–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonvoigtlander P. F., Lahti R. A., Ludens J. H. U-50,488: a selective and structurally novel non-Mu (kappa) opioid agonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Jan;224(1):7–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura K., Huidobro-Toro J. P., Lee N. M., Löh H. H., Way E. L. Kappa opioid properties of dynorphin and its peptide fragments on the guinea-pig Ileum. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Jul;222(1):71–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


